Abstract
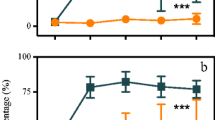
Rapid expansion of juvenile fish after biomanipulation can delay the successful restoration of submerged macrophytes, leading to a turbid water status in subtropical shallow lakes. Aimed to test the effects of direct removal of juvenile crucian carp (Carassius carassius) on water quality and growth of two submerged macrophytes Vallisneria natans and Hydrilla verticillate, a short-term outdoor mesocosm experiment was conducted in the Taihu Laboratory for Lake Ecosystem Research (TLLER). The results indicated that the concentrations of TN, TP, suspended solids, and chlorophyll a decreased significantly with increasing removal density of juvenile crucian carp, thus resulting in a clear status of the water. Additionally, the mean relative growth rate of V. natans and H. verticillata in the low- and high-density removal treatments were higher than that in the controls. Moreover, the removal of juvenile crucian carp also significantly increased the stem length of V. natans, but no significant effect on that of H. verticillata. Meanwhile, the total number of V. natans and H. verticillata in the low- and high-density removal treatments was higher than that in the controls, but all of H. verticillata were lower than the initials. Our results indicated that removing juvenile crucian carp could improve the water quality, increasing relative growth rate, height, and reproduction of V. natans, and improving the survival rate of H. verticillata. The promotion of fish removal on the V. natans growth was greater than H. verticillata. The results also implied that it was necessary to continuously remove the juvenile benthivorous fish several times for restoring the submerged macrophytes in shallow lakes.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Araújo F, Becker V, Attayde JL (2016) Shallow lake restoration and water quality management by the combined effects of polyaluminium chloride addition and benthivorous fish removal: a field mesocosm experiment. Hydrobiologia 778:243–252
Bakker ES, Sarneel JM, Gulati RD, Liu Z, Donk EV (2013) Restoring macrophyte diversity in shallow temperate lakes: biotic versus abiotic constraints. Hydrobiologia 710:23–37
Benndorf J, Böing W, Koop J, Neubauer I (2002) Top-down control of phytoplankton: the role of time scale, lake depth and trophic state. Freshw Biol 47:2282–2295
Bund WJVD, Donk EV (2002) Short-term and long-term effects of zooplanktivorous fish removal in a shallow Lake: a synthesis of 15 years of data from Lake Zwemlust. Freshw Biol 47:2380–2387
Carniatto N, Fugi R, Thomaz SM, Cunhaa ER (2014) The invasive submerged macrophyte Hydrilla verticillata as a foraging habitat for small-sized fish. Nat Conserv 12:30–35
Chen FZ, Shu TT, Jeppesen E, Liu ZW, Chen YW (2013) Restoration of a subtropical eutrophic shallow lake in China: effects on nutrient concentrations and biological communities. Hydrobiologia 718:59–71
Chiang SC, Du NS (1979) Fauna Sinica; Crustacea: Freshwater Cladocera. Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Denny P (1972) Sites of nutrient absorption in aquatic macrophytes. J Ecol 60:819–829
Dong BL, Qin BQ, Gao G, Cai XL (2014) Submerged macrophyte communities and the controlling factors in large, shallow Lake Taihu (China): sediment distribution and water depth. J Great Lakes Res 40:646–655
FAO (2004–2015) Cultured aquatic species information programme: Carassius carassius. http://www.fao.org/fishery/culturedspecies/Carassius_carassius/en
Fulton RS III, Godwin WF, Schaus MH (2015) Water quality changes following nutrient loading reduction and biomanipulation in a large shallow subtropical lake, Lake Griffin, Florida, USA. Hydrobiologia 753:243–263
Godwin W, Coveney M, Lowe E, Battoe L (2011) Improvements in water quality following biomanipulation of gizzard shad (Dorosoma cepedianum) in Lake Denham, Florida. Lake Reserv Manage 27:287–297
Gu J, Jin H, He H, Ning X, Yu J, Tan BC, Jeppesen E, Li KY (2016) Effects of small-sized crucian carp (Carassius carassius) on the growth of submerged macrophytes: implications for shallow lake restoration. Ecol Eng 95:567–573
Gu J, Hu H, Jin H, Yu JL, Jeppesen E, Nairn RW, Li KY (2018) Synergistic negative effects of small-sized benthivorous fish and nitrogen loading on the growth of submerged macrophytes-relevance for shallow lake restoration. Sci Total Environ 610-611:1572–1580
Gulati RD, Pires LMD, Donk EV (2008) Lake restoration studies: failures, bottlenecks and prospects of new ecotechnological measures. Limnologica 38:233–247
Huang XF (1999) Survey observation and analysis of lake ecology. Standards Press of China, Beijing (in Chinese)
