Abstract
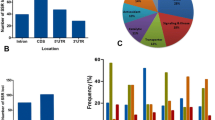
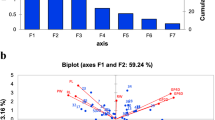
Developing host resistance is an effective measure to minimize the yield losses caused by biotic stresses in crop plants. Generation of genomic resources greatly facilitates the development of resistant plants. Microsatellite markers speed up the selection procedure and introgression of resistant alleles in rice breeding programme. Candidate gene based SSR (cgSSR) markers are preferred over genomic SSR due to their tighter linkage with the trait governing loci. This study describes the identification and analysis of cgSSR markers from biotic stress responsive genes of rice. Among the selected 308 different biotic stress responsive genes of rice, 176 gene sequences were found to harbour a total of 364 SSR loci. Tri-nucleotide motif was found to be the most abundant (51.09%), followed by di- (45.05%) and tetra-nucleotide (3.84%). Intron and CDS are the two locations where most of the cgSSR loci were found, followed by 5′UTR and 3′UTR. In order to validate, polymorphism survey was done in 25 Oryza sativa genotypes using 35 cgSSR primer pairs. Among the 35 cgSSR, 27 cgSSR exhibited loci specific amplification with an average allele number of 5.66 per primer and mean PIC value of 0.226. Further, out of 27, 21 cgSSRs were found to be cross transferable to the wild species belonging to the Sativa complex; while 19 were found to be transferable to the species belonging to the Officinalis complex. The novel biotic stress-responsive cgSSR markers developed here could be used in marker-assisted introgression and pyramiding of resistant allele into elite rice cultivars from other rice germplasm as well as from wild relatives of rice.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SSR:
-
Simple sequence repeat
- STMS:
-
Sequence tagged microsatellite site
- cgSSR:
-
Candidate gene based SSR
- UTR:
-
Untranslated region
- PIC:
-
Polymorphism information content
- QTL:
-
Quantitative trait loci
- EST:
-
Expressed sequence tag
- CDS:
-
Coding DNA sequence
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
- Ta:
-
Annealing temperature
- EDTA:
-
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
- PCoA:
-
Principal coordinates analysis
- BLB:
-
Bacterial leaf blight
- RDV:
-
Rice dwarf virus
- RSV:
-
Rice stripe virus
- ShB:
-
Sheath blight
- GO:
-
Gene ontology
References
Awika JM (2011) Major Cereal Grains Production and Use around the World thousands of years. Publication Date (Web): 30 Nov 2011
Babu BK, Agrawal PK, Gupta HS, Kumar A, Bhatt JC (2012) Identification of candidate gene–based SSR markers for lysine and tryptophan metabolic pathways in maize (Zea mays). Plant Breed 131:20–27
Baruah B, Senapoty D, Ali M (1992) False smut: a threat to rice growers in Assam. Indian J Mycol Plant Pathol 22:274–277
Bhandawat A, Singh G, Raina AS, Kaur J, Sharma RK (2016) Development of genic SSR marker resource from RNA-Seq data in Dendrocalamus latiflorus. J Plant Biochem Biotechnol 25:179–190
Botstein D, White RL, Skolnick M, Davis RW (1980) Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am J Hum Genet 32:314
Brar DS, Khush GS (2018) Wild relatives of rice: a valuable genetic resource for genomics and breeding research. In: Mondal TK, Henry RJ (eds) The Wild Oryza genomes. Springer, Cham, pp 1–25
Brondani C, Rangel PHN, Borba TCO, Brondani RPV (2003) Transferability of microsatellite and sequence tagged site markers in Oryza species. Hereditas 138:187–192
Cho YG et al (2000) Diversity of microsatellites derived from genomic libraries and GenBank sequences in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 100:713–722
Dillon NL, Innes DJ, Bally IS, Wright CL, Devitt LC, Dietzgen RG (2014) Expressed sequence tag-simple sequence repeat (EST-SSR) marker resources for diversity analysis of mango (Mangifera indica L.). Diversity 6:72–87
Feng S et al (2016) Development of SSR markers and assessment of genetic diversity in medicinal Chrysanthemum morifolium cultivars. Front Genet. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2016.00113
