Abstract
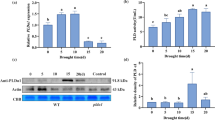
Application of lyso-phosphatidylethanolamine (LPE) is purported to suppress fruit ripening and delay foliar senescence. However, the endogenous LPE response of plants is more typically associated with propagation of wound and stress signals. Experiments were therefore carried out to determine whether exogenous LPE could elicit defense responses in plants by determining the effect of this lyso-phospholipid on activity of two key metabolic enzymes and pathogenesis-related proteins viz phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL; EC 4.3.1.5) and insoluble acid invertase (Ac INV; EC 3.2.1.26) in expanding cotyledons of Raphanus sativus L. cv. Cherry Belle (radish). Activity of both enzymes was increased following exposure of tissue to 18:0-LPE and the response was dose dependent. Soluble Ac INV activity was not enhanced by exogenous 18:0-LPE. Increased PAL activity appeared to coincide with a decline in phenolic acid content and a rise in sinapine and lignin. An increase in insoluble Ac INV by 18:0-LPE was associated with a reduction in sucrose concentration. However, levels of glucose and fructose were unaffected. In view of these findings it is proposed that applied LPE acts to co-ordinate carbohydrate partitioning locally to fulfill anabolic respiratory requirements associated with the propagation of systemic wound and stress responses. Furthermore, the impact of exogenous 18:0-LPE on insoluble Ac INV activity is discussed in relation to the proposed role of this enzyme in cytokinin-mediated senescence delay.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez-Venegas R, Sadder M, Hlavacka A, Baluška F, Xia Y, Lu G et al (2006a) The Arabidopsis homolog of trithorax, ATX1, binds phosphatidylinositol 5-phosphate, and the two regulate a common set of target genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:6049–6050. doi:10.1073/pnas.0600944103
Alvarez-Venegas R, Xia Y, Lu G, Avramova Z (2006b) Phosphoinositide 5-phosphate and phosphoinositide 4-phosphate trigger distinct specific responses of Arabidopsis genes. Plant Signal Behav 1:140–151
Ananieva K, Malbeck J, Kaminek M, van Staden J (2004) Changes in endogenous cytokinin levels in cotyledons of Cucurbita pepo (zucchini) during natural and dark-induced senescence. Physiol Plant 122:133–142. doi:10.1111/j.1399-3054.2004.00378.x
Blair R, Reichert RD (1984) Carbohydrate and phenolic constituents in a comprehensive range of rapeseed and canola fractions: nutritional significance for animals. J Sci Food Agric 35:29–35. doi:10.1002/jsfa.2740350106
Blum DE, Neff MM, Van Volkenburgh E (1994) Light-stimulated cotyledon expansion in the blu3 and hy4 mutants of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol 105:1433–1436. doi:10.1104/pp.105.4.1433
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilising the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254. doi:10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Chapman KD (1998) Phospholipase activity during plant growth and development and in response to environmental stress. Trends Plant Sci 3:419–426. doi:10.1016/S1360-1385(98)01326-0
Chen M, McClure JW (2000) Altered lignin composition in phenylalanine ammonia-lyase-inhibited radish seedlings: implications for seed-derived sinapoyl esters as lignin precursors. Phytochemistry 53:365–370. doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(99)00531-2
Cowan AK (2006) Phospholipids as plant growth regulators. Plant Growth Regul 48:97–109. doi:10.1007/s10725-005-5481-7
Cowan AK, Freeman M, Björkman P-O, Nicander B, Sitbon F, Tillberg E (2005) Effect of senescence-induced alteration in cytokinin metabolism on source-sink relationships and ontogenic and stress-induced transitions in tobacco. Planta 221:801–814. doi:10.1007/s00425-005-1489-5
