Abstract
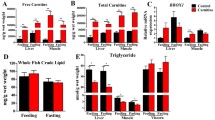
The widely available crop oil is an effective alternative to the increasingly scarce marine fish oil. However, simple alternative strategies have led to declining growth and the edible value of farmed fish. It is worthwhile to explore the effects of micro supplements in diets to improve the tolerance of fish to different dietary lipid sources, which finally optimizes the feeding strategies. This study aimed to investigate the regulation of L-carnitine and dietary oil conditions on nutrient composition, lipid metabolism, and glucose regulation of Rhynchocypris lagowskii. Four diets were prepared according to fish oil, fish oil supplemented with L-carnitine, corn oil, and corn oil supplemented with L-carnitine, and FO, LCFO, CO, and LCCO were labeled, respectively. R. lagowskii was fed experimental diets for 8 weeks, and the glucose tolerance test was performed. The CO diet significantly resulted in higher crude lipid content in muscle but a lower level of serum lipid parameters of R. lagowskii than the FO diet. However, dietary L-carnitine supplementation significantly reduced the crude lipid content in the hepatopancreas and muscle of the fish fed with the CO diet yet increased the serum lipid parameters. Additionally, the crude lipid content of muscle was reduced in the fish fed with an FO diet supplemented with L-carnitine. Compared with the FO diet, the CO diet significantly reduced the ratio of n3/n6 polyunsaturated fatty acid in the hepatopancreas and muscle of R.lagowskii. Dietary L-carnitine supplementation significantly reduced the contents of total saturated fatty acids and total monounsaturated fatty acids in hepatopancreas under both dietary lipid sources. The CO diet significantly up-regulated the expression of genes related to lipid uptake and adipogenesis in hepatopancreas, including lipoprotein lipase (lpl), acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase alpha (accα), and sterol regulatory element binding protein-1 (srebp1), compared with the FO diet. While dietary L-carnitine supplementation significantly down-regulated the expressions of lpl, accα, srebp1, and fatty acid synthase in hepatopancreas and muscle of fish under both dietary lipid sources, along with up-regulated expression of carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1 in hepatopancreas. Moreover, the fish fed with a CO diet significantly increased the expression of glucose uptake and clearance and significantly down-regulated the expressions of glucose regulation-related genes, including glucose transporter 1, glycogen synthase 1, and phosphofructokinase in hepatopancreas and muscle, resulting in slower glucose uptake and clearance than fish fed with FO diet. Nevertheless, dietary L-carnitine supplementation up-regulated the expression of gluconeogenesis-related genes, including glucose-6-phosphatase and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase in the hepatopancreas of R. lagowskii under both dietary lipid sources. In conclusion, a higher dietary n6 PUFA resulted in lipid deposition, decreased serum lipid parameters, and limited serum glucose utilization of R. lagowskii. While the regulatory effect of L-carnitine on lipid metabolism and glucose utilization of R. lagowskii varies with dietary lipid sources and tissues.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary materials.
