Abstract
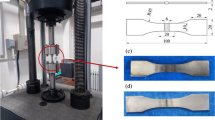
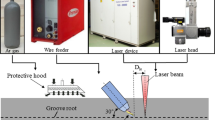
To improve the fatigue performance of laser-welded TC4 titanium alloy joints, ultrasonic rolling processing (USRP) is employed herein. Multiple passes of USRP (viz., one, three, and five) are conducted using an ultrasonic rolling device. Results reveal that USRP considerably improves the fatigue limit and life of the welded joints. At room temperature, the fatigue strength of the weldment increases by 2.04–4.58% and the corrosion fatigue life increases by 1.72–2.88 times. In addition, to reveal its strengthening mechanism, the effects of USRP on the surface morphology, microstructure, surface residual stress, and microhardness of the laser-welded TC4 titanium alloy joints are investigated. USRP leads to a shift in the crack initiation point to the subsurface and formation of a hardened layer with high residual stress on the surface via the application of considerable static pressure input and multiple passes. Consequently, fatigue striations become narrower and denser. Compared to the traditional weld surface treatment, USRP substantially improves the surface quality and fatigue performance of laser-welded TC4 titanium alloy joints.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akman E, Demir A, Canel T, Sınmazçelik T (2009) Laser welding of Ti6Al4V titanium alloys. J Mater Process Technol 209:3705–3713. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2008.08.026
Ao N, Liu D, Xu X, Zhang X, Liu D (2019) Gradient nanostructure evolution and phase transformation of α phase in Ti-6Al-4V alloy induced by ultrasonic surface rolling process. Mater Sci Eng: A 742:820–834. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2018.10.098
Ao N, Liu D, Zhang X, Wu S (2023) Improved fretting fatigue mechanism of surface-strengthened Ti-6Al-4V alloy induced by ultrasonic surface rolling process. Int J Fatigue 170:107567. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2023.107567
Chattopadhyay A, Muvvala G, Sarkar S, Racherla V, Nath AK (2021) Effect of laser shock peening on microstructural, mechanical and corrosion properties of laser beam welded commercially pure titanium. Opt Laser Technol 133:106527. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2020.106527
Chen J, Li H, Liu Y et al (2023) Deformation behavior and microstructure characteristics of the laser-welded Ti-6Al-4V joint under variable amplitude fatigue. Mater Charact 196:112606. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2022.112606
Cheng H, Zhou L, Li Q, Du D, Chang B (2021) Effect of welding parameters on spatter formation in full-penetration laser welding of titanium alloys. J Mater Res Technol 15:5516–5525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.11.006
Feng X, Pan X, He W, Liu P, An Z, Zhou L (2021) Improving high cycle fatigue performance of gas tungsten arc welded Ti6Al4V titanium alloy by warm laser shock peening. Int J Fatigue 149:106270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2021.106270
Gedney BL, Rizos DC (2022) Combining welding-induced residual stress with thermal and mechanical stress in continuous welded rail. Results Eng 16:100777. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rineng.2022.100777
Hobbacher AF (2010) New developments at the recent update of the IIW recommendations for fatigue of welded joints and components. Steel Constr 3:231–242. https://doi.org/10.1002/stco.201010030
Junaid M, Baig MN, Shamir M, Khan FN, Rehman K, Haider J (2017) A comparative study of pulsed laser and pulsed TIG welding of Ti-5Al-25Sn titanium alloy sheet. J Mater Process Technol 242:24–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2016.11.018
Li ZM, Zhu YL, Du XK (2013) The anti-fatigue mechanisms on alterations of structures and performances of alloy welded joints with ultrasonic impact treatment. Phys Procedia 50:410–415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phpro.2013.11.063
Li L, Gu X, Sun S, Wang W, Wan Z, Qian P (2018) Effects of welding residual stresses on the vibration fatigue life of a ship’s shock absorption support. Ocean Eng 170:237–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oceaneng.2018.10.011
Liu M, Li JY, Ma Y, Yuan TY, Mei QS (2016) Surface nanocrystallization and property of Ti6Al4V alloy induced by high pressure surface rolling. Surf Coat Technol 289:94–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2016.01.043
Liu C, Liu D, Zhang X et al (2019) On the influence of ultrasonic surface rolling process on surface integrity and fatigue performance of Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Surf Coat Technol 370:24–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2019.04.080
Logesh M, Selvabharathi R, Thangeeswari T, Palani S (2020) Influence of severe double shot peening on microstructure properties of Ti 6Al-4V and Titanium Grade 2 dissimilar joints using laser beam welding. Opt Laser Technol 123:105883. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2019.105883
Luo X, Dang N, Wang X (2021) The effect of laser shock peening, shot peening and their combination on the microstructure and fatigue properties of Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy. Int J Fatigue 153:106465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2021.106465
Luo X, Ren X, Qu H, Hou H, Chen J, Tian P (2022) Research on influence of deep cryogenic treatment and ultrasonic rolling on improving surface integrity of Ti6Al4V alloy. Mater Sci Eng: A 843:143142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2022.143142