Dixon RA, Paiva NL (1995) Stress-induced phenylpropanoid metabolism. Plant Cell 7:1085–1097
Farag KM, Palta JP (1991) Improving postharvest keeping quality of vine-ripened tomato fruits with a natural lipid. HortScience 26:162
Farag KM, Palta JP (1993) Use of lysophosphatidylethanolamine, a natural lipid, to retard tomato leaf and fruit senescence. Physiol Plant 87:515–521. doi:10.1111/j.1399-3054.1993.tb02501.x
Fischer U, Men S, Grebe M (2004) Lipid function in plant cell polarity. Curr Opin Plant Biol 7:670–676. doi:10.1016/j.pbi.2004.09.007
Guo J, Hu X, Duan R (2005) Interactive effects of cytokinins, light, and sucrose on the phenotypes and the syntheses of anthocyanins and lignins in cytokinin overproducing transgenic Arabidopsis. J Plant Growth Regul 24:93–101. doi:10.1007/s00344-005-0005-2
Hammond-Kosack K, Jones J (1996) Resistance gene-dependent plant defense responses. Plant Cell 8:1773–1791
Jones DH (1984) Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase: regulation of its induction and its role in plant development. Phytochemistry 23:1349–1359. doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(00)80465-3
Kim JH, Choi D, Kende H (2003) The AtGRF family of putative transcription factors is involved in leaf and cotyledon growth in Arabidopsis. Plant J 36:94–104. doi:10.1046/j.1365-313X.2003.01862.x
Lara MEB, Garcia MG, Fatima T, Ehneß R, Lee TK, Proles R et al (2004) Insoluble invertase is an essential component of cytokinin-mediated delay of senescence. Plant Cell 16:1276–1287. doi:10.1105/tpc.018929
Lee S, Suh S, Kim S, Crain RC, Kwak JM, Nam H-G et al (1997) Systemic elevation of phosphatidic acid and lysophospholipid levels in wounded plants. Plant J 12:547–556. doi:10.1046/j.1365-313X.1997.00547.x
Lee HY, Bahn SC, Kang Y, Lee KH, Kim HJ, Noh EK et al (2003) Secretory low molecular weight phospholipase A2 plays important roles in cell elongation and shoot gravitropism in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 15:1990–2002. doi:10.1105/tpc.014423
Lee HY, Bahn SC, Shin JS, Hwang I, Back K, Doelling JH et al (2005) Multiple forms of secretory phospholipase A2 in plants. Prog Lipid Res 44:52–67. doi:10.1016/j.plipres.2004.10.002
Monteiro D, Castanho Coelho P, Rodrigues C, Camacho L, Quader H, Malho R (2005) Modulation of endocytosis in pollen tube growth by phosphoinositides and phospholipids. Protoplasma 226:31–38. doi:10.1007/s00709-005-0102-x
Munnik T (2001) Phosphatidic acid: an emerging plant lipid second messenger. Trends Plant Sci 6:227–233. doi:10.1016/S1360-1385(01)01918-5
Nelson N (1944) A photometric adaptation of the Somogyi method for the determination of glucose. J Biol Chem 153:375–380
Özgen M, Park S, Palta JP (2005) Mitigation of ethylene-promoted leaf senescence by a natural lipid, lysophosphatidylethanolamine. HortScience 40:1166–1167
Roitsch T, Gonzalez M (2004) Function and regulation of plant invertases: sweet sensations. Trends Plant Sci 9:606–613. doi:10.1016/j.tplants.2004.10.009
Roitsch T, Bittner M, Godt DE (1995) Induction of apoplastic invertase of Chenopodium rubrum by D-glucose and a glucose analog and tissue-specific expression suggest a role in sink-source relations. Plant Physiol 108:285–294. doi:10.1104/pp.108.1.285
Roitsch T, Balibrea ME, Hofmann M, Proels R, Sinha AK (2003) Extracellular invertase: key metabolic enzyme and PR protein. J Exp Bot 54:513–524. doi:10.1093/jxb/erg050
Rosenkranz H, Vogel R, Greiner S, Rausch T (2001) In wounded sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.) tap-root, hexose accumulation correlates with the induction of a vacuolar invertase isoform. J Exp Bot 52:2381–2385. doi:10.1093/jexbot/52.365.2381
