Abstract
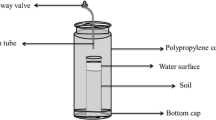
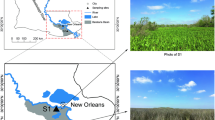
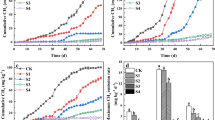
Soil salinization adversely affects sustainable land use and limitation of greenhouse gas emission. Methane (CH4) uptake and the specific activity of methanotrophs in three saline–alkaline soils—S1, electrical conductivity (EC) 4.80 dS m−1; S2, EC 2.60 dS m−1; and S3, EC 0.74 dS m−1—were observed and measured across crop phenological development in the Hetao Irrigation District of Inner Mongolia, China. There were significant differences in CH4 uptake between the three soil types. The cumulative uptake of CH4 was 97.97 mg m−2, 109.49 mg m−2, and 150.0 mg m−2 in S1, S2, and S3, respectively. Cumulative CH4 uptake was 35%, 35%, and 53% lower in S1 than in S3, and was 27%, 28%, and 19% lower in S2 than in S3 in 2014, 2015, and 2016, respectively. Differences in CH4 uptake were driven by the different specific activities of the methanotrophs in the three soils, of which the key controlling factor was soil EC. The findings demonstrate that saline–alkaline soils with high EC led to low CH4 uptake and thereby significantly increased the total greenhouse effect of CH4.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aulakh MS, Khera TS, Doran JW (2000) Mineralization and denitrification in upland, nearly saturated and flooded subtropical soil I. Effect of nitrate and ammoniacal nitrogen. Biol Fertil Soils 31:162–167
Bartlett KB, Bartlett DS, Harriss RC, Sebacher DI (1987) Methane emissions along a salt marsh salinity gradient. Biogeochemistry 4:183–202
Bocanegra-Garcia G, Carrillo-Chavez A (2003) Hydro-geochemical behavior of bicarbonate and sulfate ions leaching from a sulfide-poor silver mine in Central Mexico: potential indicator of acid mine drainage. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 71:1222–1229
Cai YF, Zheng Y, Bodelier PLE, Conrad R, Jia ZJ (2016) Conventional methanotrophs are responsible for atmospheric methane oxidation in paddy soils. Nat Commun 7:11728
Conde E, Cardenas M, Ponce-Mendoza A, Luna-Guido ML, Cruz-Mondragon C, Dendooven L (2005) The impacts of inorganic nitrogen application on mineralization of 14C-labelled maize and glucose, and on priming effect in saline–alkaline soil. Soil Biol Biochem 37:681–691
Dalal RC, Allen DE, Livesley SJ, Richards G (2008) Magnitude and biophysical regulators of methane emission and consumption in the Australian agricultural, forest, and submerged landscapes: a review. Plant Soil 309:43–76
Dedysh SN (2011) Cultivating uncultured bacteria from northern wetlands: knowledge gained and remaining gaps. Front Microbiol 2(184):1–15
Dedysh SN, Knief C, Dunfield PF (2005) Methylocella species are facultatively methanotrophic. J Bacteriol 187:4665–4670
Deng YC, Liu YQ, Dumont M, Conrad R (2017) Salinity affects the composition of the aerobic methanotroph community in alkaline lake sediments from the Tibetan Plateau. Microb Ecol 73:101–110
Dumont MG, Murrell JC (2005) Community-level analysis: key genes of aerobic methane oxidation. Methods Enzymol 397:413–427
Easley RA, Patsavas MC, Byrne RH, Liu X, Feely RA (2013) Spectrophotometric measurement of calcium carbonate saturation states in seawater. Environ Sci Technol 47(3):1468–1477
Fierer N, Jackson RB (2006) The diversity and biogeography of soil bacterial communities. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:626–631
Geng YB, Luo GQ, Yuan GF (2010) CH4 uptake flux of Leymus chinensis steppe during rapid growth season in Inner Mongolia, China. Sci China Earth Sci 53(7):977–983
Ghassemi F, Jakeman AJ, Nix HA (1995) Salinisation of land and water resources: human causes, extent, management and case studies. University of New South Wales Press Ltd, Canberra
Godsey CB, Pierzynski GM, Mengel DB, Lamond RE (2007) Changes in soil pH, organic carbon, and extractable aluminum from crop rotation and tillage. Soil Sci Soc Am J 71:1038–1044
