Abstract
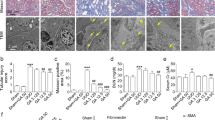
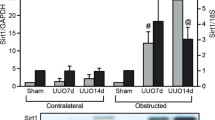
Baicalein is a natural flavonoid that possesses notable anti-inflammatory effects. In this study, we detected whether baicalein protects against inflammatory response in unilateral ureteral obstruction mice model to ameliorate tubulointerstitial fibrosis. Baicalein treatment significantly attenuated tubulointerstitial fibrosis by markedly reducing fibronectin and collagen-I. The downregulation of alpha-smooth muscle actin and upregulation of E-cadherin indicated that the epithelial–mesenchymal transition process was suppressed. Furthermore, baicalein administration blocked the infiltration of macrophages and lymphocytes, as evidenced by the significantly reduced CD68 and CD3 positive cells. Meanwhile, the mRNA expression of the pro-inflammatory cytokines tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-1β, and monocyte chemotactic protein in baicalein-treated groups was markedly reduced compared with the vehicle-treated group. More importantly, unilateral ureteral obstruction induced the activation of NF-κB and mitogen-activated protein kinase signal pathways to switch on inflammatory response to aggravate kidney fibrosis, but these effects were mitigated by baicalein. These data demonstrate that baicalein could inhibit inflammatory process via inactivation of NF-κB and MAPK signal pathways to execute its anti-fibrotic actions in obstructive kidney disease.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bani-Hani AH et al (2009) IL-18 neutralization ameliorates obstruction-induced epithelial–mesenchymal transition and renal fibrosis. Kidney Int 76:500–511. doi:10.1038/ki.2009.216
Boutet A, De Frutos CA, Maxwell PH, Mayol MJ, Romero J, Nieto MA (2006) Snail activation disrupts tissue homeostasis and induces fibrosis in the adult kidney. EMBO J 25:5603–5613. doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7601421
Crisman JM, Richards LL, Valach DP, Franzoni DF, Diamond JR (2001) Chemokine expression in the obstructed kidney. Exp Nephrol 9:241–248
de Borst MH et al (2009) c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase is crucially involved in renal tubulo-interstitial inflammation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 331:896–905. doi:10.1124/jpet.109.154179
Eddy AA (2014) Overview of the cellular and molecular basis of kidney fibrosis. Kidney Int Suppl 4:2–8. doi:10.1038/kisup.2014.2
Eddy AA, Lopez-Guisa JM, Okamura DM, Yamaguchi I (2012) Investigating mechanisms of chronic kidney disease in mouse models. Pediatr Nephrol 27:1233–1247. doi:10.1007/s00467-011-1938-2
Esteban V et al (2004) Angiotensin II, via AT1 and AT2 receptors and NF-kappaB pathway, regulates the inflammatory response in unilateral ureteral obstruction. JASN 15:1514–1529
Fan JM, Huang XR, Ng YY, Nikolic-Paterson DJ, Mu W, Atkins RC, Lan HY (2001) Interleukin-1 induces tubular epithelial-myofibroblast trans differentiation through a transforming growth factor-beta1-dependent mechanism in vitro. Am J kidney Dis 37:820–831
Gao Y, Lu J, Zhang Y, Chen Y, Gu Z, Jiang X (2013) Baicalein attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats through inhibition of miR-21. Pulm Pharmacol Ther 26:649–654. doi:10.1016/j.pupt.2013.03.006
Hou YC, Lin SP, Tsai SY, Ko MH, Chang YC, Chao PD (2011) Flavonoid pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution after repeated dosing of the roots of Scutellaria baicalensis in rats. Planta Med 77:455–460. doi:10.1055/s-0030-1250433
Inoue T, Jackson EK (1999) Strong antiproliferative effects of baicalein in cultured rat hepatic stellate cells. Eur J Pharmacol 378:129–135
Jones LK et al (2009) IL-1RI deficiency ameliorates early experimental renal interstitial fibrosis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 24:3024–3032. doi:10.1093/ndt/gfp214
Klahr S, Morrissey J (2002) Obstructive nephropathy and renal fibrosis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 283:F861–F875. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00362.2001
Kong EK, Yu S, Sanderson JE, Chen KB, Huang Y, Yu CM (2011) A novel anti-fibrotic agent, baicalein, for the treatment of myocardial fibrosis in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Eur J Pharmacol 658:175–181. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2011.02.033
Lee SB, Kalluri R (2010) Mechanistic connection between inflammation and fibrosis. Kidney Int Suppl 78:S22–S26. doi:10.1038/ki.2010.418
