Abstract
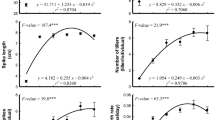
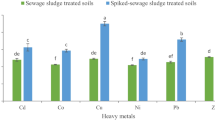
The application of sewage sludge (SS) to agricultural land can improve soil fertility and physical properties, and enhance crop production. This field study was conducted for two consecutive growing seasons to investigate the influence of SS application on winter wheat growth, grain yield, N accumulation, translocation and use, and on trace elements concentrations in soil and wheat plants under Mediterranean conditions. Treatments consisted of three rates of SS, i.e. 20, 40, and 60 Mg dry weight ha−1 year−1, one rate of inorganic fertilizer (IF, 120 kg N ha−1 year−1 plus 80 kg P2O5 ha−1 year−1), and an unamended control. The application of SS resulted in tall plants with high early dry matter and N accumulation similar to or significantly higher than those obtained with IF. The lowest SS application rate resulted in grain yield similar to that obtained with IF. Nitrogen use efficiency (NUE) in SS treatments was mainly determined by uptake efficiency, which decreased with increasing SS application rate. Values of NUE and biomass production efficiency with the lowest SS rate were similar to those obtained with IF. SS application resulted in increased concentrations of total and DTPA-extractable trace elements in the soil after the first year, but concentrations were much lower than the regulation limits. Concentrations of Cu, Mn and Zn in wheat plants did not exceed those obtained with IF. Overall, SS could be considered for use as a fertilizer in wheat production systems in the area, serving also as an alternative method of SS disposal.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Mustafa WA, El-Shall AA, Abdallah AE, Modaihsh AS (1995) Response of wheat to sewage sludge applied under two different moisture regimes. Exp Agric 31:355–359
Antolin MC, Pascual I, Garcia C, Polo A, Sanchez-Diaz M (2005) Growth, yield and solute content of barley in soils treated with sewage sludge under semiarid Mediterranean conditions. Field Crops Res 94:224–237
Antoniadis V (2013) Mineralization of organic amendment-derived nitrogen in two Mediterranean soils with different organic matter content. Commun Soil Sci Plan 44:2788–2795
Antoniadis V, Tsadilas CD, Samaras V (2010) Trace element availability in a sewage sludge-amended cotton grown Mediterranean soil. Chemosphere 80:1308–1313
Antoniadis V, Koutroubas SD, Fotiadis S (2014) Nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium availability in manure- and sewage sludge-applied soil (in press)
Arduini I, Masoni A, Ercoli L, Mariotti M (2006) Grain yield, and dry matter and nitrogen accumulation and remobilization in durum wheat as affected by variety and seeding rate. Eur J Agron 25:309–318
Austin RB, Edrich JA, Ford MA, Blackwell RD (1977) The fate of the dry matter, carbohydrates and 14C lost from the leaves and stems of wheat during grain filling. Ann Bot 41:1309–1321
Barbarika A, Sikora LJ, Colacicco D (1985) Factors affecting the mineralization of nitrogen in sewage sludge applied to soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 49:1403–1406
Binder DL, Dobermann A, Sander DH, Cassman KG (2002) Biosolids as nitrogen source for irrigated maize and rainfed sorghum. Soil Sci Soc Am J 66:531–542
Bladenopoulos KB, Koutroubas SD (2003) Influence of autumn nitrogen fertilisation and climate on winter barley in Greece. Agric Mediter 133:202–210
Blum A, Golan G, Mayer J, Sinmena B (1997) The effect of dwarfing genes on sorghum grain filling from remobilized stem reserves, under stress. Field Crops Res 52:43–54
Bremner JM (1965) Total nitrogen. In: Black CA, Evans DD, Ensuinger LE, White JK, Clark FF (eds) Methods of soil analysis, part 2, agronomy 9. American Society of Agronomy, Madison, pp 1149–1178
Cogger CG, Sullivan DM, Bary AI, Kropf JA (1998) Matching plant available nitrogen from biosolids with dryland wheat needs. J Prod Agric 11:41–47
Council Directive 86/278/EEC (1986) On the protection of the environment, and in particular of the soil, when sewage sludge is used in agriculture. Off J Eur Union L181, 4 July 1986, p 6
Cox MC, Qualset CO, Rains DW (1985) Genetic variation for nitrogen assimilation and translocation in wheat. II. Nitrogen assimilation in relation to grain yield and protein. Crop Sci 25:435–440