Gao L, Zhang C, Jia J (2005) Cross-species transferability of rice microsatellites in its wild relatives and the potential for conservation genetic studies. Genet Resour Crop Evol 52:931–940
Goicoechea JL, Ammiraju JSS, Marri PR, Chen M, Jackson S, Yu Y, Rounsley S, Wing RA (2010) The future of rice genomics: sequencing the collective Oryza genome. Rice 3(2–3):89–97
Gupta S, Bansal R, Gopalakrishna T (2014) Development and characterization of genic SSR markers for mungbean (Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek). Euphytica 195:245–258
Han Y et al (2015) Differential expression profiling of the early response to Ustilaginoidea virens between false smut resistant and susceptible rice varieties. BMC Genom 16:955
Hossain MK, Jena KK, Bhuiyan MAR, Wickneswari R (2016) Association between QTLs and morphological traits toward sheath blight resistance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Breed Sci 66(4):613–626
Jena KK, Kim S-M (2010) Current status of brown planthopper (BPH) resistance and genetics. Rice 3:161–171
Jia L et al (2012) Allelic analysis of sheath blight resistance with association mapping in rice. PLoS ONE 7:e32703
Kantety RV, La Rota M, Matthews DE, Sorrells ME (2002) Data mining for simple sequence repeats in expressed sequence tags from barley, maize, rice, sorghum and wheat. Plant Mol Biol 48:501–510
Kar MK, Bose LK, Cjhakraborti M., Azharudheen M., Ray S, Sarkar S, Dash SK, Reddy JN, Pani DR, Jena M, Mukherjee AK, Lenka S, Mohapatra SD, Jambhulkar NN (2018) Utilization of cultivated and wild Gene pools of rice for resistance to biotic stresses. In: Rice research for enhancing productivity, profitability and climate resilience, pp 52–72. ICAR-National Rice Research Institute, Cuttack, India. ISBN: 81-88409-04-9
Kayser M et al (2004) A comprehensive survey of human Y-chromosomal microsatellites. Am J Hum Genet 74:1183–1197
Khush GS, Bacalangco E, Ogawa T (1990) 18. A new gene for resistance to bacterial blight from O. longistaminata. Rice Genet News Lett 7:121–122
Li Y-C, Korol AB, Fahima T, Nevo E (2004) Microsatellites within genes: structure, function, and evolution. Mol Biol Evol 21:991–1007
Mahesh H, Shirke MD, Singh S, Rajamani A, Hittalmani S, Wang G-L, Gowda M (2016) Indica rice genome assembly, annotation and mining of blast disease resistance genes. BMC Genom 17:242
Metzgar D, Bytof J, Wills C (2000) Selection against frameshift mutations limits microsatellite expansion in coding DNA. Genome Res 10:72–80
Molla KA, Karmakar S, Chanda PK, Ghosh S, Sarkar SN, Datta SK, Datta K (2013) Rice oxalate oxidase gene driven by green tissue-specific promoter increases tolerance to sheath blight pathogen (Rhizoctonia solani) in transgenic rice. Mol Plant Pathol 14:910–922
Molla KA, Debnath AB, Ganie SA, Mondal TK (2015) Identification and analysis of novel salt responsive candidate gene based SSRs (cgSSRs) from rice (Oryza sativa L.). BMC Plant Biol 15:122
Molla KA, Karmakar S, Chanda PK, Sarkar SN, Datta SK, Datta K (2016) Tissue-specific expression of Arabidopsis NPR1 gene in rice for sheath blight resistance without compromising phenotypic cost. Plant Sci 250:105–114
Mondal TK, Henry RJ (eds) (2018) The Wild Oryza genomes. Springer, Berlin
Nessa B et al (2015) Spatial pattern of natural spread of rice false smut (Ustilaginoidea virens) disease in fields. Am J Agric Biol Sci 10:63
Oerke E-C (2006) Crop losses to pests. J Agric Sci 144:31–43
Parida SK, Kumar KAR, Dalal V, Singh NK, Mohapatra T (2006) Unigene derived microsatellite markers for the cereal genomes. Theor Appl Genet 112:808–817
Parida SK, Dalal V, Singh AK, Singh NK, Mohapatra T (2009) Genic non-coding microsatellites in the rice genome: characterization, marker design and use in assessing genetic and evolutionary relationships among domesticated groups. BMC Genom 10:140
Perrier X, Jacquemoud-Collet JP (2006) DARwin software. http://darwin.cirad.fr/
Ray DK, Mueller ND, West PC, Foley JA (2013) Yield trends are insufficient to double global crop production by 2050. PLoS ONE 8:e66428
Ray S et al (2016) Development and validation of cross-transferable and polymorphic DNA markers for detecting alien genome introgression in Oryza sativa from Oryza brachyantha. Mol Genet Genom 291:1783–1794. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-016-1214-z
