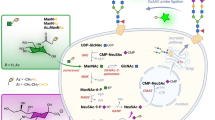
Abstract
Carbohydrates, in addition to their metabolic functions, serve important roles as receptors, ligands, and structural molecules for diverse biological processes. Insight into carbohydrate biology and mechanisms has been aided by metabolic oligosaccharide engineering (MOE). In MOE, unnatural carbohydrate analogs with novel functional groups are incorporated into cellular glycoconjugates and used to probe biological systems. While MOE has expanded knowledge of carbohydrate biology, limited metabolism of unnatural carbohydrate analogs restricts its use. Here we assess metabolism of SiaDAz, a diazirine-modified analog of sialic acid, and its cell-permeable precursor, Ac4ManNDAz. We show that the efficiency of Ac4ManNDAz and SiaDAz metabolism depends on cell type. Our results indicate that different cell lines can have different metabolic roadblocks in the synthesis of cell surface SiaDAz. These findings point to roles for promiscuous intracellular esterases, kinases, and phosphatases during unnatural sugar metabolism and provide guidance for ways to improve MOE.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Varki, A.: Sialic acids in human health and disease. Trends Mol. Med. 14, 351–360 (2008)
Varki, A.: Glycan-based interactions involving vertebrate sialic-acid-recognizing proteins. Nature 446, 1023–1029 (2007)
Du, J., Meledeo, M.A., Wang, Z., Khanna, H.S., Paruchuri, V.D.P., Yarema, K.J.: Metabolic glycoengineering: sialic acid and beyond. Glycobiology 19, 1382–1401 (2009)
Dube, D., Bertozzi, C.: Metabolic oligosaccharide engineering as a tool for glycobiology. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 7, 616–625 (2003)
Kayser, H., Zeitler, R., Kannicht, C., Grunow, D., Nuck, R., Reutter, W.: Biosynthesis of a nonphysiological sialic acid in different rat organs, using N-propanoyl-D-hexosamines as precursors. J. Biol. Chem. 267, 16934–16938 (1992)
Luchansky, S.J., Goon, S., Bertozzi, C.R.: Expanding the diversity of unnatural cell-surface sialic acids. Chembiochem 5, 371–374 (2004)
Han, S., Collins, B.E., Bengtson, P., Paulson, J.C.: Homomultimeric complexes of CD22 in B cells revealed by protein-glycan cross-linking. Nat. Chem. Biol. 1, 93–97 (2005)
Tanaka, Y., Kohler, J.J.: Photoactivatable crosslinking sugars for capturing glycoprotein interactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130, 3278–3279 (2008)
Feng, L., Hong, S., Rong, J., You, Q., Dai, P., Huang, R., Tan, Y., Hong, W., Xie, C., Zhao, J., Chen, X.: Bifunctional unnatural sialic acids for dual metabolic labeling of cell-surface sialylated glycans. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135, 9244–9247 (2013)
Pham, N.D., Parker, R.B., Kohler, J.J.: Photocrosslinking approaches to interactome mapping. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 17, 90–101 (2013)
Ramya, T.N.C., Weerapana, E., Liao, L., Zeng, Y., Tateno, H., Liao, L., Yates, J.R., Cravatt, B.F., Paulson, J.C.: In situ trans ligands of CD22 identified by glycan-protein photocross-linking-enabled proteomics. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 9, 1339–1351 (2010)
Jones, M.B., Teng, H., Rhee, J.K., Lahar, N., Baskaran, G., Yarema, K.J.: Characterization of the cellular uptake and metabolic conversion of acetylated N-acetylmannosamine (ManNAc) analogues to sialic acids. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 85, 394–405 (2004)
Sarkar, A.K., Fritz, T.A., Taylor, W.H., Esko, J.D.: Disaccharide uptake and priming in animal cells: inhibition of sialyl Lewis X by acetylated Gal beta 1–>4GlcNAc beta-O-naphthalenemethanol. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 92, 3323–3327 (1995)
Lemieux, G.A., Yarema, K.J., Jacobs, C.L., Bertozzi, C.R.: Exploiting differences in sialoside expression for selective targeting of MRI contrast reagents. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 121, 4278–4279 (1999)
Jacobs, C.L., Yarema, K.J., Mahal, L.K., Nauman, D.A., Charters, N.W., Bertozzi, C.R.: Metabolic labeling of glycoproteins with chemical tags through unnatural sialic acid biosynthesis. Meth. Enzymol. 327, 260–275 (2000)
