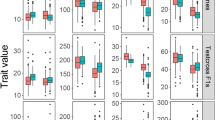
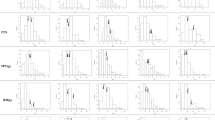
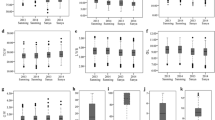
Abstract
In the present study, a set of 79 rice introgression lines (ILs) carrying variant introgressed segments of African rice (Oryza glaberrima Stued.) was used to identify quantitative trait loci (QTL) and heterotic loci (HL) associated with 7 agronomic traits. A total of 180 polymorphic markers between the donor and recurrent parents were found and 115 markers were used to identify the segregation of the introgression fragments. Based on the genotypic data of the ILs and test variety GZ63S as well as the phenotypic data of the IL and PIH, QTLs and HLs can be mapped on introgressed chromosome segments. One representative marker on each specific introgressed segment was defined as a QTL or a HL. 24 QTLs associated with six agronomic traits were mapped on 9 chromosomes and 23 interspecific HLs for seven agronomic traits were identified on 10 chromosomes in 2 years. Among them, 22 QTLs and 19 HLs were found to be associated with 5 yield-related traits respectively. The PIH (F1) testcross population showed superiority in most yield-related traits and was characterized by a high frequency of overdominant interspecific HLs. In addition, the pleiotropism was found in 5 marker loci for 11 QTLs associated with five agronomic traits and 4 marker loci for ten interspecific HLs for all the seven traits. This study is the first attempt for the identification of interspecific HLs between the two cultivated rice species, Asian rice (Oryza sativa L.) and African rice (O. glaberrima Steud.). Therefore, our results may help to lay the foundation for exploring the genetic mechanism of interspecific heterosis in rice.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DH:
-
Days to heading
- FG:
-
Filled grain per panicle
- GD:
-
Genetic diversity
- GGT:
-
Graphical genotypes
- GW:
-
Grains weight
- HL:
-
Heterotic loci
- IL:
-
Introgression line
- LOD:
-
Logarithm of odds ratio
- MPH:
-
Mid-parent heterosis
- OD:
-
Over-dominance
- PN:
-
Panicles per plant
- PD:
-
Partial-dominance
- PIH:
-
Partial interspecific hybrid
- PH:
-
Plant height
- P/TGMS:
-
Photo/thermo-sensitive genetic male sterility
- PIC:
-
Polymorphism information content
- QTL:
-
Quantitative trait loci
- SN:
-
Spikelets per panicle
- SS:
-
Seed setting rate
- SSR:
-
Simple sequence repeats
References
Adedze YM, Efisue AA, Zhang SS, Samoura D, Huang F, He WC, Xie GS, Jin DM (2012) Identification of interspecific grain yield heterosis between two cultivated rice species Oryza sativa L. and Oryza glaberrima Steud. Austr J Crop Sci 6:1558–1564
Agnoun Y, Sié M, Djedatin G, Dramé KN, Toulou B, Ogunbayo SA, Sanni KA, Tia D, Ahanchédé A, Vodouhè RS, Ndjiondjop MN (2012) Molecular profiling of interspecific lowland rice progenies resulting from crosses between TOG5681 and TOG5674 (Oryza glaberrima) and IR64 (Oryza sativa). Internat J Bio 4(3):19
Aluko G, Martinez C, Tohme J, Castano C, Bergman C, Oard JH (2004) QTL mapping of grain quality traits from the interspecific cross Oryza sativa x O. glaberrima. Theor Appl Genet 109(3):630–639
Biet E, Sun J, Dutreix M (1999) Conserved sequence preference in DNA binding among recombination proteins: an effect of ssDNA secondary structure. Nucleic Acids Res 27:596–600
Bimpong IK, Carpena AL, Mendioro MS, Fernandez JR, Ramos J, Reversat G, Brar DS (2010) Evaluation of Oryza sativa × Oryza glaberrima derived progenies for resistance to root knot nematode and identification of introgressed alien chromosome segments using SSR markers. Afr J Biotech 9:3988–3997
Brandle JE, McVetty PBE (1990) Geographic diversity, parental selection, and heterosis in oilseed rape. Can J Plant Sci 70:935–940
Chen CJ, He WC, Nassirou TY, Zhou W, Yin YL, Dong XL, Rao QQ, Shi H, Zhao W, Efisue A, Jin DM (2016) Genetic diversity and phenotypic variation in an introgression line population derived from an interspecific cross between Oryza glaberrima and Oryza sativa. PLoS ONE 11(9):e0161746. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0161746
