Abstract
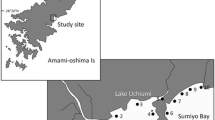
The metamorphosis of sea lamprey (Petromyzon marinus Linnaeus, 1758) allows young postmetamorphic individuals to migrate to the sea and start the hematophagous feeding. However, the information about this phase is very limited, especially for European populations. Herein, we provide for the first time a comprehensive study on the phenology of downstream migration, the timing and location of first feeding and the prey species in the River Ulla and its estuary (NW Spain). Results show that downstream migration occurs between October and May with a peak in March. At least for a part of the postmetamorphic lampreys this migration stops for several months when they reach the estuary, where lampreys find shelter and abundant food, before moving to coastal waters. Hematophagous feeding in the estuary allows postmetamorphics to increase their total length and weight exponentially. Our results also suggest that part of the postmetamorphics (10–30%) start the hematophagous feeding in the river, with a special affinity for anadromous species, probably because of their larger size.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeida, P. R., 1996. Estuarine movement patterns of adult thin-lipped grey mullet, Liza ramada (Risso) (Pisces, Mugilidae), observed by ultrasonic tracking. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 202: 137–150.
Beamish, F. W. H., 1980. Biology of the North American anadromous sea lamprey, Petromyzon marinus. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 37: 1924–1943.
Beamish, F. W. H. & I. C. Potter, 1975. The biology of the anadromous sea lamprey (Petromyzon marinus) in New Brunswick. Journal of Zoology 177: 57–72.
Berra, T. M., 2001. Freshwater Fish Distribution. Academic Press, London.
Bird, D. J., I. C. Potter, M. W. Hardisty & B. I. Baker, 1994. Morphology, body size and behaviour of recently-metamorphosed sea lampreys, Petromyzon marinus, from the lower River Severn, and their relevance to the onset of parasitic feeding. Journal of Fish Biology 44: 67–74.
Caballero, P., F. Cobo & M. A. González, 2006. Life history of a sea trout (Salmo trutta L.) population from the north-west Iberian Peninsula (River Ulla, Galicia, Spain). In Harris, G. & N. Milner (eds), Sea Trout: Biology, Conservation & Management. Blackwell, Oxford: 234–247.
Davis, R. M., 1967. Parasitism by newly transformed anadromous sea lampreys on landlocked salmon and other fishes in a coastal Maine lake. Transactions of the American Fisheries Society 96: 11–16.
Farmer, G. J., 1980. Biology and physiology of feeding in adult lampreys. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 37: 1751–1761.
Freyhof, J. & M. Kottelat, 2008. Petromyzon marinus. In: IUCN 2011. IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2011.2. www.iucnredlist.org. Downloaded on 18 June 2012.
Grajal-Blanco, M., 1980. Las corrientes marinas y su influencia en la zona del Vado en la Isla de Arosa. Cuadernos do Laboratorio Xeolóxico de Laxe 1: 249–278.
Hardisty, M. W., 2006. Lampreys: Life Without Jaws. Forrest Text, Ceredigion.
Hardisty, M. W. & I. C. Potter, 1971. The general biology of adult lampreys. In Hardisty, M. W. & I. C. Potter (eds), The Biology of Lampreys, Vol. 1. Academic Press, London: 127–206.
Henson, M. P., R. A. Bergstedt & J. V. Adams, 2003. Comparison of spring measures of length, weight, and condition factor for predicting metamorphosis in two populations of sea lamprey (Petromyzon marinus) larvae. Journal of Great Lakes Research 29: 204–213.
Kelly, F. L. & J. J. King, 2001. A review of the ecology and distribution of three lamprey species, Lampetra fluviatilis (L.), Lampetra planeri (Bloch) and Petromyzon marinus (L.): a context for conservation and biodiversity considerations in Ireland. Biology and Environment: Proceedings of the Royal Irish Academy 101B: 165–185.
Lucas, M. C. & E. Baras, 2001. Migration of Freshwater Fishes. Blackwell Science, Oxford.
Maitland, P. S., H. Morris & K. East, 1994. The ecology of lampreys (Petromyzonidae) in the Loch Lomond area. Hydrobiologia 290: 105–120.
Nichols, O. C. & P. K. Hamilton, 2004. Occurrence of the parasitic sea lamprey, Petromyzon marinus, on western North Atlantic right whales, Eubalaena glacialis. Environmental Biology of Fishes 71: 413–417.
Nichols, O. C. & U. T. Tscherter, 2011. Feeding of sea lampreys Petromyzon marinus on minke whales Balaenoptera acutorostrata in the St Lawrence Estuary. Journal of Fish Biology 78: 338–343.
Potter, I. C., 1980. Ecology of larval and metamorphosing lampreys. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 37: 1641–1657.
Potter, C. & F. W. H. Beamish, 1977. The freshwater biology of adult anadromous sea lampreys Petromyzon marinus. Journal of Zoology 181: 113–130.
Quintella, B. R., N. O. Andrade & P. R. Almeida, 2003. Distribution, larval stage duration and growth of the sea lamprey ammocoetes, Petromyzon marinus L., in a highly modified river basin. Ecology of Freshwater Fish 12: 286–293.
Swink, W. D., 2003. Host selection and lethality of attacks by sea lampreys (Petromyzon marinus) in laboratory studies. Journal of Great Lakes Research 29: 307–319.
Taverny, C. & P. Elie, 2009. Bilan des connaissances biologiques et de l’état des habitats des lamproies migratrices dans le bassin de la Gironde—Propositions d’actions prioritaires. Rapport Final. Etude Cemagref, Groupement de Bordeaux.
Taverny, C., M. Urdaci, A. M. Elie, L. Beaulaton, I. Ortusi, F. Daverat & P. Elie, 2005. Biologie, écologie et pêche des lamproies migratrices (Agnathes amphihalins)—Troisième tranche fonctionnelle. Rapport Final. Etude Cemagref, Groupement de Bordeaux.
White, A. & T. C. Fletcher, 1985. Seasonal changes in serum glucose and condition of the plaice, Pleuronectes platessa L. Journal of Fish Biology 26: 755–764.
Youson, J. H., 1980. Morphology and physiology of lamprey metamorphosis. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 37: 1687–1710.
Youson, J. H. & I. C. Potter, 1979. A description of the stages of metamorphosis in the anadromous sea lamprey, Petromyzon marinus L. Canadian Journal of Zoology 57: 1808–1817.
Acknowledgments
Part of this study has been carried out in the laboratories of the Station of Hydrobiology of the USC ‘Encoro do Con’ in Vilagarcía de Arousa. The authors thank the staff of this station due their participation in the surveys, especially D. J. Nachón. We also thank the staff of Ximonde permanent trap for their collaboration in this study. This study has been partially supported by the project 10PXIB2111059PR of Xunta de Galicia and the project MIGRANET of the Interreg IV B SUDOE (South-West Europe) Territorial Cooperation Programme (SOE2/P2/E288).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling editor: M. Power
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Silva, S., Servia, M.J., Vieira-Lanero, R. et al. Downstream migration and hematophagous feeding of newly metamorphosed sea lampreys (Petromyzon marinus Linnaeus, 1758). Hydrobiologia 700, 277–286 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-012-1237-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-012-1237-3