Abstract
China is rising and gradually developing into an innovation-oriented economy. This transition is fueled by public and private investment in education and by increasing inputs into science and technology. Little attention, however, has been paid to the great differences in China-specific context peculiarity. Hence, the paper assesses Chinese innovation networks using a comprehensive analytical model that includes network configuration, regional environment, government interference and firm attributes. The empirical analysis examines China’s machinery manufacturing industry to test the determinants of the spatial character of Chinese innovation networks based on questionnaire surveys and illustrative cases. Our study finds that Chinese innovation networks are affected not only by innovation resource endowments and firm attributes, but also by government interference and regional culture. Regarding the influence of regional culture, the typical Northern culture with the importance of guanxi plays an important role in the process of searching for partners and makes the innovation network and interpersonal network interwoven. Firms’ ownership and innovation ability are the two essential variables to determine whether any of the regional elements are of significance.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction: Chinese innovation networks
Over the past two decades, a large body of scholars in economic geography has been preoccupied with research on the interactive influence between firms and regions (Sternberg and Arndt 2001; Storper and Venables 2004; Wang and Lin 2013; Fitjar and Rodríguez-Pose 2015). Significant theoretical advancements have been made to understand the dynamics of network composition and spatial character (Hennemann et al. 2012; Broekel 2015; Boschma et al. 2017). Although there is a heated debate among different research strands, an agreement has been reached that innovation is fundamentally the consequence of the interaction of firms with their cooperative partners in nearby or distant locations.
Thus far, however, the existing theoretical frameworks and empirical results have largely been based on the studies in developed or western countries (Howells and Bessant 2012; Zhang and Peck 2016), which calls into question whether the findings can explain the issues of emerging economies, particularly those of China (Wei and Liefner 2012).
China is rising and gradually developing into an innovation-oriented economy. This transition is fueled by public and private investment in education and by increasing inputs into science, technology and R&D (Liefner et al. 2016). Meanwhile, in the case of China, the ongoing innovation process allows the coexistence of a specific variety of actors, such as public R&D institutes, universities, state-owned and private firms et al. Little attention, however, has been paid to the great differences in China-specific context peculiarity (Hu and Lin 2013; Kafouros et al. 2015). Firstly, the Chinese government is actively involved in innovation activities not only in finance and other types of support, but also as an important factor influencing the trend of the network configuration, for example with regard to the types of innovation activities carried out and partners chosen for innovation (Liefner and Zeng 2008; Hu and Lin 2013; Liefner and Jessberger 2016). Secondly, although some Chinese privately owned enterprises (POEs hereafter) have been successful in terms of innovation, state-owned enterprises (SOEs hereafter) normally dominate in certain industries and easily gain access to large-scale subsidies (Peighambari et al. 2014; Du and Mickiewicz 2016). They hence possess the ownership-specific advantages for obtaining innovation resources and benefit more easily from the construction of multi-scale innovation networks (Liefner and Zeng 2016). Thirdly, China’s science and technology system is hierarchically organized (Andersson et al. 2014; Huggins et al. 2014). Finally, regions differ enormously with respect to culture, for example a flexible Southern Chinese culture versus a stability-oriented Northern Chinese culture, which affects the strengths and functions of ties between firms and their potential cooperation partners (Park and Luo 2001; Liefner and Zeng 2008; Fu et al. 2013).
One particular question hence still remains regarding an analytical framework that explains the structure of innovation networks in China in a more specific and comprehensive manner. In this paper, we thus examine the major factors affecting the spatial character of Chinese innovation networks, paying attention to Chinese particularities. The suggested framework builds on the pillars of context and government, and integrates them in an organic way with other factors at the firm level. Hence, an attempt is made to address one important question: which factors affect the construction of innovation networks in China’s specific context? This paper’s empirical analysis examines the determinants of innovation networks in China’s machinery manufacturing industry based on data generated through semi-structured interviews and large-scale questionnaire surveys conducted between 10.2012 and 11.2015.
This paper is organized as follows. “Conceptual framework: towards a more comprehensive model of Chinese innovation networks” section critically evaluates the literature to develop an analytical framework, and then describes the hypotheses that structure the empirical analysis. “Data collection and research methodology” section provides a brief introduction to the research design, data source and study area. “Determinants of the spatial character of China’s innovation network” section focuses on the empirical analyses testing the hypotheses and explaining the most important results. Conclusions and implications for further research are discussed in the final section.
Conceptual framework: towards a more comprehensive model of Chinese innovation networks
This section will briefly review conceptual thoughts as well as China-related evaluations that address important factors influencing innovation networks. In the empirical section of this paper, the network configuration will be characterized with the help of distances—or scales—of collaboration in innovation. “Local” collaboration refers to the cooperation between actors located in the same city, “national” refers to the space outside the local city and cooperation with national partners, and “overseas” is the term used to describe all kinds of collaboration with foreign partners. While many studies exist that seek to examine the importance of spatial network configurations for certain actors’ innovation success, this paper analyzes the effect of certain innovation drivers on the configuration of the innovation network.
Before reviewing some selected key arguments discussed in the related literature that explain how the individual factors affecting innovation in China relate to certain network configurations and collaboration distances, the overall importance of an integrated examination of innovation drivers and scales of innovative linkages will be highlighted from two angles. Firstly, a broad range of theoretical and empirical literature stresses the fact that many factors which affect innovation processes and outcomes are local. Such factors may include localized resources, mainly highly qualified people, and their tacit knowledge (e.g. Maskell and Malmberg 1999), the contributions and the spillover effects of local organizations such as universities and high-tech firms (e.g. Cooke 1998; Vang and Asheim 2006), or the roles of location-specific institutions and routines (e.g. Martin 2000; Rodríguez-Pose 2013). Secondly, based on overwhelming evidence concerning the importance of these local factors, more comprehensive frameworks that seek to understand the interplay of actors from different regions, innovation and regional economic change acknowledge and incorporate these factors and attempt to establish on which scale they determine regions’ roles in innovation processes. Examples include the concepts of local intangible assets (Storper 1997), buzz and pipelines (Bathelt et al. 2004; Jeannerat and Crevoisier 2016). Although these concepts differ with regard to their focuses, they explicitly address the fact that certain characteristics and capabilities of local companies and of regional business environments are of significance for the roles that actors and contributions from other regions fulfill in innovation processes. In other words, the importance of the characteristics of actors and regions varies with the distances of collaboration in innovation processes, and some factors are more important for local innovation collaboration, while others are more significant for national or overseas linkages. Hence, factors affecting innovation influence the scale of collaboration and thus the spatial configuration of innovation networks. Building upon the extant literature, this paper identifies how China-specific factors, namely regional environment and government interference, influence the variations of innovation configuration (Fig. 1).
