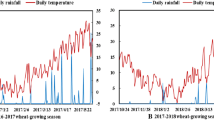
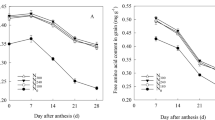
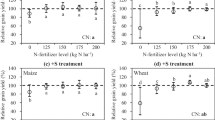
Abstract
Both the existing soil fertility and fertilizer application have important influences on crop yield and nitrogen (N) use efficiency, but knowledge about their interaction is still lacking. The interaction of N application and integrated soil fertility index on grain yield and N fertilizer use efficiency such as N recovery efficiency, soil N dependency rate, and N contribution rate of wheat was studied through 2-year in situ tests in Changshu County of the Taihu Lake region, China. The results indicated that there are desirable quantitative relationships among the assessment indices, N application level and integrated soil fertility index. The regression coefficients showed that the ratio of the relative contribution of soil fertility and N application level to wheat yield was 0.48:1, and their contribution ratios to fertilizer N utilization efficiencies were 1.10:1, 1.45:1 and 1.93:1, respectively. The effects of both soil fertility and N application level on yield and N recovery efficiency indicated that it is difficult to simultaneously improve yield and N recovery efficiency of wheat by improving soil fertility when attempting to maximize yield. Only by enhancing soil fertility, reducing the N application level and decreasing the maximum yield, can high levels of N recovery efficiency be achieved. For this study, a ratio of N application level decrement to integrated soil fertility increment greater than 0.89 was necessary to increase the N recovery efficiency to 55%. Under this optimal condition, the reduction in N application level was 16%, and the mean yield loss of wheat was only 8%.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GY:
-
Grain yield
- IFI:
-
Integrated soil fertility index
- NA:
-
N application level
- NR:
-
Ratio of N application level to the maximum application level in this study
- NCR:
-
N contribution rate
- NRE:
-
N recovery efficiency
- SNDR:
-
Soil N dependency rate
- NAMY, GYMY, NCRMY, NREMY, and SNDRMY :
-
The NA, GY, NCR, NRE, SNDR under the condition of pursuing the maximum yield
- NAHR, GYHR, NCRHR, NREHR, and SNDRHR :
-
The NA, GY, NCR, NRE, SNDR under the condition of pursuing the highest NRE
References
Brentrup F, Palliere C (2010) Nitrogen use efficiency as an agro-environmental indicator. OECD workshop on agri-environmental indicators, pp 1–9
Chen J, Huang Y, Tang YH (2011) Quantifying economically and ecologically optimum nitrogen rates for rice production in south-eastern China. Agric Ecosyst Environ 142:195–204
Chen ZM, Wang HY, Liu XW, Chen XQ, Lu DJ, Jia YS, Zhou JM (2017) Spatial and temporal nitrogen applications for winter wheat in a loamy soil in south-eastern China. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 109:43–55
Cui ZL, Zhang FS, Chen XP, Miao YX, Li JL et al (2008) On-farm evaluation of an in-season nitrogen management strategy based on soil Nmin test. Field Crops Res 105:48–55
Cui ZL, Zhang HY, Chen XP, Zhang CC et al (2018) Pursuing sustainable productivity with millions of smallholder farmers. Nature 555:363–366
Demelash N, Bayu W, Tesfaye S, Ziadat F, Sommer R (2014) Current and residual effects of compost and inorganic fertilizer on wheat and soil chemical properties. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 100:357–367
Deng MH, Shi XJ, Tian YH, Yin B, Zhang SL, Zhu ZL, Kimura SD (2012) Optimizing nitrogen fertilizer application for rice production in the Taihu Lake Region, China. Pedosphere 22:48–57
Ding ZL, Peng JW, Liu Q, Rong XM, Tian C, Zhang YP (2010) Effects of different nutrient management modes on nitrogen utilization efficiency and yield of early rice in different soil levels. China Rice 16:30–33 (in Chinese)
Gourevitch JD, Keeler BL, Ricketts TH (2018) Determining socially optimal rates of nitrogen fertilizer application. Agric Ecosyst Environ 254:292–299
Hanrahan BR, King KW, Williams MR, Duncan EW, Pease LA, LaBarge GA (2019) Nutrient balances influence hydrologic losses of nitrogen and phosphorus across agricultural fields in northwestern Ohio. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 113:231–245
Hu AY, Tan TT, Liu Q (2018) Nitrogen use efficiency in different rice-based rotations in southern China. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 112:75–86
Jaynes DB (2011) Confidence bands for measured economically optimal nitrogen rates. Precis Agric 12:196–213
Lu YH, Liao YL, Zhou X, Nie J, Xie J, Yang ZP (2015) Effect of long-term fertilization on rice yield and basic soil productivity in red paddy soil under double-rice system. Acta Pedol Sin 52:597–605
Masso C, Nziguheba G, Mutegi J, Lacaux CG, Wendt J, Bahl KB, Wairegi L, Datta A (2017) Soil fertility management in sub-Saharan Africa (eds). Sustainable agriculture reviews. Springer, Berlin, pp 205–231
