Abstract
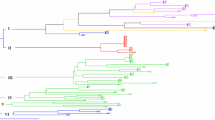
The diversity of 51 representative populations of the 5 Aegilops species from Moroccan collection was analyzed using 22 RAPD primers. We investigated the associations among these 5 Aegilops species (A. geniculata Roth (UUMM), A. triuncialis L. (UUCC), A. ventricosa Tausch (DDNN), A. peregrina (Hackel) Maire et Weiller (UUMM) and A. neglecta Req. ex Bert. subsp. recta (Zhuk.) K. Hammer (UUMMNN)); some diploid species considered as their ancestors; accessions of some neighboring countries and also accessions of Triticums. A total of 650 polymorphic RAPD fragments were amplified. A dendrogram was constructed using the un-weighed pair group method arithmetic average (UPGMA) and Jaccard`s similarity coefficient. The UPGMA clustering showed a regrouping to the level species with high level of the structuration of the diversity at A. geniculata. We confirm as reported by other authors, the proximity of N genome to U genome and C genome to M genome and also the difference between the genomes M and N. Thus, the phylogeny between the species and the different genomes were retracted.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AFLP:
-
Amplified fragment length polymorphism
- IAV:
-
Institute of Agronomy and Veterinary
- RAPD:
-
Random amplified polymorphic DNA
- RFLP:
-
Restriction fragment length polymorphism
- SSR:
-
Simple sequence repeat
References
Al-Humaid A, Motawei PI (2004) Molecular characterization of some turfgrass cultivars using randomly amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) markers. Food Agric Environ 2(1):376–380
Badaeva ED (2002) Evaluation of phylogenetic relationships between five polyploidy Aegilops L. species of the U-genome cluster by means of chromosomal analysis. Genetika 38(6):799–811
Badaeva ED, Friebe B, Gill BS (1996) Genome differentiation in Aegilops. 1. Distribution of highly repetitive DNA sequences on chromosomes of diploid species. Genome 39:293–306
Baum BR, Nevo E, Douglas A, Johnson A, Beiles A (1997) Genetic diversity in wild barley (Hordeum spontaneum C. Koch) in the Near East: a molecular analysis using random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) markers. Genet Resour Crop Evol 44:147–157
Belkadi B, Assali N, Benlhabib O (2003) Variation of specific morphological traits and ploidy level of five Aegilops L. species in Morocco. Acta Botanica 28:47–58
Benito C, Figueras AM, Gonsales-jaen MT (1987) Location of genes coding for isozyme markers on Ae. umbellulata chromosomes adds data on homoeology among Triticeae chromosomes. Theor Appl Genet 73:581–588
Benlhabib O, Diria G, Bouhssini M, Lhaloui S, Nachit M (2001) Collecting and evaluating Aegilops for germoplasm enhancement in Morocco. Actes IAV 21:3
Boissier PE (1884) Flora Orientalis 5:2, Basel, Geneva
Botstein D, White R, Skolnick M, Davis R (1980) Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphism. Am J Hum Genet 32:314–331
Bowden WL (1959) The taxonomy and nomenclature of the wheats, barleys and ryes and their wild relatives. Can J Bot 37:663 667-668, 670, 675-677
Breiman A (1987) Mitochondrial DNA diversity in the genera of Triticum and Aegilops revealed by Southern blot hybridization. Theor Appl Genet 73:563–570
Cadwell KA, Kasarda DD (1978) Assessment of genomic and species relationships in Triticum and Aegilops by PAGE and by differential staining of seed albumins and globulins. Theor Appl Genet 52:273–280
Cao W, Scoles G, Hucl P, Chibbar RN (1999) The use of RAPD analysis to classify Triticum accessions. Theor Appl Genet 98:602–607
Castagna R, Maga G, Perenzin M, Heun M, Salamini F (1994) RFLP-based genetic relationships of Einkorn wheats. Theor Appl Genet 88:818–823