Network configuration
It has become commonplace to consider that firms increasingly employ open innovation and seamlessly collaborate and exchange knowledge with external actors in order to leverage complementary resources and to accelerate the commercialization of innovation (Randhawa et al. 2016). Innovation can thus be viewed as a result of interactions through vertical or horizontal links (Tomlinson and Jackson 2013), which range from market connections to formal (contract-based) networks (R&D and innovation collaboration) and informal linkages (Trippl et al. 2017). The research proposed by Asheim and Gertler (2005) seeks to articulate and develop three types of knowledge—analytical, synthetic and symbolic—indicating a relation between different combinations of tacit and codified knowledge on the one hand and different skills, organizations, challenges and pressures on the other hand. Using similar arguments, Jensen et al. (2007) distinguish between two modes of innovation, based on the source and the relative importance of related knowledge: STI mode (Science, Technology and Innovation) and the DUI mode (Doing, Using and Interacting).
In general, STI collaboration builds on a series of formal procedures, in which analytical knowledge is crucial. Firms usually launch cooperation in order to minimize failure risks and increase their technical power, therefore relying on the technological level of STI partners (Carayol 2003; Jiang et al. 2017). However, potential partners are endowed unequally with innovation abilities, and prestige can be used to indicate both research ability and the probability of successful innovation of the potential partners (Hong and Su 2013). There is a broad consensus that the STI-mode innovation and its knowledge can be transferred across large geographical distances (Balland et al. 2013). In doing so, firms normally give priority to cognitive proximity over geographical closeness, and they would rather cooperate with the distant top-tier STI actors than with the local secondary ones (Laursen et al. 2011). Comparatively speaking, DUI collaboration is mainly focused on incremental innovation, in which synthetic knowledge is dominant. Firms normally seek cooperation in order to achieve process optimizations, market information and component improvements, thus promoting innovation performance (Lee and Berente 2013). The relevant knowledge tends to be more tacit, and the innovation process is oriented towards new combinations, new solutions and new utility concerning the industry-chain-linked innovation demands (Fu et al. 2013). To summarize, not all external knowledge and corresponding partners have the same values and spatial inclination. Following the research conducted by Fitjar and Rodríguez-Pose (2013), STI mode innovation has, by and large, resorted to research institutes, universities, scientific brokers and some foundations for scientific research. DUI mode innovation, in contrast, mainly focuses on the interaction within the supply chain and among some competitors.
Hence, the spatial character of innovation networks in China has tended to be related to the partners: (1) knowledge partners. Recent research has underpinned two important notions. On the one hand, the Chinese science and technology (S&T hereafter) system has a strong hierarchical order, with Beijing dominating on the national scale, and provincial capitals dominating on provincial scales. Although the other smaller cities are improving their innovation abilities considerably, the firms still show the obvious preference for Beijing, without affecting the overall hierarchical structure (Andersson et al. 2014). On the other hand, the legacy of China’s Soviet-style innovation system, which was characterized by a high centralization of capacities in several main cities for providing well-trained engineers and new ideas to the local manufacturers (Liu and White 2001), plus the increasing innovation activities of privately owned enterprises, can lead to a strengthening of local collaboration (Hong 2008). (2) Industry partners. As far as China’s situation is concerned, despite the tremendous economic growth in recent years, the majority of Chinese firms do not have the ability to enter into the world market. Hence, the importance of customer–producer interaction and the tremendous growth of domestic demand allow for innovation strategies that focus on the domestic market and its supply-chain partners. Moreover, in response to the new trend of “indigenous innovation” and “going out”, a large number of Chinese firms have been expanding continuously on a global scale, having gone beyond the border or are planning to do so in order to acquire foreign innovation partners (Si et al. 2013).
Consequently, the spatial patterns of collaboration with both knowledge partners and industry partners may turn out to be ambiguous. In terms of China’s reality, collaboration with knowledge partners may occur on local or national scales, whereas industry partners can be expected to collaborate on all different spatial scales: on the one hand, this depends on the location of the suppliers and customers. On the other hand, if it requires face-to-face contacts among the cooperative actors, it will focus more on geographical proximity. This paper seeks to explain the spatial character of network formation. It thus examines under which conditions Chinese firms collaborate with partners in close proximity or across larger distances. The probability of collaboration with a partner on a different spatial scale is used as the dependent variable (see “Research methodology” section).
On the basis of the literature, we posit that:
Hypothesis 1
Chinese firms will be more likely to search for knowledge partners on the local and national scales.
Hypothesis 2
Chinese firms will be more likely to search for industry partners on the local, national, and overseas scales.
Regional environment
In recent times, economic geographers have been preoccupied with the question of how and why regions vary with regard to their innovation ability (Boschma et al. 2017). Studies using concepts such as clusters, regional innovation system, innovative milieu and learning region employ a variety of terms to discuss the significance of the regional dissimilarity for innovation and the spatiality of regional inequality (Wei 2015). They suggest that innovative activities are the products of regions, and the regional economic and institutional environments affect the behavior of firms in the process of making and fulfilling innovation cooperation decisions (Sternberg and Arndt 2001; Blake and Hanson 2005; Howells and Bessant 2012; Liefner and Jessberger 2016).
In essence, the region may be understood as the container of innovation processes, providing a distinct array of firms, talent, institutions, infrastructure and other required inputs (Wei et al. 2012; Florida et al. 2017). From this angle, the importance of the regional scale is caused by externalities of geographical proximity: face-to-face contacts are essential for the development of trust, and informal communications allow for a transmission of tacit knowledge. Both drive the processes of interactive innovation (Fitjar and Rodríguez-Pose 2015). In verifying this argument, some recent empirical studies have clearly shown that firms tend to search for new cooperation actors or establish branches in similarly specialized clusters and/or metropolitan areas so as to obtain more unconscious knowledge spillover (Poon et al. 2013; Boschma et al. 2014; Gabe and Abel 2016). In addition, due to their importance for the availability of highly qualified labor (Ponds et al. 2010; Huggins et al. 2014), the presence of academic research institutes and universities is expected to influence the local actors’ knowledge base and their innovation potential. Firms located in places with rich resource endowments are more likely to discover and utilize partners on different geographical scales (Wang and Lin 2013; Hewitt-dundas 2013).
