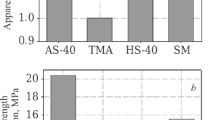
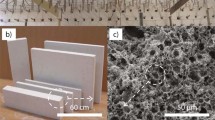
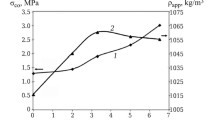
The particulars of a technology for new types of refractory and heat-insulation materials with high porosity, which are obtained by duplicating the cellular structure of the polymer base (polyurethane foam) and using pore-forming technology based on “cold” swelling of inorganic compositions, are examined. The use of electrocorundum, periclase, spinel, and zirconium dioxide as a base permits using such materials from 1750 to 2200°C. In a number of cases the heat-insulation materials which have been developed can successfully replace corundum fiber materials.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
V. S. Vladimirov, A. N. Galagan, M. A. Ilyukhin, et al., “New refractories and heat-insulating materials and their production technologies,” Novye Ogneupory, No. 1, 81 – 88 (2002).
M. V. Artamonov, V. S. Vladimirov, S. E. Moizis, et al., “Use of new refractories and heat-insulating materials with high application properties,” Novye Ogneupory, No. 9, 28 – 29 (2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Steklo i Keramika, No. 4, pp. 14 – 21, April, 2011.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vladimirov, V.S., Lukin, E.S., Popova, N.A. et al. New types of light-weight refractory and heat-insulation materials for long-term use at extremely high temperatures. Glass Ceram 68, 116 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10717-011-9335-7
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10717-011-9335-7