Castagna R, Gnocchi S, Perenzin M, Heum M (1997) Genetic variability of the wild wheat Triticum urartu revealed by RFLP and RAPD markers. Theor Appl Genet 94:424–430
Castilho A, Heslop-Harrison JS (1995) Physical mapping of 5S and 18S–25S rDNA repetitive DNA sequences in Aegilops umbellulata. Genome 38:91–96
Chennaveeraiah MS (1960) Karyomorphologic and cytotaxonomic studies in Aegilops. Acta hortigotoburgensis 23:85–178
Dawson IK, Chalmers KJ, Waugh R, Powell W (1993) Detection and analysis of genetic variation in Hordeum spontaneum populations from Israel using RAPD markers. Mol Ecol 2:151–159
De Bustos A, Soler C, Jouve N (1999) Analysis by PCR-based markers using designed primers to study relationships between species of Hordeum (Poaceae). Genome 42:129–138
Devos KM, Gale MD (1992) The use of random amplified polymorphic DNA markers in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 84:567–572
Dewey DR (1984) The genome system of classification as a guide to hybridization with the perennial Triticeae. In: Gustafson JP (ed) Gene manipulation in plant improvement. Plenum publ. Crop., New York, pp 209–279
Dos Santos JB, Nienhuis J, Skroch P, Tivang J, Slocum MK (1994) Comparison of RAPD and RFLP genetic markers in determining genetic similarity among Brassica oleracea L. genotypes. Theor Appl Genet 87:909–915
Eig A (1929) Monographische-Kritische Übersicht der Gattung Aegilops, Feddes Repert. Reg Veget Beih Band Lv Berlin 55:1–228
Fahima T, Sun GL, Beharav A, Krugman T, Beiles A, Nevo E (1999) RAPD polymorphism of wild emmer wheat populations, Triticum dicoccoides, in Israel. Theor Appl Genet 98:434–447
Feldman M, Sears ER (1981) The wild gene resources of wheat. Sci Am (New York) 244(1):98–109
Felsenstein J (1993) PHYLIP: PHYLogenetic Inference Package version 3.5c. Page web consultée en Décembre 2002, http://evolution.genetics.washington.edu/phylip/software.html
Friebe B, Mukai Y, Gill BS (1992) C-Banding polymorphisms in several accessions of Triticum tauschii (Aegilops squarrosa). Genome 35:192–199
Goriunova SV, Kochieva EZ, Chikida NN, Pukhal’skii VA (2004) Phylogenetic relationships and intraspecific variation of D-genome Aegilops L. as revealed by RAPD analysis. Genetika 400(5):642–651
Hammer K (1980) Zur Taxonomie und Nomenklatur der Gattung Aegilops L. Feddes Repert 91:225–258
Hart GE, Tuleen NA (1983) Characterizing and selecting alien genetic material of wheat alien species hybrids by analyses of isozyme variation. In: Sakamoto S (ed) Proceedings of the 6th international wheat genetics symposium, held at Kyoto, 28 November–3 December 1983. Plant Germ-plasm Institute, Kyoto University, Kyoto, pp 377–385
Jaaska V (1987) Isoenzyme contribution to the systematics and phylogeny of the Triticeae crops and grasses. In: The plant cover of the Estonian SSR flora, vegetation and ecology. Tallinn, Valgus, pp 133–159
Jaccard P (1908) Nouvelles recherches sur la distribution florale. Bull Soc Vaud Sci 44:223–270
Jiang J, Gill BS (1994) New 18S–26S ribosomal RNA gene loci: chromosomal landmarks for the evolution of polyploidy wheats. Chromosoma 103:179–185
Joshi CP, Nguyen T (1993) RAPD (random amplified polymorphic DNA) analysis based intervarietal genetic relationships among hexaploid wheats. Plant Sci 93:95–103
Kazutoshi O, Kaoru E, Bayarsukh N, Hisashi Y (1998) Genetic diversity of Central Asian and north Caucasian Aegilops species as revealed by RAPD markers. Genet Resour Crop Evol 45(4):389–394
Khalighi M, Arzani A, Poursiahbidi MA (2008) Assessment of genetic diversity in Triticum spp. and Aegilops spp. using AFLP markers. Afr J Biotechnol 7(5):546–552
Kihara H (1949) Genomanalyse bei Triticum und Aegilops IX. Systematischer Aufbau der Gattung Aegilops auf genomanalytischer Grundlage. Cytologia 14:135–144