Given the uniqueness of China, multifarious regional culture and corresponding guanxi networks, such as kinships, surnames, alumni (schoolmates or classmates), birthplace, workplaces (military and civilian), or political party affiliation, both constrain and enable a firm’s cooperation behavior (Lin 2010; Chen et al. 2013). Cooperation that is based on recommendations of close partners and extends through personal guanxi networks is likely to bring about better innovation results (Bathelt and Zeng 2012; Wu et al. 2015). From a proximity perspective, Fu et al. (2013) propose to equate guanxi with cognitive proximity. They highlight a positive influence of guanxi on the ongoing interactive learning process, while reciprocal and obligatory relationships might more often be used to gain access to particular resources, especially long-term business partners for exploiting tacit knowledge. However, the regional culture may lead to a differentiation of the intensity of effects of guanxi, which results in spatial differences regarding the organization and the profiles of regional innovation systems. Most importantly, the culture of north China attaches high value to stability, laws and regulations as well as collectivity, while the south is said to lean towards flexibility, creativity, individual success and an international orientation (Liefner and Zeng 2008). Some empirical studies, which take Beijing and Shanghai as the exemplified cases of north and south, have shown that Beijing gathers most of China’s leading academic and research institutions and that firms easily establish horizontal linkages with local universities and research institutes in particular. In contrast, firms in Shanghai seem to focus more on support from horizontal partners geared towards market demand and applied research. Shanghai has thus developed into a hub for both indigenous and overseas cooperation (Liu and Jiang 2001; Liefner and Zeng 2008; Huggins et al. 2014; Jiang et al. 2017).
On the basis of the literature, we posit that:
Hypothesis 3
Chinese firms located in regions with stronger resource endowments will be more likely to search for partners on the national and overseas scales.
Hypothesis 4
Chinese firms located in Northern cities are more likely to rely on local partners than firms in Southern cities.
Government interference
Appearing as an extreme case of a triple helix innovation pattern proposed by Etzkowitz and Leydesdorff (2000), most scholars agree that the Chinese government (and the Communist Party) are powerfully involved in the process of innovation generation and continuously affect firms’ approaches towards innovation, highlighting an important feature of the party-led and planning-oriented economy (Liefner and Jessberger 2016; Liefner et al. 2016). The general way is that the government sets up a series of formal laws/regulations and informal societal norms/habits to shape and influence firm innovation behavior (Meyer et al. 2012). Some scholars use political ties to describe the connection of Chinese firms with the government in terms of efficiency and scope. Close political ties may allow access to exclusive policy information and the acquisition of market opportunities (Xie et al. 2014). Although governments in different regions or cities have an idiosyncratic character and apply different motives or degrees of openness, this paper suggests that policy influence can be decomposed into two major levels: national and regional governments, the latter including local and provincial parts.
Comparatively speaking, large and state-owned firms are the two obvious recipients of support from the central government. On the one hand, China primarily attempted to replicate the Soviet Model, characterized by high centralization and complete state-ownership, and as a remnant of this arrangement, SOEs at some level act as spokesmen of the government. They normally control key sectors of economic and industrial development, forming large and mature conglomerates. Such SOEs possess an ownership-specific advantage, as they can reach more innovation-related resources and benefit from public procurement and government-led infrastructure developments (Liefner and Zeng 2016). This is particularly important when special industrial policies and fiscal incentives are adopted by the central government to nurture competitive ‘national champions’ (Hu and Lin 2013). On the other hand, a series of empirical studies have shown that exports may also act as factors significantly related to innovation ability (Liefner et al. 2012; Yang 2012; Liefner et al. 2016). Under China’s political push for ‘going global’ and ‘indigenous innovation’, however, state influence extends even to a firm’s exports performance. The leading private corporations, such as Huawei or Sany, normally possess higher innovation capabilities, and are thus more likely to succeed in integrating the opportunities acquired in foreign markets and the knowledge acquired from foreign innovation partners (Si et al. 2013; Wang and Lin 2013). The central government and its branches act as mediators to give them more support.
At the regional level, the government and its involvement in arranging R&D is identified as the most important factor affecting the innovation configuration (Fitjar and Rodríguez-Pose 2015), especially as some small and medium-sized firms may not have the ability to engage in any innovation activities at all without government subsidies (Czarnitzki and Licht 2006). In the case of China, the government has a habitual idiosyncrasy to strengthen the innovation relation between firms and knowledge partners, which normally helps firms to transform knowledge into commercially successful products (Kafouros et al. 2015). Moreover, political priorities are more important than economic factors in the location of cooperative choices: given the prevalence of administrative protectionism in China, involving an inward-looking orientation of governments to protect local and/or provincial actors with the aim of maximizing intra-administrative-district benefits, local or provincial collaboration is usually favored and promoted by governments (Scherngell and Hu 2011; Andersson et al. 2014). Under these circumstances, firms often have to switch their innovation focus towards local and/or provincial cooperation (Jiang et al. 2017).
On the basis of the literature, we posit that:
Hypothesis 5
Chinese firms with support from the central government will be more likely to search for partners on the overseas scale.
Hypothesis 6
Chinese firms with support from local government will be more likely to search for partners on the local scale.
Firm attributes
The importance of firm attributes for innovative performance and for firms’ ability to engage in meaningful innovation-oriented collaboration is theoretically well established (Cohen and Levinthal 1989; Zahra and George 2002), and has been a key part of many empirical studies. The set of related variables that has been included in empirical studies on Chinese firms varies, but usually incorporates measures of innovation input or output as well as superordinate factors such as age, industry, or ownership (Choi et al. 2011; Liefner et al. 2013). This paper uses ownership and innovation ability, following the logic that SOEs often enjoy a better resource endowment, which allows them to collaborate internationally, and acknowledging the fact that profound innovation ability should have the same effect on collaboration space.
On the basis of the literature, we posit that:
Hypothesis 7
State-owned enterprises will be more likely to collaborate with overseas partners.
Hypothesis 8
Firms with a high innovative ability will be more likely to collaborate on the national and overseas scales.
Data collection and research methodology
Data collection
The empirical analyses in this study are mainly based on the data obtained from a series of semi-structured interviews and a large-scale semi-standardized questionnaire survey of China’s machinery manufacturing industry conducted during the period 10.2012–11.2015.
Specifically, a total of 36 face-to-face interviews were conducted with firms’ general managers, founders or chief technology officers. Nine of the firms were located in Shanghai, 8 in Xiamen, Fujian Province, and 17 in Dongying, Shandong Province. Aside from this, 4 interviews were conducted with local government officials and with representatives of the Shanghai innovation alliance. Generally, firms were asked regarding the aspects of innovation cooperation, the development and introduction of their newest and most important products, milestone events in the development process etc.
The research was organized in the following three steps:
Firstly, based on the pre-test feedback involving group discussions with company and government representatives, carried out in Shanghai and Xiamen, the first draft of the questionnaire was designed during the period 03.2013–05.2013.