References
Alhazzaa R, Nichols PD, Carter CG (2019) Sustainable alternatives to dietary fish oil in tropical fish aquaculture. Rev Aquacult 11(4):1195–1218. https://doi.org/10.1111/raq.12287
Ali H, Morito K, Hasi RY, Aihara M, Hayashi J, Kawakami R, Kanemaru K, Tsuchiya K, Sango K, Tanaka T (2022) Characterization of uptake and metabolism of very long-chain fatty acids in peroxisome-deficient CHO cells. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids 1867(2):159088. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbalip.2021.159088
Andrikopoulos S, Blair AR, Deluca N, Fam BC, Proietto J (2008) Evaluating the glucose tolerance test in mice. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 295(6):E1323–E1332. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.90617.2008
AOAC (2005) Official Methods of Analysis, 18th edition. Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Washington DC
Bae JS, Oh AR, Cha JY (2013) Regulation of cholesterol metabolism in liver: link to NAFLD and impact of n-3 PUFAs. J Lifestyle Med 3(1):19–25
Bandarra NM, Rema P, Batista I, Pousao-Ferreira P, Valente LMP, Batista SMG, Ozorio ROA (2011) Effects of dietary n-3/n-6 ratio on lipid metabolism of gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata). Eur J Lipid Sci Tech 113(11):1332–1341. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejlt.201100087
Castro C, Corraze G, Panserat S, Oliva-Teles A (2015) Effects of fish oil replacement by a vegetable oil blend on digestibility, postprandial serum metabolite profile, lipid and glucose metabolism of European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) juveniles. Aquacult Nutr 21(5):592–603. https://doi.org/10.1111/anu.12184
Cha JY, Repa JJ (2007) The liver X receptor (LXR) and hepatic lipogenesis: the carbohydrate-response element-binding protein is a target gene of LXR*. J Biol Chem 282(1):743–751. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M605023200
Chen Y, Sun Z, Liang Z, Xie Y, Tan X, Su J, Luo Q, Zhu J, Liu Q, Wang A (2020a) Addition of l-carnitine to formulated feed improved growth performance, antioxidant status and lipid metabolism of juvenile largemouth bass, Micropterus salmoides. Aquaculture 518:734434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2019.734434
Chen YF, Sun ZZ, Liang ZM, Xie YD, Su JL, Luo QL, Zhu JY, Liu QY, Han T, Wang AL (2020b) Effects of dietary fish oil replacement by soybean oil and L-carnitine supplementation on growth performance, fatty acid composition, lipid metabolism and liver health of juvenile largemouth bass, Micropterus salmoides. Aquaculture 516:734596. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2019.734596
de Almeida CAL, de Almeida CKL, de Fátima Ferreira Martins E, Bessonart M, Pereira RT, Paulino RR, Rosa PV, Fortes-Silva R (2021) Coping with suboptimal water temperature: modifications in blood parameters, body composition, and postingestive-driven diet selection in Nile tilapia fed two vegetable oil blends. Animal 15(2):100092. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.animal.2020.100092
Dikel S, Unalan B, Eroldogan OT, Hunt AO (2010) Effects of dietary L-carnitine supplementation on growth, muscle fatty acid composition and economic profit of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Turkish J Fish Aquat Sci 10(2):173–180. https://doi.org/10.4194/trjfas.2010.0203
Dong Q, Li L, Yu YH, Dong XQ, Chen YK, Pei HQ, Wang QJ, Zhang DM (2014) Effects of exogenous carnitine on fatty acid composition and CPT I gene expression in muscle of common carp (Cyprinus carpio). J Northwest A&F Univ Nat Sci Ed 42:29–36. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Du J, Xu H, Li S, Cai Z, Mai K, Ai Q (2017) Effects of dietary chenodeoxycholic acid on growth performance, body composition and related gene expression in large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) fed diets with high replacement of fish oil with soybean oil. Aquaculture 479:584–590. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2017.06.023
Du RY, Chen JX, Zhu J, Feng JY, Luo L, Lin SM, Chen YJ (2020) Glucose homeostasis and glucose tolerance were impaired with elevated lipid to starch ratios in practical diets for the omnivorous genetically improved farmed tilapia Oreochromis niloticus. Aquaculture 523:735221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2020.735221
