Abstract
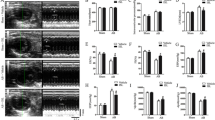
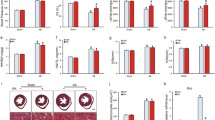
Cardiac remodeling is a key determinant in the clinical course and outcome of heart failure and characterized by cardiac hypertrophy, fibrosis, cardiomyocyte apoptosis and inflammation. The anti-inflammatory, anti-apoptotic and anti-fibrotic effects of paeoniflorin have been identified in various types of tissue and cells. However, the role of paeoniflorin in cardiac remodeling remains unclear. We performed aortic banding (AB) in mice to induce a cardiac remodeling model in response to pressure overload. Paeoniflorin (20 mg/kg) was administered by daily intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection. Paeoniflorin treatment promoted the survival rate and improved cardiac function of mice at 8 weeks post surgery. AB-induced cardiac hypertrophy, as assessed by heart weight, gross heart, HE and WGA staining, cross-sectional area of cardiomyocyte and mRNA expresssion of hypertrophic makers, was attenuated by paeoniflorin. Paeoniflorin also inhibited collagen deposition, expression of TGFβ, CTGF, collagen Iα and collagen IIIα, and phosphorylation of Smad2 and Smad3 in the heart exposed to pressure overload. Cardiomyocyte apoptosis and induction of Bax and cleaved caspase3 in response to AB were suppressed by paeoniflorin. Furthermore, paeoniflorin decreased the quantity of CD68+ cells, protein levels of TNF-α and IL-1β, and phosphorylation of IκBα and NFκB-p65 in the heart after AB. In conclusion, paeoniflorin attenuated cardiac hypertrophy, fibrosis, apoptosis and inflammation, and improved left ventricular function in pressure overloaded mice. The cardioprotective effect of paeoniflorin is associated with the inhibition of TGFβ/Smads and NF-κB pathways.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asakura M, Kitakaze M (2009) Global gene expression profiling in the failing myocardium. Circ J 73(9):1568–1576
Bui AL, Horwich TB, Fonarow GC (2011) Epidemiology and risk profile of heart failure. Nat Rev Cardiol 8(1):30–41
Cao W, Zhang W, Liu J, Wang Y, Peng X, Lu D, Qi R, Wang H (2011) Paeoniflorin improves survival in LPS-challenged mice through the suppression of TNF-alpha and IL-1beta release and augmentation of IL-10 production. Int Immunopharmacol 11(2):172–178
Chu D, Luo Q, Li C, Gao Y, Yu L, Wei W, Wu Q, Shen J (2007) Paeoniflorin inhibits TGF-beta1-mediated collagen production by Schistosoma japonicum soluble egg antigen in vitro. Parasitology 134(Pt 11):1611–1621
Chu D, Du M, Hu X, Wu Q, Shen J (2011) Paeoniflorin attenuates schistosomiasis japonica-associated liver fibrosis through inhibiting alternative activation of macrophages. Parasitology 138(10):1259–1271
Cohn JN, Ferrari R, Sharpe N (2000) Cardiac remodeling—concepts and clinical implications: a consensus paper from an international forum on cardiac remodeling. Behalf of an International Forum on Cardiac Remodeling. J Am Coll Cardiol 35(3):569–582
Creemers EE, Pinto YM (2011) Molecular mechanisms that control interstitial fibrosis in the pressure-overloaded heart. Cardiovasc Res 89(2):265–272
Dorn GW 2nd (2009) Apoptotic and non-apoptotic programmed cardiomyocyte death in ventricular remodelling. Cardiovasc Res 81(3):465–473
Euler-Taimor G, Heger J (2006) The complex pattern of SMAD signaling in the cardiovascular system. Cardiovasc Res 69(1):15–25
Gonzalez A, Ravassa S, Beaumont J, Lopez B, Diez J (2011) New targets to treat the structural remodeling of the myocardium. J Am Coll Cardiol 58(18):1833–1843
Hayden MS, Ghosh S (2008) Shared principles in NF-kappaB signaling. Cell 132(3):344–362
Hill JA, Olson EN (2008) Cardiac plasticity. N Engl J Med 358(13):1370–1380
Hutchinson KR, Guggilam A, Cismowski MJ, Galantowicz ML, West TA, Stewart JA Jr, Zhang X, Lord KC, Lucchesi PA (2011) Temporal pattern of left ventricular structural and functional remodeling following reversal of volume overload heart failure. J Appl Physiol 111(6):1778–1788
Ji Q, Yang L, Zhou J, Lin R, Zhang J, Lin Q, Wang W, Zhang K (2012) Protective effects of paeoniflorin against cobalt chloride-induced apoptosis of endothelial cells via HIF-1alpha pathway. Toxicol In Vitro 26(3):455–461
Jiang B, Qiao J, Yang Y, Lu Y (2012) Inhibitory effect of paeoniflorin on the inflammatory vicious cycle between adipocytes and macrophages. J Cell Biochem 113(8):2560–2566
