Abstract
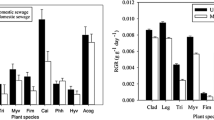
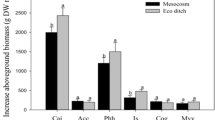
Ecological ditches (eco-ditches) are being recognized as a green method for treating wastewater from domestic sewage sources. However, the relationship between the efficiency of nutrient removal from wastewater and N2O emissions is unclear given that a higher nutrient removal efficiency might result in more N2O emissions. Therefore, we constructed an eco-ditch system with three combinations of different plants (local wetland species) to treat rural sewage in the mountainous regions of China and monitored water quality and N2O emissions. Eco-ditches are important sources of atmospheric N2O, with nutrient removal efficiencies of 22–84% and 23–87% for total nitrogen (TN) and total phosphorus (TP), respectively, and emissions of N2O ranging from 16 to 243 µg m−2 h−1. The seasonal variations in pollutant removal efficiency and N2O emissions followed similar patterns—both were considerably greater in summer than in the other seasons, with the lowest values observed in winter. Among the three plant configurations tested, ditch sections containing Acorus calamus L. and Phyllostachys heteroclada Oliv. had the highest nutrient removal efficiency and the lowest N2O emissions, with removal efficiencies of 24% and 32%, respectively, for TN and TP, and a 16% average reduction in N2O emissions, which was positively associated with NO3–N. This study highlights the importance of selecting appropriate combination of plant species for eco-ditches to efficiently remove nutrients from rural domestic sewage and reduce N2O emissions.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguiar TR Jr, Rasera K, Parron LM, Brito AG, Ferreira MT (2015) Nutrient removal effectiveness by riparian buffer zones in rural temperate watersheds: the impact of no-till crops practices. Agric Water Manag 149:74–80
Anderson JC, Joudan S, Shoichet E et al (2015) Reducing nutrients, organic micropollutants, antibiotic resistance, and toxicity in rural wastewater effluent with subsurface filtration treatment technology. Ecol Eng 84:375–385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2015.08.005
Audet J, Jéglot A, Elsgaard L et al (2021) Nitrogen removal and nitrous oxide emissions from woodchip bioreactors treating agricultural drainage waters. Ecol Eng. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2021.106328
Bigambo T, Mayo AW (2005) Nitrogen transformation in horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetlands II: effect of biofilm. Phys Chem Earth 30:668–672. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pce.2005.08.006
Chen L, Liu F, Wang Y et al (2015) Nitrogen removal in an ecological ditch receiving agricultural drainage in subtropical central China. Ecol Eng 82:487–492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2015.05.012
Edwards M, Topp E, Metcalfe CD et al (2010) Pharmaceutical and personal care products in tile drainage following surface spreading and injection of dewatered municipal biosolids to an agricultural field. Sci Total Environ 408:2180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2010.01.050
Elliott AH, Trowsdale SA (2007) A review of models for low impact urban stormwater drainage. Environ Model Softw 22:394–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2005.12.005
Gall HE, Sassman SA, Lee LS, Jafvert CT (2011) Hormone discharges from a midwest tile-drained agroecosystem receiving animal wastes. Environ Sci Technol 45:8755–8764
Garnier J, Billen G, Vilain G et al (2009) Nitrous oxide (N2O) in the Seine river and basin: observations and budgets. Agric Ecosyst Environ 133:223–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2009.04.024
Han N, Gin KY, Hao H (2015) Fecal pollution source tracking toolbox for identification, evaluation and characterization of fecal contamination in receiving urban surface waters and groundwater. Sci Total Environ 538:38–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.07.155
He S, Li Y, Yang W et al (2021) A comparison of the mechanisms and performances of Acorus calamus, Pontederia cordata and Alisma plantagoaquatica in removing nitrogen from farmland wastewater. Biores Technol 332:125105. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BIORTECH.2021.125105
Huang L, Gao X, Guo J (2013) A review on the mechanism and affecting factors of nitrous oxide emission in constructed wetlands. Environ Earth Sci 68:2171–2180. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-012-1900-z
Inamori R, Wang Y, Yamamoto T, Zhang J (2008) Chemosphere seasonal effect on N2O formation in nitrification in constructed wetlands abstract. Chemosphere 73:1071–1077. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.07.064
Jia L, Jiang B, Huang F, Hu X (2019) Nitrogen removal mechanism and microbial community changes of bioaugmentation subsurface wastewater infiltration system. Biores Technol 294:122140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122140
Jiang X, Tian Y, Ji X et al (2020) Influences of plant species and radial oxygen loss on nitrous oxide fluxes in constructed wetlands. Ecol Eng 142:105644. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2019.105644
Jin J, Tian X, Liu G et al (2022) Novel ecological ditch system for nutrient removal from farmland drainage in plain area: performance and mechanism. J Environ Manag 318:115638. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.115638
