Abstract
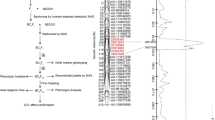
The paper presents the first taro (Colocasia esculenta L. Schott) genetic maps. Taro is an important vegetatively propagated root crop species in most subtropical areas. It is an allogamous and protogynous species with a basic chromosome number of x = 14. Two F1 progenies of 123 and 100 individuals obtained from crosses between local cultivars from Vanuatu (VU101 × VU104 and VU373 × VU314) were chosen for this study. Both genetic maps contained 169 markers, mainly AFLPs and 8 SSRs, and were characterised by a high density of markers and a short map length. The maps had 14 and 18 linkage groups (LG) respectively and were not completely saturated. Twenty-four markers were identified across the two progenies and a good co-linearity was observed for the majority of these markers. A QTL detection study was conducted on both progenies with 91 and 89 individuals respectively. Several putative QTLs were identified for corm yield and corm dimensions (which were highly correlated traits) whereas no QTL was detected for dry matter content. This result was relatively unexpected since dry matter content was a more highly heritable trait than corm yield or corm dimensions. A major dominant gene, responsible for the yellow colour of the corm flesh, was also identified. Further mapping studies on taro should include a larger number of SSR markers, larger progenies should be created and other important traits related to yield and eating quality should be included in the QTL analyses.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennett MD, Cox AV, Leich IJ (1998) Angiosperm DNA C-values database. http://www.rbgkew.org.uk/cval/database1.html
Boivin K, Deu M, Rami JF, Trouche G, Hamon P (1999) Towards a saturated sorghum map using RFLP and AFLP markers. Theor Appl Genet 98:320–328
Bonierbale M, Plaisted RL, Tanksley SD (1988) RFLP maps based on a common set of clones reveal modes of chromosomal evolution in potato and tomato. Genetics 120:1095–1103
Churchill GA, Doerge RW (1994) Empirical threshold values for quantitative trait mapping. Genetics 138:963–971
Coates DJ, Yen DE, Gaffey PM (1988) Chromosome variation in taro, Colocasia esculenta: Implications for origin in the Pacific. Cytologia 53:551–560
Da Silva JAG, Sorrels ME, Burnquist WL, Tanksley SD (1993) RFLP linkage map and genome analysis of Saccharum spontaneum. Genome 36:782–791
Devos KM, Pittaway TS, Reynolds A, Gale MD (2000) Comparative mapping reveals complex relationships between the pearl millet genome and those of foxtail millet and rice. Theor Appl Genet 100:190–198
De Vienne D (2003) Construction of genetic linkage maps. In: Molecular Markers in Plant Genetics and Biotechnology. D. de Vienne (Ed). Science Publishers, Inc, Plymouth, UK pp 47–80.
De Vienne D, Causse M (2003) Mapping and characterization of quantitative trait loci. In: Molecular Markers in Plant Genetics and Biotechnology. D. de Vienne (ed) Science Publishers, Inc, Plymouth, UK pp 89–124.
Fehr WR (1987) Principles of cultivar development. Theory and technique. Vol 1. Macmillan Publishing Company
Fregene M, Angel F, Gomez R, Rodriguez F, Chavarriaga P, Roca W, Thome J, Bonierbale M (1997) A molecular genetic map of cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz). Theor Appl Genet 95:431–441
Grattapaglia D, Sederoff R (1994) Genetic linkage maps of Eucalyptus grandis and Eucalyptus urophylla using a pseudo testcross-mapping strategy and RAPD markers. Genetics 137:1121–1137
Halldén C, Hjerdin A, Rading IM, Säll T, Fridlungh B, Johannisdottir G, Tuvesson S, Akesson C, Nilsson NO (1996) A high density RFLP linkage map of sugar beet. Genome 39:634–645
Ivancic A, Quero-García J, Lebot V (2003) Development of visual tools for selecting qualitative corm characteristics of taro (Colocasia esculenta (L.) Schott). Australian Journal of Agricultural Research 54:581–587
Ivancic A, Lebot V (2000) The genetics and breeding of taro. Séries Repères; CIRAD, Montpellier
