Abstract
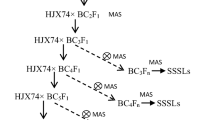
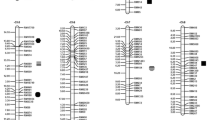
Chromosome segment substitution line (CSSL) population is potential in precisely detecting and pyramiding genes/QTL/segments due to the genetic background noise removed. To exploit and utilize the favorable wild alleles, a CSSL population with 151 lines (SojaCSSLP1) was generated using a wild soybean (Glycine soja Sieb. et Zucc.) N24852 as donor parent and the elite cultivar NN1138-2 as its genetic background. An improved CSSL construction strategy was used, i.e. continuous backcross after initial crossing followed with alternation of backcross and selfing combined with marker-assisted selection based on pedigree DNA pools and phenotypic differences among pedigrees. The SojaCSSLP1 with an average recovery ratio of 95.7 % of the NN1138-2 genome could cover the entire genome of wild soybean. Four wild alleles/segments for each of the two wild characteristics, longer plant height (PH) and more number of nodes on main stem (NN), in a total of six segments, were detected with additive effects all positive. Among them, Satt243 on Chr.10 and Sat_286 on Chr.19 associated with both PH and NN while Satt338 and SOYGPATR on Chr.4 and Satt314 neighboring with Satt192 on Chr.12 had the former and latter on each chromosome associated with PH and NN, respectively. That could explain the high positive correlation between the two traits (r = 0.88). Compared with those in the literature, three QTL/segments for PH and one for NN were detected also among cultivated soybeans, indicating allele differentiation happened not only between wild and cultivated but also among cultivated soybeans. Therefore these QTL/segments might be the key ones to explain the domestication and evolution of soybean. In addition, SojaCSSLP1 should be also potential in studies for multiple wild traits due to its broad variation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alpert KB, Tanksley SD (1996) High-resolution mapping and isolation of a yeast artificial chromosome contig containing fw2.2: a major fruit weight quantitative trait locus in tomato. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:15503–15507
Bernacchi D, Beck-Bunn T, Eshed Y, Lopez J, Petiard V, Uhlig J, Zamir D, Tanksley S (1998) Advanced backcross QTL analysis in tomato. I. Identification of QTLs for traits of agronomic importance from Lycopersicon hirsutum. Theor Appl Genet 97:381–397
Bian JM, Jiang L, Liu LL, Wei XJ, Xiao YH, Zhang LJ, Zhao ZG, Zhai HQ, Wan JM (2010) Construction of a new set of rice chromosome segment substitution lines and identification of grain weight and related traits QTLs. Breed Sci 60:305–313
Broich SL, Palmer RG (1980) A cluster analysis of wild and domesticated soybean phenotypes. Euphytica 29:23–32
Chen QS, Zhang ZC, Liu CY, Xin DW, Qiu HM, Shan DP, Shan CY, Hu GH (2007) QTL analysis of major agronomic traits in soybean. Agric Sci China 6:399–405
Concibido VC, La Vallee B, Mclaird P, Pineda N, Meyer J, Hummel L, Yang J, Wu K, Delannay X (2003) Introgression of a quantitative trait locus for yield from Glycine soja into commercial soybean cultivars. Theor Appl Genet 106:575–582
Doi K, Iwata N, Yoshimura A (1997) The construction of chromosome substitution lines of African rice (Oryza glaberrima Steud.) in the background of Japonica rice (O. sativa L.). Rice Genet Newsl 14:39–41
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1990) Isolation of plant DNA from fresh tissue. Focus 12:13–15
