Abstract
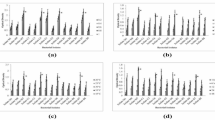
Human symbiotic bacteria, Lactobacillus reuteri (LR) in the intestines, Staphylococcus epidermidis (SE) in skin and Streptococcus salivalis (SS) in the oral cavity, contain dihexaosyl diglycerides (DH-DG) in concentrations equivalent to those of phosphatidyl glycerol (PG) and cardiolipin (CL), together with mono- to tetrahexaosyl DGs. The molecular species, as the combination of fatty acids in the DG moiety, were revealed to be bacterial species-characteristic, but to be similar between glycolipids and phospholipids in individual bacteria, the major ones being 16:0 and cy19:0 for LR, ai15:0 and ai17:0 for SE, and 16:0 and 18:1 for SS, respectively. The carbohydrate structures of DH-DGs were also bacterial species-characteristic, being Galα1-2Glcα for LR, Glcβ1-6Glcβ for SE, and Glcα1-2Glcα for SS, respectively. Also, bacterial glycolipids were revealed to provide antigenic determinants characteristic of bacterial species on immunization of rabbits with the respective bacteria. Anti-L. johnsonii antiserum intensely reacted with tri- and tetrahexaosyl DGs, in which Galα was bound to DH-DG through an α1-6 linkage, as well as with DH-DG from LR. Although anti-SE antiserum preferentially reacted with DH-DG from SE, anti-SS antiserum reacted with DH-DG from SS and, to a lesser extent, with DH-DGs from LR and SE. But, both anti-SE and anti-SS antiserum did not react at all with monohexaosyl DG or glycosphingolipids with the same carbohydrates at the nonreducing terminals. In addition, 75 % of human sera, irrespective of the ABO blood group, were found to contain IgM to tri- and tetrahexaosyl DGs from LR, but not to DH-DGs from LR, SE and SS.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CL:
-
cardiolipin
- DG:
-
diglycerides
- MH-DG:
-
monohexaosyl diglycerides
- DH-DG:
-
dihexaosyl diglycerides
- PA:
-
phosphatidic acid
- PG:
-
phosphatidyl glycerol
- TH-DG:
-
trihexaosyl diglycerides
- TetH-DG:
-
tetrahexaosyl diglycerides
- cy:
-
cyclopropane
- ai:
-
anteiso
- LJ:
-
Lactobacillus johnsonii
- LR:
-
Lactobacillus reuteri
- SE:
-
Staphylococcus epidermidis
- SS:
-
Streptococcus salivalis
References
IUPAC-IUB: Commission on biochemical nomenclature: the nomenclature of lipids. Eur. J. Biochem. 179, 11–21 (1977)
Iwamori, M., Sakai, A., Minamimoto, N., Iwamori, Y., Tanaka, K., Aoki, D., Adachi, S., Nomura, T.: Characterization of novel glycolipid antigens with an α-galactose epitope in lactobacilli detected with rabbit anti-Lactobacillus antiserum and occurrence of antibodies against them in human sera. J. Biochem. 150, 515–523 (2011)
Iwamori, M., Iwamori, Y., Adachi, S., Nomura, T.: Excretion into feces of asialo GM1 in the murine digestive tract and Lactobacillus johnsonii exhibiting binding ability toward asialo GM1. A possible role of epithelial glycolipids in the discharge of intestinal bacteria. Glycoconj. J. 28, 21–30 (2011)
Iwamori, M., Shibagaki, T., Nakata, Y., Adachi, S., Nomura, T.: Distribution of receptor glycolipids for Lactobacilli in murine digestive tract and production of antibodies cross-reactive with them by immunization of rabbits with Lactobacilli. J. Biochem. 146, 185–191 (2009)
Tamai, Y., Matsukawa, S., Satake, M.: Lipid composition of nerve cell perikarya. Brain Res. 26, 149–157 (1971)
Hamberger, A., Svennerholm, L.: Composition of gangliosides and phospholipids of neuronal and glial cell enriched fractions. J. Neurochem. 18, 1821–9 (1971)
Odutuga, A.A., Carey, E.M., Prout, R.E.: Changes in the lipid and fatty acid composition of developing rabbit brain. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 316, 115–123 (1973)
