Abstract
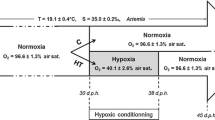
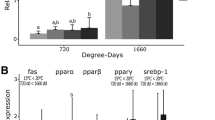
Two groups of the same batch of European seabass were used in an industrial-scale trial in sea cages in Vorios Evoikos, Greece. For about one month, one of the two cages was oxygenated by use of compressed air injected in seawater through an AirX frame (Oxyvision A/S, Norway) at 3.5 m depth, while oxygen concentration and temperature were monitored every 30 min. The liver, gut, and pyloric ceca samples were taken from fish of both groups for measurement of gene expression of phospholipase A2 (PLA2) and hormone-sensitive lipase (HSL), and for histological analysis at the middle and end of the experiment. Real-time qPCR was performed with housekeeping genes ACTb, L17, and EF1a. The expression of PLA2 increased in pyloric caeca samples from the oxygenated cage, suggesting that aeration improved the absorption rate of dietary phospholipids (p < 0.05). Expression of HSL increased significantly in liver samples from the control cage, in comparison with the aerated cage (p < 0.05). Histological examination of sea bass samples revealed an increased fat accumulation in the hepatocytes of fish in the oxygenated cage. The results of the present study showed increased lipolysis induced by low DO levels in farmed sea bass in cages.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data are presented in this manuscript.
Code availability
This is not applicable.
References
Abdel-Tawwab M, Monier MN, Hoseinifar SH, Faggio C (2019) Fish response to hypoxia stress: growth, physiological, and immunological biomarkers. Fish Physiol Biochem 45:997–1013. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-019-00614-9
Barnanbé G (1990) Rearing bass and gilthead bream. In: Barnanbé G (ed) Aquaculture, vol 2. Ellis Horhood, New York, pp 647–686
Benedito-Palos L, Ballester-Lozano G, Pérez-Sánchez J (2014) Wide gene expression analysis of lipid-relevant genes in nutritionally challenged gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata). Gene 547:34–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2014.05.073
Bennett HS, Wyrick AD, Lee SW, McNeil JH (1976) Science and art in preparing tissues embedded in plastic for light microscopy, with special reference to glycol methacrylate, glass knives, and simple stains. Stain Technol 51:71–94
Berillis P, Mente E, Nikoulli E, Makridis P, Grundvig H, Bergheim A, Gausen M (2016) Improving aeration for efficient oxygenation in sea bass cages. Blood, brain and gill morphology. Open Life Sci 11:270–279. https://doi.org/10.1515/biol-2016-0028
Beveridge MCM (2008) Problems. In: Beveridge MCM (ed) Cage aquaculture, 3rd edn. Wiley-Blackwell, London, UK ISBN: 978-1-405-10842
Bouaziz M, Bejaoui S, Rabeh I, Besbes R, El Cafsi MH, Falcon J (2017) Impact of temperature on sea bass, Dicentrarchus labrax, retina: fatty acid composition, expression of rhodopsin and enzymes of lipid and melatonin metabolism. Exp Eye Res 159:87–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exer.2017.03.010
Carbonara P, Scolamacchia M, Spedicato MT, Zupa W, McKinley RS, Lembo G (2015) Muscle activity as a key indicator of welfare in farmed European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labarax L. 1758). Aquac Res 46:2133–2146. https://doi.org/10.1111/are.12369
Claireaux G, Lagardére J-P (1999) Influence of temperature, oxygen and salinity on the metabolism of the European sea bass. J Sea Res 42:157–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1385-1101(99)00019-2
Cordero H, Morcillo P, Martínez S, Meseguer J, Pérez-Sirvent C, Chaves-Pozo E, Martínez-Sanchez MJ, Cuesta A, Esteban MA (2018) Inorganic arsenic causes apoptosis cell death and immunotoxicity on European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Mar Pollut Bull 128:324–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.01.052
Di Marco P, Priori A, Finoia MG, Massari A, Mandich A, Marino G (2008) Physiological responses of European sea bass Dicentrarchus labrax to different stocking densities and acute stress challenge. Aquaculture 275:319–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2007.12.012
Di Trapani AM, Sgroi F, Testa R, Tudisca S (2014) Economic compasiron between offshore and inshore aquaculture production systems of European sea bass in Italy. Aquaculture 434:334–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2014.09.001
Endo A, Srithongouthai S, Nashiki H, Teshiba I, Iwasaki T, Hama D, Tsutsumi H (2008) DO-increasing effects of a microscopic bubble generating system in a fish farm. Mar Pollut Bull 57:78–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2007.10.014
FEAP (2020) European aquaculture production report 2014-2019. Federation of European aquaculture producers production report. https://feap.info/wp-content/uploads/2020/10/20201007_feap-production-report-2020.pdf. Accessed 30 Sept 2020
Gracey AY, Lee T-H, Higashi RM, Fan T (2011) Hypoxia-induced mobilization of stored triglycerides in the euroxic goby Gillichthys mirabilis. J Exp Biol 214:3005–3012. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.059907
Green BW, Rawles SD, Beck BH (2012) Response of channel × blue catfish to chronic diurnal hypoxia. Aquaculture 350-353:183–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2012.03.041
Huang H, Zhang Y, Cao M, Xue L, Shen W (2018) Effects of fasting on the activities of mRNA expression levels of lipoprotein lipase (LPL), hormone-sentitive lipase (HSL) and fatty acid synthetase (FAS) in spotted seabass Lateolabrax maculatus. Fish Physiol Biochem 44:387–400. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-017-0442-4
Jónsdóttir KE, Volent Z, Alfredsen JA (2021) Current flow and dissolved oxygen in a full-scale stocked fish-cage with and without lice shielding skirts. Appl Ocean Res 108:103509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apor.2020.102509