Cheng SH, Li YC, Jie YZ et al (2007) Super hybrid rice breeding in China: achievements and prospects. J Integr Plant Biol 49(6):805–810
Dai XD, Ding YN, Tan LB, Fu YC, Liu FX, Zhu ZF, Sun XY, Sun XW, Gu P, Cai HW, Sun CQ (2012) HD1, an allele of DTH8/Ghd8, controls late heading date in common wild rice (Oryza rufipogon). J Integr Plant Biol 54:790–799
Davenport CB (1908) Degeneration, albinism and inbreeding. Science 28(718):454–455
Efisue AA, Tongoona P, Derera J, Ubi BE (2009) Screening early-generation progenies of interspecific rice genotypes for drought-stress tolerance during vegetative phase. J Crop Improv 23:174–193
Feng XM, Juan H, Qi HH, Huang YQ, Zhu LY, Zhao YF, Zheng Q, Li WZ, Bing Y (2012) Identification of heterotic loci for seven yield and yield-related traits in maize with a set of introgression lines. Austr J Crop Sci 6(12):1661–1665
Fukuta Y, Konisho K, Senoo-Namai S, Yanagihara S, Tsunematsu H, Fukuo A, Kumashiro T (2012) Genetic characterization of rainfed upland New Rice for Afirca (NERICA) varieties. Breed Sci 62:27–37
Ghesquière A, Séquier J, Second G, Lorieux M (1997) First steps towards a rational use of African rice, Oryza glaberrima, in rice breeding through a ‘contig line’ concept. Euphytica 96(1):31–39
Guo X, Guo YP, Ma J, Wang F, Sun MZ, Gui LJ, Zhou JJ, Song XL, Sun XZ, Zhang TZ (2013) Mapping heterotic loci for yield and agronomic traits using chromosome segment introgression lines in cotton. J Integr Plant Biol 55(8):759–774
Gutierrez AG, Carabali SJ, Giraldo OX, Martinez CP, Correa F, Prado G, Tohme J, Lorieux M (2010) Identification of a rice stripe necrosis virus resistance locus and yield component QTLs using Oryza sativa x O. glaberrima introgression lines. BMC Plant Bio. doi:10.1186/1471-2229-10-6
Heuer S, Miezan KM (2003) Assessing hybrid sterility in Oryza glaberrima × O. sativa hybrid progenies by PCR marker analysis and crossing with wide compatibility varieties. Theor Appl Genet 107(5):902–909
Hu FY, Tao DY, Yang YQ, Xu P, Li J, Zhou JW (2002) Studies of vegetative heterosis of interspecific hybrids between Oryza sativa and Oryza glaberrima. J Southwest Agric Univ 2002-02
Hu FY, Xu P, Deng XN et al (2006) Molecular mapping of a pollen killer gene S29 (t) in Oryza glaberrima and co-linear analysis with S22 in O. glumaepatula. Euphytica 151(3):273–278
Hu ZJ, He HH, Zhang SY, Sun F, Xin XY, Wang WX, Qian X, Yang JS, Luo XJ (2012) A kelch motif-containing serine/threonine protein phosphatase determines the large grain QTL trait in rice. J Integr Plant Biol 54:979–990
Hua JP, Xing YZ, Wu WR, Xu CG, Sun XL, Yu SB, Zhang QF (2003) Single-locus heterotic effects and dominance by dominance interaction can adequately explain the genetic basis of heterosis in an elite hybrid. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:2574–2579
Huang F, Xi F, Efisue AA, Zhang SS, Xie GS, He WC, Adedze YMN, Jin DM (2012) Genetically characterizing a new indica cytoplasmic male sterility with Oryza glaberrima cytoplasm for its potential use in hybrid rice production. Crop Sci 53(1):132–140. doi:10.2135/cropsci2012.07.0444
Hull FH (1945) Recurrent selection for specific combining ability in corn. J Am Soc Agron 37(2):134–145
Ikeda R, Yoshimi S, Inoussa A (2009) Seed fertility of F1 hybrids between upland rice NERICA cultivars and Oryza sativa L. or O.glaberrima Steud. Breed Sci 59:27–35
Ikehashi H, Araki H (1986) Genetics of F1 sterility in remote crosses of rice. Rice genetics. International Rice Research Institute, Manila, pp 119–130
Jaikishan I, Rajendrakumar P, Ramesha MS et al (2010) Prediction of heterosis for grain yield in rice using key informative EST-SSR. Plant Breed 129(1):108–111
Jin DM, Nassirou TY (2015) Progress and perspectives of distant heterosis in rice. In: Al-Khayri JM, Jain SM, Dennis VJ (eds) Advances in plant breeding strategies: breeding, biotechnology and molecular tools, vol 1. Springer, Switzerland. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-22521-0
Jin DM, Efisue AA, Zhang SS, et al. (2012) Developing a new indica CMS system and introgression restorer lines via interspecific crosses between Oryza glaberrima Steud. and Oryza sativa L. Abstract presented at the international conference on utilization of heterosis in crops, Xi’an, China, pp 264–265