Kroger R, Cooper CM, Moore MT (2008) A preliminary study of an alternative controlled drainage strategy in surface drainage ditches: low-grade weirs. Agric Water Manag 95:678–684. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2008.01.006
Kumwimba MN, Zhu B (2017) Effectiveness of vegetated drainage ditches for domestic sewage effluent mitigation. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 98:682–689. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-017-2054-1
Li S, Wang X, Tu J et al (2016) Nitrogen removal in an ecological ditch based on an orthogonal test. Water Air Soil Pollut 227:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11270-016-3085-7/FIGURES/6
Liang Y, Zhu H, Bañuelos G et al (2017) Removal of nutrients in saline wastewater using constructed wetlands: plant species, influent loads and salinity levels as influencing factors. ECSN. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.08.087
Liang Y, Wang Q, Huang L et al (2020) Insight into the mechanisms of biochar addition on pollutant removal enhancement and nitrous oxide emission reduction in subsurface flow constructed wetlands: microbial community structure, functional genes and enzyme activity. Biores Technol 307:123249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123249
Liu F, Wang Y, Xiao R et al (2015) Influence of substrates on nutrient removal performance of organic channel barriers in drainage ditches. J Hydrol 527:380–386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.04.049
Ma L, Tong W, Chen H et al (2018) Quantification of N2O and NO emissions from a small-scale pond-ditch circulation system for rural polluted water treatment. Sci Total Environ 619–620:946–956. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.11.192
Mander Ü, Tournebize J, Kasak K, Mitsch WJ (2013) Climate regulation by free water surface constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment and created riverine wetlands. Ecol Eng. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2013.05.004
Moeder M, Carranza-diaz O, López-angulo G et al (2017) Potential of vegetated ditches to manage organic pollutants derived from agricultural runoff and domestic sewage : a case study in. Sci Total Environ 598:1106–1115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.04.149
Muerdter CP, Smith DJ, Davis AP (2020) Impact of vegetation selection on nitrogen and phosphorus processing in bioretention containers. Water Environ Res 92:236–244. https://doi.org/10.1002/wer.1195
Ongley ED, Xiaolan Z, Tao Y (2010) Current status of agricultural and rural non-point source pollution assessment in China. Environ Pollut 158:1159–1168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2009.10.047
Peng L, Ni BJ, Ye L, Yuan Z (2015) The combined effect of dissolved oxygen and nitrite on N2O production by ammonia oxidizing bacteria in an enriched nitrifying sludge. Water Res 73:29–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2015.01.021
Qiu ZC, Wang M, Lai WL et al (2011) Plant growth and nutrient removal in constructed monoculture and mixed wetlands related to stubble attributes. Hydrobiologia 661:251–260. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-010-0530-2
Ren X, Zhu B, Bah H, Raza ST (2020) How tillage and fertilization influence soil N2O emissions after forestland conversion to cropland. Sustainability (switzerland) 12:8–11. https://doi.org/10.3390/SU12197947
Schmadel NM, Harvey JW, Schwarz GE (2019) Small ponds in headwater catchments are a dominant influence on regional nutrient and sediment budgets geophysical research letters. Geophys Res Lett 46:9669–9677. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019GL083937
Smith RA, Schwarz GE, Boyer EW et al (2008) Differences in phosphorus and nitrogen delivery to the Gulf of Mexico from the Mississippi river basin. Environ Sci Technol 42:822–830
Sun B, Zhang L, Yang L et al (2012) Agricultural non-point source pollution in China: causes and mitigation measures. Ambio 41:370–379. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13280-012-0249-6
Tixier G, Lafont M, Grapentine L et al (2011) Ecological risk assessment of urban stormwater ponds : literature review and proposal of a new conceptual approach providing ecological quality goals and the associated bioassessment tools. Ecol Ind 11:1497–1506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2011.03.027
Walter P, Heimann M (2000) A process-based, climate-sensitive model to derive methane emissions from natural wetlands: application to five wetland sites, sensitivity to model parameters, and climate. Global Biogeochem Cycles 14:745–765
Wang Y, Inamori R, Kong H et al (2008) Nitrous oxide emission from polyculture constructed wetlands: effect of plant species. Environ Pollut 152:351–360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2007.06.017
Wang H, Chen Z-X, Zhang X-Y et al (2013) Plant species richness increased belowground plant biomass and substrate nitrogen removal in a constructed wetland. Clean: Soil, Air, Water 41:657–664. https://doi.org/10.1002/clen.201200348
Wang Z, Liu C, Liao J et al (2014) Nitrogen removal and N2O emission in subsurface vertical flow constructed wetland treating swine wastewater: effect of shunt ratio. Ecol Eng 73:446–453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2014.09.109
