Abstract
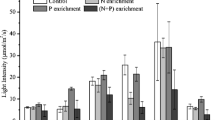
Nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) are key factors that limit phytoplankton growth in freshwater lakes. Controlling external P loading is a widely recognized measure for reducing eutrophication, but the usefulness of limiting N inputs remains under debate. Shallow lakes with frequent sediment resuspension events exacerbate internal P loading and limit the potential for in-lake P reduction. A two-way factorial mesocosm experiment was carried out using two levels of N inputs (with and without addition of potassium nitrate as N source) and sediment resuspension (with and without resuspension) for 35 days in order to examine the effect of N inputs on phytoplankton growth during sediment resuspension events. N addition alone did not affect phytoplankton biomass in mesocosms in treatments without sediment resuspension, likely due to the P limitation. However, internal P loading, via sediment resuspension, shifted mesocosms from P- to N-limited systems in which N addition significantly boosted phytoplankton biomass. Our results suggested that external loading comprising N alone may enhance phytoplankton growth in shallow, eutrophic lakes with frequent resuspension events like Lake Taihu, China. In such lakes, P-only management is unlikely to usefully reduce eutrophication, and a strategy to reduce both N and P is needed.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen, F. Z., T. T. Shu, E. Jeppesen, Z. W. Liu & Y. W. Chen, 2013. Restoration of a subtropical eutrophic shallow lake in china: effects on nutrient concentrations and biological communities. Hydrobiologia 718: 59–71.
Conley, D. J., H. W. Paerl, R. W. Howarth, D. F. Boesch, S. P. Seitzinger, K. E. Havens, C. Lancelot & G. E. Likens, 2009. Controlling eutrophication: nitrogen and phosphorus. Science (Washington) 323: 1014–1015.
Elser, J. J., W. F. Fagan, R. F. Denno, D. R. Dobberfuhl, A. Folarin, A. Huberty, S. Interlandi, S. S. Kilham, E. McCauley & K. L. Schulz, 2000. Nutritional constraints in terrestrial and freshwater food webs. Nature 408: 578–580.
Elser, J. J., M. E. S. Bracken, E. E. Cleland, D. S. Gruner, W. S. Harpole, H. Hillebrand, J. T. Ngai, E. W. Seabloom, J. B. Shurin & J. E. Smith, 2007. Global analysis of nitrogen and phosphorus limitation of primary producers in freshwater, marine and terrestrial ecosystems. Ecology Letters 10: 1135–1142.
Fan, C. X., L. Zhang & W. C. Qu, 2001. Lake sediment resuspension and caused phosphate release simulation study. Journal of Environmental Science 13: 406–410.
Gilpin, L., K. Davidson & E. Roberts, 2004. The influence of changes in nitrogen: silicon ratios on diatom growth dynamics. Journal of Sea Research 51: 21–35.
Heiskanen, A. S. & K. Olli, 1996. Sedimentation and buoyancy of Aphanizomenon cf. flos-aquae (Nostocales, Cyanophyta) in a nutrient-replete and nutrient-depleted coastal area of the baltic sea. Phycologia 35: 94–101.
Hu, H. J., 2006. The Freshwater Algae of China: Systematics, Taxonomy and Ecology. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese).
Jensen, H. S., P. Kristensen, E. Jeppesen & A. Skytthe, 1992. Iron: phosphorus ratio in surface sediment as an indicator of phosphate release from aerobic sediments in shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 235: 731–743.
Jeppesen, E., P. Kristensen, J. P. Jensen, M. Søndergaard, E. Mortensen & T. Lauridsen, 1991. Recovery resilience following a reduction in external phosphorus loading of shallow, eutrophic Danish lakes: duration, regulating factors and methods for overcoming resilience. Memorie dell’ Istituto italiano di idrobiologia dott. Marco de Marchi, 48, 127–148.
Jeppesen, E., M. Søndergaard, J. P. Jensen, K. E. Havens, O. Anneville, L. Carvalho, M. F. Coveney, R. Deneke, M. T. Dokulil & B. Foy, 2005. Lake responses to reduced nutrient loading: an analysis of contemporary long-term data from 35 case studies. Freshwater Biology 50: 1747–1771.
Jin, X. C. & Q. Y. Tu, 1990. The Standard Methods for Observation and Analysis in Lake Eutrophication, 2nd ed. Environmental Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese).
Marsden, M. W., 1989. Lake restoration by reducing external phosphorus loading: the influence of sediment phosphorus release. Freshwater Biology 21: 139–162.
Paerl, H. W., H. Xu, M. J. McCarthy, G. W. Zhu, B. Q. Qin, Y. Li & W. S. Gardner, 2011. Controlling harmful cyanobacterial blooms in a hyper-eutrophic lake (Lake Taihu, China): the need for a dual nutrient (N&P) management strategy. Water Research 45: 1973–1983.
Qin, B. Q., W. P. Hu, G. Gao, L. C. Luo & J. S. Zhang, 2004. Dynamics of sediment resuspension and the conceptual schema of nutrient release in the large shallow Lake Taihu, China. Chinese Science Bulletin 49: 54–64.
Qin, B. Q., G. W. Zhu, L. Zhang, L. C. Luo, G. Gao & B. H. Gu, 2006. Estimation of internal nutrient release in large shallow Lake Taihu, China. Science of China Series D 49: 38–50.
