Abstract
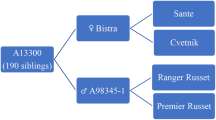
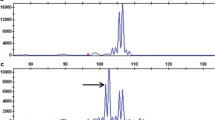
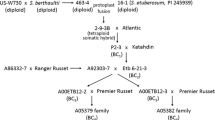
Potato leafroll virus (PLRV; Genus Polerovirus; Family Luteoviridae) is one of the most important virus pathogens of potato worldwide and breeders are looking for new sources of resistance. Solanum etuberosum Lindl., a wild potato species native to Chile, was identified as having resistances to PLRV, potato virus Y, potato virus X, and green peach aphid. Barriers to sexual hybridization between S. etuberosum and cultivated potato were overcome through somatic hybridization. Resistance to PLRV has been identified in the BC1, BC2 and BC3 progeny of the somatic hybrids of S. etuberosum (+) S. tuberosum haploid × S. berthaultii Hawkes. In this study, RFLP markers previously mapped in potato, tomato or populations derived from S. palustre (syn S. brevidens) × S. etuberosum and simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers developed from tomato and potato EST sequences were used to characterize S. etuberosum genomic regions associated with resistance to PLRV. The RFLP marker TG443 from tomato linkage group 4 was found to segregate with PLRV resistance. This chromosome region has not previously been associated with PLRV resistance and therefore suggests a unique source of resistance. Synteny groups of molecular markers were constructed using information from published genetic linkage maps of potato, tomato and S. palustre (syn. S. brevidens) × S. etuberosum. Analysis of synteny group transmission over generations confirmed the sequential loss of S. etuberosum chromosomes with each backcross to potato. Marker analyses provided evidence of recombination between the potato and S. etuberosum genomes and/or fragmentation of the S. etuberosum chromosomes.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bantarri EE, Ellis PJ, Khurana SMP (1993) Management of diseases caused by viruses and virus-like pathogens. In: Rowe RC (ed) Potato health management. American Phytopathological Society Press, St. Paul, Minnesota, pp 127–133
Barker H, Solomon RM (1990) Evidence of simple genetic control in potato of ability to restrict potato leaf roll virus concentration in leaves. Theor Appl Genet 80(2):188–192
Barker H, Solomon-Blackburn RM, McNicol JW, Bradshaw JE (1994) Resistance to potato leafroll virus multiplication is under major gene control. Theor Appl Genet 88:754–758
Bernatsky R, Tanksley SD (1986) Genetics of actin-related sequences in tomato. Theor Appl Genet 72:314–321
Bonierbale MW, Plaisted RL, Tanksley SD (1988) RFLP maps based on a common set of clones reveal modes of chromosomal evolution in potato and tomato. Genetics 120(4):1095–1103
Brown CR, Thomas PE (1994) Resistance to potato leafroll virus derived from Solanum chacoense: characterization and inheritance. Euphytica 74:51–57
Chavez R, Brown CR, Iwanaga M (1988) Transfer of resistance to PLRV titer buildup from Solanum etuberosum to a tuber-bearing solanum gene pool. Theor Appl Genet 76:129–135
Corsini DL, Brown CR (2001) Important potato cultivars. In: Loebenstein G, Berger PH, Brunt AA, Lawson RH (eds) Virus and virus-like diseases of potatoes and production of seed-potatoes. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, pp 39–52
Corsini DL, Pavek JJ, Martin MW, Brown CR (1994) Potato germplasm with combined resistance to leafroll virus and viruses X and Y. Am Potato J 71:377–385
Dong F, Novy RG, Helgeson JP, Jiang J (1999) Cytological characterization of potato Solanum etuberosum somatic hybrids and their backcross progenies by genomic in situ hybridization. Genome 42(5):987–992
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1987) A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochem Bull 19:11–15
Jansky SH (2000) Breeding for disease resistance in potato. In: Janick J (ed) Plant breeding reviews. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York, pp 69–155
Kojima R, Lapierre H (1988) Potato leafroll virus. In: Smith IM, Dunez V, Philips DH, Leliot RA, Archer SA (eds) European handbook of plant diseases. Blackwell Scientific Publishers, Oxford, UK, pp 23–24
Marczewski W, Flis B, Syller J et al (2001) A major quantitative trait locus for resistance to Potato leafroll virus is located in a resistance hotspot on potato chromosome XI and is tightly linked to N-gene-like markers. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 14(12):1420–1425