Secondly, we started applying the questions in two series of interviews in Dongying during the period 06.06.2013–10.06.2013 and at the Shanghai Heavy Machinery Fair during the period 25.06.2013–27.06.2013. 44 firms in total were included in the experimental phase. In the course of these interviews, the use of terms, statements and test indexes was further modified in order to ensure a common understanding of the main concepts and terms used in the questionnaire, helping to increase validity and credibility. This process resulted in the forming of a final and semi-standardized questionnaire. The questionnaire contains three sections: (1) detailed information on the newest and most important machines that the firms produce, (2) innovation-related linkages and information on government support and corresponding evaluations, (3) basic status of the enterprise, such as location, R&D, ownership, age, financing channels etc.
Thirdly, subsequent large-scale surveys were carried out at four industrial exhibitions, the 15th Shanghai International Machine Tool Exhibition (02.07.2013–05.07.2013), the China International Petroleum Equipment and Technology Exhibition 2013 (17.09.2013–19.09.2013), and the 15th and 17th China International Industry Fairs (05.11.2013–09.11.2013; 03.11.2015–07.11.2015). The targeted respondents in each firm were the managers, directors of engineering, R&D managers, or engineering managers.
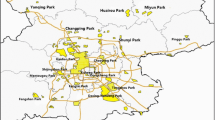
The total number of firms included in the surveys is 174. The firms’ locations are not spread evenly across China, but instead show marked concentrations in Eastern China, the core area of the industry researched. However, the company sample can be nicely split between North and South China, with a total of 54 valid questionnaires from the Northern Chinese cultural region including Beijing, Tianjin, Hebei Province and Shandong Province. Another 120 firms are located in the Southern Chinese cultural region that includes Shanghai, Jiangsu Province and Zhejiang Province (Fig. 2). In more detail, 6 firms are located in Beijing (0 SOEs vs. 6 Non-SOEs), 3 in Tianjin (0 SOEs vs. 3 Non-SOEs), 8 in Heibei (2 SOEs vs. 6 Non-SOEs), 37 in Shandong (8 SOEs vs. 29 Non-SOEs), 53 in Shanghai (3 SOEs vs. 50 Non-SOEs), 34 in Jiangsu (1 SOE vs. 33 Non-SOEs) and 33 in Zhejiang (0 SOEs vs. 33 Non-SOEs). The number of SOEs and Non-SOEs are 14 and 160 respectively. Meanwhile, using the foundation year as a benchmark, the 0–10-year-old firms account for 37.93% (17 in Northern China vs. 49 in Southern China), the 10–20-year-old firms account for 44.83% (21 in Northern China vs. 57 in Southern China) and the over–20-year-old firms account for 17.24% (16 in Northern China vs. 14 in Southern China). In terms of the firms’ employees, 25 firms have more than 1000 (12 in Northern China vs. 13 in Southern China), 64 firms have more than 100 (22 in Northern China vs. 42 in Southern China), and 85 firms have fewer than 100 (20 in Northern China vs. 65 in Southern China).
Research methodology
This article seeks to explain the factors that affect the construction of innovation networks, with a particular focus on China-specific factors. While exploring the relationship between innovation networks, regional environment, government interference and firm attributes, a logistic regression model is applied to establish and to test the presented hypotheses, using the following form:
where the dependent variable Yij refers to the probability of company i located in city j collaborating with an innovation partner across different spatial scales (local scale, national scale, international scale). Network configuration refers to two variables that identify knowledge partners (university, research institute, technology intermediary) and industry partners (customer, supplier and competitor). Regional environment refers to two variables that characterize the region j in which company i is located: innovation resource endowment and local culture. Government interference refers to two variables that express central and local government support. Firm attribute refers to the two variables firm ownership and innovation ability. Table 1 shows the specific items used. Overall, the majority of variables are assessed with a 5-point Likert scale, on which a higher score denoted a higher degree of the item concerned, except the two dummy variables regional culture (North, South) and firm ownership (SOE, Non-SOE). The rank of each city or province in China’s science and technology system (variable x3) is established in accordance with Andersson et al. (2014).
Determinants of the spatial character of China’s innovation network
Descriptive results
Table 2 shows an extension of the descriptive data for the firms in the sample, including ownership, size, age and its market scope. A clear result found in the firm representatives’ statements and of overall importance for understanding the results discussed in this paper is the following: all the SOEs which still show a strong or even dominant state involvement belong to large and mature firm groups. Moreover, 42.86% of them are mainly oriented towards the international market, while Non-SOEs are obviously characterized by being of middle and small size, founded for only a short time, having low overseas market shares, and hence having limited competitiveness and innovation capacity.
Starting with the question of firms’ priority to collaborate, the paper calculates the location of each innovation partner identified, differentiating between locations within the same city (local scale), other locations in China (national scale) and overseas locations. As shown by Table 3, the collaboration is most frequently carried out on the national scale (61.67%), while the overseas scale is less prominent (13.67%). Moreover, cooperation with industry partners (64.67%) is more common than cooperation with knowledge partners (35.33%). Overall, cooperation with national industry partners (39.67% of all collaboration cases) is most frequent, cooperation with national knowledge partners (22%) comes second, followed by cooperation with local industry partners (13.00%), with overseas industry partners (12.00%) and with local knowledge partners (11.67%). Cooperation with overseas knowledge partners (1.67%) is of minimal importance. The above result is decided by the fundamental feature of innovation processes of machinery manufacturing industry, which should highlight the importance of customers in defining exactly the purpose and technical solution for which a particular machine should be developed (Liefner and Zeng 2016).
Hypotheses testing
Table 4 reports the summary statistics for the independent variables including the means (M), standard deviations (SD) and multicollinearity diagnostics, suggesting no serious problem having been detected. According to the mean of firm ownership and innovation ability, 0.08 and 2.71 respectively, the surveys mainly focus on the privately owned firms, whose ability in terms of product innovation is generally considered to stay at the intermediate level. Moreover, it is not surprising that the innovation in China’s machinery manufacturing industry is largely driven by customer needs and focuses on the cooperation with industry partners. The average cooperation between a firm and industry partners is thus 2.40, higher than knowledge partners with 1.44. Special emphasis is placed on the difference between central and local government, which is extremely significant with 2.36 and 4.27 respectively, meaning that the majority of firms have the perception of support from local government, whereas the support from the central government is relatively lower.
Table 5 summarizes the results of the logistic regression analyses, independently run for cooperation on the three different spatial scales. Overall, all of these three models correctly assess 61.3, 55.0 and 60.7% of the cases respectively. In other words, the independent variables chosen explain well the probability of cooperation in the innovation network of China’s machinery manufacturing industry.