Jones JW (1926) Hybrid vigour in rice. J Am Soc Agr 18(5):423–428
Jones MP, Dingkuhn M, DE Johnson, Sow A (1998) Growth and yield potential of Oryza sativa and O. glaberrima upland rice cultivars and their interspecific progenies. Field Crop Res 57(1):57–69
Li ZK, Xie QG, Zhu ZL, Liu JL, Han SX, Tian B, Yuan QQ, Tian JC (2010) Analysis of plant height heterosis based on QTL mapping in wheat. Acta Agron Sin 36:771–778
Li F, Liu FH, Morinaga DZ (2011) A new gene for hybrid sterility from a cross between Oryza sativa and O. glaberrima. Plant Breed 130(2):165–171
Linares OF (2002) African rice (Oryza glaberrima): history and future potential. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99(25):16360–16365
Liu RH, Meng JL (2003) MapDraw: a Microsoft Excel macro for drawing genetic linkage maps based on given genetic linkage data. Heraditas (Beijing) 25(3):317–321
Liu K, Muse SV (2005) PowerMaker: an integrated analysis environment for genetic maker analysis. Bioinformatics 21(9):2128–2129
Lorieux M, Ndjiondjop MN, Ghesquière A (2000) A first interspecific Oryza sativa × Oryza glaberrima microsatellite-based genetic linkage map. Theor Appl Genet 100(3):593–601
Luo XJ, Fu YC, Zhang PJ, Wu S, Tian F, Liu JY, Zhu ZF, Yang JS, Sun CQ (2009) Additive and over-dominant effects resulting from epistatic loci are the primary genetic basis of heterosis in rice. J Integr Plant Biol 51:393–408
Luo XJ, Wu S, Tian F, Xin XY, Zha XJ, Dong XX, Fu YC, Wang XK, Yang JS, Sun CQ (2011) Identification of heterotic loci associated with yield-related traits in Chinese common wild rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.). Plant Sci 181:14–22
Ma LY, Bao JS, Guo LB, Zeng DL, Li XM, Ji ZJ, Xia YW, Yang CD, Qian Q (2009) Quantitative trait loci for panicle layer uniformity identified in doubled haploid lines of rice in two environments. J Integr Plant Biol 51:818–824
Monforte AJ, Tanksley SD (2000) Development of a set of near isogenic and backcross recombinant inbred lines containing most of the Lycopersicon hirsutum genome in a L. esculentum genetic background: a tool for gene mapping and gene discovery. Genome 43:803–813
Nassirou TY, He YQ (2011) NERICA: a hope for fighting hunger and poverty in Africa. Mol Plant Breed. doi:10.5376/mpb.2011.02.0011
Ndjiondjop MN, Futakuchi K, Seck PA, Cisse F, Bocco R, Fatondji B (2012) Morpho-agronomic evaluation of Oryza glaberrima accessions and interspecific Oryza sativa × Oryza glaberrima derived lines under drought conditions. Afr J Agric Res 7:2527–2538
Pasam RK, Sharma R, Malosetti M, van Eeuwijk FA et al (2012) Genome-wide association studies for agronomical traits in a worldwide spring barley collection. BMC Plant Biol 27:12–16
Piffanelli P, Droc G, Mieulet D, Lanau N, Bes M, Bourgeois E, Rouviere C, Gavory F, Cruaud C, Ghesquière A et al (2007) Large-scale characterization of Tos17 insertion sites in a rice T-DNA mutant library. Plant Mol Biol 65(5):587–601
Powers L (1944) An expansion of Jones’s theory for the explanation of heterosis. Am Nat 78:275–280
Qiu SQ, Liu K, Jiang JX et al (2005) Delimitation of the rice wide compatibility gene S5n to a 40-kb DNA fragment. Theor Appl Genet 111(6):1080–1086
Sano Y (1986) Sterility barriers between Oryza sativa and O. glaberrima. International Rice Research Institute-Rice Genet, IRRI, Manila, pp 109–118
Sarla N, Swamy B (2005) Oryza glaberrima a source for the improvement of Oryza sativa. Curr Sci 89(6):955–963
Sasaki T (2003) Rice genome analysis: understanding the genetic secrets of the rice plant. Breed Sci 53(4):281–289
Semagn K, Ndjiondjop MN, Lorieux M, Cissoko M, Jones M, McCouch S (2007) Molecular profiling of an interspecific rice population derived from a cross between WAB 56-104 (Oryza sativa) and CG 14 (Oryza glaberrima). Afr J Biotech 6(17):2014–2022
Semel Y, Nissenbaum J, Menda N, Zinder M, Krieger U, Issman N, Pleban T, Lippman Z, Gur A, Zamir D (2006) Overdominant quantitative trait loci for yield and fitness in tomato. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:12981–12986