Kimber G, Feldman M (1987) Wild wheat, an introduction, special Report 353. University of Missouri, USA
Kyoko Y, Taihachi K (2005) Intra- and interspecific phylogenetic relationships among diploid Triticum-Aegilops species (Poaceae) based on base-pair substitutions, indels, and microsatellites in chloroplast noncoding sequences. Am J Bot 92:1887–1898
Lagudah ES, Clarke BS, Appels R (1989) Phylogenetic relationships of Triticum tauschii, the D-genome donor to hexaploid wheat. 4. Variation and chromosomal location of 5S DNA. Genome 32:1017–1025
Lilienfeld FA (1951) Concluding review. In: Kihara H (ed) Genome analysis in Triticum and Aegilops. X. Cytologia, vol 16, no 2, pp 115
Loarce Y, Gallego R, Ferrer E (1996) A comparative analysis of the genetic relationships between rye cultivars using RFLP and RAPD markers. Euphytica 88:107–115
Lubbers EL, Gill KS, Cox TS, Gill BS (1991) Variation of molecular markers among geographically diverse accessions of Triticum tauschii. Genome 34:354–361
Miyashita NT, Mori N, Tsunewaki K (1994) Molecular variation in chloroplast DNA regions in ancestral species of wheat. Genetics 137:883–889
Monte JV, Casanova C, Soler C (1999) Genetic variation in Spanish populations of the genus Aegilops reveled by RAPD. Agronomie 19:419–427
Monte JV, De Nova PJ, Soler C (2001) AFLP-based analysis to study genetic variability and relationships in the Spanish species of the genus Aegilops. Hereditas 135(2–3):233–238
Morris R, Sears ER (1967) The cytogenetics of wheat and its relatives. In: Quisenberry KS, Reitz LP (eds) Wheat and wheat improvement: 20–21 (table 1) 23, 87
Murray M, Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of high-molecular-weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 8:4321–4325
Nakai Y (1979) Isozyme variation in Aegilops and Triticum. IV. The origin of common wheat revealed from the study of esterase isozymes in synthesized hexaploid wheats. Jpn J Genet 54:175–189
Owuor ED, Fahima T, Beiles A, Korol A, Nevo E (1997) Population genetic response to microsite ecological stress in wild barley, Hordeum spontaneum. Mol Ecol 6:1177–1187
Petersen G, Seberg O, Yde M, Berthelsen K (2006) Phylogenetic relationships of Triticum and Aegilops and evidence for the origin of the A, B and D genomes of commun wheat (Triticum aestivum). Mol Phylogenet Evol 39(1):70–82
Provan J, Powell W, Hollingsworth PM (2001) Chloroplast microsatellites: new tools for studies in plant ecology and evolution. Trends Ecol Evol 16:142–147
Provan J, Wolters P, Caldwell KH, Powell W (2004) High resolution organellar genome analysis of Triticum and Aegilops sheds new light on cytoplasm evolution in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 108:1182–1190
Puterka GJ, Black IVWC, Steiner WM, Burton RL (1993) Genetic variation and phylogenetic relationships among world-wide collections of the Russian wheat aphid, Diuraphis noxia (Mordvilko), inferred from allozyme and RAPD-PCR markers. Heredity 70:604–618
Rayburn AL, Gill BS (1987) Molecular analysis of the D-genome of the Triticeae. Theor Appl Genet 73:385–388
Saghai-Maroof MA, Soliman KM, Jorgensen RA, Allard RW (1984) Ribosomal DNA spacer length polymorphisms in barley: Mendelian inheritance, chromosome location and population dynamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:8014–8018
Sakamoto S (1982) The Middle East as a cradle for crops and weeds. In: Holzner W, Numata W (eds) Biology and ecology of weeds, Chap 9. Kluwer, Boston, pp 97–109
Sasanuma T, Chabane K, Endo TR, Valkoun J (2004) Characterization of genetic variation in and phylogenetic relationships among diploid Aegilops species by AFLP: incongruity of chloroplast and nuclear data. Theor Appl Genet 108:612–618