Ebitani T, Takeuchi Y, Nonoue Y, Yamamoto T, Takeuchi K, Yano M (2005) Construction and evaluation of chromosome segment substitution lines carrying overlapping chromosome segments of Indica rice cultivar in a genetic background of Japonica elite cultivar ‘Koshihikari’. Breed Sci 55:65–73
Eshed Y, Zamir D (1994) A genomic library of Lycopersicon pennellii in L. esculentum: a tool for fine mapping of genes. Euphytica 79:175–179
Eshed Y, Zamir D (1995) An introgression line population of Lycopersicon pennellii in the cultivated tomato enables the identification and fine mapping of yield-associated QTL. Genetics 141:1147–1162
Finkers R, van Heusden AW, Meijer-Dekens F, van Kan JAL, Maris P, Lindhout P (2007) The construction of a Solanum habrochaites LYC4 introgression line population and the identification of QTLs for resistance to Botrytis cinerea. Theor Appl Genet 114:1071–1080
Hao W, Jin J, Sun SY, Zhu MZ, Lin HX (2006) Construction of chromosome segment substitution lines carrying overlapping chromosome segments of the whole wild rice genome and identification of quantitative trait loci for rice quality. J Plant Physiol Mol Biol 32:354–362 (in Chinese)
Hirabayashi H, Sato H, Nonoue Y, Kuno-Takemoto Y, Takeuchi Y, Kato H, Nemoto H, Ogawa T, Yano M, Imbe T, Ando I (2010) Development of introgression lines derived from Oryza rufipogon and O. glumaepatula in the genetic background of Japonica cultivated rice (O. sativa L.) and evaluation of resistance to rice blast. Breed Sci 60:604–612
Hyten DL, Choi IY, Song QJ, Specht JE, Carter TE, Shoemaker RC, Hwang EY, Matukumalli LK, Cregan PB (2010) A high density integrated denetic linkage map of soybean and the development of a 1536 universal soy linkage panel for quantitative trait locus mapping. Crop Sci 50:960–968
Jin J, Huang W, Gao JP, Yang J, Shi M, Zhu MZ, Luo D, Lin HX (2008) Genetic control of rice plant architecture under domestication. Nat Genet 40:1365–1369
Kornegay J, White JW, Cruz OO (1992) Growth habit and gene pool effects on inheritance of yield in common bean. Euphytica 62:171–180
Kubo T, Aida Y, Nakamura K, Tsunematsu H, Doi K, Yoshimura A (2002) Reciprocal chromosome segment substitution series derived from Japonica and Indica cross of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Breed Sci 52:319–325
Kuspira J, Unrau J (1957) Genetic analysis of certain characters in common wheat using whole chromosome substitution lines. Can J Plant Sci 37:300–326
Lee SH, Bailey MA, Mian MAR, Carter T Jr, Ashley D, Hussey R, Parrott W, Boerma H (1996a) Molecular markers associated with soybean plant height, lodging, and maturity across locations. Crop Sci 36:728–734
Lee SH, Bailey MA, Mian MAR, Shipe ER, Ashley DA, Parrott WA, Hussey RS, Boerma HR (1996b) Identification of quantitative trait loci for plant height, lodging, and maturity in a soybean population segregating for growth habit. Theor Appl Genet 92:516–523
Li HH, Ye GY, Wang JK (2007) A modified algorithm for the improvement of composite interval mapping. Genetics 175:361–374
Li DD, Pfeiffer TW, Cornelius PL (2008) Soybean QTL for yield and yield components associated with Glycine soja alleles. Crop Sci 48:571–581
Li CD, Jiang HW, Guo T, Wang ZX, Wu XH, Zheng W, Chen QS, Hu GH (2011) QTL identification of plant height and analysis of genotype to soybean in selection population. Soybean Sci 30:15–19 (in Chinese)
Liu S, Zhou R, Dong Y, Li P, Jia J (2006) Development, utilization of introgression lines using a synthetic wheat as donor. Theor Appl Genet 112:1360–1373
Manly KF, Cudmore JRH, Meer JM (2001) Map Manager QTX, cross-platform software for genetic mapping. Mamm Genome 12:930–932