Ray S, Vijayan J, Chakraborti M, Sarkar S, Bose LK, Singh ON (2018) Oryza officinalis complex. In: Mondal TK, Henry RJ (eds) The Wild Oryza genomes. Springer, Cham, pp 239–258
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Sallaud C et al (2003) Identification of five new blast resistance genes in the highly blast-resistant rice variety IR64 using a QTL mapping strategy. Theor Appl Genet 106:794–803
Sharma A, Chauhan R (2008) Identification of candidate gene-based markers (SNPs and SSRs) in the zinc and iron transporter sequences of maize (Zea mays L). Curr Sci 95(8):1051–1059
Singh H et al (2010) Highly variable SSR markers suitable for rice genotyping using agarose gels. Mol Breed 25:359–364
Sun R, Lin F, Huang P, Zheng Y (2016) Moderate genetic diversity and genetic differentiation in the relict tree Liquidambar formosana Hance revealed by genic simple sequence repeat markers. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01411
Temnykh S, DeClerck G, Lukashova A, Lipovich L, Cartinhour S, McCouch S (2001) Computational and experimental analysis of microsatellites in rice (Oryza sativa L.): frequency, length variation, transposon associations, and genetic marker potential. Genome Res 11:1441–1452
Thumilan BM, Sajeevan R, Biradar J, Madhuri T, Nataraja KN, Sreeman SM (2016) Development and characterization of genic SSR markers from Indian mulberry transcriptome and their transferability to related species of Moraceae. PLoS ONE 11:e0162909
Tian T, Liu Y, Yan H, You Q, Yi X, Du Z, Xu W, Su Z (2017) agriGO v2. 0: a GO analysis toolkit for the agricultural community, 2017 update. Nucl Acids Res 45(W1):W122–W129
van Berloo R (2008) GGT 2.0: versatile software for visualization and analysis of genetic data. J Hered 99(2):232–236
Varshney RK, Thiel T, Stein N, Langridge P, Graner A (2002) In silico analysis on frequency and distribution of microsatellites in ESTs of some cereal species. Cell Mol Biol Lett 7:537–546
Yu J-K, Dake TM, Singh S, Benscher D, Li W, Gill B, Sorrells ME (2004) Development and mapping of EST-derived simple sequence repeat markers for hexaploid wheat. Genome 47:805–818
Yue X-y, Liu G-q, Zong Y, Teng Y-w, Cai D-y (2014) Development of genic SSR markers from transcriptome sequencing of pear buds. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 15:303
Zhang S et al (2014) Development of highly polymorphic simple sequence repeat markers using genome-wide microsatellite variant analysis in Foxtail millet [Setaria italica (L.) P. Beauv.]. BMC Genom 15:78
Zheng X et al (2015) Development and characterization of genic-SSR markers from different Asia lotus (Nelumbo nucifera) types by RNA-seq. Genet Mol Res 14:11171–11184
Acknowledgements
Authors are thankful to the Director, ICAR-National Rice Research Institute for encouragement and providing all facilities to carry out research work. Thanks are due to the Genebank of ICAR-NRRI, Cuttack for providing the germplasm.
Funding
The work was funded by Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), New Delhi. The Funding body has no role in the design of the study and collection, analysis, and interpretation of data and in writing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KAM conceptualized, designed and planned the study. KAM, TPMA, SR, AS and SS performed the experiments. KAM, TPMA, SR, SS, MC, JV, ONS, MJB and AKM analysed the data. KAM wrote the manuscript. TPMA, MC, SR and SS edited the manuscript. JV, ONS, MJB and AKM critically revised the manuscript. KAM, TPMA, SR and AS are responsible for preparing different tables and figures. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article and in additional files (Additional file 1-6).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Molla, K.A., Azharudheen, T.P.M., Ray, S. et al. Novel biotic stress responsive candidate gene based SSR (cgSSR) markers from rice. Euphytica 215, 17 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-018-2329-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-018-2329-6