Marczewski W, Flis B, Syller J et al (2004) Two allelic or tightly linked genetic factors at the PLRV.4 locus on potato chromosome XI control resistance to potato leafroll virus accumulation. Theor Appl Genet 109(8):1604–1609
Matsubayashi M (1991) Phylogenetic relationships in the potato and its related species. In: Tsuchiya T, Gupta P (eds) Chromosome engineering in plants: genetics, breeding, evolution. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 93–118
McGrath JM, Wielgus SM, Helgeson JP (1996) Segregation and recombination of Solanum brevidens synteny groups in progeny of somatic hybrids with S. tuberosum: intragenomic equals or exceeds intergenomic recombination. Genetics 142(4):1335–1348
McGrath JM, Wielgus SM, Uchytil TF et al (1994) Recombination of Solanum brevidens chromosomes in the second backcross generation from a somatic hybrid with S. tuberosum. Theor Appl Genet 88(8):917–924
Milbourne D, Meyer RC, Collins AJ et al (1998) Isolation, characterisation and mapping of simple sequence repeat loci in potato. Mol Gen Genet 259(3):233–245
Nolte P, Miller JS, Geary BD, Corsini DL (2003) Disease management. In: Stark JC, Love SL (eds) Potato production systems. University of Idaho Extension, USA, pp 157–183
Novy RG, Helgeson JP (1994) Somatic hybrids between Solanum etuberosum and diploid, tuber bearing Solanum clones. Theor Appl Genet 89:775–782
Novy RG, Nasruddin A, Ragsdale DW, Radcliffe EB (2002) Genetic resistances to potato leafroll virus, potato virus Y, and green peach aphid in progeny of Solanum etuberosum. Am J Potato Res 79(1):9–18
Perez F, Menendez A, Dehal P, Quiros CF (1999) Genomic structural differentiation in Solanum: comparative mapping of the A- and E-genomes. Theor Appl Genet 98:1183–1193
Sambrook J, Frirsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
Solanaceae Genomics Network (2003) SSRList_30fb6ce883d6d21b http://sgn.cornell/edu Cornell University, Cited 26 Aug 03
Spooner DM, Hijmans R (2001) Potato systematics and germplasm collecting, 1989–2000. Am J Potato Res 78:237–268
Swiezynski KM, Dziewonska MA, Ostrowska K (1990) Inheritance of the potato leafroll virus (PLRV) in the potato. In: MacKerron DKL, Edmond HD, Hall D, Kirkman MA, Lang RW, Mackay GR, McRae DC, Oxley JP (eds) Abstracts of the 11th triennial conference of the European association for potato research. European Association for Potato Research, UK, pp 538–539
Tanksley SD, Ganal MW, Prince JP et al (1992) High density molecular linkage maps of the tomato and potato genomes. Genetics 132:1141–1160
Thieme R, Gavrilenko T, Thieme T, Heimbach U (1999) Production of potato genotypes with resistance to potato virus Y (PVY) by biotechnological methods. In: Altmann A, Ziv M, Izhar S (eds) Plant biotechnology and in vitro biology in the 21st century: proceedings of the IXth international congress of the international association of plant tissue culture and biotechnology, Jerusalem, Israel, June 1999. Current plant science and biotechnology in agriculture. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 557–560
USDA ARS National Genetic Resources Program (2003) Germplasm Resources Information Network-(GRIN). [Online Database] http://www.ars-grin.gov/cgi-bin/npgs/html/obs.pl?1189587 National Germplasm Resources Laboratory, Cited 23 Sept 2003
Valkonen JPT, Brigneti G, Salazar LF et al (1992) Interactions of the Solanum spp. of the Etuberosa group and nine potato-infecting viruses and a viroid. Annal Appl Biol 120:301–313
Van der Hoeven R, Fulton T, Ilut DC, Tanksley SD (2001) Development of a Solanaceae genome database: SGN. Plant and animal genome IX conference, 2001, San Diego, CA. Abstract #W54_06. Available: http://sgn.cornell.edu
Williams CE, Hunt GJ, Helgeson JP (1990) Fertile somatic hybrids of Solanum species-RFLP analysis of a hybrid and its sexual progeny from crosses with potato. Theor Appl Genet 80:545–551
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gillen, A., Novy, R. Molecular characterization of the progeny of Solanum etuberosum identifies a genomic region associated with resistance to potato leafroll virus. Euphytica 155, 403–415 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-006-9342-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-006-9342-x