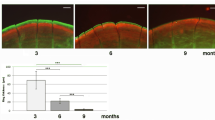
Abstract
This study was carried out to investigate the effects of exposure to estrogen antagonist nafoxidine hydrochloride (NH) and/or melatonin (Mlt) on certain bone metabolism parameters in killifish Aphanius fasciatus, a species suggested to be a suitable model for studying spinal deformities such as scoliosis. Immature females of A. fasciatus receiving 10 μg/L NH and/or 100 μg/L of Mlt were used and were sacrificed 30 days after the treatment. The spinal column, brain, and liver were collected and analyzed by various histological, biochemical, chemical, and molecular investigations. NH exposure increased frequency of histological alterations and caused signs of spinal column demineralization such as significant decrease in the percentage of nonorganic components content and calcium concentration. These changes were accompanied by decreased alkaline phosphatase activity (AP), hepatic insulin growth factor-1 (IGF-1) content, and, interestingly, cerebral Mlt concentration. Concomitant treatment with Mlt and NH enhanced expression of the gene encoding the Mlt receptor “mtnr1aa”and significantly restored the normal skeletal histology and the normal metabolism bone parameters. Our data suggest that disturbance of estrogen pathway in A. fasciatus induces cerebral Mlt depletion and, then, causes skeletal tissue alterations and bone demineralization and that exogenous Mlt supplementation has a protective effect. Thus, estrogen receptor antagonists and Mlt become important compounds to consider for the accurate prediction and assessment of bone physiology and spinal deformities in fish.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amstrup AK, Sikjaer T, Heickendorff L, Mosekilde L, Rejnmark L (2015) Melatonin improves bone mineral density at the femoral neck in postmenopausal women with osteopenia: a randomized controlled trial. J Pineal Res 59(2):221–229
Banni M, Negri A, Mignone F, Boussetta H, Viarengo A, Dondero F (2011) Gene expression rhythms in the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis (Lam.) across an annual cycle. PLoS One 6(5):e18904
Bjornstrom L, Sjoberg M (2005) Mechanisms of estrogen receptor signaling: convergence of genomic and non genomic actions on target genes. Mol Endocrinol 19:833–842
Boughammoura S, Kessabi K, Chouchene L, Messaoudi I, (2013) Effects of Cadmium and High Temperature on Some Parameters of Calcium Metabolism in the Killifish (Aphanius fasciatus). Biological Trace Element Research 154(1):73–80
Bourdeau M, Courtenay SC, MacLatchy DL, Berude CH, Parrot JL, Van der Kraak GJ (2005) Utility of morphology and abnormalties during early-life development of the estuarine mummichog Fundulus heteroclitus as an indicator of estrogenie and antiestrogenie endocrine disruption. Environ Toxicol Chem 23:2415–425
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Carnevali O, Gioacchini G, Piccinetti CC, Maradonna F, Lombardo F, Giorgini E, Tosi G (2010) Melatonin control of oogenesis and metabolic resources in zebrafish. J Appl Ichthyol 26:826–830
Clemon M, Goss P (2001) Estrogen and the risk of breast cancer. N Engl J Med 344(4):276–285
Dubousset J, Queneau P, Thillard M (1983) Experimental scoliosis induced by pineal and diencephalic lesions in young chickens: its relation with clinical findings. Orthop Trans 7:7p
Falcón J (2007) Nocturnal melatonin synthesis: how to stop it. Endocrinology 2007(148):1473–1474
Fjelldal PG, Grotmol S, Kryvi H, Gjerdet NR, Taranger GL, Hansen T, Porter MJ, Totland GK (2004) Pinealectomy induces malformation of the spine and reduces the mechanical strength of the vertebrae in Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar. J Pineal Res 36(2):132–139
Giwercman A (2011) Estrogens and phytoestrogens in male infertility. Curr Opin Urol 21:519–526
Hall MJ, John F, Kenneth C, Korach S (2001) The multifaceted mechanisms of estradiol and estrogen receptor signaling. J Biol Chem 276:36869–36872
Han Y, Kim YM, Kim HS, Lee KY (2017) Melatonin promotes osteoblast differentiation by regulating osterix protein stability and expression. Sci Rep 7(1):5716
Iwamuro S, Sakakibara M, Terao M, Ozawa A, Kurobe C, Shigeura T, Kato M, Kikuyama S (2003). Teratogenic and anti-metamorphic effects of bisphenol A on embryonic and larval Xenopus laevis. Gen Comp Endocrinol 133:189–198