Hakemian AS, Rosenzweig AC (2007) The biochemistry of methane oxidation. Annu Rev Biochem 76:223–241
Hart SC (2006) Potential impacts of climate change on nitrogen transformations and greenhouse gas fluxes in forests: a soil transfer study. Glob Change Biol 12:1032–1046
He YB, DeSutter T, Prunty L, Hopkins D, Jia XH, Wysocki DA (2012) Evaluation of 1:5 soil to water extract electrical conductivity methods. Geoderma 185–186:12–17
Henckel T, Roslev P, Conrad R (2000) Effects of O2 and CH4 on presence and activity of the indigenous methanotrophic community in rice field soil. Environ Microbiol 2(6):666–679
Ho A, Lüke C, Frenzel P (2011) Recovery of methanotrophs from disturbance: population dynamics, evenness and functioning. ISME J 5(4):750–758
Ho A, Mo YL, Lee HJ, Sauheitl L, Jia ZJ, Horn MA (2018) Effect of salt stress on aerobic methane oxidation and associated methanotrophs; a microcosm study of a natural community from a non-saline environment. Soil Biol Biochem 125:210–214
Holmes AJ, Costello AM, Lidstrom ME, Murrell JC (1995) Evidence that particulate methane monooxygenase and ammonia monooxygenase may be evolutionarily related. FEMS Microbiol Lett 132(3):203–208
King GM, Schnell S (1998) Effects of ammonium and non-ammonium salt additions on methane oxidation by Methylosinus trichosporium OB3b and Maine forest soils. Appl Environ Microb 64:253–257
Knief C, Dunfield PF (2005) Response and adaptation of different methanotrophic bacteria to low methane mixing ratios. Environ Microbiol 7:1307–1317
Kolb S, Knief C, Dunfield PF, Conrad R (2005) Abundance and activity of uncultured methanotrophic bacteria involved in the consumption of atmospheric methane in two forest soils. Environ Microbiol 7:1150–1161
Lim SS, Choi WJ (2014) Changes in microbial biomass, CH4 and CO2 emissions, and soil carbon content by fly ash co-applied with organic inputs with contrasting substrate quality under changing water regimes. Soil Biol Biochem 68:494–502
Lozupone CA, Knight R (2007) Global patterns in bacterial diversity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:11436–11440
Menyailo OV, Hungate BA, Abraham WR, Conrad R (2008) Changing land use reduces soil CH4 uptake by altering biomass and activity but not composition of high-affinity methanotrophs. Glob Change Biol 14:2405–2419
Mosier AR, Parton WJ, Valentine DW, Ojima DS, Schimel DS, Heinemeyer O (1997) CH4 and N2O fluxes in Colorado shortgrass steppe. 2. Long-term impact of land use change. Glob Biogeochem Cycles 11:29–42
Myhre G, Shindell D, Bréon FM (2013) Anthropogenic and natural radiative forcing. In: Stocker TF, Qin D, Plattner GK et al (eds) Climate change 2013: the physical science basis. Contribution of working group I to the fifth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 659–740
Pisinaras V, Tsihrintzis VA, Petalas C, Ouzounis K (2010) Soil salinization in the agricultural lands of Rhodope District, northeastern Greece. Environ Monit Assess 166:79–94
Qin R, Wang XF, Liu ST (2005) Advances in saline alkali soil improvement. Contemp Eco-Agric 1:32–34 (in Chinese)
Reim A, Lüke C, Krause S, Pratscher J, Frenzel P (2012) One millimetre makes the difference: high-resolution analysis of methane-oxidizing bacteria and their specific activity at the oxic–anoxic interface in a flooded paddy soil. ISME J 6:2128–2139
Saari A, Smolander A, Martikainen PJ (2004) Mathane consumption in a frequently nitrogen-fertilized and limed spruce forest soil after clear-cutting. Soil Use Manag 20:65–73
Schlichting E, Blume HP, Stahr K (1995) Bodenkundliches Praktikum. Blackwell, Berlin
Semrau JD, DiSpirito AA, Yoon S (2010) Methanotrophs and copper. FEMS Microbiol Rev 34:496–531
Serrano-Silva N, Valenzuela-Encinas C, Marsch R, Dendooven L, Alcántara-Hernández RJ (2014) Changes in methane oxidation activity and methanotrophic community composition in saline alkaline soils. Extremophiles 18:561–571