Pewzner-Jung, Y., Ben-Dor, S., Futerman, A.H.: When do Lasses (longevity assurance genes) become CerS (ceramide synthases)?: Insights into the regulation of ceramide synthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 25001–25005 (2006)
Yohe, H.C., Roark, D.E., Rosenberg, A.: C20-sphingosine as a determining factor in aggregation of gangliosides. J. Biol. Chem. 251, 7083–7087 (1976)
Lands, W.E.: Metabolism of glycerolipides; a comparison of lecithin and triglyceride synthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 231, 883–888 (1958)
Lewin, T.M., Wang, P., Coleman, R.A.: Analysis of amino acid motifs diagnostic for the sn-glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase reaction. Biochemistry 38, 764–771 (1999)
Bartlett, G.R.: Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J. Biol. Chem. 234, 466–468 (1959)
Folch, J., Lees, M.: A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 226, 497–509 (1957)
Iwamori, M., Takamizawa, K., Momoeda, M., Iwamori, Y., Taketani, Y.: Gangliosides in human, cow and goat milk, and their abilities as to neutralization of cholera toxin and botulinum type A neurotoxin. Glycoconj. J. 25, 675–683 (2008)
Harrison, R., Lunt, G.G.: Biological membranes, Blackie, Glasgow/London (1980)
Füllekrug, J., Simons, K.: Lipid rafts and apical membrane traffic. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1014, 164–169 (2004)
Hirschberg, C.B., Kennedy, E.P.: Mechanism of the enzymatic synthesis of cardiolipin in Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 69, 648–651 (1972)
Testet, E., Laroche-Traineau, J., Noubhani, A., Coulon, D., Bunoust, O., Camougrand, N., Manon, S., Lessire, R., Bessoule, J.J.: Ypr140wp, ‘the yeast tafazzin’, displays a mitochondrial lysophosphatidylcholine (lyso-PC) acyltransferase activity related to triacylglycerol and mitochondrial lipid synthesis. Biochem. J. 387, 617–626 (2005)
Xu, Y., Condell, M., Plesken, H., Edelman-Novemsky, I., Ma, J., Ren, M., Schlame, M.: A Drosophila model of Barth syndrome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 103, 11584–11588 (2006)
Shaw, N., Baddiley, J.: Structure and distribution of glycosyl diglycerides in bacteria. Nature 217, 142–144 (1968)
Koch, H.U., Fischer, W.: Acyldiglucosyldiacylglycerol-containing lipoteichoic acid with a poly(3-O-galabiosyl-2-O-galactosyl-sn-glycero-1-phosphate) chain from Streptococcus lactis Kiel 42172. Biochemistry 17, 5275–5281 (1978)
Smith, P.F.: Lipid composition of Mycoplasma neurolyticum. J. Bacteriol. 112, 554–558 (1972)
Sugiyama, T., Smith, P.F., Langworthy, T.A., Mayberry, W.R.: Immunological analysis of glycolipids and lipopolysaccharides derived from various mycoplasmas. Infect. Immun. 10, 1273–1279 (1974)
Shaw, N.: Bacterial glycolipids. Bacteriol. Rev. 34, 365–377 (1970)
Tanemura, M., Miyagawa, S., Koyota, S., Koma, M., Matsuda, H., Tsuji, S., Shirakura, R., Taniguchi, N.: Reduction of the major swine xenoantigen, the alpha-galactosyl epitope by transfection of the alpha2,3-sialyltransferase gene. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 16421–16425 (1998)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iwamori, M., Nakasa, M., Yamazaki, K. et al. Bacterial species-characteristic profiles of molecular species, and the antigenicity of phospholipids and glycolipids in symbiotic Lactobacillus, Staphylococcus and Streptococcus species. Glycoconj J 29, 199–209 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-012-9393-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-012-9393-2