Abstract
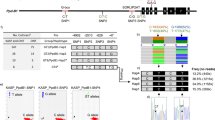
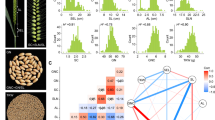
Fruit shape is one of the important quantitative traits in pear (Pyrus spp.) breeding program, thus genetic study related to fruit shape could be beneficial to pear breeding. Quantitative trait loci (QTL) analysis was carried out using ‘Whangkeumbae’ (P. pyrifolia, round) × ‘Yali’ (P. bretschneideri, pyriform) and high-resolution melting (HRM) markers were developed. The genetic linkage map of ‘Whangkeumbae’ × ‘Yali’ was constructed using single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) derived from Axiom Pear 70 K Genotyping Array and simple sequence repeats. The integrated genetic linkage map of ‘Whangkeumbae’ × ‘Yali’ showed ~ 90% of genome coverage, a total genetic distance of 998.2 cM, and a marker density of 1.6 cM. F1 progenies of ‘Whangkeumbae’ × ‘Yali’ showed normal distribution of fruit length (L), diameter (D), and L/D ratio. Three QTLs located in linkage group (LG) 6, 7, and 12 were identified with LOD thresholds of 2.8–3.0. Six HRM markers were developed using array-SNPs anchored in the QTLs and predicted fruit shape with 28.6–65.3% accuracy. Notably, accuracy was increased by ~ 90% using an HRM marker combination consisting of CBp06sn02, CBp07sn01, and CBp12sn03. These results could provide a better understanding of the genetic mechanism of fruit shape development and reducing pear breeding period.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bain JM (1961) Some morphological, anatomical, and physiological changes in the pear fruit (Pyrus communis var. Williams Bon Chrétien) during development and following harvest. Aust J of Bot 9:99–123
Bassil NV, Davis TM, Zhang H, Ficklin S, Mittmann M, Webster T, Mahoney L, David W et al (2015) Development and preliminary evaluation of a 90 K Axiom® SNP array for the allo-octoploid cultivated strawberry Fragaria × ananassa. BMC Genom 16:155. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-015-1310-1
Bianco L, Cestaro A, Linsmith G, Muranty H, Denancé C, Théron A, Poncet C, Micheletti D et al (2016) Development and validation of the Axiom® Apple480K SNP genotyping array. Plant J 86:62–74. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.13145
Chen H, Song Y, Li L, Khan MA, Li X, Schuyler S, Korban SS, Wu J, Zhang SL (2015) Construction of a high-density simple sequence repeat consensus genetic map for pear (Pyrus spp.). Plant Mol Biol Rep 33:316–325. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-014-0745-x
Collard BCY, Jahufer MZZ, Brouwer JB, Pang ECK (2005) An introduction to markers, quantitative trait loci (QTL) mapping and marker-assisted selection for crop improvement: the basic concepts. Euphytica 142:169–196. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-005-1681-5
Elshire RJ, Glaubitz JC, Sun Q, Poland JA, Kawamoto K, Buckler ES, Mitchell SE (2011) A robust, simple genotyping-by-sequencing (GBS) approach for high diversity species. PLoS ONE 6:e19379. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0019379
Gianfranceschi L, Seglias N, Tarchini R, Komjanc M, Gessle C (1998) Simple sequence repeats for the genetic analysis of apple. Theor Appl Genet 96:1069–1076. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001220050841
Grandillo S, Ku HM, Tanksley SD (1999) Identifying the loci responsible for natural variation in fruit size and shape in tomato. Theor Appl Genet 99:978–987. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001220051405
Han H, Oh Y, Kim K, Oh S, Cho S, Kim YK, Kim D (2019) Integrated genetic linkage maps for Korean pears (Pyrus hybrid) using GBS-based SNPs and SSRs. Hortic Environ Biotechnol 60:779–786. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-019-00171-3
Lee HR, An HJ, Yang DC, Choi SH, Kim HJ, Rhee HG, Harn CH (2012) Development of a high resolution melting (HRM) marker linked to genic male sterility in Capsicum annuum L. Plant Breed 131:444–448. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0523.2012.01956.x
Liebhard R, Gianfranceschi L, Koller B, Ryder CD, Tarchini R, van De Weg E, Gessler C (2002) Development and characterization of 140 new microsatellites in apple (Malus × domestica Borkh.). Mol Breed 10:217–241. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020525906332
Montanari S, Bianco L, Allen BJ, Martínez-García PJ, Bassil NV, Postman J, Knäbel M, Kitson B et al (2019) Development of a highly efficient Axiom™ 70 K SNP array for Pyrus and evaluation for high-density mapping and germplasm characterization. BMC Genom 20:331. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-019-5712-3
Nishitani C, Terakami S, Sawamura Y, Takada N, Yamamoto T (2009) Development of novel EST-SSR markers derived from Japanese pear (Pyrus pyrifolia). Breed Sci 59:391–400. https://doi.org/10.1270/jsbbs.59.391
Oh S, Oh Y, Kim K, Han H, Kim Y, Won K, Kim D (2020) Construction of high-resolution genetic linkage map in pear pseudo-BC1 ((Pyrus pyrifolia × P. communis) × P. pyrifolia) using GBS-SNPs and SSRs. Hortic Environ Biotechnol 61:745–753. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-020-00261-7