Duwaerts CC, Maher JJ (2019) Macronutrients and the adipose-liver axis in obesity and fatty liver. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol 7(4):749–761. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcmgh.2019.02.001
Eckel RH (1989) Lipoprotein lipase. A multifunctional enzyme relevant to common metabolic diseases. N Engl J Med 320(16):1060–1068. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM198904203201607
Farmaki EG, Thomaidis NS, Pasias IN, Rousis NI, Baulard C, Papaharisis L, Efstathiou CE (2021) Advanced multivariate techniques for the classification and pollution of marine sediments due to aquaculture. Sci Total Environ 763:144617. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144617
Fawole FJ, Labh SN, Hossain MS, Overturf K, Small BC, Welker TL, Hardy RW, Kumar V (2021) Insect (black soldier fly larvae) oil as a potential substitute for fish or soy oil in the fish meal-based diet of juvenile rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Anim Nutr 7(4):1360–1370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aninu.2021.07.008
Garg ML, Sebokova E, Wierzbicki A, Thomson AB, Clandinin MT (1988) Differential effects of dietary linoleic and alpha-linolenic acid on lipid metabolism in rat tissues. Lipids 23(9):847–852. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02536203
Godoy AC, Santos OO, Oxford JH, de Amorim Melo IW, Rodrigues RB, Neu D, Vianna Nunes R, Boscolo WR (2019) Soybean oil for Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) in finishing diets: economic, zootechnical and nutritional meat improvements. Aquaculture 512:734324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2019.734324
Gu ZX, Mu H, Shen HH, Deng KY, Liu D, Yang MX, Zhang Y, Zhang WB, Mai KS (2019) High level of dietary soybean oil affects the glucose and lipid metabolism in large yellow croaker Larimichthys crocea through the insulin-mediated PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Comp Biochem Phys B 231:34–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpb.2018.12.003
Harpaz S (2005) L-carnitine and its attributed functions in fish culture and nutrition - a review. Aquaculture 249(1–4):3–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2005.04.007
He AY, Ning LJ, Chen LQ, Chen YL, Xing Q, Li JM, Qiao F, Li DL, Zhang ML, Du ZY (2015) Systemic adaptation of lipid metabolism in response to low- and high-fat diet in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Physiol Rep 3(8):e12485. https://doi.org/10.14814/phy2.12485
He LY, Qin YM, Wang YF, Li D, Chen WJ, Ye JD (2021) Effects of dietary replacement of fish oil with soybean oil on the growth performance, plasma components, fatty acid composition and lipid metabolism of groupers Epinephelus coioides. Aquacult Nutr 27(5):1494-1511. https://doi.org/10.1111/anu.13292
Hossain MS, Peng M, Small BC (2021) Optimizing the fatty acid profile of novel terrestrial oil blends in low fishmeal diets of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) yields comparable fish growth, total fillet n-3 LC-PUFA content, and health performance relative to fish oil. Aquaculture 545:737230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2021.737230
Huang CC, Sun J, Ji H, Oku H, Chang ZG, Tian JJ, Yu EM, Xie J (2019) Influence of dietary alpha-lipoic acid and lipid level on the growth performance, food intake and gene expression of peripheral appetite regulating factors in juvenile grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus). Aquaculture 505:412–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2019.02.054
Infante JP, Huszagh VA (2000) Secondary carnitine deficiency and impaired docosahexaenoic (22:6n–3) acid synthesis: a common denominator in the pathophysiology of diseases of oxidative phosphorylation and beta-oxidation. FEBS Lett 468(1):1–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0014-5793(00)01083-8
Jin M, Pan TT, Cheng X, Zhu TT, Sun P, Zhou F, Ding XY, Zhou QC (2019a) Effects of supplemental dietary L-carnitine and bile acids on growth performance, antioxidant and immune ability, histopathological changes and inflammatory response in juvenile black seabream (Acanthopagrus schlegelii) fed high-fat diet. Aquaculture 504:199–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2019.01.063