Schlüter PM, Harris SA (2006) Analysis of multilocus fingerprinting data sets containing missing data. Mol Ecol Notes 6:569–572
Schmidt J-C, Schubert V, Blüthner WD (1993) Use of isozymes to characterize Triticum aestivum–Aegilops markgrafii addition lines. Biochem Physiol Pflanzen 188:385–392
Sneath PHA, Sokal RR (1973) Numerical taxonomy. The principles and practice of numerical classification. W.H. Freeman and company, San Francisco
Stebbins GL (1956) Taxonomy and the evolution of genera, with special reference to the family Gramineae. Evolution 10:235–247
Sun GL, Salomon B, Von Bothmer R (1997) Analysis of tetraploid Elymus species using wheat microsatellite markers and RAPD markers. Genome 40:806–814
Takashi RE, Yamamoto M, Mukai Y (1994) Structural changes of rye chromosome IR induced by a gametocidal chromosome. Jpn J Genet 69:13–19
Tautz D (1989) Hypervariability of simple sequences as a general source for polymorphic DNA markers. Nucleic Acid Res 17:6463–6471
Tsujimoto H, Tsunewaki K (1985) Gametocidal genes in wheat and its relatives 2. Suppressor of the chromosome 3c gametocidal gene of Aegilops-Triuncialis. Can J Genet Cytol 27:178–185
Tsunewaki K, Takumi S, Mori N, Achiwa T, Liu YG (1991) Origin of polyploid wheats revealed by RFLP analysis. In: Sasakuma T, Kinoshita T (eds) Nuclear and organellar genomes of wheat species. Kihara Memorial Foundation Yokohama, pp 33–39
Tzvelev NN (1983) Tribe 3. Triticeae Dumort. In: Fedorow AA (ed) Grasses of the Soviet Union. I. Oxonian Press, New Delhi, pp 147–181
Van Slageren MW (1990) The significance of taxonomic methods in handling genetic diversity. In: Srivastava JP, Damania AB (eds) Wheat genetic resources: meeting diverse needs. Wiley, Chichester
Van Slageren MW (1994) Wild wheats: a monograph of Aegilops L. and Amblyopyrum (Jaub. & Spach) Eig (Poaceae). Agricultural University ICARDA, Wageningen 512 pp
Vieira RF, Goldsbrough P, Simon JE (2003) Genetic diversity of basil (Ocimum spp.) based on RAPD markers. J Am Soc Hort Sci 128:94–99
Vos P, Hogers R, Bleeker M, Reijans M, van de Lee T, Hornes M et al (1995) AFLP: a new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucleic Acids Res 23(21):4407–4414
Wang ZY, Transkley SD (1989) Restriction fragment length polymorphism in Oryza sativa L. Genome 32:1113–1118
Williams JGK, Kubelik AR, Livak KJ, Rafalski JA, Tingey SV (1990) DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucleic Acids Res 18:6531–6535
Witcombe JR (1983) A guide to the species of Aegilops L. Their taxonomy, morphology and distribution, IBPGR, Rome, Italy: i–vi, 1–74
Zaharieva MN, David J, This D, Monneveux P (1999) Analyse de la diversité génétique d’Aegilops geniculata Roth en Bulgarie. Cahiers Agric 8:181–188
Zaharieva MN, Santoni S, David J (2001) Use of RFLP markers to study genetic diversity and to build a core-collection of the wild wheat relative Ae. geniculata Roth (=Ae. ovata L.). Genet Sel Evol 33(suppl):S269–S288
Zhang Q, Saghai Maroof MA, Lu TY, Shen BZ (1992) Genetic diversity and differentiation of indica and japonica rice detected by RFLP analysis. Theor Appl Genet 83:459–495
Zhukovsky PM (1928) A critical-systematical survey of the species of the genus Aegilops L. Bull Appl Bot Genet Plant Breed 18:417–609
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to all the suppliers of seed (Table 1). We thank Mrs. F. Gabon for help with statistic analysis and Dr. Laila SBABOU with critical reading.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Belkadi, B., Assali, N., Filali-Maltouf, A. et al. Diversity analysis of Aegilops species from Morocco using RAPD markers. Genet Resour Crop Evol 58, 271–282 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-010-9570-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-010-9570-8