De Giorgio D, Montemurro F (2006) Nutritional status and nitrogen utilization efficiency of durum wheat in a semiarid Mediterranean environment. Agric Mediter 160:91–101
De Vita P, Di Paolo E, Fecondo G, Di Fonzo N, Pisante M (2007) No-tillage and conventional tillage effects on durum wheat yield, grain quality and soil moisture content in southern Italy. Soil Till Res 92:69–78
Fageria NK, Baligar VC (2005) Enhancing nitrogen use efficiency in crop plants. Adv Agron 88:97–185
Fernández JM, Plaza C, García-Gil JC, Polo A (2009) Biochemical properties and barley yield in a semiarid Mediterranean soil amended with two kinds of sewage sludge. Appl Soil Ecol 42:18–24
García C, Hernández T, Pascual JA, Moreno JL, Ros M (2000) Microbial activity in soils of SE Spain exposed to degradation and desertification processes: strategies for their rehabilitation. In: García C, Hernández T (eds) Research and perspectives of soil enzymology in Spain. CEBAS, CSIC, Murcia, pp 93–143
Ghaedi M, Shokrollahi A, Kianfar AH, Mirsadeghi AS, Pourfarokhi A, Soylak M (2008) The determination of some heavy metals in food samples by flame atomic absorption spectrometry after their separation-preconcentration on bis salicyl aldehyde, 1,3 propan diimine (BSPDI) loaded on activated carbon. J Hazard Mater 154:128–134
Harper LA, Sharpe RR, Langdale GW, Giddens JE (1987) Nitrogen cycling in a wheat crop: soil, plant and aerial nitrogen transport. Agron J 79:965–973
Huggins DR, Pan WL (1993) Nitrogen efficiency component analysis: an evaluation of cropping system differences in productivity. Agron J 85:898–905
Kamprath EJ, Moll RH, Rodriquez N (1982) Effects of N fertilization and recurrent selection on performance of hybrid populations of corn. Agron J 74:955–958
Kato Y, Kamoshita A, Yamagishi J, Abe J (2006) Growth of rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars under upland conditions with different levels of water supply. 1. Nitrogen content and dry matter production. Plant Prod Sci 9:422–434
Katsantonis D, Koutroubas SD, Ntanos DA, Lupotto E (2008) Effect of blast disease on nitrogen accumulation and remobilization to rice grain. J Plant Pathol 90:263–272
Keller M, Karutz Ch, Schmid JE, Stamp P, Winzeler M, Keller B, Messmer MM (1999) Quantitative trait loci for lodging resistance in a segregating wheat spelt population. Theor Appl Genet 98:1171–1182
King RW, Evans LT (1967) Photosynthesis in artificial communities of wheat, lucerne, and subterranean clover plants. Aust J Biol Sci 20:623–635
Koutroubas SD, Papakosta DK, Gagianas AA (1998) The importance of early dry matter and nitrogen accumulation in soybean yield. Eur J Agron 9:1–10
Koutroubas SD, Papageorgiou M, Fotiadis S (2009) Growth and nitrogen dynamics of spring chickpea genotypes in a Mediterranean-type climate. J Agric Sci 147:445–458
Koutroubas SD, Fotiadis S, Damalas CA (2012) Biomass and nitrogen accumulation and translocation in spelt (Triticum spelta) grown in a Mediterranean area. Field Crop Res 127:1–8
Ladha JK, Kirk GJD, Bennett J, Peng S, Reddy CK, Reddy PM, Singh U (1998) Opportunities for increased nitrogen-use efficiency from improved lowland rice germplasm. Field Crops Res 56:41–71
Le Gouis J, Delebarre O, Beghin D, Heumez E, Pluchard P (1999) Nitrogen uptake and utilization efficiency of two-row and six-row winter barley genotypes grown at two N levels. Eur J Agron 10:73–79
Mantovi P, Baldoni G, Toderi G (2005) Reuse of liquid, dewatered, and composted sewage sludge on agricultural lands: effects of long-term application on soil and crop. Water Resour 39:289–296
Marinari S, Masciandaro G, Ceccanti B, Grego S (2000) Influence of organic and mineral fertilisers on soil biological and physical properties. Bioresour Technol 72:9–17
Metzger L, Yaron B (1987) Influence of sludge organic matter on soil physical properties. Adv Soil Sci 7:141–163
Moll RH, Kamprath EJ, Jackson WA (1982) Analysis and interpretation of factors which contribute to efficiency of nitrogen utilization. Agron J 74:562–564
Motta SR, Maggiore T (2013) Evaluation of nitrogen management in maize cultivation grows on soil amended with sewage sludge and urea. Eur J Agron 45:59–67
Muurinen S, Kleemola J, Peltonen-Sainio P (2007) Accumulation and translocation of nitrogen in spring cereal cultivars differing in nitrogen use efficiency. Agron J 99:441–449
