Abstract
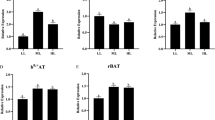
This study was conducted to evaluate the effects of different dipeptides (lysine-leucine, lysine-glycine, and leucine-glycine) and free amino acids (lysine and leucine) on the growth, gene expression of intestinal peptide and amino acid transporters, and serum free amino acid concentrations in turbot. Fish (11.98 ± 0.03 g) were fed four experimental diets supplementing with crystalline amino acids (CAA), lysine-leucine (Lys-Leu), lysine-glycine (Lys-Gly), and leucine-glycine (Gly-Leu). Fish protein hydrolysate (FPH) containing a mixture of free amino acids and small peptides was designed as a positive control diet. There was no significant difference in the growth and feed utilization among three dipeptide diets (Lys-Leu, Lys-Gly, and Gly-Leu). Compared with the CAA group, feed efficiency ratio was significantly higher in the Lys-Leu and Lys-Gly groups, and protein efficiency ratio was significantly higher in the Lys-Leu group. For peptide transporter, oligopeptide transporter 1 (PepT1) mRNA level was not affected by dietary treatments. For amino acid transporters, lower expression of B0 neutral amino acid transporter 1 (B0AT1) and proton-coupled amino acid transporter 1 (PAT1) were observed in fish fed the dipeptide and FPH diets compared with the CAA diet. In conclusion, juvenile turbot fed Lys-Leu, Gly-Leu, and Lys-Gly had a similar growth performance, whereas lysine and leucine in the Lys-Leu form can be utilized more efficiently for feed utilization than those in free amino acid from. In addition, compared to free amino acids, dipeptides and fish protein hydrolysate in diets may down-regulate the expression of amino acid transporters but did not affect the expression of PepT1.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abimorad EG, Ducatti C, Castellani D, Jomori RK, Portella MC, Carneiro DJ (2014) The use of stable isotopes to investigate the effects of supplemental lysine and methionine on protein turnover and amino acid utilization in pacu, Piaractus mesopotamicus, juveniles. Aquaculture 433:119–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2014.06.006
Ambardekar AA, Reigh RC, Williams MB (2009) Absorption of amino acids from intact dietary proteins and purified amino acid supplements follows different time-courses in channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus). Aquaculture 291:179–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2009.02.044
Association of Official Analytical Chemists (AOAC) (2005) Official Methods of Analysis of Official Analytical Chemists International, 18th edn. Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Gaithersburg, MD
Bakke S, Jordal AEO, Gómez-Requeni P, Verri T, Kousoulaki K, Aksnes A, Rønnestad I (2010) Dietary protein hydrolysates and free amino acids affect the spatial expression of peptide transporter PepT1 in the digestive tract of Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua). Comp Biochem Physiol B-Biochem Mol Biol 156(1):48–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpb.2010.02.002
Bogé G, Rigal A, Peres G (1981) Rates of in vivo intestinal absorption of glycine and glycylglycine by rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri R.). Comp Biochem Physiol A-Physiol 69(3):455–459. https://doi.org/10.1016/0300-9629(81)93004-8
Boll M, Daniel H, Gasnier B (2004) The slc36 family: proton-coupled transporters for the absorption of selected amino acids from extracellular and intracellular proteolysis. Pflügers Arch-Eur J Physiol 447(5):776–779. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-003-1073-4
Bröer S (2008) Amino acid transport across mammalian intestinal and renal epithelia. Physiol Rev 88(1):249–286. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00018.2006
Chen C, Yin Y, Tu Q, Yang H (2018) Glucose and amino acid in enterocyte: absorption, metabolism and maturation. Front Biosci 23:1721–1739. https://doi.org/10.2741/4669
Dabrowski K, Lee KJ, Rinchard J (2003) The smallest vertebrate, teleost fish, can utilize synthetic dipeptide-based diets. J Nutr 133(12):4225–4229. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/133.12.4225