The regression results reveal a significant positive effect of knowledge partners on local and national cooperation (βlocal = 0.320, p < 0.001; βnational = 0.417, p < 0.001), providing strong support for H1; the results of industry partners are positively related to the national and overseas scales (βnational = 0.702, p < 0.001; βoverseas = 0.386, p < 0.001) and hence partly support H2. On the whole, cooperation with knowledge partners is marked at the local and national level, while industry partners are chosen on national and international levels, and the influence of industry partners is stronger than that of knowledge partners on the national level. The results provide a much more differentiated picture than earlier attempts, contrasting prevailing theories on the geographical dimensions of innovation collaboration, which usually show that knowledge partners may transfer across larger spatial scales than industry partners. The main cause of the phenomena mentioned about industry partner collaboration might be the overlap effect between the market area and the innovation nature: innovation in the machinery manufacturing industry is often driven by customer needs, labeled instructed innovation, and thus focuses on the needs along the industry chain, which is usually organized nationally (Liefner and Zeng 2016). In this vein, firms address more the market need, which for the majority of manufacturing firms means a focus on domestic demand. Only the stronger POEs and SOEs may possess higher innovation capability that enables them to establish overseas links. Otherwise, as far as knowledge partners are concerned, the transformation context and spatial bias of the Chinese S&T system become obvious (Hong 2008; Andersson et al. 2014). Since the reform of the S&T sector around 2000, universities have been capable of carrying out basic as well as applied R&D and can play a major role, in particular with increasing innovation activities of privately owned enterprises, which brings about the enhancing of local collaboration (Hong 2008). Meanwhile, firms are prone to searching for translocal high-tier knowledge partners in the absence of local premium resources (Laursen et al. 2011), particularly in the center of the hierarchical system, such as Beijing, Shanghai, Tianjin, Chongqing and some provincial capitals (Andersson et al. 2014).
Turning to the relationship between the regional environment and cooperation scales, the results partly confirm H3, according to which a city’s resource endowment is positively related to international collaboration (βoverseas = 0.011, p < 0.05). In accordance with existing research, this result indicates that the ability or intention to cooperate across large distances is contingent on the quality of knowledge partners in the local area. The cities with a strong local knowledge base provide sufficient endowment in education and knowledge as well as openness to translocal innovation, and firms can benefit from utilizing multi-spatial innovation channels that are not confined to nearby partners (Hewitt-dundas 2013; Fitjar and Rodríguez-Pose 2015). The logit estimates further highlight how regional culture affects innovation cooperation scales: firms located in Northern China have an obvious tendency towards local cooperation (βlocal = 1.252, p < 0.001), supporting H4. Culture and corresponding guanxi networks in particular influence the importance that firms attach to geographical and administrative proximity. On the one hand, in the context of the more stable Northern culture, it is easier to establish local or provincial linkages through guanxi networks, such as the recommendations by friends and relatives (Liefner and Zeng 2008). On the other hand, the effect of administrative borders and protectionism in Northern parts is much more powerful, therefore firms switch their innovation focus towards co-localized partners to catch R&D support from the government (Huggins et al. 2014; Jiang et al. 2017).
The results for the government-specific variables are of particular interest. Inconsistent with our prediction, H5, dealing with the relationship between local government and innovation space, is refuted. In contrast, the coefficient of central government on overseas cooperation is positive and significant (βoverseas = 0.329, p < 0.001), and H6 is hence accepted. To be specific, China’s central government has issued a variety of policies, strategies and programs to push Chinese firms to become champions in terms of innovation, as part of the goal to transform China into a global powerhouse by improving its capacity to generate independent indigenous innovation (Liefner and Zeng 2016). Firms with stronger innovation ability may meet the target and then access exclusive policy information and opportunities to reach out to international innovation partners ahead of domestic competitors, such as Huawei and Sany (Si et al. 2013; Wang and Lin 2013).
As expected, the firm-specific characteristics exert significant influence on the spatial structure of innovation networks of China’s machinery manufacturing industry. First of all, the ownership variable (βoverseas = 0.274, p < 0.01) is positive on the overseas scale, indicating that SOEs collaborate frequently on the international scale, supporting H7. The firms’ innovation ability variable is significantly negative on the local scale (βlocal = − 0.399, p < 0.001) and positive on the overseas scale (βoverseas = 0.333, p < 0.001), partly supporting H8. Obviously, strong innovation ability decreases the probability of local collaboration, underlining the fact that firms with low innovative capability are restricted to cooperation on the local scale. Instead, the firms possessing strong innovative capabilities often go beyond cooperating with the nearby partners and consciously seek long-distance collaboration.
Illustrative case study
As a consequence of reviewing the theoretical and empirical research on innovation in China, and based on the research results presented in the previous section, this paper proposes a simplified but more China-specific model to understand the specific spatial patterns of China’s innovation networks (Fig. 3). The framework will be illustrated with one case study, which discusses currently observed practices of innovation activities of the oil equipment industry in Dongying, Shandong province. Dongying provides the most interesting case for the proposed discussion for two reasons. Firstly, Dongying can be regarded as the quintessential example of Northern culture, where guanxi plays a vital role in building and maintaining the innovation links. Secondly, in line with China’s huge success in industrializing, Dongying’s oil equipment industry has developed from providing rather low-tech and cheap products towards producing more sophisticated and advanced equipment. The innovation network is hence made up of local and global linkages with a strong involvement of various domestic and overseas actors.
As shown by Table 6, the innovation network in Dongying’s oil equipment industry has two important features: (1) firms in Dongying vary regarding their cooperation practices. Three types can be identified: examples for the first type, and the most sophisticated cooperation practice, are the firms with strong innovative abilities and international influence. This group includes some SOEs, one reformed POE and one large POE, such as Creat Group etc. The middle-level group is found among the medium-sized POEs, which have medium-range innovation and market experience as well as a stable customer group and regular domestic market, such as Shengli power machinery group etc. The other small firms, with low-level cooperation practices, such as Dadonglian Oil Equipment etc., form a third type. (2) The firms in Donging use collaboration with knowledge partners (mainly China University of Petroleum, Shengli Oilfield Petroleum Institute) to conduct joint tests of new components or technical solutions. Moreover, the cooperative research also functions as a key channel to cultivate talents, and senior engineers in particular. It is interesting to note that the cooperation mode with local knowledge partners in Dongying is similar to the German dual education system, in which students acquire theoretical knowledge in a university or school and practical skills in the firms.