Shen GJ, Zhan W, Chen HX, Xing YZ (2014) Dominance and epistasis are the main contributors to heterosis for plant height in rice. Plant Sci 215–216:11–18
Syed NH, Chen ZJ (2005) Molecular marker genotypes, heterozygosity and genetic interactions explain heterosis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Heredity 94:295–304
Tang JH, Yan JB, Ma XQ, Teng WT, Wu WR, Dal JR, Dhillon BS, Mechinger AE, Li JS (2010) Dissection of the genetic basis of heterosis in an elite maize hybrid by QTL mapping in an immortalized F2 population. Theor Appl Genet 120:333–340
Van Andel T (2010) African rice (Oryza glaberrima Steud.): lost crop of the enslaved Africans discovered in Suriname. Eco Bot 64(1):1–10
Van Berloo R (1999) GGT: software for the display of graphical genotypes. J Hered 90:328–329
Virmani SS, Chaudhary RC, Khush GS (1981) Current outlook on hybrid rice. Oryza 18:67–84
Wang LQ, Zhao YF, Xue YD, Zhang ZX, Zheng YL, Chen JT (2007) Development and evaluation of two link-up single segment introgression lines (SSILs) in Zea mays. Acta Agron Sin 33:663–668
Wang ZQ, Jian L, Yin CB, Wang XL, Lei JG, Xiao YL, Liu X, Liu SJ, Chen LM, Yu CY, Wan JM (2013) QTL mapping of heterotic loci of yield-related traits in rice. Chin J Rice Sci 27(6):569–576. doi:10.3969/j.issn1001G7216.2013.06.002
Wang MH, Yu YS, Georg H, Pradeep RM et al (2014) The genome sequence of African rice (Oryza glaberrima) and evidence for independent domestication. Nature Genet. doi:10.1038/ng.3044
Wang ZQ, Wang XL, Lei JG, Xiao YL, Li MZ, Yu CY (2015) QTL mapping and analysis of heterotic loci in three-line hybrid rice by using chromosome segment substitution lines. Acta Agric Univ Jiangxi 37(5):765–773. doi:10.13836/j.jjau.2015116
Wang J, Li H, Zhang L, Meng L (2016) Users’ manual of QTL IciMapping. The Quantitative Genetics Group, Institute of Crop Science, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS), Genetic Resources Program, International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT), Beijing, Mexico
Wei XY, Bin W, Qian P, Feng W, Mao KJ, Zhang XG, Pei S, Liu ZH, Tang JH (2015) Heterotic loci for various morphological traits of maize detected using a single segment substitution lines test-cross population. Mol Breed 35:94. doi:10.1007/s11032-015-0287-4
Wing RA, Ammiraju JS, Luo M, Kim H, Yu Y, Kudrna D, Goicoechea JL, Wang W, Nelson W, Rao K et al (2005) The Oryza map alignment project: the golden path to unlocking the genetic potential of wild rice species. Plant Mol Biol 59(1):53–62
Xin XY, Wang WX, Yang JS, Luo XJ (2011) Genetic analysis of heterotic loci detected in a cross between indica and japonica rice (Oryza sativa L.). Breed Sci 61:380–388
Young ND, Tanksley SD (1989) Restriction fragment length polymorphism maps and the concept of graphical genotypes. Theor Appl Genet 77:95–101
Yu SB, Li JX, Xu CG, Tan YF, Gao YJ, Zhang QF, Maroof MA (1997) Importance of epistasis as the genetic basis of heterosis in an elite rice hybrid. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:9226–9231
Zhao FM, Zhang GQ, Zeng RZ, Yang ZL, Ling YH, Sang XC, He GH (2011) Analysis of epistatic and additive effects of QTLs for grain shape using single segment substitution lines in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Acta Agron Sin 37:469–476
Zhuang JY, Fan YY, Wu JL, Xia YW, Zheng KL (2001) Overdominant effect plays an important role in heterosis of rice. Sci China Ser C 31:106–113
Acknowledgements
We are thankful to Dr. Andrew A. Efisue, Ph.D., Departments of Crop and Soil Science, University of Port Harcourt, Port Harcourt, Nigeria, for providing the African rice variety material. This study was funded by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2013PY134), Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education (20130146110026).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nassirou, T.Y., He, W., Chen, C. et al. Identification of interspecific heterotic loci associated with agronomic traits in rice introgression lines carrying genomic fragments of Oryza glaberrima . Euphytica 213, 176 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-017-1967-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-017-1967-4