Ivancic A, Okpul T (1995) Population approach to genetic improvement of taro (Colocasia esculenta). Paper presented at the Taro Seminar. 26–30 June 1995, Papua New Guinea University of Technology, Lae
Kosambi DD (1944) The estimation of map distance from recombination values. Ann Eugen 12:172–17
Kreike CM, Van Eck HJ, Lebot V (2004) Genetic diversity of taro (Colocasia esculenta (L.) Schott) in South-East Asia and the Pacific. Theor Appl Genet 109:761–768
Lebot V, Aradhya KM (1991) Isozyme variation in taro (Colocasia esculenta (L.) Schott) from Asia and Oceania. Euphytica 56:55–66
Lespinasse D, Rodier-Goud M, Leconte A, Legnate H, Seguin M (2000) A saturated genetic linkage map of rubber tree (Hevea spp) based on AFLP, RAPD, microsatellite, and isozyme markers. Theor Appl Genet 100:127–138
Mester DI, Ronin YI, Hu Y, Peng J, Nevo E, Korol AB (2003) Efficient multipoint mapping: making use of dominant repulsion-phase markers. Theor Appl Genet 107:1102–1112
Mignouna HD, Mank RA, Ellis THN, van den Bosch N, Asiedu R, Ng SYC, Peleman J (2002a) A genetic linkage map of Guinea yam (Dioscorea rotundata Poir.) based on AFLP markers. Theor Appl Genet 105:716–725
Mignouna HD, Mank RA, Ellis THN, van den Bosch N, Asiedu R, Abang MM, Peleman J (2002b) A genetic linkage map of water yam (Dioscorea alata L.) based on AFLP markers and QTL analysis for anthracnose resistance. Theor Appl Genet 105:726–735
Patterson HD, Williams ER (1976) A new class of resolvable incomplete block designs. Biometrica 63:83–90
Pekkinen M, Varvio S, Kulju KKM, Kärkkäinen H, Smoland S, Viherä-Aarnio A, Koski V, Sillanpää MJ (2005) Linkage map of birch, Betula pendula Roth, based on microsatellites and amplified fragment length polymorphisms. Genome 48:619–625
Quero-García, J, Noyer JL, Perrier X, Marchand JL, Lebot V (2004) A germplasm stratification of taro (Colocasia esculenta) based on agro-morphological descriptors, validation by AFLP markers. Euphytica 137:387–395
Quero-García J (2004) Diversité génétique et amélioration des taros du Vanuatu. PhD Thesis. Ecole Nationale Supérieure Agronomique de Montpellier France, 197 p
Quero-García J, Ivancic A, Letourmy P, Feldmann Ph, Molisale T, Lebot V (2006) Heritability of the main agronomic traits of taro (Colocasia esculenta L.) Schott). Crop Science (In Press).
Risterucci AM, Grivet L, N'Goran JAK, Pieretti I, Flament MH, Lanaud C (2000) A high density linkage map of Theobroma cacao L. Theor Appl Genet 101:948– 955
Ritter E, Gebhardt C, Salamini F (1990) Estimation of recombination frequencies and construction of RFLP linkage maps in plant from crosses between heterozygous parents. Genetics 125:645–654
SAS Institute Inc, 1999–2001. SAS Release 8.02, Cary, NC, USA
Sreekumari MT (1997) Cytological studies in taro-A review. Journal of Root Crops 23:1–7
Stam P (1993) Construction of integrated genetic linkage maps by means of a new computer package: JoinMap. The Plant Journal 3:739–744
TANSAO (Taro Network for Southeast Asia and Oceania), (2002). Final report (covering period from January 1998 to December 2001). CIRAD, Montpellier, 207 p
Van Ooijen JW, Voorrips RE (2001) JoinMap® 3.0, Software for the calculation of genetic linkage maps. Plant Research International, Wageningen, The Netherlands
Van Ooijen JW (2004) MapQTL® 5, Software for the mapping of quantitative trait loci in experimental populations. Plant Research International, Wageningen, The Netherlands
Vuylsteke M, Mank R, Antonise R, Bastiaans E, Senior ML, Stuber CW, Melchinger AE, Lübberstedt T, Xia XC, Stam P, Zabeau M, Kuiper M (1999) Two high-density AFLP linkage maps of Zea mays L.: analysis of distribution of AFLP markers. Theor Appl Genet 99:921–935
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Quero-García, J., Courtois, B., Ivancic, A. et al. First genetic maps and QTL studies of yield traits of taro (Colocasia esculenta (L.) Schott). Euphytica 151, 187–199 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-006-9139-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-006-9139-y