With respect to the factors affecting the spatial character of the innovation network, the firms assess that the regional market, regional institutional involvements and the Shandong culture interweave and determine the characteristics of the local–global innovation network. (1) Dongying city originated from Shengli Oilfield, and its cluster has already upgraded with global–local cooperation. To be specific, around the 2000s, all the organizations in Shengli Oilfield were divided into two parts, Shengli Oilfield Company Ltd and Shengli Petroleum Administration, and only subsidiaries focusing on the oilfield, such as drilling, remained in the system. All other entities had been singled out and reformed to become POEs. The huge transformation went along with major restructuring, modernization and massive job losses, and many new firms have been founded by employees who once all belonged to the same firm. As a result, the owners and managers of most POEs are former colleagues, linked to each other by the traditional guanxi ties, such as fellow villagers, relatives or friends. This densely networked local context facilitates buzz, flows of talents, as well as frequent resource sharing, which propels knowledge acquisition and market expansion, and has a great influence on the configuration of the innovation network. For example, one interviewee remarked: “I was born in Donying and worked in the Shengli Oilfield before. There is no doubt that I have a lot of advantages here, you know, Shandong people don’t want to leave home, I have a lot of interpersonal resources, most relatives, friends who are part of these networks live in the same or nearby village, they can help me to solve a lot of problems, some technological problems in particular.” [authors’ translation]. (2) Due to the access rule of Shengli Oilfield, most firms have no right to sell their products on the local market and have to turn to external oilfields. Moreover, given the different specifications of the geological conditions of oilfields, the machines must be tailored towards different situations. The firms hence usually set up a branch or department in the targeted market, which will not only provide after-sales service, but also collects information for continued product improvement and innovation. A firm’s entry into a developed market area, such as Houston in Texas or Calgary in Canada, thus requires actions such as establishing a subsidiary or a post-doctoral center, or setting up a joint venture with foreign firms in local markets for close cooperation on R&D. (3) Functioning as a coordinating agency, the government is positively involved in innovation activities not only as a local or national factor of institutional arrangements, but also as a bridge to actively construct overseas linkages. In more detail, firstly, the local government has founded industrial parks and economic development zones, providing a platform for related firms to work together. As a result, increasing numbers of firms are agglomerating in the neighboring areas, which not only contributes to the usage of resources and the reduction of costs, including infrastructure and transportation, but also benefits personal connection and formal collaboration between them. Secondly, the local government can formulate preferential policies and control the approval of research projects. Thirdly, the government becomes actively involved in innovation activities and market expansion, for example the organization of fairs and seminars, governments’ recommendation to a new market and the operation of industry associations. For example, one interviewee remarked: “All our most important partners are in foreign countries, such as Cameron and Parker, and the acquisition of innovative cooperation is a gradual process, which is usually recommended by the Chinese’s embassy in the market country and some petroleum firms.” [authors’ translation].
The illustrative case carried out for this part has two significances. The first concerns the MNEs and the governmental policy with respect to the expansion of overseas cooperation, and the second concerns the relative importance of regional culture in affecting innovation. Concretely, based on the strong production capacity and high innovation capability, Dongying’s MNEs play a dominant role in bridging between international markets and local clusters, and easily get the government’s support. Normally, they establish various innovation nodes to acquire knowledge according to the innovation levels of different markets: in developed markets, subsidiaries, post-doctoral research centers and joint ventures are established to attract local talent and R&D cooperation, while in developing markets, generally offices are built in charge of sales and after-sales service. Regarding the influence of regional culture, the typical Northern culture with the importance of guanxi plays an important role in the process of searching for partners and makes the innovation network and interpersonal network interwoven.
Conclusion
Research on innovation networks which allow the utilization of internal and external innovation resources has for some time been a hot spot in several research fields. However, the existing theoretical frameworks and empirical results are largely based on studies in developed economies. Hence, they do not fully explain the situation in China and they miss the chance to integrate features relevant in the context of China, and perhaps other newly industrializing countries. In order to respond to this void, this study has developed an analytical framework which combines regional context, government influence and firm attributes to explain different spatial configurations of innovation networks. The empirical analyses were based on a sample of 174 manufacturing firms and a detailed case study.
Our research results have three theoretical implications for the existing literature in general, and for the research strand on context and developing economies in particular. Firstly, in line with Liefner and Zeng (2008), the paper moves beyond the traditional focus on how local innovation sources influence the structure of the innovation network and its spatial character. We provide a framework that integrates China’s specific context into the analysis of the structure of local–global innovation networks, and prove that regional culture and local guanxi networks affect the strengths and functions of relations between firms and their innovation partners. Meanwhile, the results highlight the effect of the local knowledge base on enhancing the multi-scalar links, as the cities with a superior innovation resource base provide sufficient endowments in education and knowledge as well as openness to translocal innovation. Secondly, it also echoes a recent call for more studies on firm attributes. In the context of China, ownership and innovation ability are the two essential variables to determine whether any of the regional elements are of significance. Normally, SOEs are marked with high innovation ability. If one high-ranking innovation firm is to occupy the world or developed market, the firm will actively seek more complex R&D activities and technical breakthroughs, especially through the cooperation with international partners. Favorable local resources in the home city help to enlarge the knowledge search breadth. Thirdly, one practical implication concerns the innovation network of the machinery manufacturing industry: the findings suggest that as the typical producer-driven and technology-driven industry, the customers and the key corresponding industry partners are the dominant actors in the innovation network. National cooperation happens more frequently than local cooperation, and turns out to be the optimal choice for the firms at the present stage. The research hence raises some corresponding policy suggestions to optimize and enhance the innovation of China’s machinery manufacturing industry, namely: cultivating the superiority of supply-chain links, weakening local networking while encouraging regional innovation cooperation, establishing the institution system to meet the needs of the industry.
Whilst the research provides some valuable insights into innovation network characteristics, several limitations should be addressed for additional research. One of these is that the empirical results are derived from a sample of the machinery manufacturing industry and hence the findings might be industry-specific. Moreover, the data for this study are based on the cooperation and experiences of the respondents, which may vary widely across ownerships, ages and scales within the firm. Furthermore, there is a wide range of cultural difference issues in China, and more regional comparisons would be helpful to understand the implication of context elements.
References
Andersson, D. E., Gunessee, S., Matthiessen, C. W., & Find, S. (2014). The geography of Chinese science. Environment and Planning a, 46(12), 2950–2971.
Asheim, B. T., & Gertler, M. S. (2005). The geography of innovation: Regional innovation systems. In J. Fagerberg, D. Mowery, & R. Nelson (Eds.), The Oxford handbook of innovation (pp. 291–317). Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Balland, P.-A., De Vaan, M., & Boschma, R. (2013). The dynamics of interfirm networks along the industry life cycle: The case of the global video game industry, 1987–2007. Journal of Economic Geography, 13(5), 741–765.