Dabrowski K, Terjesen BF, Zhang Y, Phang J, Lee KJ (2005) A concept of dietary dipeptides: a step to resolve the problem of amino acid availability in the early life of vertebrates. J Exp Biol 208(15):2885–2894
El-Husseiny O, El-Haroun ER, Goda A, Hassan I, Woodward B, Suloma A (2017) Effects of lysine and tryptophan supplementations in plant protein-based diets on the performance of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). J Appl Aquac 29(3-4):266–276. https://doi.org/10.1080/10454438.2017.1364684
FAO (2018) The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture. Rome, Italy, pp 5–7
Fotiadis D, Kanai Y, Palacín M (2013) The SLC3 and SLC7 families of amino acid transporters. Mol Aspects Med 34(2-3):139–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mam.2012.10.007
Furuya WM, Pezzato LE, Barros MM, Pezzato AC, Furuya VR, Miranda EC (2004) Use of ideal protein concept for precision formulation of amino acid levels in fish-meal-free diets for juvenile Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus L.). Aquac Res 35(12):1110–1116. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2109.2004.01133.x
Gatlin DM III, Barrows F, Bellis D, Brown P, Campen J, Dabrowski K, Gaylord TG, Hardy RW, Herman EM, Hu G, Krogdahl A, Nelson R, Overturf KE, Rust M, Sealey W, Skonberg D, Souza EJ, Stone D, Wilson RF (2007) Expanding the utilization of sustainable plant products in aquafeeds: a review. Aquac Res 38(6):551–579. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2109.2007.01704.x
He L, Yang H, Hou Y, Li T, Fang J, Zhou X, Yin Y, Wu L, Nyachoti M, Wu G (2013) Effects of dietary L-lysine intake on the intestinal mucosa and expression of CAT genes in weaned piglets. Amino Acids 45(2):383–391. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-013-1514-0
Hevrøy EM, Espe M, Waagbø R, Sandnes K, Ruud M, Hemre GI (2005) Nutrient utilization in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) fed increased levels of fish protein hydrolysate during a period of fast growth. Aquacult Nutr 11(4):301–313. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2095.2005.00357.x
Kamaszewski M, Prasek M, Ostaszewska T, Dabrowski K (2014) The influence of feeding diets containing wheat gluten supplemented with dipeptides or free amino acids on structure and development of the skeletal muscle of carp (Cyprinus carpio). Aquacult Int 22(1):259–271. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-013-9683-0
Kaushik SJ, Seiliez I (2010) Protein and amino acid nutrition and metabolism in fish: current knowledge and future needs. Aquac Res 41(3):322–332. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2109.2009.02174.x
Kim SS, Lee KJ (2013) Comparison of leucine requirement in olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) by free or synthetic dipeptide forms of leucine. Anim Feed Sci Technol 183(3-4):195–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2013.05.008
Kwasek K, Terova G, Wojno M, Dabrowski K, Wick M (2012) The effect of dietary dipeptide lysine-glycine on growth, muscle proteins, and intestine PepT1 gene expression in juvenile yellow perch. Rev Fish Biol Fisheries 22(3):797–812. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11160-012-9266-6
Lansard M, Panserat S, Plagnes-Juan E, Dias K, Seiliez I, Skiba-Cassy S (2010) L-Leucine, L-methionine, and L-lysine are involved in the regulation of intermediary metabolism-related gene expression in rainbow trout hepatocytes. J Nutr 141(1):75–80. https://doi.org/10.3945/jn.110.124511
Larsen BK, Dalsgaard J, Pedersen PB (2012) Effects of plant proteins on postprandial, free plasma amino acid concentrations in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 326:90–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2011.11.028
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 25(4):402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Margheritis E, Terova G, Oyadeyi AS, Renna MD, Cinquetti R, Peres A, Bossi E (2013) Characterization of the transport of lysine-containing dipeptides by PepT1 orthologs expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Comp Biochem Physiol A-Mol Integr Physiol 164(3):520–528. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2012.12.016