Ntanos DA, Koutroubas SD (2002) Dry matter and N accumulation and translocation for Indica and Japonica rice under Mediterranean conditions. Field Crop Res 74:93–101
Ortiz-Monasterio JI, Sayre KD, Rajaram S, McMahon M (1997) Genetic progress in wheat yield and nitrogen use efficiency under four nitrogen rates. Crop Sci 37:898–904
Pagliai M, Guidi G, La Marca M, Giachetti M, Lucamante G (1981) Effects of sewage sludges and composts on soil porosity and aggregation. J Environ Qual 10:556–561
Papakosta DK, Gagianas AA (1991) Nitrogen and dry matter accumulation, remobilization, and losses for Mediterranean wheat during grain filling. Agron J 83:864–870
Parton WJ, Morgan JA, Altenhofen JM, Harper LA (1988) Ammonia volatilization from spring wheat plants. Agron J 80:419–425
Peeters KMU, Van Laere AJ (1992) Ammonium and amino acid metabolism in excised leaves of wheat (Triticum aestivum) senescing in the dark. Physiol Plant 84:243–249
Pescod MB (1992) Wastewater treatment and use in agriculture. P. 117. FAO irrigation and drainage Publication N 47, Rome, Italy
Przulj N, Momcilovic V (2001) Genetic variation for dry matter and nitrogen accumulation and translocation in two-rowed spring barley. I. Dry matter translocation. Eur J Agron 15:241–254
Rowell DL (1994) Soil science: methods and applications. Longman Scientific & Technical, Longman Group UK Ltd, Harlow
Sabey BR, Hart WE (1975) Land application of sewage sludge: I. Effect on growth and chemical composition of plants. J Environ Qual 4:252–256
Samaras V, Tsadilas CD, Stamatiadis S (2008) Effects of repeated application of municipal sewage sludge on soil fertility, cotton yield, and nitrate leaching. Agron J 100:477–483
Sort X, Alcañiz JM (1999) Modification of soil porosity after application of sewage sludge. Soil Till Res 49:337–345
Spiertz JHJ, de Vos NM (1983) Agronomical and physiological aspects of the role of nitrogen in yield formation of cereals. Plant Soil 75:379–391
Steel RGD, Torrie JH (1980) Principles and procedures of statistics: a biometrical approach, 2nd edn. McGraw-Hill, New York
Sukreeyapongse O, Panichsakpatana S, Hansen H (2002) Transfer of heavy metals from sludge amended soil to vegetables and leachates. Paper presented at the 17th world congress of soil science (WCSS), 14th–21st August 2002, Thailand, symposium no. 29, paper no. 1969
Tahir ISA, Nakata N (2005) Remobilization of nitrogen and carbohydrate from stems of bread wheat in response to heat stress during grain filling. J Agron Crop Sci 191:106–115
Tejada M, González JL (2007a) Application of different organic wastes on soil properties and wheat yield. Agron J 99:1597–1606
Tejada M, González JL (2007b) Influence of organic amendments on soil structure and soil loss under simulated rain. Soil Till Res 93:197–205
Tester CF (1990) Organic amendment effects on physical and chemical properties of a sandy soil. Soil Sci Soc Am J 54:827–831
Tester CF, Sikora LJ, Taylor JM, Parr JF (1982) Nitrogen utilization by tall fescue from sewage sludge compost amended soils. Agron J 74:1013–1018
Usman K, Khan S, Ghulam S, Khan MU, Khan N, Khan MA, Khalil SK (2012) Sewage sludge: an important biological resource for sustainable agriculture and its environmental implications. Am J Plant Sci 3:1708–1721
Van Sanford DA, MacKown CT (1987) Cultivar differences in nitrogen remobilization during grain fill in soft red winter wheat. Crop Sci 27:295–300
Zadoks JC, Chang TT, Konzak CF (1974) A decimal code for the growth stage of cereals. Weed Res 14:415–421
Zilberstein M, Blum A, Eyal Z (1985) Chemical desiccation of wheat plants as a simulator of postanthesis speckled leaf blotch stress. Phytopathology 75:226–230
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by the Prefecture of Evros. The authors thank the Municipal Wastewater Treatment of the town of Orestiada for providing sewage sludge.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koutroubas, S.D., Antoniadis, V., Fotiadis, S. et al. Growth, grain yield and nitrogen use efficiency of Mediterranean wheat in soils amended with municipal sewage sludge. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 100, 227–243 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-014-9641-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-014-9641-x