Bathelt, H., Malmberg, A., & Maskell, P. (2004). Clusters and knowledge: Local buzz, global pipelines and the process of knowledge creation. Progress in Human Geography, 28(1), 31–56.
Bathelt, H., & Zeng, G. (2012). Strong growth in weakly-developed networks: Producer–user interaction and knowledge brokers in the Greater Shanghai chemical industry. Applied Geography, 32(1), 158–170.
Blake, M. K., & Hanson, S. (2005). Rethinking innovation: Context and gender. Environment and planning A, 37(4), 681–701.
Boschma, R., Coenen, L., Frenken, K., & Truffer, B. (2017). Towards a theory of regional diversification: Combining insights from Evolutionary Economic Geography and Transition Studies. Regional Studies, 51(1), 31–45.
Boschma, R., Heimeriks, G., & Balland, P.-A. (2014). Scientific knowledge dynamics and relatedness in biotech cities. Research Policy, 43(1), 107–114.
Broekel, T. (2015). The co-evolution of proximities—A network level study. Regional Studies, 49(6), 921–935.
Carayol, N. (2003). Objectives, agreements and matching in science–industry collaborations: Reassembling the pieces of the puzzle. Research Policy, 32(6), 887–908.
Chen, C. C., Chen, X. P., & Huang, S. (2013). Chinese Guanxi: An integrative review and new directions for future research. Management and Organization Review, 9(1), 167–207.
Choi, S. B., Lee, S. H., & Williams, C. (2011). Ownership and firm innovation in a transition economy: Evidence from China. Research Policy, 40(3), 441–452.
Cohen, W. M., & Levinthal, D. A. (1989). Innovation and learning: The two faces of R&D. The Economic Journal, 99(397), 569–596.
Cooke, P. (1998). Introduction: Origins of the concept. In H.-J. Braczyk, P. N. Cooke, & M. Heidenreich (Eds.), Regional innovation systems: The role of governances in a globalized world (pp. 2–25). London: Routledge.
Czarnitzki, D., & Licht, G. (2006). Additionality of public R&D grants in a transition economy. Economics of Transition, 14(1), 101–131.
Du, J., & Mickiewicz, T. (2016). Subsidies, rent seeking and performance: Being young, small or private in China. Journal of Business Venturing, 31(1), 22–38.
Etzkowitz, H., & Leydesdorff, L. (2000). The dynamics of innovation: From national systems and “mode 2” to a triple helix of university–industry–government relations. Research Policy, 29(2), 109–123.
Fitjar, R. D., & Rodríguez-Pose, A. (2013). Firm collaboration and modes of innovation in Norway. Research Policy, 42(1), 128–138.
Fitjar, R. D., & Rodríguez-Pose, A. (2015). Networking, context and firm-level innovation: Cooperation through the regional filter in Norway. Geoforum, 63, 25–35.
Florida, R., Adler, P., & Mellander, C. (2017). The city as innovation machine. Regional Studies, 51(1), 86–96.
Fu, W., Revilla Diez, J., & Schiller, D. (2013). Interactive learning, informal networks and innovation: Evidence from electronics firm survey in the Pearl River Delta, China. Research Policy, 42(3), 635–646.
Gabe, T. M., & Abel, J. R. (2016). Shared knowledge and the coagglomeration of occupations. Regional Studies, 50(8), 1360–1373.
Hennemann, S., Rybski, D., & Liefner, I. (2012). The myth of global science collaboration—Collaboration patterns in epistemic communities. Journal of Informetrics, 6(2), 217–225.
Hewitt-Dundas, N. (2013). The role of proximity in university-business cooperation for innovation. The Journal of Technology Transfer, 38(2), 93–115.
Hong, W. (2008). Decline of the center: The decentralizing process of knowledge transfer of Chinese universities from 1985 to 2004. Research Policy, 37(4), 580–595.
Hong, W., & Su, Y. S. (2013). The effect of institutional proximity in non-local university–industry collaborations: An analysis based on Chinese patent data. Research Policy, 42(2), 454–464.
Howells, J., & Bessant, J. (2012). Introduction: Innovation and economic geography: A review and analysis. Journal of Economic Geography, 12(5), 929–942.
Hu, F. Z., & Lin, G. C. (2013). Placing the transformation of state-owned enterprises in North-east China: The state, region and firm in a transitional economy. Regional Studies, 47(4), 563–579.
Huggins, R., Luo, S., & Thompson, P. (2014). The competitiveness of China’s leading regions: Benchmarking their knowledge-based economies. Tijdschrift voor economische en sociale geografie, 105(3), 241–267.
Jeannerat, H., & Crevoisier, O. (2016). From ‘territorial innovation models’ to ‘territorial knowledge dynamics’: On the learning value of a new concept in regional studies. Regional Studies, 50(2), 185–188.
Jensen, M. B., Johnson, B., Lorenz, E., & Lundvall, B. Å. (2007). Forms of knowledge and modes of innovation. Research Policy, 36(5), 680–693.
Jiang, S.-q., Shi, A.-n., Peng, Z.-h., & Li, X. (2017). Major factors affecting cross-city R&D collaborations in China: Evidence from cross-sectional co-patent data between 224 cities. Scientometrics, 111(3), 1251–1266.
Kafouros, M., Wang, C., Piperopoulos, P., & Zhang, M. (2015). Academic collaborations and firm innovation performance in China: The role of region-specific institutions. Research Policy, 44(3), 803–817.
Laursen, K., Reichstein, T., & Salter, A. (2011). Exploring the effect of geographical proximity and university quality on university–industry collaboration in the United Kingdom. Regional Studies, 45(4), 507–523.
Lee, J., & Berente, N. (2013). The era of incremental change in the technology innovation life cycle: An analysis of the automotive emission control industry. Research Policy, 42(8), 1469–1481.
Liefner, I., Brömer, C., & Zeng, G. (2012). Knowledge absorption of optical technology companies in Shanghai, Pudong: Successes, barriers and structural impediments. Applied Geography, 32(1), 171–184.
Liefner, I., & Jessberger, S. (2016). The use of the analytical hierarchy process as a method of comparing innovation across regions: The examples of the equipment manufacturing industries of Shanghai and Xiamen, China. Environment and Planning A, 48(6), 1188–1208.
Liefner, I., Kroll, H., & Peighambari, A. (2016). Research-driven or party-promoted? Factors affecting patent applications of private small and medium-sized enterprises in China’s Pearl River Delta. Science and Public Policy, 43(6), 849–858.