Liu Y (2011) Cellular and molecular mechanisms of renal fibrosis. Nat Rev Nephrol 7:684–696. doi:10.1038/nrneph.2011.149
Liu A et al (2014) Baicalein protects against polymicrobial sepsis-induced liver injury via inhibition of inflammation and apoptosis in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 748C:45–53. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.12.014
Ni H, Chen J, Pan M, Zhang M, Zhang J, Chen P, Liu B (2013) FTY720 prevents progression of renal fibrosis by inhibiting renal microvasculature endothelial dysfunction in a rat model of chronic kidney disease. J Mol Histol 44:693–703. doi:10.1007/s10735-013-9521-8
Nightingale J, Oncostatin M et al (2004) A cytokine released by activated mononuclear cells, induces epithelial cell-myofibroblast transdifferentiation via Jak/Stat pathway activation. JASN 15:21–32
Oh KS, Oh BK, Park CH, Mun J, Won SH, Lee BH (2012) Baicalein potently inhibits Rho kinase activity and suppresses actin stress fiber formation in angiotensin II-stimulated H9c2 cells. Biol Pharm Bull 35:1281–1286
Panzer U et al (2009) Resolution of renal inflammation: a new role for NF-kappaB1 (p50) in inflammatory kidney diseases American journal of physiology. Renal Physiol 297:F429–F439. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.90435.2008
Ricardo SD, van Goor H, Eddy AA (2008) Macrophage diversity in renal injury and repair. J Clin Investig 118:3522–3530. doi:10.1172/JCI36150
Rodriguez-Pena AB, Grande MT, Eleno N, Arevalo M, Guerrero C, Santos E, Lopez-Novoa JM (2008) Activation of Erk1/2 and Akt following unilateral ureteral obstruction. Kidney Int 74:196–209. doi:10.1038/ki.2008.160
Schreiner GF, Harris KP, Purkerson ML, Klahr S (1988) Immunological aspects of acute ureteral obstruction: immune cell infiltrate in the kidney. Kidney Int 34:487–493
Shimizu I (2000) Sho-saiko-to: Japanese herbal medicine for protection against hepatic fibrosis and carcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 15(Suppl):D84–D90
Shimizu I (2001) Antifibrogenic therapies in chronic HCV infection. Curr Drug Targets Infect Disord 1:227–240
Stambe C, Atkins RC, Tesch GH, Masaki T, Schreiner GF, Nikolic-Paterson DJ (2004) The role of p38alpha mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in renal fibrosis. JASN 15:370–379
Sun H, Che QM, Zhao X, Pu XP (2010) Antifibrotic effects of chronic baicalein administration in a CCl4 liver fibrosis model in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 631:53–60. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2010.01.002
Tashiro K et al (2003) Attenuation of renal fibrosis by proteasome inhibition in rat obstructive nephropathy: possible role of nuclear factor kappaB. Int J Mol Med 12:587–592
Vielhauer V, Kulkarni O, Reichel CA, Anders HJ (2010) Targeting the recruitment of monocytes and macrophages in renal disease. Semin Nephrol 30:318–333. doi:10.1016/j.semnephrol.2010.03.006
Wang YGM, Sun S, Dai J, Cao H, Zheng N, Fang J, Gou X, Lu X, Zhang Y (2012) The effects of baicalein on rat renal fibrosis and the experssions of TGF-β1 and Smad-2 (in Chinese). J Chang Univ Tradit Chin Med 28:383–385
Wu Y, Deng J, Rychahou PG, Qiu S, Evers BM, Zhou BP (2009) Stabilization of snail by NF-kappaB is required for inflammation-induced cell migration and invasion. Cancer Cell 15:416–428. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2009.03.016
Wu K, Li H, Tian J, Lei W (2014) Protective effect of baicalein on renal ischemia/reperfusion injury in the rat. Renal Fail 1–7. doi:10.3109/0886022X.2014.991999
Zhang X et al (2014) Baicalein ameliorates inflammatory-related apoptotic and catabolic phenotypes in human chondrocytes. Int Immunopharmacol 21:301–308. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2014.05.006
Zheng X et al. (2013) Protective effects of chronic resveratrol treatment on vascular inflammatory injury in streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetic rats: role of NF-kappa B signaling. Eur J Pharmacol. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.10.034
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Wei Wang and Pang-hu Zhou have contributed equally to this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, W., Zhou, Ph., Xu, Cg. et al. Baicalein attenuates renal fibrosis by inhibiting inflammation via down-regulating NF-κB and MAPK signal pathways. J Mol Hist 46, 283–290 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-015-9621-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-015-9621-8