Rasheed A, Hao Y, Xia X, Khan A, Xu Y, Varshney RK, He Z (2017) Crop breeding chips and genotyping platforms: progress, challenges, and perspectives. Mol Plant 10:1047–1064. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2017.06.008
Sadrnia H, Rajabipour A, Jafary A, Javadi A, Mostofi Y (2007) Classification and analysis of fruit shapes in long type watermelon using image processing. Int J Agric Biol 1:68–70
Sawamura Y, Saito T, Takada N, Yamamoto T, Kimura T, Hayashi T, Kotobuki K (2004) Identification of percentage of Japanese pear ‘Housui.’ J Jpn Soc Hortic Sci 73:511–518
Simko I (2016) High-resolution DNA melting analysis in plant research. Trends Plant Sci 21:528–537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2016.01.004
Vales MI, Schön CC, Capettini F, Chen XM, Corey AE, Mather DE, Mundt CC, Richardson KL, Sandoval-Islas JS, Utz HF, Hayes PM (2005) Effect of population size on the estimation of QTL: a test using resistance to barley stripe rust. Theor Appl Genet 111:1260–1270. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-005-0043-y
Verde I, Bassil N, Scalabrin S, Gilmore B, Lawley CT, Gasic K, Micheletti D, Rosyara UR (2012) Development and evaluation of a 9K SNP array for peach by internationally coordinated SNP detection and validation in breeding germplasm. PLoS ONE 7:e35668. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0035668
Wang CH, Li W, Tian YK, Hou DL, Bai MD (2016) Development of molecular markers for genetic and physical mapping of the PcDw locus in pear (Pyrus communis L.). J Hortic Sci Biotechnol 91:299–307. https://doi.org/10.1080/14620316.2016.1155319
White AG, Alspach PA, Weskett RH, Brewer LR (2000) Heritability of fruit shape in pears. Euphytica 112:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003761118890
Wu J, Li LT, Li M, Khan MA, Li XG, Chen H, Yin H, Zhang SL (2014) High-density genetic linkage map construction and identification of fruit-related QTLs in pear using SNP and SSR markers. J Exp Bot 65:5771–5781. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eru311
Wu S, Zhang B, Keyhaninejad N, Rodríguez GR, Kim HJ, Chakrabarti M, Illa-Berenguer E, Taitano NK et al (2018) A common genetic mechanism underlies morphological diversity in fruits and other plant organs. Nat Commun 9:4734. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-07216-8
Xie M, Huang Y, Zhang Y, Wang X, Yang H, Yu O, Dai W, Fang C (2013) Transcriptome profiling of fruit development and maturation in Chinese white pear (Pyrus bretschneideri Rehd). BMC Genom 14:823. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-14-823
Yamamoto T, Kimura T, Shoda M, Imai T, Saito T, Sawamura Y, Kotobuki K, Hayashi T, Matsuta N (2002a) Genetic linkage maps constructed by using an interspecific cross between Japanese and European pears. Theor Appl Genet 106:9–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-002-0966-5
Yamamoto T, Kimura T, Sawamura Y, Manabe T, Kotobuki K, Hayashi T, Ban Y, Matsuta N (2002b) Simple sequence repeats for genetic analysis in pear. Euphytica 124:129–137. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015677505602
Yamamoto T, Kimura T, Shoda M, Ban Y, Hayashi T, Matsuta N (2002c) Development of microsatellite markers in the Japanese pear (Pyrus pyrifolia Nakai). Mol Ecol Notes 2:14–16. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1471-8286.2002.00128.x
Yamamoto T, Terakami S (2016) Genomics of pear and other Rosaceae fruit trees. Breed Sci 66:148–159. https://doi.org/10.1270/jsbbs.66.148
Yamamoto T, Terakami S, Takada N, Nishio S, Onoue N, Nishitani C, Kunihisa M, Inoue E, Iwata H, Hayashi T, Itai A, Saito T (2014) Identification of QTLs controlling harvest time and fruit skin color in Japanese pear (Pyrus pyrifolia Nakai). Breed Sci 64:351–361. https://doi.org/10.1270/jsbbs.64.351
Zhang RP, Wu J, Li XG, Khan MA, Chen H, Korban SS, Zhang SL (2013) An AFLP, SRAP, and SSR genetic linkage map and identification of QTLs for fruit traits in pear (Pyrus L.). Plant Mol Biol Rep 31:678–687. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-012-0544-1
Zhang C, Lee U, Tanabe K (2008) Hormonal regulation of fruit set, parthenogenesis induction and fruit expansion in Japanese pear. Plant Growth Regul 55:231. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-008-9279-2
Acknowledgements
This work was carried out with the support of “Cooperative Research Program for Agriculture Science and Technology Development (No. PJ015682)” Rural Development Administration, Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SC and SO performed the overall experiments, data analysis, and wrote the manuscript together. HH contributed to bioinformatics analysis. KK and HJ contributed to phenotyping. DK designed and managed whole experiments and finalized the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Sun-Heum Cho and Sewon Oh authors contributed equally to this work.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cho, SH., Oh, S., Han, H. et al. QTL analysis and development of HRM markers associated with fruit shape in interspecific pears (Pyrus pyrifolia × P. bretschneideri). Euphytica 218, 122 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-022-03079-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-022-03079-9