Liefner, I., Wei, Y. D., & Zeng, G. (2013). The innovativeness and heterogeneity of foreign-invested high-tech companies in Shanghai. Growth and Change, 44(3), 522–549.
Liefner, I., & Zeng, G. (2008). Cooperation patterns of high-tech companies in Shanghai and Beijing: Accessing external knowledge sources for innovation processes. Erdkunde, 62(3), 245–258.
Liefner, I., & Zeng, G. (2016). China’s mechanical engineering industry: Offering the potential for indigenous innovation? In Y. Zhou, W. Lazonick, & Y. Sun (Eds.), China as an innovation nation (pp. 98–132). Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Lin, N. (2010). Capitalism in China: A centrally managed capitalism (CMC) and its future. Management and Organization Review, 7(1), 63–96.
Liu, H., & Jiang, Y. (2001). Technology transfer from higher education institutions to industry in China: Nature and implications. Technovation, 21(3), 175–188.
Liu, X., & White, S. (2001). Comparing innovation systems: A framework and application to China’s transitional context. Research Policy, 30(7), 1091–1114.
Martin, R. (2000). Institutional approaches in economic geography. In E. S. Sheppard & T. J. Barnes (Eds.), A companion to economic geography (pp. 77–94). Oxford, UK: Blackwell.
Maskell, P., & Malmberg, A. (1999). Localised learning and industrial competitiveness. Cambridge Journal of Economics, 23(2), 167–185.
Meyer, S., Schiller, D., & Revilla Diez, J. (2012). The localization of electronics manufacturing in the Greater Pearl River Delta, China: Do global implants put down local roots? Applied Geography, 32(1), 119–129.
Park, S. H., & Luo, Y. (2001). Guanxi and organizational dynamics: Organizational networking in Chinese firms. Strategic Management Journal, 22(5), 455–477.
Peighambari, A., Hennemann, S., & Liefner, I. (2014). Success factors for upgrading and innovation in the electronics industry: An analysis of private small and medium-sized enterprises in the Pearl River Delta. International Journal of Technology Management, 65(1–4), 49–69.
Ponds, R., Van Oort, F., & Frenken, K. (2010). Innovation, spillovers and university–industry collaboration: an extended knowledge production function approach. Journal of Economic Geography, 10(2), 231–255.
Poon, J. P., Kedron, P., & Bagchi-Sen, S. (2013). Do foreign subsidiaries innovate and perform better in a cluster? A spatial analysis of Japanese subsidiaries in the US. Applied Geography, 44, 33–42.
Randhawa, K., Wilden, R., & Hohberger, J. (2016). A bibliometric review of open innovation: Setting a research agenda. Journal of Product Innovation Management, 33(6), 750–772.
Rodríguez-Pose, A. (2013). Do institutions matter for regional development? Regional Studies, 47(7), 1034–1047.
Scherngell, T., & Hu, Y. (2011). Collaborative knowledge production in China: Regional evidence from a gravity model approach. Regional Studies, 45(6), 755–772.
Si, Y., Liefner, I., & Wang, T. (2013). Foreign direct investment with Chinese characteristics: A middle path between ownership-location-internalization model and linkage-leverage-learning model. Chinese Geographical Science, 23(5), 594–606.
Sternberg, R., & Arndt, O. (2001). The firm or the region: What determines the innovation behavior of European firms? Economic Geography, 77(4), 364–382.
Storper, M. (1997). The regional world: Territorial development in a global economy. New York, London: Guilford Press.
Storper, M., & Venables, A. J. (2004). Buzz: Face-to-face contact and the urban economy. Journal of Economic Geography, 4(4), 351–370.
Tomlinson, P. R., & Jackson, I. (2013). Cooperative ties and the impact of external factors upon innovation in an industrial district: Some insights from the North Staffordshire table and giftware sector. Regional Studies, 47(4), 580–596.
Trippl, M., Grillitsch, M., & Isaksen, A. (2017). Exogenous sources of regional industrial change: Attraction and absorption of non-local knowledge for new path development. Progress in Human Geography. https://doi.org/10.1177/0309132517700982.
Vang, J., & Asheim, B. (2006). Regions, absorptive capacity and strategic coupling with high-tech TNCs: Lessons from India and China. Science Technology & Society, 11(1), 39–66.
Wang, C. C., & Lin, G. C. (2013). Dynamics of innovation in a globalizing china: Regional environment, inter-firm relations and firm attributes. Journal of Economic Geography, 13(3), 397–418.
Wei, Y. D. (2015). Spatiality of regional inequality. Applied Geography, 61, 1–10.
Wei, Y. D., & Liefner, I. (2012). Globalization, industrial restructuring, and regional development in China. Applied Geography, 32(1), 102–105.
Wei, Y. D., Zhou, Y., Sun, Y., & Lin, G. C. (2012). Production and R&D networks of foreign ventures in China: Implications for technological dynamism and regional development. Applied Geography, 32(1), 106–118.
Wu, A., Wang, C. C., & Li, S. (2015). Geographical knowledge search, internal R&D intensity and product innovation of clustering firms in Zhejiang, China. Papers in Regional Science, 94(3), 553–572.
Xie, Y., Liu, H., & Gao, S. (2014). Innovation generation and appropriation: The dual roles of political ties in Chinese firms’ new product development. International Journal of Technology Management, 65(1–4), 215–239.
Yang, C. (2012). Restructuring the export-oriented industrialization in the Pearl River Delta, China: Institutional evolution and emerging tension. Applied Geography, 32(1), 143–157.
Zahra, S. A., & George, G. (2002). Absorptive capacity: A review, reconceptualization, and extension. Academy of Management Review, 27(2), 185–203.
Zhang, J., & Peck, J. (2016). Variegated capitalism, Chinese style: Regional models, multi-scalar constructions. Regional Studies, 50(1), 52–78.
Acknowledgements
The authors greatly appreciate the helpful comments of reviewers and editors, which have significantly contributed to improving the quality of the paper. We are also grateful to Sabine Jessberger for her work on organizing the project and carrying out the interviews. Thanks are also due to Professor Gang Zeng, East China Normal University, Shanghai, and his group for their help conducting research in China. This research was funded by grants from the German Research Foundation (DFG Li981/8-1), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41371147, 41771143) and the Sino-German (CSC-DAAD) Postdoc Scholarship Program (201600260053).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The paper complies with the ethical standards as put forward by GeoJournal. Moreover, no potential conflict of interest relevant to this paper was reported.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Lyu, G., Liefner, I. The spatial configuration of innovation networks in China. GeoJournal 83, 1393–1410 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10708-017-9844-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10708-017-9844-1