Jones WK, Brown M, Ren X, He S, McGuinness M (2003) NF-kappaB as an integrator of diverse signaling pathways: the heart of myocardial signaling? Cardiovasc Toxicol 3(3):229–254
Kehat I, Molkentin JD (2010) Molecular pathways underlying cardiac remodeling during pathophysiological stimulation. Circulation 122(25):2727–2735
Kim ID, Ha BJ (2010) The effects of paeoniflorin on LPS-induced liver inflammatory reactions. Arch Pharm Res 33(6):959–966
Koitabashi N, Danner T, Zaiman AL, Pinto YM, Rowell J, Mankowski J, Zhang D, Nakamura T, Takimoto E, Kass DA (2011) Pivotal role of cardiomyocyte TGF-beta signaling in the murine pathological response to sustained pressure overload. J Clin Invest 121(6):2301–2312
Li X, Shen J, Zhong Z, Wen H, Luo Q, Wei W (2009) Paeoniflorin: a monomer from traditional Chinese medical herb ameliorates Schistosoma japonicum egg-induced hepatic fibrosis in mice. J Parasitol 95(6):1520–1524
Li JZ, Yu SY, Wu JH, Shao QR, Dong XM (2012) Paeoniflorin protects myocardial cell from doxorubicin-induced apoptosis through inhibition of NADPH oxidase. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 90(12):1569–1575
Liu Q, Chen Y, Auger-Messier M, Molkentin JD (2012) Interaction between NFkappaB and NFAT coordinates cardiac hypertrophy and pathological remodeling. Circ Res 110(8):1077–1086
Manabe I, Shindo T, Nagai R (2002) Gene expression in fibroblasts and fibrosis: involvement in cardiac hypertrophy. Circ Res 91(12):1103–1113
Mann DL (2002) Inflammatory mediators and the failing heart: past, present, and the foreseeable future. Circ Res 91(11):988–998
Nizamutdinova IT, Jin YC, Kim JS, Yean MH, Kang SS, Kim YS, Lee JH, Seo HG, Kim HJ, Chang KC (2008) Paeonol and paeoniflorin, the main active principles of Paeonia albiflora, protect the heart from myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Planta Med 74(1):14–18
Shah AM, Mann DL (2011) In search of new therapeutic targets and strategies for heart failure: recent advances in basic science. Lancet 378(9792):704–712
Steenman M, Chen YW, Le Cunff M, Lamirault G, Varro A, Hoffman E, Leger JJ (2003) Transcriptomal analysis of failing and nonfailing human hearts. Physiol Genomics 12(2):97–112
Wankun X, Wenzhen Y, Min Z, Weiyan Z, Huan C, Wei D, Lvzhen H, Xu Y, Xiaoxin L (2011) Protective effect of paeoniflorin against oxidative stress in human retinal pigment epithelium in vitro. Mol Vis 17:3512–3522
Wei L (2011) Immunological aspect of cardiac remodeling: T lymphocyte subsets in inflammation-mediated cardiac fibrosis. Exp Mol Pathol 90(1):74–78
Whelan RS, Kaplinskiy V, Kitsis RN (2010) Cell death in the pathogenesis of heart disease: mechanisms and significance. Annu Rev Physiol 72:19–44
Yan L, Wei X, Tang QZ, Feng J, Zhang Y, Liu C, Bian ZY, Zhang LF, Chen M, Bai X, Wang AB, Fassett J, Chen Y, He YW, Yang Q, Liu PP, Li H (2011) Cardiac-specific mindin overexpression attenuates cardiac hypertrophy via blocking AKT/GSK3beta and TGF-beta1-Smad signalling. Cardiovasc Res 92(1):85–94
Yang HO, Ko WK, Kim JY, Ro HS (2004) Paeoniflorin: an antihyperlipidemic agent from Paeonia lactiflora. Fitoterapia 75(1):45–49
Zhou H, Bian D, Jiao X, Wei Z, Zhang H, Xia Y, He Y, Dai Y (2011a) Paeoniflorin protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice by alleviating inflammatory cell infiltration and microvascular permeability. Inflamm Res 60(10):981–990
Zhou H, Shen DF, Bian ZY, Zong J, Deng W, Zhang Y, Guo YY, Li H, Tang QZ (2011b) Activating transcription factor 3 deficiency promotes cardiac hypertrophy, dysfunction, and fibrosis induced by pressure overload. PLoS ONE 6(10):e26744
Zhou H, Bian ZY, Zong J, Deng W, Yan L, Shen DF, Guo H, Dai J, Yuan Y, Zhang R, Lin YF, Hu X, Li H, Tang QZ (2012) Stem cell antigen 1 protects against cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis after pressure overload. Hypertension 60(3):802–809
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [81270303, 81000036 and 81000095] and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of China [2012302020212 and 201130202020007].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
He-Xin Yang and Heng Zhou are joint first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, H., Yang, HX., Yuan, Y. et al. Paeoniflorin attenuates pressure overload-induced cardiac remodeling via inhibition of TGFβ/Smads and NF-κB pathways. J Mol Hist 44, 357–367 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-013-9491-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-013-9491-x