Jeppesen E, Søndergaard M, Mazzeo N, Meerhoff M, Christina CB, Huszar V, Scasso F (2005) Lake restoration and biomanipulation in temperate lakes: relevance for subtropical and tropical lakes. In: Vikram R (ed) Tropical eutrophic lakes: their restoration and management. Science Publishers Inc, Enfield, NH, USA, pp 341–359
Jin XC, Tu Q (1990) The standard methods for observation and analysis in lake eutrophication, 2nd edn. Environmental Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Jurajda P, Adámek Z, Janáč M, Roche K, Mikl L, Rederer L, Zapletal T, Koza V, Špaček J (2016) Use of multiple fish-removal methods during biomanipulation of a drinking water reservoir-evaluation of the first four years. Fish Res 173:101–108
Jůza T, Durasb J, Blabolil P, Sajdlová Z, Hess J, Chocholoušková Z, Kubečka J (2019) Recovery of the Velky Bolevecky pond (Plzen, Czech Republic) via biomanipulation – key study for management. Ecol Eng 136:167–176
Kloskowski J (2011) Impact of common carp Cyprinus carpio on aquatic communities: direct trophic effects versus habitat deterioration. Fundam Appl Limnol 178:245–255
Langeland KA (1996) Hydrilla (L.F.) Royle (Hydrocharitaceae), “The perfect aquatic weed”. Castanea 61:293–304
Lathrop RC, Johnson BM, Johnson TB, Vogelsang MT, Carpenter SR, Hrabik TR, Kitchell JF, Magnuson JJ, Rudstam LG, Stewart RS (2002) Stocking piscivores to improve fishing and water clarity: a synthesis of the Lake Mendota biomanipulation project. Freshw Biol 47:2410–2424
Lauridsen TL, Jensen JP, Jeppesen E, Søndergaard M (2003) Response of submerged macrophytes in Danish lakes to nutrient loading reductions and biomanipulation. Hydrobiologia 506-509:641–649
Levi PS, Riis T, Alnøe AB, Peipoch M, Maetzke K (2015) Macrophyte complexity controls nutrient uptake in lowland streams. Ecosystems 18:914–931
Li CH (2008) Effects of fish on tropical shallow lakes and the implication for lake restoration. University of Jinan, Dissertation (in Chinese)
Liu ZW, Hu JR, Zhong P, Zhang XF, Ning JJ, Larsen SE, Chen DY, Gao YM, He H, Jeppesen E (2018) Successful restoration of a tropical shallow eutrophic lake: strong bottom-up but weak top-down effects recorded. Water Res 146:88–97
Lorenz AW, Stoll S, Sundermann A, Haase P (2013) Do adult and YOY fish benefit from river restoration measures? Ecol Eng 61:174–181
Mehner T (2010) No empirical evidence for community-wide top-down control of prey fish density and size by fish predators in lakes. Limnol Oceanogr 55:203–213
Mehner T, Arlinghaus R, Berg S, Dörner H, Jacobsen L, Kasprzak P, Koschel R, Schulze T, Skov C, Wolter C, Wysujack K (2004) How to link biomanipulation and sustainable fisheries management: a step-by-step guideline for lakes of the European temperate zone. Fish Manag Ecol 11:261–275
Nurminen L, Horppila J (2009) Life form dependent impacts of macrophyte vegetation on the ratio of resuspended nutrients. Water Res 43:3217–3226
Ofir E, Heymans JJ, Shapiro J, Goren M, Spanier E, Gal G (2017) Predicting the impact of lake biomanipulation based on food-web modeling—Lake Kinneret as a case study. Ecol Model 348:14–24
Roberts E, Kroker J, Korner S, Nicklisch A (2003) The role of periphyton during the re-colonization of a shallow lake with submerged macrophytes. Hydrobiologia 506:525–530
Rodrigo MA, Rojo C, Alonso-Guillén JL, Vera P (2013) Restoration of two small mediterranean lagoons: the dynamics of submerged macrophytes and factors that affect the success of revegetation. Ecol Eng 54:1–15
Rosińska J, Rybak M, Gołdyn R (2017) Patterns of macrophyte community recovery as a result of therestoration of a shallow urban lake. Aquat Bot 138:45–52
Rosińska J, Kozak A, Dondajewska R, Kowalczewska-Madura K, Gołdyn R (2018) Water quality response to sustainable restoration measures – case study of urban Swarzędzkie Lake. Ecol Indic 84:437–449
Rosińska J, Romanowicz-Brzozowska W, Kozak A, Gołdyn R (2019) Zooplankton changes during bottom-up and top-down control due to sustainable restoration in a shallow urban lake. Environ Sci Pollut R 26:19575–19587
Scharf W (2007) Biomanipulation as a useful water quality management tool in deep stratifying reservoirs. Hydrobiologia 583:21–42
Scheffer M, Hosper SH, Meijer ML, Moss B, Jeppesen E (1993) Alternative equilibria in shallow lakes. Trends Ecol Evol 8:275–279
Seda J, Hejzlar J, Kubecka J (2000) Trophic structure of nine Czech reservoirs regularly stocked with piscivorous fish. Hydrobiologia 429:141–149