Kurtovic I, Marshall SN, Zhao X, Simpson BK (2009) Lipases from mammals and fishes. Rev Fish Sci 17(1):18–40. https://doi.org/10.1080/10641260802031322
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the -2ΔΔCT method. Methods 25:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Madin J, Chong VC, Harstein ND (2010) Effects of water flow velocity and fish culture on net biofouling in fish cages. Aquac Res 41:e602–e617. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2109.2010.02567.x
Makridis P, Mente E, Grundvig H, Gausen M, Koutsikopoulos C, Bergheim A (2018) Monitoring of oxygen fluctuations in seabass cages (Dicentrarchus labrax L.) in a commercial fish farm in Greece. Aquac Res 49:684–691. https://doi.org/10.1111/are.13498
McDowell EM, Trump BF (1976) Histologic fixatives suitable for diagnostic light and electron microscopy. Arch Pathol Lab Med 100:405–414
Papadakis IE, Zaiss MM, Kyriakou Y, Georgiou G, Divanach P, Mylonas CC (2009) Histological evaluation of the elimination of Artemia nauplii from larval rearing protocols on the digestive system ontogeny of shi drum (Umbrina cirrosa L.). Aquaculture 286:45–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2008.08.028
Person-Le-Ruyet J, Mahé K, Le Bayon N, Le Delliou H (2004) Effects of temperature on growth and metabolism in a Mediterranean population of European sea bass, Dicentrarchus labrax L. Aquaculture 237:269–280
Pichavant K, Person-Le-Ruyet J, Le Bayon N, Severe A, Le Roux A, Boeuf G (2001) Comparative effects of long-term hypoxia on growth, feeding and oxygen consumption in juvenile turbot and European seabass. J Fish Biol 59:875–883. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8649.2001.tb00158.x
Saroglia M, Caricato G, Fritella F, Brambilla F, Terova G (2010) Dissolved oxygen regimen (PO2) may affect osmorespiratory compromise in European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.). Ital J Anim Sci 9:e15. https://doi.org/10.4081/ijas.2010.e15
Secor SM (2011) Cost of digestion and assimilation. In: Farell AP (ed) Encyclopedia of fish physiology from genome to environment, Volume 3. Academic Press, pp 1608–1616
Sliskovic M, Jelic-Mrcelic G, Antolic B, Anicic I (2011) The fouling of fish farm cage nets as bioindicator of aquaculture pollution in the Adriatic Sea (Croatia). Environ Monit Assess 173:519–532. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1402-y
Srithongouthai S, Hama D, Endo A, Tsutsumi H (2007) Effects of micro-bubbles injection in DO level and growth rate in red sea bream cage farm. In: Proceedings of fall meeting 2007 of the Oceanographic Society of Japan, p. 282
Terova G, Rimoldi S, Cora S, Bernardini G, Gornati R, Saroglia M (2008) Acute and chronic hypoxia affects HIF-1α mRNA levels in sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Aquaculture 279:150–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2008.03.041
Thetmeyer H, Waller U, Black KD, Inselmann S, Rosenthal H (1999) Growth of European sea bass (Dicentrachus labrax L.) under hypoxic and oscillating oxygen conditions. Aquaculture 174:355–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0044-8486(99)00028-9
Yang Y, Wang Z, Wang J, Lyu F, Xu K, Mu W (2021) Histopathological, hematological, and biochemical changes in high latitude fish Phoxinus lagowskii exposed to hypoxia. Fish Physiol Biochem 47:919–938. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-021-00947-4
Zar JH (1998) Biostatistical analysis. Prentice-Hall International Editions, Engelwood Hills, NJ, USA ISBN 0-13-086398-X
Zimmermann R, Lass A, Haemmerle G, Zechner R (2009) Fate of fat: the role of adipose triglyceride lipase in lipolysis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1791:494–500. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbalip.2008.10.005
Acknowledgments
We thank the manager of the farm of Zervas-Kyriazis A/S, Mr. Christos Zervas, for his help during the planning and execution of the trial. The authors thank Prof. Katerina Moutou, University of Thessaly, Department of Biochemistry and Biotechnology for fruitful discussion on gene expression analysis, and Dr. Ioanna Georga for reviewing the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by European Commission through the research project “Oxygenation by efficient air diffusion system for aquaculture farms (cages and earthen ponds),” reference nr. 315412 in 7th Framework Programme. Research for SMEs.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AG performed the analytical work, facilitated the research, and contributed to the final draft of the manuscript. EK performed the analytical work, facilitated the research, and contributed to the final draft of the manuscript. IEP analyzed the data and contributed to the final draft of the manuscript. AB conceived and performed the experiments, facilitated the research, and contributed to the final draft of the manuscript. PM run the experiment, analyzed the data, and wrote the original draft of the manuscript. All authors approved the final draft of this manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All experimental protocols and methods were carried out following The Code of Ethics of the World Medical Association (Declaration of Helsinki) for animal experiments. We took samples from dead fish harvested following the routine procedures of the farm.
Consent to participate
This is not applicable.
Consent for publication
This is not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Grimpampi, A., Kakaridi, E., Papadakis, I.E. et al. Oxygenation of European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.) in cages through aeration and effect on lipid metabolism. Fish Physiol Biochem 49, 209–218 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-023-01174-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-023-01174-9