Margheritis E, Imperiali FG, Cinquetti R, Vollero A, Terova G, Rimoldi S, Girardello R, Bossi E (2016) Amino acid transporter B0AT1 (slc6a19) and ancillary protein: impact on function. Pflügers Arch-Eur J Physiol 468(8):1363–1374. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-016-1842-5
Morales A, Buenabad L, Castillo G, Vázquez L, Espinoza S, Htoo JK, Cervantes M (2017) Dietary levels of protein and free amino acids affect pancreatic proteases activities, amino acids transporters expression and serum amino acid concentrations in starter pigs. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr 101(4):723–732. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpn.12515
Olsen RL, Toppe J (2017) Fish silage hydrolysates: Not only a feed nutrient, but also a useful feed additive. Trends Food Sci Technol 66:93–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2017.06.003
Orozco ZGA, Soma S, Kaneko T, Watanabe S (2017) Effects of fasting and refeeding on gene expression of slc15a1a, a gene encoding an oligopeptide transporter (PepT1), in the intestine of Mozambique tilapia. Comp Biochem Physiol B-Biochem Mol Biol 203:76–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpb.2016.09.006
Osmanyan AK, Harsini SG, Mahdavi R, Fisinin VI, Arkhipova AL, Glazko TT, Kovalchuk SN, Kosovsky GY (2018) Intestinal amino acid and peptide transporters in broiler are modulated by dietary amino acids and protein. Amino acids 50(2):353–357. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-017-2510-6
Ostaszewska T, Dabrowski K, Kamaszewski M, Grochowski P, Verri T, Rzepkowska M, Wolnicki J (2010a) The effect of plant protein-based diet supplemented with dipeptide or free amino acids on digestive tract morphology and PepT1 and PepT2 expressions in common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Comp Biochem Physiol A-Mol Integr Physiol 157(2):158–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2010.06.162
Ostaszewska T, Kamaszewski M, Grochowski P, Dabrowski K, Verri T, Aksakal E, Szatkowska I, Nowak Z, Dobosz S (2010b) The effect of peptide absorption on PepT1 gene expression and digestive system hormones in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Comp Biochem Physiol A-Mol Integr Physiol 155(1):107–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2009.10.017
Ostaszewska T, Dabrowski K, Kamaszewski M, Kwasek K, Grodzik M, Bierla J (2013) The effect of dipeptide, Lys-Gly, supplemented diets on digestive tract histology in juvenile yellow perch (Perca flavescens). Aquacult Nutr 19(1):100–109. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2095.2012.00948.x
Peres H, Oliva-Teles A (2005) The effect of dietary protein replacement by crystalline amino acid on growth and nitrogen utilization of turbot Scophthalmus maximus juveniles. Aquaculture 250:755–764. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2005.04.046
Perez-Velazquez M, Gatlin DM III, González-Félix ML, García-Ortega A (2018) Partial replacement of fish meal and fish oil by algal meals in diets of red drum Sciaenops ocellatus. Aquaculture 487:41–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2018.01.001
Poncet N, Taylor PM (2013) The role of amino acid transporters in nutrition. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 16(1):57–65. https://doi.org/10.1097/MCO.0b013e32835a885c
Rahimnejad S, Lee KJ (2014) Comparison of free and dipeptide lysine utilization in diets for juvenile olive flounder Paralichthys olivaceus. Fish Aquat Sci 17(4):433–439. https://doi.org/10.5657/FAS.2014.0433
Rimoldi S, Bossi E, Harpaz S, Cattaneo AG, Bernardini G, Saroglia M, Terova G (2015) Intestinal B0AT1 (SLC6A19) and PEPT1 (SLC15A1) mRNA levels in European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) reared in fresh water and fed fish and plant protein sources. J Nutr Sci 4:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1017/jns.2015.9
Romano A, Barca A, Storelli C, Verri T (2014) Teleost fish models in membrane transport research: the PEPT1 (SLC15A1) H+-oligopeptide transporter as a case study. J Physiol 592(5):881–897. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2013.259622
Swanepoel JC, Goosen NJ (2018) Evaluation of fish protein hydrolysates in juvenile African catfish (Clarias gariepinus) diets. Aquaculture 496:262–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2018.06.084
