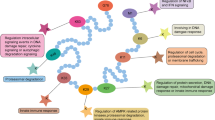
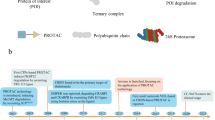
Abstract
Sialidases (EC 3.2.1.18, also called neuraminidases) catalyze the removal of α-glycosidically linked sialic acid residues from glycoproteins and glycolipids; this is the initial step in the degradation of these glycoconjugates. Sialidases of mammalian origin have been implicated in not only lysosomal catabolism but also the modulation of functional molecules involved in many biological processes. To date, four types of mammalian sialidases have been cloned and designated as Neu1, Neu2, Neu3 and Neu4. These sialidases differ in their subcellular localization and enzymatic properties, as well as their chromosomal localization, and they are expressed in a tissue-specific manner. Among the sialidases, the plasma membrane-associated sialidase Neu3 appears to play particular roles in controlling transmembrane signaling through the modulation of gangliosides, and its aberrant expression is closely related to various pathogeneses, including that of cancer. Interestingly, the human orthologue NEU3 acts in two ways, catalytic hydrolysis of gangliosides and protein interactions with other signaling molecules. Aberrant NEU3 expression can induce various pathological conditions. This review briefly summarizes recent studies, focusing on the involvement of NEU3 in various pathological phenomena.
Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
14 July 2022
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-022-10075-7
References
Bonten, E., van der Spoel, A., Fornerod, M., Grosveld, G., d’Azzo, A.: Characterization of human lysosomal neuraminidase defines the molecular basis of the metabolic storage disorder sialidosis. Genes Dev. 10, 3156–3169 (1996)
Milner, C.M., Smith, S.V., Carrillo, M.B., Taylor, G.L., Hollinshead, M., Campbell, R.D.: Identification of a sialidase encoded in the human major histocompatibility complex. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 4549–4558 (1997)
Pshezhetsky, A.V., Richard, C., Michaud, L., Igdoura, S., Wang, S., Elsliger, M.A., Qu, J., Leclerc, D., Gravel, R., Dallaire, L., Potier, M.: Cloning, expression and chromosomal mapping of human lysosomal sialidase and characterization of mutations in sialidosis. Nat. Genet. 15, 316–320 (1997)
Carrillo, M.B., Milner, C.M., Ball, S.T., Snoek, M., Campbell, R.D.: Cloning and characterization of a sialidase from the murine histocompatibility-2 complex: low levels of mRNA and a single amino acid mutation are responsible for reduced sialidase activity in mice carrying the Neu1a allele. Glycobiology. 7, 975–986 (1997)
Miyagi, T., Konno, K., Emori, Y., Kawasaki, H., Suzuki, K., Yasui, A., Tsuik, S.: Molecular cloning and expression of cDNA encoding rat skeletal muscle cytosolic sialidase. J. Biol. Chem. 268, 26435–26440 (1993)
Miyagi, T., Wada, T., Iwamatsu, A., Hata, K., Yoshikawa, Y., Tokuyama, S., Sawada, M.: Molecular cloning and characterization of a plasma membrane-associated sialidase specific for gangliosides. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 5004–5011 (1999)
Wada, T., Yoshikawa, Y., Tokuyama, S., Kuwabara, M., Akita, H., Miyagi, T.: Cloning, expression, and chromosomal mapping of a human ganglioside sialidase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 261, 21–27 (1999)
Monti, E., Bassi, M.T., Papini, N., Riboni, M., Manzoni, M., Venerando, B., Croci, G., Preti, A., Ballabio, A., Tettamanti, G., Borsani, G.: Identification and expression of NEU3, a novel human sialidase associated to the plasma membrane. Biochem. J. 349, 343–351 (2000)
Seyrantepe, V., Landry, K., Trudel, S., Hassan, J.A., Morales, C.R., Pshezhetsky, A.V.: Neu4, a novel human lysosomal lumen sialidase, confers normal phenotype to sialidosis and galactosialidosis cells. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 37021–37029 (2004)
Yamaguchi, K., Hata, K., Koseki, K., Shiozaki, K., Akita, H., Wada, T., Moriya, S., Miyagi, T.: Evidence for mitochondrial localization of a novel human sialidase (NEU4) Biochem. J. 390, 85–93 (2005)