Potthoff M, Dyckmans J, Flessa H, Muhs A (2005) Dynamics of maize (Zea mays L.) leaf straw mineralization as affected by the presence of soil and the availability of nitrogen. Soil Biol Biochem 37:1259–1266
R Development Core Team (2017) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. The R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna. http://www.R-project.org/
Roberts TL (2008) Improving nutrient use efficiency. Turk J Agric For 32:177–182
Rutting T, Aronsson H, Delin S (2018) Efficient use of nitrogen in agriculture. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 110:1–5
Shen RF, Wang C, Sun B (2018) Soil related scientific and technological problems in implementing strategy of “storing grain in land and technology”. Bull Chin Acad Sci 33:135–144 (in Chinese)
Soils census office of Changshu County (SCOCC) (1983) Soil records of Changshu city, Jiangsu province. Soils Census Office of Changshu County, Suzhou (in Chinese)
Spyridon DK, Vasileios Sideris F, Christos AD (2014) Growth, grain yield and nitrogen use efficiency of Mediterranean wheat in soils amended with municipal sewage sludge. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 100:227–243
Srivastava RK, Panda RK, Chakraborty A, Halder D (2018) Enhancing grain yield, biomass and nitrogen use efficiency of maize by varying sowing dates and nitrogen rate under rainfed and irrigated conditions. Field Crop Res 221:339–349
Suzhou Municipal Bureau of Statistics (SMBS) (2017) Suzhou statistical yearbook-2017. Yearbook Press, Beijing (in Chinses)
Tao HH, Donough C, Gerendas J, Hoffmann MP, Cahyo A et al (2018) Fertilizer management effects on oil palm yield and nutrient use efficiency on sandy soils with limited water supply in Central Kalimanta. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 112:317–333
Vanlauwe B, Van-Asten P, Blomme G (2014) Challenges and opportunities for agricultural intensification of the humid highland systems of sub Saharan Africa (eds). Challenges and opportunities for agricultural intensification of the humid highland systems of sub-Saharan Africa. Springer, Berlin, pp 69–80
Wang GB, Cao FL (2011) Integrated evaluation of soil fertility in Ginkgo (Ginkgo biloba L.) agroforestry systems in Jiangsu, China. Agrofor Syst 83:89–100
Wang WN, Lu JW, Ren T, Li XK, Su W, Lu MX (2012) Evaluating regional mean optimal nitrogen rates in combination with indigenous nitrogen supply for rice production. Field Crop Res 137:37–48
Wang LF, Sun JT, Zhang ZB, Xu P, Shangguan ZP (2018) Winter wheat grain yield in response to different production practices and soil fertility in northern China. Soil Till Res 176:10–17
Xu ZC, Yu DS, Pan Y, Wang XY, Huang JJ, Sun B (2018) Temporal characteristics of soil fertility of cropland requisition-compensation in the typical region of Yangtze River Delta, China. Chin J Appl Ecol 29:617–625
Yan X, Ti C, Vitousek P, Chen DL, Leip A, Cai ZC, Zhu ZL (2014) Fertilizer nitrogen recovery efficiencies in crop production systems of China with and without consideration of the residual effect of nitrogen. Environ Res Lett 9:1–9
Yang XY, Sun BH, Zhang SL (2014) Trends of yield and soil fertility in a long-term wheat-maize system. J Integr Agric 13:402–414
Zhang GL, Gong ZT (2012) Soil survey laboratory methods. Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Zhang FS, Cui ZL, Chen XP, Ju XT et al (2012) Integrated nutrient management for food security and environmental quality in China. Adv Agron 116:1–40
Zhang FS, Chen XP, Vitousek P (2013) Chinese agriculture: an experiment for the world. Nature 497:33–35
Zhang X, Bol R, Rahn C, Xiao GM, Meng FQ, Wu WL (2017) Agricultural sustainable intensification improved nitrogen use efficiency and maintained high crop yield during 1980–2014 in Northern China. Sci Total Environ 596–597:61–68
Zhu ZL, Zhang FS (2010) Basic research on nitrogen behavior and efficient utilization of nitrogen fertilizer in main farmland ecosystem. Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Acknowledgements
This paper was supported by the Special project of the national key research and development program (No. 2016YFD0200301), the Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41571206), the Special project of the national science and technology basic work (No. 2015FY110700-S2), and the Key project of science and technology service (STS) network of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. 2018STS-01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, X., Yu, D., Chen, Y. et al. Yield and nitrogen use efficiency of winter wheat with different soil fertility. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 116, 165–177 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-019-10033-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-019-10033-0