Thamotharan M, Gomme J, Zonno V, Maffia M, Storelli C, Ahearn GA (1996a) Electrogenic, proton-coupled, intestinal dipeptide transport in herbivorous and carnivorous teleosts. Am J Physiol-Regulatory Integrative Comp Physiol 270(39):R939–R947. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.1996.270.5.R939
Thamotharan M, Zonno V, Storelli C, Ahearn GA (1996b) Basolateral dipeptide transport by the intestine of the teleost Oreochromis mossambicus. Am J Physiol-Regulatory Integrative Comp Physiol 270(5):R948–R954. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.1996.270.5.R948
Thwaites DT, Anderson CM (2011) The SLC36 family of proton-coupled amino acid transporters and their potential role in drug transport. Br J Pharmacol 164(7):1802–1816. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01438.x
Verrey F, Closs EI, Wagner CA, Palacin M, Endou H, Kanai Y (2004) CATs and HATs: the SLC7 family of amino acid transporters. Pflügers Arch-Eur J Physiol 447(5):532–542. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-003-1086-z
Verri T, Barca A, Pisani P, Piccinni B, Storelli C, Romano A (2017) Di-and tripeptide transport in vertebrates: the contribution of teleost fish models. J Comp Physiol B 187(3):395–462. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-016-1044-7
Wei Y, Liang M, Mu Y, Zheng K, Xu H (2016) The effect of ultrafiltered fish protein hydrolysate level on growth performance, protein digestibility and mRNA expression of PepT1 in juvenile turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.). Aquacult Nutr 22(5):1006–1017. https://doi.org/10.1111/anu.12319
Wei Y, Liang M, Xu H (2020a) Fish protein hydrolysate affected amino acid absorption and related gene expressions of IGF-1/AKT pathways in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus). Aquacult Nutr 26(1):145–155. https://doi.org/10.1111/anu.12976
Wei Y, Xu H, Liang M (2020b) Amino acid absorption and protein synthesis responses of turbot Scophthalmus maximus to lysine and leucine in free, dipeptide and tripeptide forms. Aquacult Nutr 26(2):358–367. https://doi.org/10.1111/anu.12998
Xu D, He G, Mai K, Zhou H, Xu W, Song F (2016) Postprandial nutrient-sensing and metabolic responses after partial dietary fish meal replacement by soyabean meal in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.). Br J Nutr 115(3):379–388. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114515004535
Yun H, Park G, Ok I, Katya K, Hung S, Bai SC (2016) Determination of the dietary lysine requirement by measuring plasma free lysine concentrations in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss after dorsal aorta cannulation. Fish Aquat Sci 19(1):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41240-016-0004-1
Zhang Y, Dabrowski K, Hliwa P, Gomulka P (2006) Indispensable amino acid concentrations decrease in tissues of stomachless fish, common carp in response to free amino acid-or peptide-based diets. Amino Acids 31(2):165–172. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-006-0345-7
Zhang S, Qiao S, Ren M, Zeng X, Ma X, Wu Z, Thacker P, Wu G (2013) Supplementation with branched-chain amino acids to a low-protein diet regulates intestinal expression of amino acid and peptide transporters in weanling pigs. Amino Acids 45(5):1191–1205. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-013-1577-y
Funding
This research was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (31672663, 31902387, 31972803), China Agriculture Research System (CARS-47-G15, Government of China), and Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund, CAFS (2020TD48).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All experimental methods and procedures used in this study were approved by Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the Yellow Sea Fisheries Research Institute.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, Y., Li, B., Xu, H. et al. Effects of lysine and leucine in free and different dipeptide forms on the growth, amino acid profile and transcription of intestinal peptide, and amino acid transporters in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus). Fish Physiol Biochem 46, 1795–1807 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-020-00828-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-020-00828-2