Qin, B. Q., P. Z. Xu, Q. L. Wu, L. C. Luo & Y. L. Zhang, 2007. Environmental issues of Lake Taihu, China. Hydrobiologia 581: 3–14.
Scheffer, M., S. Rinaldi, A. Gragnani, L. R. Mur & E. H. van Nes, 1997. On the dominance of filamentous cyanobacteria in shallow, turbid lakes. Ecology 78: 272–282.
Schindler, D. W., 1974. Eutrophication and recovery in experimental lakes: implications for lake management. Science 184: 897–899.
Schindler, D. W., 1977. Evolution of phosphorus limitation in lakes. Science 195: 260–262.
Schindler, D. W., 2006. Recent advances in the understanding and management of eutrophication. Limnology and Oceanography 51: 356–363.
Schindler, D. W., R. Hecky, D. Findlay, M. Stainton, B. Parker, M. Paterson, K. Beaty, M. Lyng & S. Kasian, 2008. Eutrophication of lakes cannot be controlled by reducing nitrogen input: results of a 37-year whole-ecosystem experiment. Proceedings of the National Acadamy of the Science of the United States of America 105: 11254–11258.
Schöllhorn, E. & E. Granéli, 1996. Influence of different nitrogen to silica ratios and artificial mixing on the structure of a summer phytoplankton community from the swedish west coast (Gullmar Fjord). Journal of Sea Research 35: 159–167.
Scott, J. T. & M. J. McCarthy, 2010. Nitrogen fixation may not balance the nitrogen pool in lakes over timescales relevant to eutrophication management. Limnology and Oceanography 55: 1265–1270.
SEPA, 2002. Analytical Methods for Water and Wasterwater Monitor, 4th ed. Chinese Enviromental Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese).
Smith, V. H. & D. W. Schindler, 2009. Eutrophication science: where do we go from here? Trends in Ecology & Evolution 24: 201–207.
Søndergaard, M., P. Kristensen & E. Jeppesen, 1992. Phosphorus release from resuspended sediment in the shallow and wind-exposed Lake Arresø, Denmark. Hydrobiologia 228: 91–99.
Søndergaard, M., J. P. Jensen & E. Jeppesen, 2003. Role of sediment and internal loading of phosphorus in shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 506: 135–145.
Søndergaard, M., J. P. Jensen & E. Jeppesen, 2005. Seasonal response of nutrients to reduced phosphorus loading in 12 Danish lakes. Freshwater Biology 50: 1605–1615.
Song, X. L., Z. W. Liu, G. J. Yang & Y. W. Chen, 2010. Effects of resuspension and eutrophication level on summer phytoplankton dynamics in two hypertrophic areas of Lake Taihu, China. Aquatic Ecology 44: 41–54.
Van Luijn, F., D. T. Van der Molen, W. J. Luttmer & P. C. M. Boers, 1995. Influence of benthic diatoms on the nutrient release from sediments of shallow lakes recovering from eutrophication. Water Science and Technology 32: 89–97.
Wang, H., 2009. Mitigation of lake eutrophication: loosen nitrogen control and focus on phosphorus abatement. Progress in Natural Science 19: 1445–1451.
Welch, E. B., 2009. Should nitrogen be reduced to manage eutrophication if it is growth limiting? Evidence from moses lake. Lake and Reservior Management 25: 401–409.
Xu, H., H. W. Paerl, B. Q. Qin, G. W. Zhu & G. Gao, 2010. Nitrogen and phosphorus inputs control phytoplankton growth in eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. Limnology and Oceangraphy 2010: 420–432.
Zhang, Z. S. & X. F. Huang, 1991. Methods in Freshwater Plankton Study. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese).
Zhang, X. F., Z. W. Liu, R. D. Gulati & E. Jeppesen, 2013. The effect of benthic algae on phosphorus exchange between sediment and overlying water in shallow lakes: a microcosm study using 32P as tracer. Hydrobiologia 710: 109–116.
Zhu, G. W., B. Q. Qin & G. Gao, 2005. Direct evidence of phosphorus outbreak release from sediment to overlying water in a large shallow lake caused by strong wind wave disturbance. Chinese Science Bulletin 50: 577–582.
Zhu, G. W., B. Q. Qin, L. Zhang & L. C. Luo, 2006. Geochemical forms of phosphorus in sediments of three large, shallow lakes of China. Pedosphere 16: 726–734.
Acknowledgments
The authors express their gratitude to Xiaodan Di, Jinlei Yu, Ming Zhang, Yachan Ji, and Xiaoxia Chen for support in field and laboratory work, and Amy-Jane Beer for the English improvements of this manuscript. This study was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (No. 2012CB956100), the National Science Foundation of China (No. U1033602 and 41073057), the Key Project of 135 program of Nanjing Institute of Geography and Limnology, and the CAS/SAFEA International Partnership Program for Creative Research Teams.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling editor: Boping Han
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, H., Kang, Y. & Liu, Z. Nitrogen inputs enhance phytoplankton growth during sediment resuspension events: a mesocosm study. Hydrobiologia 744, 297–305 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-014-2085-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-014-2085-0