Wang L, Zhang Y, Luo X et al (2016) Effects of earthworms and substrate on diversity and abundance of denitrifying genes (nirS and nirK) and denitrifying rate during rural domestic wastewater treatment. Bioresour Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.04.044
Wang T, Kumwimba M, Zhu B, Wang X (2017) Nutrient distribution and risk assessment in drainage ditches with different surrounding land uses. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-017-9840-3
Wang J, Chen G, Zou G et al (2019a) Comparative on plant stoichiometry response to agricultural non-point source pollution in different types of ecological ditches. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:647–658. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3567-9
Wang T, Zhu B, Zhou M (2019b) Ecological ditch system for nutrient removal of rural domestic sewage in the hilly area of the central Sichuan Basin, China. J Hydrol 570:839–849. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.01.034
Williams PH, Jarvis SC, Dixon E (1998) Emission of nitric oxide and nitrous oxide from soil under field and laboratory conditions. Soil Biol Biochem 30:1885–1893
Wrage N, Velthof GL, Van BML, Oenema O (2001) Role of nitrifier denitrification in the production of nitrous oxide. Soil Biol Biochem 33:1723–1732
Wu J, Zhang J, Jia W et al (2009) Relationships of nitrous oxide fluxes with water quality parameters in free water surface constructed wetlands. Front Environ Sci Eng China 3:241–247. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-009-0023-6
Wu M, Tang X, Li Q et al (2013) Review of ecological engineering solutions for rural non-point source water pollution control in Hubei Province, China. Water Air Soil Pollut. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-013-1561-x
Wu H, Xu K, He X, Wang X (2016) Removal of nitrogen by three plant species in hydroponic culture: plant uptake and microbial degradation. Water Air Soil Pollut. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-3036-3
Wu K, Chen D, Tu C et al (2017) CO2-induced alterations in plant nitrate utilization and root exudation stimulate N2O emissions. Soil Biol Biochem 106:9–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SOILBIO.2016.11.018
Xia Y, Thomas K, Zhang Q, Gao Y (2012) Nitrogen and phosphorus removal of locally adapted plant species used in constructed wetlands in China. Water Sci Technol 66:695–703. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2012.200
Zhang S, Liu F, Luo P et al (2019) Nitrous oxide emissions from pilot scale three-stage constructed wetlands with variable nitrogen loading. Biores Technol 289:121687. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121687
Zhang BW, Zhou MH, Zhu B (2021) Simultaneous quantification of greenhouse gas and nitric oxide emissions from subtropical conventional vegetable systems: a 2-site field case study in Sichuan Basin. J Mt Sci 18:671–682. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-020-6088-1
Zhang B, Zhou M, Zhu B et al (2021) Soil type affects not only magnitude but also thermal sensitivity of N2O emissions in subtropical mountain area. Sci Total Environ 797:149127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.149127
Zhou M, Zhu B, Butterbach-Bahl K et al (2014) Nitrous oxide emissions during the non-rice growing seasons of two subtropical rice-based rotation systems in southwest China. Plant Soil 383:401–414. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-014-2174-x
Acknowledgements
This paper was presented at the ISCRAES 2022 conference in Dublin on 28–31 August 2022, which was sponsored by the OECD Co-operative Research Programme: Sustainable Agricultural and Food Systems, whose financial support enabled my travel to the Conference. This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (42171067) and the Key Program of China National Tobacco Corporation Sichuan (SCYC202213).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xianglong Liu: Conceptualization, Writing - Original draft, Writing - Review & Editing, Data Curation, Investigation, Statistical analyses. Xiaoguo Wang: Conceptualization, Writing - Review & Editing, Funding acquisition, Project administration. Qiuhong Li: Performed field & lab work. Yingjie Zhang, Jialin Bai, Zongjin Zhang, Fangfang Yan: Writing - Review & Editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This special issue, titled ‘Towards Net Zero Emissions Without Compromising Agricultural Sustainability: What Is Achievable?’, is guest-edited by M.I. Khalil, B. Osborne, and A. Wingler. It originates from the ISCRAES 2022 (www.iscraes.org) Panel Discussion, which was sponsored by the OECD Co-operative Research Programme: Sustainable Agricultural and Food Systems.
The OECD disclaimer is: The opinions expressed and arguments employed in this publication are the sole responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily reflect those of the OECD or of the governments of its Member countries.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Wang, X., Li, Q. et al. Dynamics of nutrient removal and N2O emissions in an ecological ditch with different plant combinations. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-024-10342-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-024-10342-z