Jin M, Lu Y, Pan T, Zhu T, Yuan Y, Sun P, Zhou F, Ding X, Zhou Q (2019b) Effects of dietary n-3 LC-PUFA/n-6 C18 PUFA ratio on growth, feed utilization, fatty acid composition and lipid metabolism related gene expression in black seabream, Acanthopagrus schlegelii. Aquaculture 500:521–531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2018.10.056
Jones PM, Butt Y, Messmer B, Boriak R, Bennett MJ (2006) Medium-chain fatty acids undergo elongation before β-oxidation in fibroblasts. Biochem Bioph Res Co 346:193–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.05.107
Khoomrung S, Raber G, Laoteng K, Francesconi KA (2014) Identification and characterization of fish oil supplements based on fatty acid analysis combined with a hierarchical clustering algorithm. Eur J Lipid Sci Tech 116(7):795–804. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejlt.201300369
Kramer IM (2016) Chapter 7 - bringing the signal into the nucleus: regulation of gene expression. In: Kramer IM (ed) Signal Transduction, 3rd edn. Academic Press, Boston, pp 441–476. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-394803-8.00007-3
Li Y, Zhao YT, Zhang YK, Liang X, Zhang Y, Gao J (2015) Growth performance, fatty acid composition, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors gene expressions, and antioxidant abilities of blunt snout bream, Megalobrama amblycephala, Fingerlings Fed Different Dietary Oil Sources. J World Aquacult Soc 46(4):395–408. https://doi.org/10.1111/jwas.12203
Li JM, Li LY, Qin X, Ning LJ, Lu DL, Li DL, Zhang ML, Wang X, Du ZY (2017) Systemic regulation of L-carnitine in nutritional metabolism in zebrafish, Danio Rerio. Sci Rep-Uk 7(1):40815. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep40815
Li BS, Wang JY, Huang Y, Hao TT, Wang SX, Huang BS, Sun YZ (2019) Effects of replacing fish oil with wheat germ oil on growth, fat deposition, serum biochemical indices and lipid metabolic enzyme of juvenile hybrid grouper (Epinephelus fuscoguttatus♀ × Epinephelus lanceolatus♂). Aquaculture 505:54–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2019.02.037
Li LY, Limbu SM, Ma Q, Chen LQ, Zhang ML, Du ZY (2019) The metabolic regulation of dietary L-carnitine in aquaculture nutrition: present status and future research strategies. Rev Aquacult 11(4):1228–1257. https://doi.org/10.1111/raq.12289
Li LY, Lu DL, Jiang ZY, Limbu SM, Qiao F, Chen LQ, Zhang ML, Du ZY (2020) Dietary L-carnitine improves glycogen and protein accumulation in Nile tilapia via increasing lipid-sourced energy supply: an isotope-based metabolic tracking. Aquacult Rep 17:100302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aqrep.2020.100302
Li LY, Wang Y, Limbu SM, Li JM, Qiao F, Chen LQ, Zhang ML, Du ZY (2021) Reduced fatty acid β-oxidation improves glucose catabolism and liver health in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) juveniles fed a high-starch diet. Aquaculture 535:736392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2021.736392
Liu Y, Yan Y, Han Z, Zheng Y, Wang X, Zhang M, Li H, Xu J, Chen X, Ding Z, Cheng H (2022) Comparative effects of dietary soybean oil and fish oil on the growth performance, fatty acid composition and lipid metabolic signaling of grass carp, Ctenopharyngodon Idella. Aquacult Rep 22:101002. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aqrep.2021.101002
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 25(4):402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Ma JJ, Xu ZR, Shao QJ, Xu JZ, Hung SSO, Hu WL, Zhou LY (2008) Effect of dietary supplemental L-carnitine on growth performance, body composition and antioxidant status in juvenile black sea bream, Sparus macrocephalus. Aquacult Nutr 14(5):464–471. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2095.2007.00551.x
Maldonado-Othón CA, Perez-Velazquez M, Gatlin DM, González-Félix ML (2020) Replacement of fish oil by soybean oil and microalgal meals in diets for Totoaba macdonaldi (Gilbert, 1890) juveniles. Aquaculture 529:735705. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2020.735705
Martínez-Fernández L, Laiglesia LM, Huerta AE, Martínez JA, Moreno-Aliaga MJ (2015) Omega-3 fatty acids and adipose tissue function in obesity and metabolic syndrome. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat 121:24–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2015.07.003
