Abstract
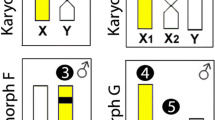
The wolf fish Hoplias malabaricus includes well differentiated sex systems (XY and X1X2Y in karyomorphs B and D, respectively), a nascent XY pair (karyomorph C) and not recognized sex chromosomes (karyomorph A). We performed the evolutionary analysis of these sex chromosomes, using two X chromosome-specific probes derived by microdissection from the XY and X1X2Y sex systems. A putative-sex pair in karyomorph A was identified, from which the differentiated XY system was evolved, as well as the clearly evolutionary relationship between the nascent XY system and the origin of the multiple X1X2Y chromosomes. The lack of recognizable signals on the sex chromosomes after the reciprocal cross-FISH experiments highlighted that they evolved independently from non-homologous autosomal pairs. It is noteworthy that these distinct pathways occur inside the same nominal species, thus exposing the high plasticity of sex chromosome evolution in lower vertebrates. Possible mechanisms underlying this sex determination liability are also discussed.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 2n:
-
Diploid number
- DAPI:
-
4′,6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole
- dNTP:
-
Deoxyribonucleotide triphosphate
- DOP-PCR:
-
Degenerate oligonucleotide primed PCR
- dUTP:
-
Deoxyuridine triphosphate
- FISH:
-
Fluorescence in situ hybridization
- Hm-X:
-
X chromosome-specific probe
- Hm-X1 :
-
X1 chromosome-specific probe
- SSC:
-
Sodium Chloride-Sodium Citrate buffer
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- WCP:
-
whole chromosome probe
References
Bell MA, Foster SA (1994) The evolutionary biology of the three spine stickleback. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Bertollo LAC, Takahashi CS, Moreira-Filho O (1978) Cytotaxonomic considerations on Hoplias lacerdae (Pisces, Erythrinidae). Brazil J Genet 1:103–120
Bertollo LAC, Born GG, Dergam JA, Fenocchio AS, Moreira-Filho O (2000) A biodiversity approach in the Neotropical Erythrinidae fish, Hoplias malabaricus. Karyotypic survey, geographic distribution of cytotypes and cytotaxonomic considerations. Chromosome Res 8:603–613. doi:10.1023/A:1009233907558
Born GG, Bertollo LAC (2000) An XX/XY sex chromosome system in a fish species, Hoplias malabaricus, with a polymorphic NOR-bearing X chromosome. Chromosome Res 8:111–118
Bull JJ (1983) Evolution of sex determining mechanisms. Benjamin/Cummings, San Francisco
Charlesworth D, Charlesworth B (1980) Sex differences in fitness and selection for centric fusions between sex-chromosomes and autosomes. Genet Res 35:205–214
Charlesworth B, Sniegowski P, Stephan W (1994) The evolutionary dynamics of repetitive DNA in eukaryotes. Nature 371:215–220
Cioffi MB, Bertollo LAC (2010) Initial steps in XY chromosome differentiation in Hoplias malabaricus and the origin of an X1X2Y sex chromosome system in this fish group. Heredity 105:554–561
Cioffi MB, Martins C, Bertollo LAC (2009) Comparative chromosome mapping of repetitive sequences. Implications for genomic evolution in the fish, Hoplias malabaricus. BMC Genetics 10:34–44
Cioffi MB, Martins C, Vicari MR, Rebordinos L, Bertollo LAC (2010a) Differentiation of the XY sex chromosomes in the fish Hoplias malabaricus (Characiformes, Erythrinidae). Unusual accumulation of repetitive sequences on the X chromosome. Sex Dev 4:176–185
Cioffi MB, Martins C, Bertollo LAC (2010b) Chromosome spreading of associated transposable elements and ribossomal DNA in the fish Erythrinus erythrinus. Implications for genome change and karyoevolution in fish. BMC Evol Biol 10:271
Cioffi MB, Camacho JPM, Bertollo LAC (2011a) Repetitive DNAs and the differentiation of se chromosomes in Neotropical fishes. Cytogenet Genome Res 132:188–194
Cioffi MB, Sánchez A, Marchal JA, Kosyakova N, Liehr T, Trifonov V, Bertollo LAC (2011b) Cross-species chromosome painting tracks the independent origin of multiple sex chromosomes in two cofamiliar Erythrinidae fishes. BMC Evol Biol 11:186
Devlin RH, Nagahama T (2002) Sex determination and sex differentiation in fish: an overview of genetic, physiological, and environmental influences. Aquaculture 208:191–364
Diniz D, Laudicina A, Cioffi MB, Bertollo LAC (2008) Microdissection and whole chromosome painting. Improving sex chromosome analysis in Triportheus (Teleostei, Characiformes). Cytogenet Genome Res 122:163–168
Ferguson-Smith MA, Trifonov V (2007) Mammalian karyotype evolution. Nature 8:950–962
Filatov D (2005) Evolutionary genetics: stickleback’s view of sex chromosome evolution. Heredity 94:275–276
Fisher RA (1931) The evolution of dominance. Biol Rev 6:345–368
Griffin DK, Robertson LBW, Tempest HG, Skinner BM (2007) The evolution of the avian genome as revealed by comparative molecular cytogenetics. Cytogenet Genome Res 117:64–77
Henning F, Trifonov V, Ferguson-Smith MA, Almeida-Toledo LF (2008) Non-homologous sex chromosomes in two species of the genus Eigenmannia (Teleostei: Gymnotiformes). Cytogenet Genome Res 121:55–58
Henning F, Moysés CB, Calcagnotto D, Meyer A, Almeida-Toledo LF (2011) Independent fusions and recent origins of sex chromosomes in the evolution and diversification of glass knife fishes (Eigenmannia). Heredity 106:391–400