Rossard S, Luini E, Pérault J-M, Bonmort J, Roblin G (2006) Early changes in membrane permeability, production of oxidative burst and modification of PAL activity induced by ergosterol in cotyledons of Mimosa pudica. J Exp Bot 57:1245–1252. doi:10.1093/jxb/erj090
Ryu SB (2004) Phospholipid-derived signaling mediated by phospholipase A in plants. Trends Plant Sci 9:229–235. doi:10.1016/j.tplants.2004.03.004
Schenk PM, Kazan K, Rusu AG, Manners JM, Maclean DJ (2005) The SEN1 gene of Arabidopsis is regulated by signals that link plant defence responses and senescence. Plant Physiol Biochem 43:997–1005. doi:10.1016/j.plaphy.2005.09.002
Scherer GFE (2002) Secondary messengers and phospholipase A2 in auxin signal transduction. Plant Mol Biol 49:357–372. doi:10.1023/A:1015290510483
Somogyi M (1952) Notes on sugar determination. J Biol Chem 195:19–23
Suzuki Y, Shioi Y (2004) Changes in chlorophyll and carotenoid contents in radish (Raphanus sativus) cotyledons show different time courses during senescence. Physiol Plant 122:291–296. doi:10.1111/j.1399-3054.2004.00401.x
Testerink C, Munnik T (2005) Phosphatidic acid: a multifunctional stress signaling lipid in plants. Trends Plant Sci 10:368–375. doi:10.1016/j.tplants.2005.06.002
Titto RJ (1985) Phenolic constituents on leaves of northern willows: methods for the analysis of certain phenolics. J Agric Food Chem 33:213–217. doi:10.1021/jf00062a013
Tsukaya H, Tsuge T, Uchimiya H (1994) The cotyledon—a superior system for studies of leaf development. Planta 195:309–321. doi:10.1007/BF00199692
van Schooten B, Testerink C, Munnik T (2006) Signalling diacylglycerol pyrophosphate, a new phosphatidic acid metabolite. Biochim Biophys Acta 1761:151–159
Wang X (2004) Lipid signaling. Curr Opin Plant Biol 7:329–336. doi:10.1016/j.pbi.2004.03.012
Wang X (2005) Regulatory functions of phospholipase D and phosphatidic acid in plant growth, development, and stress responses. Plant Physiol 139:566–573. doi:10.1104/pp.105.068809
Wang X, Devaiah SP, Zhang W, Welti R (2006) Signaling functions of phosphatidic acid. Prog Lipid Res 45:250–278. doi:10.1016/j.plipres.2006.01.005
Way HM, Kazan K, Mitter N, Goulter KC, Birch RG, Manners JM (2002) Constitutive expression of a phenylalanine ammonia-lyase gene from Stylosanthes humilis in transgenic tobacco leads to enhanced disease resistance but impaired plant growth. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 60:275–282
Welti R, Wang X (2004) Lipid species profiling: a high-throughput approach to identify lipid compositional changes and determine the function of genes involved in lipid metabolism and signaling. Curr Opin Plant Biol 7:1–8. doi:10.1016/j.pbi.2004.03.011
Welti R, Li W, Li M, Sang Y, Biesiada H, Zhou H-E et al (2002) Profiling membrane lipids in plant stress responses: role of phospholipase Dα in freezing-induced lipid changes in Arabidopsis. J Biol Chem 277:31994–32002. doi:10.1074/jbc.M205375200
Zouaghi M, Rollin P (1976) Phytochrome control of β-fructosidase activity in radish. Phytochemistry 15:897–901. doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(00)84365-4
Acknowledgements
The work described in this paper was carried out at Nutra-Park Inc., Middleton, WI. Claire Leung and Chandra Santori are thanked for valuable technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, J.H., Chung, G.H. & Cowan, A.K. Lyso-phosphatidylethanolamine-enhanced phenylalanine ammonia-lyase and insoluble acid invertase in isolated radish cotyledons. Plant Growth Regul 57, 69–78 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-008-9323-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-008-9323-2