Monti, E., Bassi, M.T., Bresciani, R., Civini, S., Croci, G.L., Papini, N., Riboni, M., Zanchetti, G., Ballabio, A., Preti, A., Tettamanti, G., Venerando, B., Borsani, G.: Molecular cloning and characterization of NEU4, the fourth member of the human sialidase gene family. Genomics. 83, 445–453 (2004)
Bigi, A., Morosi, L., Pozzi, C., Forcella, M., Tettamanti, G., Venerando, B., Monti, E., Fusi, P.: Human sialidase NEU4 long and short are extrinsic proteins bound to outer mitochondrial membrane and the endoplasmic reticulum, respectively. Glycobiology. 20, 148–157 (2010)
Roggentin, P., Schauer, R., Hoyer, L.L., Vimr: E R. The sialidase superfamily and its spread by horizontal gene transfer: Mol. Microbiol. 9, 915–921 (1993)
Koseki, K., Wada, T., Hosono, M., Hata, K., Yamaguchi, K., Nitta, K., Miyagi, T.: Human: cytosolic sialidase NEU2-low general tissue expression but involvement in PC-3 prostate cancer cell survival.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 428,142–149 (2012)
Mozzi, A., Forcella, M., Riva, A., Difrancesco, C., Molinari, F., Martin, V., Papini, N. Bernasconi, B., Nonnis, S., Tedeschi, G., Mazzucchelli, L., Monti, E., Fusi, P. Frattini M.: NEU3 activity: enhances EGFR activation without affecting EGFR expression and acts on its sialylation levels. Glycobiology. 25, 855–868 (2015)
Hata, K., Wada, T., Hasegawa A,Kiso M,Miyagi, T.: Purification and characterization of a membrane-associated ganglioside sialidase from bovine brain. J. Biochem. (Tokyo). 123, 899–905 (1998)
Akita, H., Miyagi, T., Hata, K., Kagayama, M.: Immunohistochemical evidence for the existence of rat cytosolic sialidase in rat skeletal muscles. Histochem. Cell. Biol. 107, 495–503 (1997)
Hasegawa, T., Yamaguchi, K., Wada, T., Takeda, A., Itoyama, Y., Miyagi, T.: Molecular cloning of mouse ganglioside sialidase and its increased expression in Neuro2a cell differentiation. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 8007–8015 (2000)
Li, S.C., Li, Y.T., Moriya, S., Miyagi, T.: Degradation of G(M1) and G(M2) by mammalian sialidases. Biochem. J. 360, 233–237 (2001)
Cirillo, F., Ghiroldi, A., Fania, C., Piccoli, M., Torretta, E., Tettamanti, G., Gelfi, C.: Anastasia L.NEU3 sialidase protein interactors in the plasma membrane and in the endosomes. J. Biol. Chem. 291, 10615–10624 (2016)
Miyagi, T., Wada, T., Yamaguchi, K., Hata, K., Shiozaki, K.: Plasma membrane- associated sialidase as a crucial regulator of transmembrane signalling. J. Biochem. 144, 279–285 (2008)
Yamaguchi, K., Hata, K., Wada, T., Moriya, S., Miyagi, T.: Epidermal growth factor-induced mobilization of a ganglioside-specific sialidase (NEU3) to membrane ruffles. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 346, 484–490 (2006). (2006)
Shiozaki, K., Takahashi, K., Hosono, M., Yamaguchi, K., Hata, K., Shiozaki, M., Bassi, R., Prinetti, A., Sonnino, S., Nitta, K., Miyagi, T.: Phosphatidic acid-mediated activation and translocation to the cell surface of sialidase NEU3, promoting signaling for cell migration.FASEB J,29,2099–2111(2015)
Rodriguez-Walker, M., Vilcaes, A.A., Garbarino-Pico, E., Daniotti, J.L.: Role of plasma-membrane-bound sialidase NEU3 in clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Biochem. J. 470, 131–144 (2015)
Valaperta, R., Chigorno, V., Basso, L., Prinetti, A., Bresciani, R., Preti, A., Miyagi, T., Sonnino, S.: Plasma membrane production of ceramide from ganglioside GM3 in human fibroblasts. FASEB J. 20, 1227–1229 (2006)
Rodriguez-Walker, M., Daniotti, J.L.: Human sialidase Neu3 is S-acylated and behaves like an integral membrane protein. Sci. Rep. 7, 4167 (2017)
Lau, K.S., Dennis, J.W.: N-Glycans in cancer progression. Glycobiology. 18, 750–760 (2008)
Hakomori, S.I.:Glycosynaptic, microdomains controlling tumor cell phenotype through alteration of: cell growth, adhesion, and motility. FEBS Lett. 584, 1901–1906 (2010)
Schengrund, C.-L., Lausch, R.N., Rosenberg, A.: Localization of sialidase in the plasma membrane of rat liver cells. J. Biol. Chem. 248, 4424–4428 (1973)