Sampathkumar, S.-G., Jones, M.B., Yarema, K.J.: Metabolic expression of thiol-derivatized sialic acids on the cell surface and their quantitative estimation by flow cytometry. Nat. Protoc. 1, 1840–1851 (2006)
Almaraz, R.T., Aich, U., Khanna, H.S., Tan, E., Bhattacharya, R., Shah, S., Yarema, K.J.: Metabolic oligosaccharide engineering with N-acyl functionalized ManNAc analogs: cytotoxicity, metabolic flux, and glycan-display considerations. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 109, 992–1006 (2012)
Mantey, L.R., Keppler, O.T., Pawlita, M., Reutter, W., Hinderlich, S.: Efficient biochemical engineering of cellular sialic acids using an unphysiological sialic acid precursor in cells lacking UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase. FEBS Lett. 503, 80–84 (2001)
Bond, M.R., Zhang, H., Vu, P.D., Kohler, J.J.: Photocrosslinking of glycoconjugates using metabolically incorporated diazirine-containing sugars. Nat. Protoc. 4, 1044–1063 (2009)
Zhan, X., Shi, X., Zhang, Z., Chen, Y., Wu, J.I.: Dual role of Brg chromatin remodeling factor in Sonic hedgehog signaling during neural development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 108, 12758–12763 (2011)
Bond, M.R., Zhang, H., Kim, J., Yu, S.-H., Yang, F., Patrie, S.M., Kohler, J.J.: Metabolism of diazirine-modified N-acetylmannosamine analogues to photo-cross-linking sialosides. Bioconjug Chem. 22, 1811–1823 (2011)
Dettmer, K., Nürnberger, N., Kaspar, H., Gruber, M.A., Almstetter, M.F., Oefner, P.J.: Metabolite extraction from adherently growing mammalian cells for metabolomics studies: optimization of harvesting and extraction protocols. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 399, 1127–1139 (2011)
Tomiya, N., Ailor, E., Lawrence, S.M., Betenbaugh, M.J., Lee, Y.C.: Determination of nucleotides and sugar nucleotides involved in protein glycosylation by high-performance anion-exchange chromatography: sugar nucleotide contents in cultured insect cells and mammalian cells. Anal. Biochem. 293, 129–137 (2001)
Yu, S.-H., Boyce, M., Wands, A.M., Bond, M.R., Bertozzi, C.R., Kohler, J.J.: Metabolic labeling enables selective photocrosslinking of O-GlcNAc-modified proteins to their binding partners. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 109, 4834–4839 (2012)
Laxman, S., Sutter, B.M., Wu, X., Kumar, S., Guo, X., Trudgian, D.C., Mirzaei, H., Tu, B.P.: Sulfur amino acids regulate translational capacity and metabolic homeostasis through modulation of tRNA thiolation. Cell 154, 416–429 (2013)
Tu, B.P., Mohler, R.E., Liu, J.C., Dombek, K.M., Young, E.T., Synovec, R.E., McKnight, S.L.: Cyclic changes in metabolic state during the life of a yeast cell. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 104, 16886–16891 (2007)
Bond, M.R., Whitman, C.M., Kohler, J.J.: Metabolically incorporated photocrosslinking sialic acid covalently captures a ganglioside-protein complex. Mol Biosyst. 6, 1796–1799 (2010)
Keppler, O.T., Hinderlich, S., Langner, J., Schwartz-Albiez, R., Reutter, W., Pawlita, M.: UDP-GlcNAc 2-epimerase: a regulator of cell surface sialylation. Science 284, 1372–1376 (1999)
Dallolio, F., Chiricolo, M., Lollini, P., Lau, J.T.Y.: Human colon cancer cell lines permanently expressing α2,6-sialylated sugar chains by transfection with rat β-galactoside α2,6 sialyltransferase cDNA. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 211, 554–561 (1995)
Gross, H.J., Brossmer, R.: Enzymatic transfer of sialic acids modified at C-5 employing four different sialyltransferases. Glycoconj. J. 12, 739–746 (1995)
Gross, H.J., Rose, U., Krause, J.M., Paulson, J.C., Schmid, K., Feeney, R.E., Brossmer, R.: Transfer of synthetic sialic acid analogues to N- and O-linked glycoprotein glycans using four different mammalian sialyltransferases. Biochemistry 28, 7386–7392 (1989)
Galuska, S.P., Geyer, H., Weinhold, B., Kontou, M., Röhrich, R.C., Bernard, U., Gerardy-Schahn, R., Reutter, W., Münster-Kühnel, A., Geyer, R.: Quantification of nucleotide-activated sialic acids by a combination of reduction and fluorescent labeling. Anal. Chem. 82, 4591–4598 (2010)