Pang Z, Wang S, Yin X, Yu S, Du N (2022) Effect of spindle speed during ultrasonic rolling on surface integrity and fatigue performance of Ti6Al4V alloy. Int J Fatigue 159:106794. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2022.106794
Paranthaman V, Dhinakaran V, Sai MS, Devaraju A (2021) A systematic review of fatigue behaviour of laser welding titanium alloys. Mater Today: Proc 39:520–523. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.08.249
Qu S, Ren Z, Hu X et al (2021) The effect of electric pulse aided ultrasonic rolling processing on the microstructure evolution, surface properties, and fatigue properties of a titanium alloy Ti5Al4Mo6V2Nb1Fe. Surf Coat Technol 421:127408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2021.127408
Ren Z, Lai F, Qu S, Zhang Y, Li X, Yang C (2020) Effect of ultrasonic surface rolling on surface layer properties and fretting wear properties of titanium alloy Ti5Al4Mo6V2Nb1Fe. Surf Coat Technol 389:125612. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2020.125612
Ren Z, Li Z, Zhou S, Wang Y, Zhang L, Zhang Z (2022) Study on surface properties of Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy by ultrasonic rolling. Simul Model Pract Theory 121:102643. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.simpat.2022.102643
Ren ZY, Hu YL, Tong Y et al (2023) Wear-resistant NbMoTaWTi high entropy alloy coating prepared by laser cladding on TC4 titanium alloy. Tribol Int 182:108366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2023.108366
Shi X, Feng X, Teng J, Zhang K, Zhou L (2021) Effect of laser shock peening on microstructure and fatigue properties of thin-wall welded Ti-6A1-4V alloy. Vacuum 184:109986. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2020.109986
Shi H, Liu D, Jia T, Zhang X, Zhao W (2023) Effect of the ultrasonic surface rolling process and plasma electrolytic oxidation on the hot salt corrosion fatigue behavior of TC11 alloy. Int J Fatigue 168:107443. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2022.107443
Shui J, Chen SL, Xia TT et al (2022) Effect of non-equilibrium solid state phase transformation on welding temperature field during keyhole mode laser welding of Ti6Al4V alloy. Opt Laser Technol 145:107461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2021.107461
Wang F, Men X, Liu Y, Fu X (2020) Experiment and simulation study on influence of ultrasonic rolling parameters on residual stress of Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Simul Model Pract Theory 104:102121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.simpat.2020.102121
Wang B, Peng H, Chen Z (2021) Microstructure and mechanical properties of a laser welded Ti–6Al–4V titanium alloy/FeCoNiCrMn high entropy alloy with a Cu filler layer. J Mater Res Technol 12:1970–1978. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.04.010
Wang B, Cheng L, Li D (2022) Study on very high cycle fatigue properties of forged TC4 titanium alloy treated by laser shock peening under three-point bending. Int J Fatigue 156:106668. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2021.106668
Wang Z, Zhou W, Luo K, Lu H, Lu J (2023) Strengthening mechanism in thermomechanical fatigue properties of Ti6Al4V titanium alloy by laser shock peening. Int J Fatigue 172:107631. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2023.107631
Wu D, Lv H, Wang H, Yu J (2022) Surface micro-morphology and residual stress formation mechanisms of near-net-shaped blade produced by low-plasticity ultrasonic rolling strengthening process. Mater Des 215:110513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2022.110513
Xu P, Li L, Zhang (Sam) C (2014) Microstructure characterization of laser welded Ti-6Al-4V fusion zones. Mater Charact 2014(87):179–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2013.11.005
Xu S, Cao Y, Duan B, Liu H, Wang J, Si C (2023) Enhanced strength and sliding wear properties of gas nitrided Ti-6Al-4V alloy by ultrasonic shot peening pretreatment. Surf Coat Technol 458:129325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2023.129325
Yunlian Q, Ju D, Quan H, Liying Z (2000) Electron beam welding, laser beam welding and gas tungsten arc welding of titanium sheet. Mater Sci Eng R Rep A 280:177–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-5093(99)00662-0
Zhao W, Liu D, Zhang X et al (2019) Improving the fretting and corrosion fatigue performance of 300M ultra-high strength steel using the ultrasonic surface rolling process. Int J Fatigue 121:30–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2018.11.017
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 52105157); Liaoning Provincial Education Department (grant number JYT2020037).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
GJ: conceive research; perform the experiments; conceptualization; validation; formal analysis; data curation; writing—original draft preparation; writing—review and editing; visualization. CJ: supervision; project administration; supervision; funding acquisition; investigation; resources. ZS: conceptualization; methodology; validation. ZZ: check the manuscript. WJ and WN: Measure; record.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jiahui, C., Jiayuan, G., Song, Z. et al. Effect of ultrasonic rolling on the fatigue performance of laser-welded TC4 titanium alloy joints. Int J Fract (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10704-024-00783-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10704-024-00783-6