Miyagi, T., Sagawa, J., Kuroki, T., Matsuya, Y., Tsuiki, S.: Tumor-promoting phorbol ester induces alterations of sialidase and sialyltransferase activities of JB6 cells. Jpn J. Cancer Res. 81, 1286–1292 (1990)
Miyagi, T., Wada, T., Yamaguchi, K., Shiozaki, K., Sato, I., Kakugawa, Y., Yamanami, H., Fujiya, T.: Human sialidase as a cancer marker. Proteomics. 8, 3303–3311 (2008)
Mandal, C., Tringali, C., Mondal, S., Anastasia, L., Chandra, S., Venerando, B.: Down regulation of membrane-bound Neu3 constitutes a new potential marker for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia and induces apoptosis suppression of neoplastic cells. Int. J. Cancer. 126, 337–349 (2010)
Takahashi, K., Proshin, S., Yamaguchi, K., Yamashita, Y., Katakura, R., Yamamoto, K., Shima, S., Hosono, M., Miyagi, T.: Sialidase NEU3 defines invasive potential of human glioblastoma cells by regulating calpain-mediated proteolysis of focal adhesion proteins. BBA - General Subjects. 1861, 2778–2788 (2017)
Kakugawa, Y., Wada, T., Yamaguchi, K., Yamanami, H., Ouchi, K., Sato, I., Miyagi, T.: Up-regulation of plasma membrane-associated ganglioside sialidase (Neu3) in human colon cancer and its involvement in apoptosis suppression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A. 99, 10718–10723 (2002)
Kato, K., Shiga, K., Yamaguchi, K., Hata, K., Kobayashi, T., Miyazaki, K., Saijo, S., Miyagi, T.: Plasma-membrane-associated sialidase (NEU3) differentially regulates integrin-mediated cell proliferation through laminin- and fibronectin-derived signalling. Biochem. J. 394, 647–656 (2006)
Ueno, S., Saito, S., Wada, T., Yamaguchi, K., Satoh, M., Arai, Y., Miyagi, T.: Plasma membrane-associated sialidase is up-regulated in renal cell carcinoma and promotes interleukin-6-induced apoptosis suppression and cell motility. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 7756–7764 (2006)
Kawamura, S., Sato, I., Wada, T., Yamaguchi, K., Li, Y., Li, D., Zhao, X., Ueno, S., Aoki, H., Tochigi, T., Kuwahara, M., Kitamura, T., Takahashi, K., Moriya, S., Miyagi, T.: Plasma membrane-associated sialidase (NEU3) regulates progression of prostate cancer to androgen-independent growth through modulation of androgen re- ceptor signaling. Cell. Death Differ. 19, 170–179 (2012)
Forcella, M., Oldani, M., Epistolio, S., Freguia, S., Monti, E., Fusi, P., Frattini, M.: Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), EGFR downstream pathway activation and TKI targeted therapies sensitivity: Effect of the plasma membrane-associated NEU3.PLoS One.12,e0187289.(2017)
Orizio, F., Triggiani, L., Colosini, A., Buglione, M., Pasinetti, N., Monti, E., Bresciani, R.: Overexpression of sialidase NEU3 increases the cellular radioresistance potential of U87MG glioblastoma cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 508, 31–36 (2019)
Hata, K., Tochigi, T., Sato I.,3Kawamura S.,2, Shiozaki, K., Wada T.,1Takahashi T., Moriya, S. 1 Yamaguchi, K., Hosono, M., Miyagi, T. Increased sialidase activity in serum of cancer patients: Identification of sialidase and inhibitor activities in humanserum Cancer Sci,106,383–389(2015)
Paolini, L., Orizio, F., Busatto, S., Radeghieri, A., Bresciani, R., Bergese, P., Monti, E.: Exosomes secreted by HeLa Cell shuttle on their surface the plasma membrane-associated sialidase NEU3. Biochemistry. 56,6401–6408. (2017)
Wada, T., Hata, K., Yamaguchi, K., Shiozaki, K., Koseki, K., Moriya, S., Miyagi, T.: A crucial role of plasma membrane- associated sialidase in the survival of human cancer cells. Oncogene. 26, 2483–2490 (2007)
Yamamoto, K., Takahashi, K., Shiozaki, K.,. Yamagushi, K., Moriya, S.,. Hosono, M., Shima, H., Miyagi, T. Potentiation of epidermal growth factor -mediated oncogenic transformation by sialidase NEU3 leading to Src activation.PLoS One, 10(3), e0120578, (2015)
Shiozaki, K., Yamaguchi, K., Sato, I., Miyagi, T.: Plasma membrane-associated sialidase (NEU3) promotes formation of colonic aberrant crypt foci in azoxymethane-treated transgenic mice. Cancer Sci. 100, 588–594 (2009)