Kondo M, Nanda I, Hornung U, Schmid M, Schartl M (2004) Evolutionary origin of the medaka Y chromosome. Curr Biol 14:1664–1669
Martins C (2007) Chromosomes and repetitive DNAs: a contribution to the knowledge of fish genome. In: Pisano E, Ozouf-Costaz C, Foresti F, Kapoor BG (eds) Fish cytogenetics. Science Publisher, Inc., Enfield, pp 421–453
Matsuda M, Nagahama Y, Shinomiya A, Sato T, Matsuda C et al (2002) DMY is a Y-specific DM-domain gene required for male development in the medaka fish. Nature 417:559–563
Muller HJ (1914) A gene for the fourth chromosome of Drosophila. J Exp Zool 17:325–336
Nagamachi CY, Pieczarka JC, Milhomem SSR, O’Brien PCM, de Souza ACP, Ferguson-Smith MA (2010) Multiple rearrangements in cryptic species of electric knifefish, Gymnotus carapo (Gymnotidae, Gymnotiformes) revealed by chromosome painting. BMC Genetics 11:28
Nanda I, Feichtinger W, Schmid M, Schroder JH, Zischler H, Epplen JT (1990) Simple repetitive sequences are associated with differentiation of the sex chromosomes in the guppy fish. J Mol Evol 30:456–462
Peichel CL, Ross JA, Matson CK, Dickson M, Grimwood J, Schmutz J et al (2004) The master sex-determination locus in three spine sticklebacks is on a nascent Y chromosome. Curr Biol 14:1416–1424
Phillips RB, Konkol NR, Reed KM, Stein D (2001) Chromosome painting supports lack of homology among sex chromosomes in Oncorhynchus. Salmo and Salvelinus (Salmonidae). Genetica 111:119–123
Phillips RB, DeKoning J, Morasch MR, Park LK, Devlin RH (2007) Identification of the sex chromosome pair in chum salmon (Oncorhynchus keta) and pink salmon (Oncorhynchus gorbuscha). Cytogenet Genome Res 116:298–304
Ráb P, Rábová M, Pereira CS, Collares-Pereira MJ, Pelikánová S (2008) Chromosome studies of European cyprinid fishes: interspecific homology of leuciscine cytotaxonomic marker—the largest subtelocentric chromosome pair as revealed by cross-species painting. Chromosome Res 16:863–873
Reed KM, Bohlander SK, Phillips RB (1995) Microdissection of the Y chromosome and FISH analysis of the sex chromosomes of lake trout, (Salvelinus namaycush). Chromosome Res 5:221–227
Rice WR (1987) The accumulation of sexually antagonistic genes as a selective agent promoting the evolution o reduced recombination between primitive sex chromosomes. Evolution 41:911–914
Rosa R, Vanzela AL, Rubert M, Martins-Santos IC, Giuliano-Caetano L (2009) Differentiation of Y chromosome in the X1X1X2X2/X1X2Y sex chromosome system of Hoplias malabaricus (Characiformes, Erythrinidae). Cytogenet Genome Res 127:54–60
Schartl M (2004) Sex chromosome evolution in nonmammalian vertebrates. Curr Opin Genet Dev 14:634–641
Shetty S, Griffin DK, Graves JAM (1999) Comparative painting reveals strong chromosome homology over 80 million years of bird evolution. Chromosome Res 7:289–295
Stanyon R, Rocchi M, Capozzi O, Roberto R, Misceo D, Ventura M, Cardone MF, Bigoni F, Archidiacono N (2008) Primate chromosome evolution: Ancestral karyotypes, marker order and neocentromeres. Chromosome Res 16:17–39
Steinemann S, Steinemann M (2005) Retroelements: tools for sex chromosome evolution. Cytogenet Genome Res 110:134–143
Telenius H, Carter NP, Bebb CE, Nordenskjold M, Ponder BA, Tunnacliffe A (1992) Degenerate oligonucleotideprimed PCR: general amplification of target DNA by a single degenerate primer. Genomics 13:718–725
Teruel M, Cabrero J, Montiel EE, Acosta MJ, Sánchez A, Camacho JP (2009) Microdissection and chromosome painting of X and B chromosomes in Locusta migratoria. Chromosome Res 17:11–18
Wang X, Zhang Q, Ren J, Jiang Z, Wang C, Zhuang W, Zhai T (2009) The preparation of sex-chromosome-specific painting probes and construction of sex chromosome DNA library in half-smooth tongue sole (Cynoglossus semilaevis). Aquaculture 297:78–84
Woram RA, McGowan C, Stout JA, Gharbi K, Ferguson MM, Hoyheim B et al (2004) A genetic linkage map for Arctic char (Salvelinus alpinus): evidence for higher recombination rates and segregation distortion in hybrid versus pure strain mapping parents. Genome 47:304–315
Yang F, Graphodatsky AS (2009) Animal probes and ZOO-fish. In: Liehr T (ed) Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH)—application guide. Springer, Berlin, pp 323–346
Yang F, Trifonov V, Ng BL, Kosyakova N, Carter NP (2009) Generation of paint probes by flow-sorted and microdissected chromosomes. In: Liehr T (ed) Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH)—application guide. Springer, Berlin, pp 35–52
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Brazilian agencies FAPESP (Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo), CNPq (Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico) and CAPES (Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior). and the Spanish Ministerio de Ciencia y Tecnología (pr. CGL2009-07754) co-funded by the European Regional Development Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Bello Cioffi, M., Sánchez, A., Marchal, J.A. et al. Whole chromosome painting reveals independent origin of sex chromosomes in closely related forms of a fish species. Genetica 139, 1065–1072 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-011-9610-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-011-9610-0