Shao R, Xu M, Li RQ, Dai XQ, Liu LX, Yuan Y, Wang HM, Yang FT (2017) Land use legacies and nitrogen fertilization affect methane emissions in the early years of rice field development. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 107:369–380
Sitaula BK, Bakken LRR, Abrahamsen G (1995) CH4 uptake by temperate forest soil effect of N input and soil acidification. Soil Biol Biochem 27:871–880
Sjogersten S, Wookey PA (2002) Spatio-temporal variability and environmental controls of methane fluxes at the forest-tundra ecotone in the fennoscandian mountains. Glob Change Biol 8:885–894
Sorokin DY, Jones BE, Kuenen JG (2000) An obligate methylotrophic, methane-oxidizing methylomicrobiura species from a highly alkaline environment. Extremophiles 4:145–155
Trotsenko YA, Murrell JC (2008) Metabolic aspects of aerobic obligate methanotrophy. Adv Appl Microbiol 63:183–229
Tsubota J, Eshinimaey BT, Khmelenina VN, Trotsenko YA (2005) Methylothermus thermalis gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel moderately thermophilic obligate methanotroph from a hot spring in Japan. Int J Syst Evolut Microbiol 55:1877–1884
Unteregelsbacher S, Gasche R, Lipp L, Sun W, Kreyling O, Geitlinger H, Kögel-Knabner I, Papen H, Kiese R, Schmid HP, Dannenmann M (2013) Increased methane uptake but unchanged nitrous oxide flux in montane grasslands under simulated climate change conditions. Eur J Soil Sci 64:586–596
Van Zandvoort A, Lapen DR, Clark LD, Flemming C, Craiovan E, Sunohara MD, Boutz R, Gottschall N (2017) Soil CO2, CH4, and N2O fluxes over and between tile drains on corn, soybean, and forage fields under tile drainage management. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 109:115–132
Vorobev AV, Baani M, Doronina NV, Brady AL, Liesack W, Dunfield PF, Dedysh SN (2011) Methyloferula stellata gen. nov., sp. nov., an acidophilic, obligately methanotrophic bacterium that possesses only a soluble methane monooxygenase. Int J Syst Evolut Microbiol 61:2456–2463
Wang ZQ, Zhu SQ, Yu RP (1993) Chinese salty soil. Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Wang YF, Chen H, Zhu QA, Peng CH, Wu N, Yang G, Zhu D, Tian JQ, Tian LX, Kang XM, He YX, Gao YH, Zhao XQ (2014) Soil methane uptake by grasslands and forests in China. Soil Biol Biochem 74:70–81
Whalen SC (2000) Influence of N and non-N salts on atmospheric methane oxidation by upland boreal forest and tundra soils. Biol Fertil Soils 31:279–287
Yan Y, Tian J, Fan MS, Zhang FS, Li XL, Christie P, Chen HQ, Lee JW, Kuzyakov Y, Six J (2012) Soil organic carbon and total nitrogen in intensively managed arable soils. Agric Ecosyst Environ 150:110–120
Yang QB, Fan FL, Wang WX, Liang YC, Li ZJ, Cui XA, Wei D (2010) Effects of different long-term fertilizations on community properties and functions of methanotrophs in dark brown soil. Environ Sci 31:2756–2762 (in Chinese)
Yang MD, Jiao Y, Li X, Wen HY (2015) Specific activity of methanotrophs in saline–alkaline soils retrieved from a fluorescent quantitative real-time PCR technique. Ecol Environ Sci 24:797–803 (in Chinese)
Zhang JF, Li ZJ, Ning TY, Gu SB (2011) Methane uptake in salt-affected soils shows low sensitivity to salt addition. Soil Biol Biochem 43:1434–1439
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 41675140, 41565009, 41765010) and the Inner Mongolia Youth Innovative Talent Training Program of Prairie Excellence Project 2016.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, W., Jiao, Y., Yang, M. et al. Methane uptake by saline–alkaline soils with varying electrical conductivity in the Hetao Irrigation District of Inner Mongolia, China. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 112, 265–276 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-018-9943-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-018-9943-5