Matus I, Corey A, Filchkin T, Hayes PM, Vales MI, Kling J, Riera-Lizarazu O, Sato K, Powell W, Waugh R (2003) Development and characterization of recombinant chromosome substitution lines (RCSLs) using Hordeum vulgare subsp. spontaneum as a source of donor alleles in a Hordeum vulgare subsp. vulgare background. Genome 46:1010–1023
Monforte AJ, Tanksley SD (2000) Development of a set of near isogenic and backcross recombinant inbred lines containing most of the Lycopersicon hirsutum genome in a L. esculentum genetic background: a tool for gene mapping and gene discovery. Genome 43:803–813
Orf JH, Chase K, Jarvik T, Mansur LM, Cregan PB, Adler FR, Lark KG (1999) Genetics of soybean agronomic traits: I. Comparison of three related recombinant inbred populations. Crop Sci 39:1652–1656
Panaud O, Chen X, McCouch SR (1996) Development of microsatellite markers and characterization of simple sequence length polymorphism (SSLP) in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Mol Gen Genet 252:597–607
Paterson AH (1995) Molecular dissection of quantitative traits: progress and prospects. Genome Res 5:321–333
Peleman JD, van der Voort JR (2003) Breeding by design. Trends Plant Sci 8:330–334
Pillen K, Zacharias A, Leon J (2003) Advanced backcross QTL analysis in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Theor Appl Genet 107:340–352
Pillen K, Zacharias A, Leon J (2004) Comparative AB-QTL analysis in barley using a single exotic donor of Hordeum vulgare ssp. spontaneum. Theor Appl Genet 101:340–352
Reinprecht Y, Poysa VW, Yu KF, Rajcan I, Ablett GR, Pauls KP (2006) Seed and agronomic QTL in low linolenic acid, lipoxygenase-free soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merrill) germplasm. Genome 49:1510–1527
Song QJ, Marek LF, Shoemaker RC, Lark KG, Concibido VC, Delannay X, Specht JE, Cregan PB (2004) A new integrated genetic linkage map of the soybean. Theor Appl Genet 109:122–128
Specht JE, Chase K, Macrander M, Graef GL, Chung J, Markwell JP, Germann M, Orf JH, Lark KG (2001) Soybean response to water: a QTL analysis of drought tolerance. Crop Sci 41:493–509
Takai T, Nonoue Y, Yamamoto S-I, Yamanouchi U, Matsubara K, Liang Z-W, Lin H-X, Ono N, Uga Y, Yano M (2007) Development of chromosome segment substitution lines derived from backcross between indica donor rice cultivar ‘Nona Bokra’ and japonica recipient cultivar ‘Koshihikari’. Breed Sci 57:257–261
Tan LB, Liu FX, Xue W, Wang GJ, Ye S, Zhu ZF, Fu YC, Wang XK, Sun CQ (2007) Development of Oryza rufipogon and O. sativa introgression lines and assessment for yield-related quantitative trait loci. J Integr Plant Biol 49:871–884
Tan LB, Li XR, Liu FX, Sun XY, Li CG, Zhu ZF, Fu YC, Cai HW, Wang XK, Xie DX, Sun CQ (2008) Control of a key transition from prostrate to erect growth in rice domestication. Nat Genet 40:1360–1364
Tanksley SD, Nelson JC (1996) Advanced backcross QTL analysis: a method for the simultaneous discovery and transfer of valuable QTLs from unadapted germplasm into elite breeding lines. Theor Appl Genet 92:191–203
Tian F, Li DJ, Fu Q, Zhu ZF, Fu YC, Wang XK, Sun CQ (2006) Construction of introgression lines carrying wild rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.) segments in cultivated rice (Oryza sativa L.) background and characterization of introgressed segments associated with yield-related traits. Theor Appl Genet 112:570–580
Torjek O, Meyer RC, Zehnsdorf M, Teltow M, Strompen G, Witucka-Wall H, Blacha A, Altmann T (2008) Construction and analysis of 2 reciprocal arabidopsis introgression line populations. J Hered 99:396–406
van Berloo R (2008) GGT 2.0: versatile software for visualization and analysis of genetic data. J Hered 99:232–236