McGarry JD, Brown NF (1997) The mitochondrial carnitine palmitoyltransferase system. From concept to molecular analysis. Eur J Biochem 244(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1432-1033.1997.00001.x
Merkel M, Eckel RH, Goldberg IJ (2002) Lipoprotein lipase. J Lipid Res 43(12):1997–2006. https://doi.org/10.1194/jlr.R200015-JLR200
Merkle S, Giese E, Rohn S, Karl H, Lehmann I, Wohltmann A, Fritsche J (2017) Impact of fish species and processing technology on minor fish oil components. Food Control 73:1379–1387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2016.11.003
Michelato M, de Oliveira Vidal LV, Xavier TO, de Moura LB, de Almeida FLA, Pedrosa VB, Furuya VRB, Furuya WM (2016) Dietary lysine requirement to enhance muscle development and fillet yield of finishing Nile tilapia. Aquaculture 457:124–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2016.02.022
Miller MR, Nichols PD, Carter CG (2008) n-3 Oil sources for use in aquaculture–alternatives to the unsustainable harvest of wild fish. Nutr Res Rev 21(2):85–96. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0954422408102414
Nayak M, Saha A, Pradhan A, Samanta M, Giri SS (2017) Dietary fish oil replacement by linseed oil: Effect on growth, nutrient utilization, tissue fatty acid composition and desaturase gene expression in silver barb (Puntius gonionotus) fingerlings. Comp Biochem Physiol B: Biochem Mol Biol 205:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpb.2016.11.009
Ozorio RO, Uktoseja JL, Huisman EA, Verreth JA (2001) Changes in fatty acid concentrations in tissues of African catfish, Clarias gariepinus Burchell, as a consequence of dietary carnitine, fat and lysine supplementation. Br J Nutr 86(5):623–636. https://doi.org/10.1079/BJN2001447
Peng S, Chen L, Qin JG, Hou J, Yu N, Long Z, Ye J, Sun X (2008) Effects of replacement of dietary fish oil by soybean oil on growth performance and liver biochemical composition in juvenile black seabream, Acanthopagrus schlegeli. Aquaculture 276:154–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2008.01.035
Peng M, Xu W, Mai K, Zhou H, Zhang Y, Liufu Z, Zhang K, Ai Q (2014) Growth performance, lipid deposition and hepatic lipid metabolism related gene expression in juvenile turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.) fed diets with various fish oil substitution levels by soybean oil. Aquaculture 433:442–449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2014.07.005
Peng M, Xu W, Tan P, Du J, Mai K, Zhou H, Zhang Y, Nian R, Macq B, Ai Q (2017) Effect of dietary fatty acid composition on growth, fatty acids composition and hepatic lipid metabolism in juvenile turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.) fed diets with required n3 LC-PUFAs. Aquaculture 479:591–600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2017.06.032
Piedecausa MA, Mazón MJ, García García B, Hernández MD (2007) Effects of total replacement of fish oil by vegetable oils in the diets of sharpsnout seabream (Diplodus puntazzo). Aquaculture 263(1):211–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2006.09.039
Preiss-Landl K, Zimmermann R, Hämmerle G, Zechner R (2002) Lipoprotein lipase: the regulation of tissue specific expression and its role in lipid and energy metabolism. Curr Opin Lipidol 13(5):471–481. https://doi.org/10.1097/00041433-200210000-00002
Qin Y, He L, Wang Y, Li D, Chen W, Ye J (2022) Growth performance, fatty acid composition, and lipid metabolism are altered in groupers (Epinephelus coioides) by dietary fish oil replacement with palm oil. Anim Nutr 8(1):102–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aninu.2021.04.007
Ren HT, Yu JH, Xu P, Tang YK (2012) Influence of dietary fatty acids on muscle fatty acid composition and expression levels of Δ6 desaturase-like and Elovl5-like elongase in common carp (Cyprinus carpio var. Jian). Comp Biochem Physiol B: Biochem Mol Biol 163(2):184–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpb.2012.05.016
Ribeiro A, Mangeney M, Cardot P, Loriette C, Rayssiguier Y, Chambaz J, Bereziat G (1991) Effect of dietary fish oil and corn oil on lipid metabolism and apolipoprotein gene expression by rat liver. Eur J Biochem 196(2):499–507. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15842.x