SEPA (2002) Analytical methods for water and wasterwater monitor, 4th edn. Chinese Enviromental Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Shearer JF, Grodowitz MJ, McFarland DG (2007) Nutritional quality of Hydrilla verticillata (L.f.) Royle and its effects on a fungal pathogen Mycoleptodiscus terrestris (Gerd.) Ostazeski. Biol Control 41:175–183
Shen JR, Du NS (1979) Fauna Sinica; Crustacea: freshwater Copepoda. Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Søndergaard M, Liboriussen L, Pedersen AR, Jeppesen E (2008) Lake restoration by fish removal: short-and long-term effects in 36 Danish lakes. Ecosystems 11:1291–1305
Sun J, Wang L, Ma L, Min FL, Tao H, Zhang Y, Wu ZB, He F (2017) Factors affecting palatability of four submerged macrophytes for grass carp Ctenopharyngodon idella. Environ Sci Pollut R 24:28046–28054
Sun J, Wang L, Ma L, Huang T, Cheng WP, Min FL, Zhang Y, Wu ZB, He F (2018) Determinants of submerged macrophytes palatability to grass carp Ctenopharyngodon idellus. Ecol Indic 85:657–663
Van TK, Haller WT, Bowes G (1976) Comparison of the photosynthetic characteristics of three submersed aquatic plants. Plant Physiol 58:761–768
Vanderstukken M, Mazzeo N, Van Colen W, Declerck SAJ, Muylaert K (2011) Biological control of phytoplankton by the subtropical submerged macrophytes Egeria densa and Potamogeton illinoensis: a mesocosm study. Freshw Biol 56:1837–1849
Vašek M, Prchalová M, Peterka J, Ketelaars HAM, Wagenvoort AJ, Čech M, Draštík V, Říha M, Jůza T, Kratochvíl M, Mrkvička T, Blabolil P, Boukal DS, Duras J, Kubečk J (2013) The utility of predatory fish in biomanipulation of deep reservoirs. Ecol Eng 52:104–111
Waajen GWAM, Bruggen NCBV, Pires LMD, Lengkeek W, Lürling M (2016) Biomanipulation with quagga mussels (dreissena rostriformis bugensis) to control harmful algal blooms in eutrophic urban ponds. Ecol Eng 90:141–150
Wang JJ (1961) Fauna Sinica; Rotifer. Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Wei XF (2015) The influence of Megahbrama amblycephala to the competitive landscape of Vallisneria natans and Hydrilla verticillata. Huazhong Agricultural University, Dissertation (in Chinese)
Wen T (2008) Effect of water turbidity on the growth and development of Vallisneria asiatic and Hydrilla verticillata. Nanjing Normal University, Dissertation (in Chinese)
Ye C, Li CH, Yu HC, Song XF, Zou GY, Liu J (2011) Study on ecological restoration in near-shore zone of a eutrophic lake, Wuli Bay, Taihu Lake. Ecol Eng 37:1434–1437
Yi CL, Guo LG, Ni L, Yin CJ, Wan J, Yuan CB (2016a) Biomanipulation in mesocosms using silver carp in two chinese lakes with distinct trophic states. Aquaculture 452:233–238
Yi CL, Guo LG, Ni LY, Luo CQ (2016b) Silver carp exhibited an enhanced ability of biomanipulation to control cyanobacteria bloom compared to bighead carp in hypereutrophic Lake Taihu mesocosms. Ecol Eng 89:7–13
Yu JL, Liu ZW, He H, Zhen W, Guan BH, Chen FZ, Li KY, Zhong P, Mello FTD, Jeppesen E (2016a) Submerged macrophytes facilitate dominance of omnivorous fish in a subtropical shallow lake: implications for lake restoration. Hydrobiologia 775:97–107
Yu JL, Liu ZW, Li KY, Chen FZ, Guan BH, Hu YH, Zhong P, Tang Y, Zhao XF, He H, Zeng H, Jeppesen E (2016b) Restoration of shallow lakes in subtropical and tropical China: response of nutrients and water clarity to biomanipulation by fish removal and submerged plant transplantation. Water 8:438
Zeng L, He F, Dai ZG, Xu D, Liu BY, Zhou QH, Wu ZB (2017) Effect of submerged macrophyte restoration on improving aquatic ecosystem in a subtropical, shallow lake. Ecol Eng 106:578–587
Zhang XF, Liu ZW (2011) Interspecific competition effects on phosphorus accumulation by Hydrilla verticillata and Vallisneria natans. J Environ Sci 23:1274–1278
Acknowledgments
We express our gratitude to Shurong Qian and Xiaoxia Chen for their assistance in field and laboratory work, and Zhaoshi Wu and Xiaolong Huang for improving the language in the manuscript. We also thank two anonymous reviewers for their useful comments. This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31930074; 31971473), the Major Science and Technology Program for Water Pollution Control and Treatment (2017ZX07203-005), and the Science and Technology Service Network Initiative Project of Chinese Academy of Sciences (KFJ-STS-QYZD-156), and NIGLAS 135 Project (NIGLAS2018GH04).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, Y., Gu, J., Li, Q. et al. Effects of juvenile crucian carp (Carassius carassius) removal on submerged macrophyte growth—implications for subtropical shallow lake restoration. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 42198–42209 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07217-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07217-0