Wan XY, Weng JF, Zhai HQ, Wang JK, Lei CL, Liu XL, Guo T, Jiang L, Su N, Wan JM (2008) Quantitative trait loci (QTL) analysis for rice grain width and fine mapping of an identified QTL allele gw-5 in a recombination hotspot region on chromosome 5. Genetics 179:2239–2252
Wang D, Graef GL, Procopiuk AM, Diers BW (2004) Identification of putative QTL that underlie yield in interspecific soybean backcross populations. Theor Appl Genet 108:458–467
Wang LQ, Zhao YF, Xue YD, Zhang ZX, Zheng YL, Chen JT (2007) Development and evaluation of two link-up single segment introgression lines (SSILs) in Zea mays. Acta Agron Sin 33:663–668 (in Chinese)
Wang P, Ding YZ, Lu QX, Guo WZ, Zhang TZ (2008) Development of Gossypium barbadense chromosome segment substitution lines in the genetic standard line TM-1 of Gossypium hirsutum. Chin Sci Bull 53:1512–1517
Wei XJ, Liu LL, Xu JF, Jiang L, Zhang WW, Wang JK, Zhai HQ, Wan JM (2010) Breeding strategies for optimum heading date using genotypic information in rice. Mol Breed 25:287–298
Xi ZY, He FH, Zeng RZ, Zhang ZM, Ding XH, Li WT, Zhang GQ (2006) Development of a wide population of chromosome single-segment substitution lines in the genetic background of an elite cultivar of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Genome 49:476–484
Xiao JH, Grandillo S, Ahn SN, McCouch SR, Tanksley SD, Li JM, Yuan LP (1996) Genes from wild rice improve yield. Nature 384:223–224
Xu HS, Sun YJ, Zhou HJ, Yu SB (2007) Development and characterization of contiguous segment substitution lines with background of an elite restorer line. Acta Agron Sin 33:979–986 (in Chinese)
Yamamoto T, Lin HX, Sasaki T, Yano M (2000) Identification of heading date quantitative trait locus Hd6 and characterization of its epistatic interactions with Hd2 in rice using advanced backcross progeny. Genetics 154:885–891
Yang J, Zhu J, Williams RW (2007) Mapping the genetic architecture of complex traits in experimental populations. Bioinformatics 23:1527–1536
Young ND, Tanksley SD (1989) Restriction fragment length polymorphism maps and the concept of graphical genotypes. Theor Appl Genet 77:95–101
Zamir D (2001) Improving plant breeding with exotic genetic libraries. Nat Rev Genet 2:983–989
Zhang WK, Wang YJ, Luo GZ, Zhang JS, He CY, Wu XL, Gai JY, Chen SY (2004) QTL mapping of ten agronomic traits on the soybean (Glycine max L. Merr.) genetic map and their association with EST markers. Theor Appl Genet 108:1131–1139
Zhou B, Xing H, Chen SY, Gai JY (2010a) Density-enhanced genetic linkage map of RIL population NJRIKY and its impacts on mapping genes and QTLs in soybean. Acta Agro Sinica 36:36–46 (in Chinese)
Zhou R, Chen HF, Wang XZ, Zhang XJ, Shan ZH, Wu XJ, Qiu DZ, Wu BD, Sha AH, Yang ZL, Zhou XA (2010b) Dynamic analysis of QTL for plant height and stem diameter at different developmental stages in soybean. J Plant Genet Resour 11:345–359 (in Chinese)
Acknowledgments
We would thank all the participants in the research for their assistance, advice and encouragement. This work was supported by the National Key Basic Research Program of China (2009CB1184, 2010CB1259, 2011CB1093), the National Hightech R&D Program of China (2011AA10A105, 2012AA101106), the Natural Science Foundation of China (31071442), the MOA Public Profit Program (200803060) and the MOE 111 Project (B08025).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, W., He, Q., Yang, H. et al. Development of a chromosome segment substitution line population with wild soybean (Glycine soja Sieb. et Zucc.) as donor parent. Euphytica 189, 293–307 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-012-0817-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-012-0817-7