Abstract
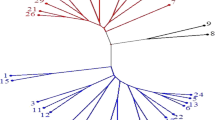
Wild species of safflower, Carthamus oxyacanthus Bieb., is highly crossable with cultivated species, C. tinctorius L. and could be directly exploited in broadening safflower gene pool and improving the crop for biotic and abiotic stress environments. In this study, genetic diversity among accessions of C. oxyacanthus and their relationships with cultivated safflower were evaluated using agro-morphological traits and polymorphic inter-simple sequence repeats (ISSR) markers. Significant variation was observed among accessions particularly for seeds per capitulum, seed yield per plant, harvest index and capitula per plant. Cluster analysis based on agro-morphological traits classified the wild accessions in two groups according to their geographical regions, and separated them from the cultivated genotypes. ISSR marker also revealed a high genetic variation among the accessions, and cluster analysis based on this marker divided genotypes into four groups, with cultivated ones in a separate clade. Genetic variation observed among the wild safflower germplasm at the DNA level was higher than the agro-morphological traits, indicating that ISSR is an effective marker system for detecting diversity among safflower genotypes and their genetic relationships. Accessions of C. oxyacanthus with high genetic relationship to cultivated species could be used for interspecific hybridization in breeding programs of safflower.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Able GH, Driscoll MF (1976) Sequential trait development and breeding for high yield in safflower. Crop Sci 16:213–216
Amini F, Saeidi G, Arzani A (2008) Study of genetic diversity in safflower genotypes using agro-morphological traits and RAPD markers. Euphytica 163:21–30. doi:10.1007/s10681-007-9556-6
Ash GJ, Raman R, Crump NS (2003) An investigation of genetic variation in Carthamus lanatus in New South Wales, Australia, using inter simple sequece repeats (ISSR) analysis. Weed Res 43:208–213. doi:10.1046/j.1365-3180.2003.00335.x
Ashri A (1971a) Evaluation of the world collection of safflower, Carthamus tinctorius L. II. Resistance to the safflower fly, Acanthiophilus helianthi R. Euphytica 20:410–415. doi:10.1007/BF00035666
Ashri A (1971b) Evaluation of the world collection of safflower, Carthamus tinctorius L. I. Reaction to several disease and associations with morphological characters in Israel. Crop Sci 11:253–257
Ashri A (1975) Evaluation of the germplasm collection of safflower Carthamus tinctorius L. V. Distribution and regional divergence for morphological characters. Euphytica 24:651–659. doi:10.1007/BF00132903
Ashri A, Knowles PF (1960) Cytogenetics of safflower (Carthamus L.) species and their hybrids. Agron J 52:11–17
Botstein B, White RL, Skolnick M, Davis RW (1980) Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am J Hum Genet 32:314–331
Dittrich M, Petrak F, Rechinger KH, Wagenitz G (1979) Compositae III—Cynareae. In: Rechinger KH (ed) Flora Iranica. No. 139, 468 S
Falconer DS, Mackay TFC (1996) Introduction to quantitative genetics, 4th edn. Longmans Green, Harlow
Jaradat AA, Shahid M (2006) Patterns of phenotypic variation in a germplasm collection of Carthamus tinctorius L. from the Middle East. Genet Resour Crop Evol 53:225–244. doi:10.1007/s10722-004-6150-9
Johnson RC, Kisha TJ, Evans MA (2007) Characterization safflower germplasm with AFLP molecular markers. Crop Sci 47:1728–1736. doi:10.2135/cropsci2006.12.0757
Joshi SP, Gupta VS, Aggarwal RK, Ranjekar PK, Brar DS (2000) Genetic diversity and phylogenetic relationship as revealed by inter simple sequence repeat (ISSR) polymorphism in the genus Oryza. Theor Appl Genet 100:1311–1320. doi:10.1007/s001220051440
Kantetky RV, Zhang X, Bennetzen JL, Zehr BZ (1995) Assessment of genetic diversity in dent and popcorn (Zea mays L.) inbred lines using inter-simple sequence repeat (ISSR) amplification. Mol Breed 1:365–372. doi:10.1007/BF01248414
Knowles PF (1975) Recent research on safflower, sunflower and cotton. J Am Oil Chem Soc 52:374–376. doi:10.1007/BF02639200
Knowles PF, Ashri A (1995) Safflower: Carthamus tinctorius (Compositae). In: Smartt J, Simmonds NW (eds) Evolution of crop plants. Longman, Harlow, pp 47–50
Li D, Mündel HH (1996) Safflower: Carthamus tinctorius L. promoting the conservation and use of underutilized and neglected crops 7. Institute of Plant Genetics and Crop Plant Research (IPK), Gatersleben, Germany/International Plant Genetic Resources Institute (IPGRI), Rome, Italy
Mantel N (1967) The detection of disease clustering and a generalized regression approach. Cancer Res 27:209–220
Murray MG, Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 8:4321–4325. doi:10.1093/nar/8.19.4321
Nei M, Li WH (1979) Mathematical model for studying in genetic variation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:5269–5273. doi:10.1073/pnas.76.10.5269
Poehlman JM, Sleper DA (1995) Breeding field crops. Iowa state University Press, Ames
Rohlf FJ (1994) NTSYS-pc, numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system, v. 1.80. Exeter Software, New York
Sabzalian MR, Saeidi G, Mirlohi A (2008) Oil content and fatty acid composition in seeds of three safflower species. J Am Oil Chem Soc 85:717–721. doi:10.1007/s11746-008-1254-6
SAS Institute, Inc (1999) SAS/STAT user’s guide. Institute, Inc., Cary
Schaal BA, Leverich WJ, Rogstad SH (1991) Comparison of methods for assessing genetic variation in plant conservation biology. In: Falk DA, Holsinger KE (eds) Genetics and conservation of rare plants. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 123–134
Sehgal D, Raina SN (2005) Genotyping safflower (Carthamus tinctorius) cultivars by DNA fingerprints. Euphytica 146:67–76. doi:10.1007/s10681-005-8496-2
Vilatersana R, Susanna A, Garcia-Jacas N, Garnatje T (2000) Generic delimitation and phylogeny of the Carduncellus–Carthamus complex (Asteraceae) based on ITS sequences. Plant Syst Evol 221:89–105. doi:10.1007/BF01086383
Vilatersana R, Garnatje T, Susanna A, Garcia-Jacas N (2005) Taxonomic problems in Carthamus (Asteraceae): RAPD markers and sectional classification. Bot J Linn Soc 147:375–383. doi:10.1111/j.1095-8339.2005.00375.x
Weiss EA (2000) Oilseed crops, 2nd edn. Blackwell Science Ltd, Oxford
Yang WP, Oliveira AC, Godwin I, Schertz K, Bennetzen JL (1996) Comparison of DNA marker technologies in characterizing plant genome diversity: variability in Chinese sorghums. Crop Sci 36:1669–1676
Yang YX, Wu W, Zheng YL, Chen L, Liu RJ, Huang CY (2007) Genetic diversity and relationships among safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) analyzed by inter-simple sequence repeats (ISSRs). Genet Resour Crop Evol 54:1043–1051. doi:10.1007/s10722-006-9192-3
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Mr. Aboulfazl Masoudi for his assisting in seed collection, and acknowledge Isfahan University of Technology for financially supporting this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sabzalian, M.R., Mirlohi, A., Saeidi, G. et al. Genetic variation among populations of wild safflower, Carthamus oxyacanthus analyzed by agro-morphological traits and ISSR markers. Genet Resour Crop Evol 56, 1057–1064 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-009-9426-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-009-9426-2