Johns SM, Denslow ND, Kane MD, Watanabe KH, Orlando EF, Sepúlveda MS (2011) Effects of estrogens and antiestrogens on gene expression of fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas) early life stages. Environ Toxicol 26(2):196–206
Kessabi K, Kerkeni A, Saïd K, Messaoudi I (2009) Involvement of cd bioaccumulation in spinal deformities occurrence in natural populations of Mediterranean killifish. Biol Trace Elem Res 128:72–81
Kessabi K, Annabi A, Hassine A, Bazin I et al. Possible chemical causes of skeletal deformities in natural populations of Aphanius fasciatus collected from the Tunisian coast. Chemosphere 90:2683-2689
Khosla S, Oursler MJ, Monroe DG (2012) Estrogen and the skeleton. Trends Endocrinol Metab 23:576–581
Knani L, Bartolini D, Kechiche S, Tortoioli C, Murdolo G, Moretti M, Messaoudi I, Reiter JR, Galli F (2019) Melatonin prevents cadmium-induced bone damage: first evidence on an improved osteogenic/adipogenic differentiation balance of mesenchymal stem cells as underlying mechanism. J Pineal Res 67(3):e12597
Koyama H, Nakade O, Takada Y, Kaku T, Lau KH (2002) Melatonin at pharmacologic doses increases bone mass by suppressing resorption through down-regulation of the RANKL mediated osteoclast formation and activation. J Bone Miner Res 17(7):1219–1229
Krassas GE, Papadopoulou P (2001) Oestrogen action on bone cells. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact 2(2):143–151
Maria S, Samsonraj RM, Munmun F, Glas J, Silvestros M, Kotlarczyk MP, Rylands R, Dudakovic A, van Wijnen AJ, Enderby LT, Lassila H, Dodda B, Davis VL, Balk J, Burow M, Bunnell BA, Witt-Enderby PA (2018) Biological effects of melatonin on osteoblast/osteoclast cocultures, bone, and quality of life: implications of a role for MT2 melatonin receptors, MEK1/2, and MEK5 in melatonin-mediated osteoblastogenesis. J Pineal Res 64(3). doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12465
Messaoudi I, Kessabi K, Kacem A, Saïd K, (2009) Incidence of spinal deformities in natural populations of Nardo, 1827 from the Gulf of Gabes, Tunisia. African Journal of Ecology 47(3):360–366
Nemec V, Socha R (1988) Phosphatases and pteridines in Malpighian tubules: a possible marker of the mosaic mutant in Pyrrhocoris apterus (Heteroptera: Pyrrhocoridae). Acta Entomol Bohemoslov 85:321–326
Reiter RJ, Rosales-Corral S, Tan DX, Jou MJ, Galano A, Xu B (2017) Melatonin as a mitochondria-targeted antioxidant: one of evolution's best ideas. Cell Mol Life Sci 74(21):3863–3881
Renuka K, Joshi BN (2010) Melatonin-induced changes in ovarian function in the freshwater fish Channa punctatus (Bloch) held in long days and continuous light. Gen Comp Endocrinol 165(1):42–46
Roth JA, Kim BG, Song F, Lin WL, Cho MI (1999) Melatonin promotes osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. J Biol Chem 274:32528–32528
Ryan KJ (1982) Biochemistry of aromatase: significance to female reproductive physiology. Cancer Res 42(8):3342–3344
Satomura K, Tobiume S, Tokuyama R, Yamasaki Y, Kudoh K, Maeda E, Nagayama M (2007) Melatonin at pharmacological doses enhances human osteoblastic differentiation in vitro and promotes mouse cortical bone formation in vivo. J Pineal Res 42:231–239
Schiessl H, Frost HM, Jee WS (1998) Estrogen and bone-muscle strength and mass relationships. Bone 22(1):1–6
Suzuki N, Hayakawa K, Kameda T, Triba A, Tang N, Tabata MJ, Takada K, Wada S, Omori K, Srivastav AK et al (2009) Monohydroxylated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons inhibit both osteoclastic and osteoblastic activities in teleost scales. Life Sci 84:482–488
Turner RTJ (1999) Mice, estrogen, and postmenopausal osteoporosis. Bone Miner Res 14(2):187–191
Wu C, Patino R, Davis KB, Chang X (2001) Localization of estrogen receptor alpha and beta RNA in germinal and non germinal epithelia of the channel catfish testis. Gen Comp Endocrinol 124:12–20
Zhu F, Liu Z, Ren Y (2018) Mechanism of melatonin combined with calcium carbonate on improving osteoporosis in aged rats. Exp Therap Med 16(1):192–196
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict(s) of interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lahmar, S., Kessabi, K., Banni, M. et al. First evidence on protective effect of exogenous melatonin supplementation against disruption of the estrogenic pathway in bone metabolism of killifish (Aphanius fasciatus). Fish Physiol Biochem 46, 747–757 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-019-00748-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-019-00748-w