Abstract
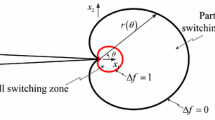
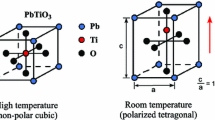
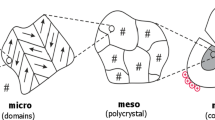
In this paper, Crack Opening Displacement (COD) is introduced to study the fracture and fatigue of ferroelectrics. A fundamental solution for the COD of ferroelectrics is derived considering both the piezoelectric effect and ferroelectric effect. Bases on this solution, a nonlinear COD fracture model of ferroelectrics, which takes into account the effect of domain switching, is developed and accords well with the experimental results. Furthermore, fatigue crack growth in ferroelectrics is analytically investigated using this COD model. Comparison between the experimental results and the predicted electric-field-induced fatigue crack growth shows the applicability of the proposed COD model.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benveniste Y (1992) The determination of the elastic and electric-fields in a piezoelectric inhomogeneity. J Appl Phys 72: 1086–1095
Benveniste Y (1993) On the micromechanics of fibrous piezoelectric composites. Mech Mater 18: 183–193
Benveniste Y, Dvorak GJ (1992) Uniform-fields and universal relations in piezoelectric composites. J Mech Phys Solids 40: 1295–1312
Cao HC, Evans AG (1994) Electric-field-induced fatigue crack growth in piezoelectrics. J Am Ceram Soc 77: 1783–1786
Cui YQ, Yang W (2006) Toughening under non-uniform ferro-elastic domain switching. Int J Solids Struct 43: 4452–4464
Dunn ML (1994) Electroelastic Green-functions for transversely isotropic piezoelectric media and their application to the solution of inclusion and inhomogeneity problems. Int J Eng Sci 32: 119–131
Dunn ML, Taya M (1993) Micromechanics predictions of the effective electroelastic moduli of piezoelectric composites. Int J Solids Struct 30: 161–175
Dunn ML, Taya M (1993) An analysis of piezoelectric composite materials containing ellipsoidal inhomogeneities. Proc Roy Soc A 443: 265–287
Eshelby JD (1957) The determination of the elastic field of an ellipsoidal inclusion and related problem. Proc R Soc A 241: 376–396
Fang DN, Liu B, Sun CT (2004a) Fatigue crack growth in ferroelectric ceramics driven by alternating electric fields. J Am Ceram Soc 87: 840–846
Fang DN, Zhang ZK, Soh AK, Lee KL (2004b) Fracture criteria of piezoelectric ceramics with defects. Mech Mater 36: 917–928
Fang DN, Zhang YH, Mao GQ (2010) Electric field induced fatigue crack growth in ferroelectric ceramics. Theor Appl Fract Mech Accepted
Fang F, Yang W (2000) Poling-enhanced fracture resistance of lead zirconate titanate ferroelectric ceramics. Mater Lett 46: 131–135
Fett T, Kounga AB, Rodel J (2004) Stresses and stress intensity factor from COD of Vickers indentation cracks. J Mater Sci 39: 2219–2221
Fett T, Munz D, Njiwa ABK, Rodel J, Quinn GD (2005) Bridging stresses in sintered reaction-bonded Si3N4 from COD measurements. J Eur Ceram Soc 25: 29–36
Fett T, Njiwa ABK, Rodel J (2005) Crack opening displacements of Vickers indentation cracks. Eng Fract Mech 72: 647–659
Gao H, Zhang TY, Tong P (1997) Local and global energy release rate for an electrically yield crack in a piezoelectric ceramic. J Mech Phys Solids 45: 491–510
Glazounov AE, Fett T, Reszat JT, Hoffmann MJ (2001) Influence of domain switching state on R-curves interpreted by using X-ray diffraction study. J Mater Sci Lett 20: 877–880
Hao TH, Shen ZY (1994) A new electric boundary condition of electric fracture mechanics and its applications. Eng Fract Mech 47: 793–802
Hao TH, Gong X, Suo Z (1996) Fracture mechanics for the design of ceramics multiplayer actuators. J Mech Phys Solids 44: 23–48
Hwang SC, Lynch CS, McMeeking RM (1995) Ferroelectric/ferroelastic interactions and a polarization switching model. Acta Metall Mater 43: 2073–2084
Jiang LZ, Sun CT (1999) Crack growth behavior in piezoceramics under cyclic loads. Ferroelectrics 233: 211–223
Jiang QY, Cross LE (1993) Effects of porosity on electric fatigue behavior in PLZT and PZT ferroelectric ceramics. J Mater Sci 28: 4536–4543
Jiang QY, Subbarao EC, Cross LE (1994) Grain size dependence of dielectric fatigue behavior of hot-pressed PLZT ferroelectric ceramics. Acta Metall Mater 42: 3687–3694
Jiang Y, Zhang Y, Liu B, Fang D (2009) Study on crack propagation in ferroelectric single crystal under electric loading. Acta Mater 57: 1630–1638