Richard N, Kaushik S, Larroquet L, Panserat S, Corraze G (2006) Replacing dietary fish oil by vegetable oils has little effect on lipogenesis, lipid transport and tissue lipid uptake in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Brit J Nutr 96(2):299–309. https://doi.org/10.1079/Bjn20061821
Rothblat GH, Mahlberg FH, Johnson WJ, Phillips MC (1992) Apolipoproteins, membrane cholesterol domains, and the regulation of cholesterol efflux. J Lipid Res 33(8):1091–1097. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-2275(20)40761-8
Sabzi E, Mohammadiazarm H, Salati AP (2017) Effect of dietary L-carnitine and lipid levels on growth performance, blood biochemical parameters and antioxidant status in juvenile common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Aquaculture 480:89–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2017.08.013
Sales J, Glencross B (2011) A meta-analysis of the effects of dietary marine oil replacement with vegetable oils on growth, feed conversion and muscle fatty acid composition of fish species. Aquacult Nutr 17(2):E271–E287. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2095.2010.00761.x
Sanchez MSDS, Lins-Rodrigues M, Pessini JE, Bittencourt F, Boscolo WR, Signor A (2021) Dietary supplementation with L-carnitine for Nile tilapia juveniles. Aquaculture 539:736616. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2021.736616
Sarameh SP, Bahri AH, Salarzadeh A, Falahatkar B (2019) Effects of fish oil replacement with vegetable oil in diet of sterlet sturgeon (Acipenser ruthenus) broodstock on expression of lipid metabolism related genes in eggs. Aquaculture 505:441–449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2019.02.031
Schoonjans K, Gelman L, Haby C, Briggs M, Auwerx J (2000) Induction of LPL gene expression by sterols is mediated by a sterol regulatory element and is independent of the presence of multiple E boxes1 1Edited by M. Yaniv. J Mol Biol 304(3):323–334. https://doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.2000.4218
Seward SL, Blankenship JM, Broussard JL (2021) Continuous glucose monitoring in sleep and circadian research. In: Reference Module in Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Psychology. Elsevier, Amsterdam. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-822963-7.00274-7
Sharifzadeh E, Yeganeh S, Firouzbakhsh F, Oraji H (2017) Effects of L-carnitine and vitamin c on the growth indices, body composition and serum biochemical parameters of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) juveniles. J Vet Res 72(2):173–182
Sharma P, Agnihotri N (2020) Fish oil and corn oil induced differential effect on beiging of visceral and subcutaneous white adipose tissue in high-fat-diet-induced obesity. J Nutr Biochem 84:108458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutbio.2020.108458
Shearer GC, Savinova OV, Harris WS (2012) Fish oil — how does it reduce plasma triglycerides? Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids 1821(5):843–851. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbalip.2011.10.011
Small L, Ehrlich A, Iversen J, Ashcroft SP, Trošt K, Moritz T, Hartmann B, Holst JJ, Treebak JT, Zierath JR, Barrès R (2022) Comparative analysis of oral and intraperitoneal glucose tolerance tests in mice. Mol Metab 57:101440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmet.2022.101440
Subhadra B, Lochmann R, Rawles S, Chen R (2006) Effect of dietary lipid source on the growth, tissue composition and hematological parameters of largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides). Aquaculture 255(1):210–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2005.11.043
Sul HS, Smas CM, Wang D, Chen L (1998) Regulation of fat synthesis and adipose differentiation. In: Moldave K (Ed), Progress in Nucleic Acid Research and Molecular Biology. Academic Press, pp 317-345. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0079-6603(08)60896-X
Sun S, Castro F, Monroig Ó, Cao X, Gao J (2020) fat-1 transgenic zebrafish are protected from abnormal lipid deposition induced by high-vegetable oil feeding. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 104(17):7355–7365. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10774-x
Tacon AGJ, Metian M (2015) Feed matters: satisfying the feed demand of aquaculture. Rev Fish Sci Aquac 23(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1080/23308249.2014.987209
