Abstract
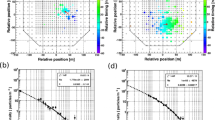
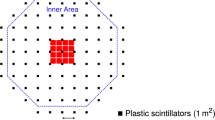
The observation of γ-ray sources above 100 TeV is one of the most intriguing fields in the investigation of the origin of cosmic rays. The YangBaJing Hybrid Array (YBJ-HA) experiment consist of scintillation detectors and underground muon detectors, the main objective is to measure gamma rays >10 TeV. In this study, we investigated an energy estimation method based on particle density and fixed distance from the shower axis by conducting a detailed Monte Carlo simulation of an extensive air shower using the YBJ-HA in Tibet. By comparing the results of the new method with those of other previously used estimators, we found that the new method can effectively improve the energy resolution of gamma rays. At an energy of 100 TeV for a zenith angle θ < 30°, the new energy estimation method has an improvement about 10% compared for the other estimators.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abeysekara, A.U., et al.: Sensitivity of the high altitude water Cherenkov detector to sources of multi-TeV gamma rays. Astropart. Phys. 50-52, 26–32 (2013)
Abeysekara, A., et al.: Observation of the crab nebula with the HAWC gamma-ray observatory. Astrophys. J. 843(1), 39 (2017)
Abu-Zayyad, T., et al.: The cosmic-ray energy spectrum observed with the surface detector of the telescope array experiment. Astrophys. J. Lett. 768(1), L1 (2013)
Aharonian, F.A.: Very High Energy Cosmic Gamma Radiation: A Crucial Window on the Extreme Universe, pp. 354–359. World Scientific Publishing Company, Singapore (2004)
Aharonian, F.A.: The very-high-energy gamma-ray sky. Science. 315(5808), 70–72 (2007)
Amenomori, M., et al.: Future plan for observation of cosmic gamma rays in the 100 TeV energy region with the Tibet air shower array: simulation and sensitivity. arXiv:0710.2752 (2007)
Amenomori, M., et al.: Multi-TeV gamma-ray observation from the crab nebula using the Tibet-III air shower array finely tuned by the cosmic ray Moon’s shadow. Astrophys. J. Lett. 692(1), 61 (2009)
Amenomori, M., et al.: First detection of photons with energy beyond 100 TeV from an astrophysical source. Phys. Rev. Lett. 123(5), 051101 (2019)
Cao, Z., et al.: Introduction to large high altitude air shower observatory (LHAASO). Chin. Astron. Astrophys. 43, 457–478 (2019)
Feng, Y.-L., et al.: Lateral distribution of EAS muons measured for the primary cosmic ray energy around 100 TeV. Chin. Phys. C. 43(7), 075002 (2019)
Funk, S.: Ground- and space-based gamma-ray astronomy. Annu. Rev. Nucl. Part. Sci. 65(1), 245–277 (2015)
Grenier, I.A., et al.: Gamma-ray pulsars: a gold mine. Comptes Rendus Physique. 16(6–7), 641–660 (2015)
Heck, D., et al.: CORSIKA: A Monte Carlo code to simulate extensive air showers. Technical Note, FZKA 6019, Forschungszentrum, Karlsruhe, (1998)
Kamata, K., et al.: The lateral and the angular structure functions of electron showers. Prog. Theor. Phys. Supp. 6, 93–155 (1958)
Kawata, K., et al.: Energy determination of gamma-ray induced air showers observed by an extensive air shower array. Exp. Astron. 44(1), 1–9 (2017)
Liu, C., et al.: Performance of the muon detector A under TIBET III array. Chin. Phys. C. 37(2), 026001 (2013)
Lorenz, E., et al.: Very-high energy gamma-ray astronomy. Eur. Phys. J. H. 37(3), 459–513 (2012)
Makoto, A., et al.: GEANT4: a simulation toolkit. Trans. Am. Nucl. Soc. 95(12/16), 757 (2006)
Ostapchenko, S.: QGSJET-II: towards reliable description of very high energy hadronic interactions. Nucl. Phys. B. 151(1), 143–146 (2004)
Sinnis, G.: Water Cherenkov technology in gamma-ray astrophysics. Nucl. Instrum. Methods. Phys. Res. A. 623(1), 410–412 (2010)
Wang, Z., et al.: Performance of a scintillation detector array operated with LHAASO-KM2A electronics. Exp. Astron. 45(3), 363–377 (2018)
Acknowledgments
We thank the support of Cheng Liu,Yiqing Guo and Youliang Feng in the installation, debugging, and maintenance of the detectors. We also thank the support of the National Natural Science Foundation of China, and the Tibet University.
Availability of data and material
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Funding
This work is supported in China by the National Natural Science Foundation (NSFC) (grant number11765019, 11963004, 11873005, 12047575), and Cultivation Foundation of Tibet University (grant number ZDTSJH19-13), and Funding support for the first-class discipline construction of Tibet University in 2020.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest/competing interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, Q., Liu, M., Chen, . et al. Calibration of γ-ray energy in an extensive air shower using the YangBaJing hybrid Array. Exp Astron 52, 35–43 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10686-021-09780-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10686-021-09780-2