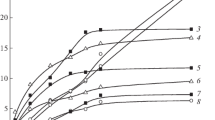
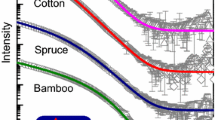
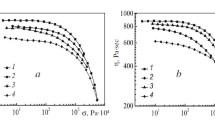
Fibers of bacterial cellulose were obtained for the first time from solutions in N-methylmorpholine N-oxide (NMMO) by using the concept of solid-phase dissolution of bacterial cellulose. The mechanism of solid-phase dissolution of bacterial cellulose in NMMO is examined with due regard to the structural and morphological characteristics of native bacterial cellulose. By investigating the structure of the fibers it was possible to reveal the different orientation of the main diffraction planes of the outer shell and inner part of the fiber reflecting the structural aspect of the shell–core morphology. The fibrillar morphology of the fiber was established by scanning electron microscopy. The thermal characteristics of the fibers of bacterial cellulose differ radically from the characteristics of fibers of plant origin in the preponderance of condensation processes that produce exo effects on the thermograms and lead to increase of the carbon residue. The mechanical characteristics of the obtained fibers were characterized.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Z. A. Rogovin, Chemistry of Cellulose [in Russian], Khimiya, Moscow (1972), 520 pp.
Z. A. Rogovin, L. S. Gal’braikh, Chemical Transformations and Modification of Cellulose [in Russian], Khimiya, Moscow (1979), 206 pp.
I. Sulaeva, U. Henniges, et al., Biotechnol. Adv., 33, No. 8, 1547-1571 (2015).
T. I. Gromovykh, V. S. Sadykova, et al., Appl. Biochem. Microbiol., 53,. No. 1, 59-66 (2017).
M. Iguchi, S. Yamanaka, A. J. Budhiono, J. Mater. Sci., 35, No. 2, 261-270 (2000). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004775229149.
A. Okiyama, H. Shirae, et al., Food Hydrocolloids, 6, No. 5, 471-477 (1992). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0268-005X(09)80032-5.
Y. Jia, X. Wang, et al., Nanomaterials Nanotechnology, 7, 1-8 (2017). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/1847980417707172.
Fan Mi Han, Biotechnology of Bacterial Cellulose Using Strain Producer Gluconacetobacter hansenii GH-1/2008: Author’s Abstract of Thesis [in Russian], 03.01.06. M. V. Lomonosov Moscow State University (2013), 25 pp.
E. K. Gladysheva, Fundamental’nye Issledovaniya, No. 5 (Part.1), 53-57 (2015).
T. I. Gromovykh, S. V. Lutsenko, et al., Inter-Medikal, 13, . No. 7, 4-9 (2015).
W. K. Czaja, D. J. Young, et al., Biomacromolecules, 8, No. 1, 1-12 (2007). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bm060620d.
Y. Hu, J. M. Catchmark, Acta Biomaterialia, 7, No. 7, 2835-45 (2011). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/ j.actbio.2011.03.028.
Y.-J. Lee, S.-J. An, et al., Materials, 10, No. 320, 1-13 (2017). DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10030320.
L. K. Golova, V. G. Kulichikhin, S. P. Papkov, Vysokomol Soed., Ser. A, 27, No. 9, 1795-1809 (1986).
A. M. Bochek, Rus. J. Appl. Chemistry, 76, No. 11, 1711-1719 (2003). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:RJAC.0000018669.88546.56.
X. Lu, X. Shen, Carbohydrate Polymers, 86, No. 1, 239-244 (2011). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.04.042.
R. Yudianti, A. Syampurwadi, et al., Polymer Adv. Technol., 27, No. 8, 1102-1107 (2016). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/pat.3782.
M. Gericke, K. Schlufter, et al., Biomacromolecules, No. 10, 1188-1194 (2009).
T. Budtova, P. Navard, Nordic Pulp & Paper Res. J., 30, No. 1, 99-104 (2015). DOI: https://doi.org/10.3183/npprj-2015- 30-01-p099-104.
US Pat. 3, 447, 939. 3.06.1969.
L. K. Golova, Fibre Chemistry, 28, No. 1, 5-16 (1996). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01130691.
Q. Gao, X. Shen, X. Lu, Carbohydrate Polymers, 83, 1253-1256 (2011). DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.09.029.
G. Shanshan, W. Jianqing, J. Zhengwei, Carbohydrate Polymers, 87, No. 2, 1020-1025 (2012). DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.06.040.
Golova L. K., O. E. Borodina, et al., Fibre Chemistry, 32, No. 4, 243-251 (2000). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004194913945.
T. I. Gromovykh et al., RF Pat., No. 2464307 (2012).
L. K. Goliova et al., RF Pat. 1645308 (1992).
D. L. Kaplan, Biopolymers from Renewable Resources, Springer Science & Business Media (2013), p. 420.
T. Takahashi, Fibers, 25, No. 3, 122-127 (1969). DOI: https://doi.org/10.2115/fiber.25.122.
Y. Zhang, H. Shao, X. Hu, Polymer J., 34, No. 9, 666-673 (2002). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1295/polymj.34.666.
I. S. Makarov, L. K. Golova, et al., Fibre Chemistry, 49, No. 4, 231-236 (2017). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10692-018-9874-6.
H. Yang, R. Yan, et al., Fuel, 86, 1781-1788 (2007). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2006.12.013.
The authors express their gratitude to L. K. Kuznetsova.
The work was carried out with support from the Russian Science Fund (grant No. 17-79-30108) using equipment from the Federal Scientific-Research Center “Crystallography and Photonics”, Russian Academy of Sciences with support from Minobrnauki.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Khimicheskie Volokna, No. 3, pp. 24-30, May-June, 2019.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Makarov, I.S., Golova, L.K., Vinogradov, M.I. et al. Cellulose Fibers from Solutions of Bacterial Cellulose in N-Methylmorpholine N-Oxide. Fibre Chem 51, 175–181 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10692-019-10069-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10692-019-10069-6