Takeno S, Sakuradani E, Murata S, Inohara-Ochiai M, Kawashima H, Ashikari T, Shimizu S (2005) Molecular evidence that the rate-limiting step for the biosynthesis of arachidonic acid in Mortierella alpina is at the level of an elongase. Lipids 40(1):25–30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-005-1356-6
Tian J, Wen H, Zeng LB, Jiang M, Wu F, Liu W, Yang CG (2013) Changes in the activities and mRNA expression levels of lipoprotein lipase (LPL), hormone-sensitive lipase (HSL) and fatty acid synthetase (FAS) of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) during fasting and re-feeding. Aquaculture 400–401:29–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2013.01.032
Tocher DR (2010) Fatty acid requirements in ontogeny of marine and freshwater fish. Aquac Res 41(5):717–732. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2109.2008.02150.x
Tocher DR (2015) Omega-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids and aquaculture in perspective. Aquaculture 449:94–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2015.01.010
Twibell RG, Brown PB (2000) Effects of dietary carnitine on growth rates and body composition of hybrid striped bass (Morone saxatilis male x M. chrysops female). Aquaculture 187(1):153–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0044-8486(99)00387-7
van der Hoek MD, Madsen O, Keijer J, van der Leij FR (2018) Evolutionary analysis of the carnitine- and choline acyltransferases suggests distinct evolution of CPT2 versus CPT1 and related variants. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids 1863(8):909–918. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbalip.2018.05.001
Vestergren AS, Trattner S, Pan J, Johnsson P, Kamal-Eldin A, Brännäs E, Moazzami AA, Pickova J (2013) The effect of combining linseed oil and sesamin on the fatty acid composition in white muscle and on expression of lipid-related genes in white muscle and liver of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquacult Int 21(4):843–859. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-012-9511-y
Wang C, Zhang C, Yu H, Zan Z, Li J, Li P, Zhang X, Ji H, Gao Q (2022) Glycerol monolaurate and triglycerol monolaurate alleviated high-fat diet induced lipid accumulation and damage of liver in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Aquaculture 561:738616. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2022.738616
Wang S, Chen YK, Ghonimy A, Yu T, Gao YS, Wu ZC, Wang QJ, Zhang DM (2020) L-Carnitine supplementation improved population growth, photosynthetic pigment synthesis and antioxidant activity of marine Chlorella sp. Aquacult Rep 17:100394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aqrep.2020.100394
Xu H, Liao Z, Wang C, Wei Y, Liang M (2019) Hepatic transcriptome of the euryhaline teleost Japanese seabass (Lateolabrax japonicus) fed diets characterized by α-linolenic acid or linoleic acid. Comp Biochem Physiol d: Genomics Proteomics 29:106–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbd.2018.11.005
Yang SD, Wen YC, Liou CH, Liu FG (2010) Influence of dietary l-carnitine on growth, biological traits and meat quality in Tilapia. Aquac Res 40(12):1374–1382. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2109.2009.02234.x
Yang SD, Liu FG, Liou CH (2012) Effects of dietary L-carnitine, plant proteins and lipid levels on growth performance, body composition, blood traits and muscular carnitine status in juvenile silver perch (Bidyanus bidyanus). Aquaculture 342:48–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2012.02.002
Yin P, Xie S, Zhuang Z, He X, Tang X, Tian L, Liu Y, Niu J (2021) Dietary supplementation of bile acid attenuate adverse effects of high-fat diet on growth performance, antioxidant ability, lipid accumulation and intestinal health in juvenile largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides). Aquaculture 531:735864. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2020.735864
Yıldız M, Eroldoğan TO, Ofori-Mensah S, Engin K, Baltacı MA (2018) The effects of fish oil replacement by vegetable oils on growth performance and fatty acid profile of rainbow trout: Re-feeding with fish oil finishing diet improved the fatty acid composition. Aquaculture 488:123–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2017.12.030