Yamaguchi, K., Koseki, K., Shiozaki, M., Shimada, Y., Wada, T., Miyagi, T.: Regulation of plasma-membrane-associated sialidase NEU3 gene by Sp1/Sp3 transcription factors. Biochem J. 430:107–117:. (2010)
Wierstra, I. Sp1: emerging roles– beyond constitutive activation of TATA-less housekeeping genes: Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 372, 1–13 (2008)
Xie, C., Yagai, T., Luo, Y., Liang, X., Chen, T., Wang, Q., Sun, D., Zhao, J., Ramakrishnan, S.K., Sun, L., Jiang, C., Xue, X., Tian, Y., Krausz, K.W., Patterson, A.D., Shah, Y.M., Wu, Y., Jiang, C., Gonzalez, F.J.: Activation of intestinal hypoxia-inducible factor 2α during obesity contributes to hepatic steatosis. Nat. Med. 23, 1298–1308 (2017)
Pilling, D., Karhadkar, T.R., Gomer, R.H.: High-fat diet–induced adipose tissue and liver Inflammation and steatosis in Mice Are reduced by inhibiting sialidases. Am. J. Pathol. 191, 131–143 (2021)
Piccoli, M., Conforti, E., Varrica, A., Ghiroldi, A., Cirillo, F., Resmini, G., Pluchinotta, F., Tettamanti, G., Giamberti, A., Frigiola, A., Anastasia, L.: NEU3 sialidase role in activating HIF-1alpha in response to chronic hypoxia in cyanotic congenital heart patients. Int. J. Cardiol. 230, 6–13 (2017)
Ghiroldi, A., Piccoli, M., Creo, P., Cirillo, F., Rota, P., D’Imperio, S., Ciconte, G., Monasky, M.M., Micaglio, E., Garatti, A., Aureli, M., Carsana, E.V., Menicanti, L., Pappone, C., Anastasia, L.: Role of sialidase Neu3 and ganglioside GM3 in cardiac fibroblasts activation. Biochem. J. 477, 3401–3415 (2020)
Karhadkar, T.R., Pilling, D., Cox, D., Gomer, N.: Sialidase inhibitors attenuate pulmonary fibrosis in a mouse model. Sci. Rep. 7, 15069 (2017)
Karhadkar, T.R., Chen, W., Gomer, R.H.: Attenuated pulmonary fibrosis in sialidase-3 knockout (Neu3–/–) mice. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 318, L165–L179 (2020)
Yang, W.H., Heithoff, D.M., Aziz, P.V., Sperandio, M., Nizet, V., Mahan, M.J., Marth, J.D. Recurrent infection progressively disables host protection against intestinal inflammation. Science. Dec 22;358(6370): eaao5610 (2017)
Yang, W.H., Westman, J.S., Heithoff, D.M., Sperandio, M., Cho, J.W., Mahan, M.J., Marth, J.D. Neu3 neuraminidase induction triggers intestinal inflammation and colitis in a model of recurrent human food-poisoning.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.118(29):e2100937118
Demina, E.P., Smutova, V., Pan, X., Fougerat, A., Guo, T., Zou, C., Chakraberty, R., Snarr Shiao, B.D., Roy, T.C., Orekhov, R., Miyagi, A.N., Laffargue, T., Sheppard, M., CairoCW, D.C., Pshezhetsky, A.V.: Neuraminidases 1 and 3 trigger atherosclerosis by desialylating low-density lipoproteins and increasing their uptake by macrophages. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 10(4), e018756 (2021)
Hata, K., Koseki, K., Yamaguchi, K., Moriya, S., Suzuki,Y., Yingsakmongkon, Hirai, S., Sodeoka, G., von Itzstein, M., Miyagi, M., T.:Limited inhibitory effects of oseltamivir and zanamivir on human sialidases.Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 52, 3484– 3491 (2008)
Guo, T., Dätwyler, P., Demina, E., Richards, M.R., Ge, P., Zou C, Zheng R, Fougerat A. Pshezhetsky, A.V., Ernst, B., Cairo, C.W.: Selective Inhibitors of Human Neuraminidase 3. J. Med. Chem. 8, 611990–612008 (2018)
Howlader, M.A., Guo, T., Chakraberty, R., Cairo, C.W. Isoenzyme-selective inhibitors migration: ACS Chem. Biol. 15(6), 1328–1339 (2020)
Acknowledgements
We would like to express our sincere gratitude to the late professor Hakomori, S.I. for his many pioneering studies and his leadership in the field of glycolipids in cancer.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None declared conflict of interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miyagi, T., Yamamoto, K. Sialidase NEU3 and its pathological significance. Glycoconj J 39, 677–683 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-022-10067-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-022-10067-7