Mathew, M.P., Tan, E., Shah, S., Bhattacharya, R., Adam Meledeo, M., Huang, J., Espinoza, F.A., Yarema, K.J.: Extracellular and intracellular esterase processing of SCFA–hexosamine analogs: implications for metabolic glycoengineering and drug delivery. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 22, 6929–6933 (2012)
Tallman, K.R., Beatty, K.E.: Far-red fluorogenic probes for esterase and lipase detection. Chembiochem 16, 70–75 (2015)
Staudinger, J.L., Xu, C., Cui, Y.J., Klaassen, C.D.: Nuclear receptor-mediated regulation of carboxylesterase expression and activity. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 6, 261–271 (2010)
Hawley, S.A., Fullerton, M.D., Ross, F.A., Schertzer, J.D., Chevtzoff, C., Walker, K.J., Peggie, M.W., Zibrova, D., Green, K.A., Mustard, K.J., Kemp, B.E., Sakamoto, K., Steinberg, G.R., Hardie, D.G.: The ancient drug salicylate directly activates AMP-activated protein kinase. Science 336, 918–922 (2012)
Oetke, C., Hinderlich, S., Reutter, W., Pawlita, M.: Epigenetically mediated loss of UDP-GlcNAc 2-epimerase/ManNAc kinase expression in hyposialylated cell lines. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 308, 892–898 (2003)
Jacobs, C.L., Goon, S., Yarema, K.J., Hinderlich, S., Hang, H.C., Chai, D.H., Bertozzi, C.R.: Substrate specificity of the sialic acid biosynthetic pathway. Biochemistry 40, 12864–12874 (2001)
Tian, L., Yang, Y., Wysocki, L.M., Arnold, A.C., Hu, A., Ravichandran, B., Sternson, S.M., Looger, L.L., Lavis, L.D.: Selective esterase-ester pair for targeting small molecules with cellular specificity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 109, 4756–4761 (2012)
Kornfeld, S., Kornfeld, R., Neufeld, E.F., O-Brien, P.J.: The feedback control of sugar nucleotide biosynthesis in liver. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 52, 371–379 (1964)
Seppala, R., Lehto, V.P., Gahl, W.A.: Mutations in the human UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase gene define the disease sialuria and the allosteric site of the enzyme. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 64, 1563–1569 (1999)
Zaro, B.W., Chuh, K.N., Pratt, M.R.: Chemical reporter for visualizing metabolic cross-talk between carbohydrate metabolism and protein modification. ACS Chem. Biol. 9, 1991–1996 (2014)
Rodriguez, A.C., Kohler, J.J.: Recognition of diazirine-modified O-GlcNAc by human O-GlcNAcase. MedChemComm. 5, 1227–1234 (2014)
Chang, P.V., Dube, D.H., Sletten, E.M., Bertozzi, C.R.: A strategy for the selective imaging of glycans using caged metabolic precursors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132, 9516–9518 (2010)
Acknowledgments
We thank Sunil Laxman and Benjamin Tu for guidance on LC-MS/MS analysis. We thank Maciej Kukula at the Shimadzu Center for Advanced Analytical Chemistry (SCAAC) at the University of Texas at Arlington for aiding us with mass spectrometry identification of NeuAc-9-P. We thank Yibing Wang, Randy Parker, Amberlyn Wands, Akiko Fujita, and Fan Yang for experimental assistance and thank Akiko Fujita and Amberlyn Wands for comments on the manuscript. We acknowledge support from the National Institutes of Health (NIH R01GM090271), the Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas (CPRIT RP110080), and the Welch Foundation (I-1686). NDP was supported by a predoctoral fellowship from the NIH (F30AG040909) and ACR received support from a training grant from the NIH (T32GM007062).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Charles S. Fermaintt and Andrea C. Rodriguez contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 688 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pham, N.D., Fermaintt, C.S., Rodriguez, A.C. et al. Cellular metabolism of unnatural sialic acid precursors. Glycoconj J 32, 515–529 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-015-9593-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-015-9593-7