Jiang YJ, Fang DN, Li FX (2007) In situ observation of electric-field-induced domain switching near a crack tip in poled PMNT62/38 single crystal. Appl Phys Lett 90: 222907
Jones JL, Salz CRJ, Hoffman M (2005) Ferroelastic fatigue of a soft PZT ceramic. J Am Ceram Soc 88: 2788–2792
Landis CM (2004) Energetically consistent boundary conditions for electromechanical fracture. Int J Solids Struct 41: 6291–6315
Loewy RG (1997) Recent developments in smart structures with aeronautical applications. Smart Mater Struct 6: 11–42
Lynch CS, Chen L, Suo Z, McMeeking RM, Yang W (1995) Crack-growth in ferroelectric ceramics driven by cyclic polarization switching. J Intell Mater Syst Struct 6: 191–198
Mao GZ, Fang DN (2004) Fatigue crack growth induced by domain switching under electromechanical load in ferroelectrics. Theor Appl Fract Mech 41: 115–123
McMeeking RM (1999) Crack tip energy release rate for a piezoelectric compact tension specimen. Eng Fract Mech 64: 217–244
McMeeking RM (2001) Towards a fracture mechanics for brittle piezoelectric and dielectric materials. Int J Fract 108: 25–41
McMeeking RM (2004) The energy release rate for a Griffith crack in a piezoelectric material. Eng Fract Mech 71: 1149–1163
Mehta K, Virkar AV (1990) Fracture mechanisms in ferroelectric-ferroelastic lead Zirconate Titanate (Zr:Ti=0.54:0.46) ceramics. J Am Ceram Soc 73: 567–574
Njiwa ABK, Fett T, Lupascu DC, Rodel J (2003) Crack-tip toughness of a soft lead zirconate titanate. J Am Ceram Soc 86: 1973–1975
Njiwa ABK, Yousef SG, Fett T, Rodel J (2005) Influence of microcracking on crack-tip toughness of alumina. Eng Fract Mech 72: 1011–1019
Nuffer J, Lupascu DC, Glazounov A, Kleebe HJ, Rodel J (2002) Microstructural modifications of ferroelectric lead zirconate titanate ceramics due to bipolar electric fatigue. J Eur Ceram Soc 22: 2133–2142
Pak YE (1992) Linear electro-elastic fracture mechanics of piezoelectric materials. Int J Fracture 54: 79–100
Park S, Sun CT (1995) Fracture criteria for piezoelectric ceramics. J Am Ceram Soc 78: 1475–1480
Parton VZ (1976) Fracture mechanics of piezoelectric materials. Acta Astronaut 3: 671–683
Rajapakse RKND, Zeng X (2001) Toughening of conducting cracks due to domain switching. Acta Mater 49: 877–885
Shieh J, Huber JE, Fleck NA (2006) Fatigue crack growth in ferroelectrics under electrical loading. J Eur Ceram Soc 126: 95–109
Shih CF (1981) Relationship between the J-integral and crack opening displacement for stationary and extending cracks. J Mech Phys Solids 29: 305–326
Soh AK, Lee KL, Fang DN (2003) On the effects of an electric field on the fracture toughness of poled piezoelectric ceramics. Mater Sci Eng A 360: 306–314
Suo Z (1991) Mechanics concepts for failure in ferroelectric ceramics. In: Srinivasan AV (ed) Smart structures and materials, Atlanta 1–6
Suo Z, Kuo CM, Barnett DM, Willis JR (1992) Fracture mechanics for piezoelectric ceramics. J Mech Phys Solids 40: 739–765
Tobin AG, Pak E (1993) Effect of electric fields on fracture behavior of PZT ceramics. Proc SPIE 1916: 78–86
Westram I, Oates WS, Lupascu DC, Rödel J, Lynch CS (2007) Mechanism of electric fatigue crack growth in lead zirconate titanate. Acta Mater 55: 301–312
Yang W, Suo Z (1994) Crack in ceramic actuators caused by electrostriction. J Mech Phys Solids 42: 649–663
Zeng X, Rajapakse RKND (2001) Domain switching induced fracture toughness variation in ferroelectrics. Smart Mater Struct 10: 203–211
Zhang TY, Zhao MH, Tong P (2002) Fracture of Piezoelectric Ceramics. Adv Appl Mech 38: 147–289
Zhu T, Yang W (1997) Toughness variation of ferroelectrics by polarization switch under non-uniform electric field. Acta Mater 45: 4695–4702
Zhu T, Yang W (1999) Fatigue crack growth in ferroelectrics driven by cyclic electric loading. J Mech Phys Solids 47: 81–97
Zhu T, Fang F, Yang W (1999) Fatigue crack growth in ferroelectrics ceramics below the coercive field. J Mater Sci Lett 18: 1025–1027
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, D., Zhang, Y. & Mao, G. A COD fracture model of ferroelectric ceramics with applications in electric field induced fatigue crack growth. Int J Fract 167, 211–220 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10704-010-9546-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10704-010-9546-x