Yu T, Wang QJ, Chen XM, Chen YK, Ghonimy A, Zhang DM, Wang GQ (2020) Effect of dietary L-carnitine supplementation on growth performance and lipid metabolism in Rhynchocypris lagowski Dybowski fed oxidized fish oil. Aquac Res 51(9):3698–3710. https://doi.org/10.1111/are.14719
Yu J, Wen X, You C, Wang S, Chen C, Tocher DR, Li Y (2021) Comparison of the growth performance and long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (LC-PUFA) biosynthetic ability of red tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus♀ × O. niloticus♂) fed fish oil or vegetable oil diet at different salinities. Aquaculture 542:736899. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2021.736899
Zhang L, Liu WB, Brown PB, Xu C, Shi HJ, Zheng XC, Zhang L, He C, Huang YY, Li, XF (2020) Utilization of raw and gelatinized starch by blunt snout bream Megalobrama amblycephala as evidenced by the glycolipid metabolism, glucose tolerance and mitochondrial function. Aquaculture 529:735603. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2020.735603
Zhang Y, Lin L, Chen Y, Gao Y, Wang S, Wang G, Wu Z, Wang Q, Zhang D (2022a) A comparative study on the effects of supplemental L-carnitine on fatty acids composition, energy status and related genes expression in Cyprinus carpio var. Jian and Rhynchocypris lagowskii (Dybowski, 1869). Aquacult Rep 24:101161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aqrep.2022.101161
Zhang ZY, Limbu SM, Zhao SH, Chen LQ, Luo Y, Zhang ML, Qiao F, Du ZY (2022b) Dietary l-carnitine supplementation recovers the increased pH and hardness in fillets caused by high-fat diet in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Food Chem 382:132367
Zhou JC, Han D, Jin JY, Xie SQ, Yang YX, Zhu XM (2014) Compared to fish oil alone, a corn and fish oil mixture decreases the lipid requirement of a freshwater fish species, Carassius auratus gibelio. Aquaculture 428:272–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2014.03.029
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 30671621 and 31372540), the Key Research and Development Projects of Jilin Provincial Department of Science and Technology (Nos. 20210202036NC and 20210202098NC), the Jilin Province Science and Technology Department Youth Growth Science and Technology Program Project (No. 20210508010RQ), the Jilin Provincial Department of Education 2021 Science and Technology Project (JJKH20210370KJ), the Major Scientific Research Project of Jilin Provincial Department of Education (No. JJKH20220368KJ), the Modern Agro-industry Technology Research System (No. CARS-46), and the Jilin Provincial Department of Science and Technology Key R&D Project (No. 20180201017NY).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Dongming Zhang, Qiuju Wang, and Sen Wang contributed to the study’s conception and design. Funding acquisition and resources were provided by Dongming Zhang, Qiuju Wang, Zhixin Guo, and Yuke Chen. Material preparation was performed by Sen Wang, Rongxin Zheng, Nan Zheng, and Wenhao Fang. Data collection was performed by Sen Wang, Xin Wang, Jiajing Wang, and Ning Wang. Data analysis was performed by Sen Wang. Project administration and supervision were performed by Dongming Zhang, Qiuju Wang, Zhixin Guo, and Yuke Chen. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Wang Sen. Writing—review and editing were performed by Dongming Zhang, Qiuju Wang, Zhixin Guo, and Yuke Chen. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This experiment animal care was performed conformity with NIH Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. All fish used in this study were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Jilin Agricultural University.
Consent to participate
Participation in this article has been consented to by all authors.
Consent for publication
All authors approved the manuscript for publication.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, S., Guo, Z., Wang, X. et al. Dietary L-carnitine supplementation changes lipid metabolism and glucose utilization of Rhynchocypris lagowskii fed diets with different lipid sources. Fish Physiol Biochem 50, 77–96 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-022-01166-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-022-01166-1