Abstract
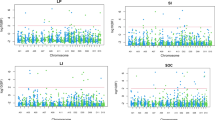
A population of 112 F1-derived doubled haploid lines was produced from a reciprocal cross of Brassica juncea. The parents differed for seed quality, seed color and many agronomic traits. A detailed RFLP linkage map of this population, comprising 316 loci, had been constructed, and was used to map quantitative trait loci (QTL) for seed yield and yield components, viz. siliqua length, number of seeds per siliqua, number of siliques per main raceme and 1000-seed weight. Stable and significant QTLs were identified for all these yield components except seed yield. For yield components, a selection index based on combined phenotypic and molecular data (QTL effects) could double up the efficiency of selection compared to the expected genetic advance by phenotypic selection. Selection indices for high seed yield, based on the phenotypic data of yield and yield components, could only improve the efficiency of selection by 4% of the genetic advance that can be expected from direct phenotypic selection for yield alone. Inclusion of molecular data together with the phenotypic data of yield components in the selection indices did not improve the efficiency of selection for higher seed yield. This is probably due to often negative relationships among the yield components. Most of the QTLs for yield components were compensating each other, probably due to linkage, pleiotropy or developmentally induced relationships among them. The breeding strategy for B. juncea and challenges to marker assisted selection are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MAS:
-
marker assisted selection
- PS:
-
phenotypic selection
- QTL:
-
quantitative trait loci
References
Aastveit, A.H. & K. Aastveit, 1993. Effects of genotype-environment interactions on genetic correlations. Theor Appl Genet 86: 1007–1013.
Adams, M.W., 1967. Basis of component compensation in crop plants with special reference to the field bean, Phaseolus vulgaris. Crop Sci 7: 505–510.
Bazant, J., D. Laurie, N. Pratchett, J. Chojecki & M. Kearsey, 1997. Mapping QTL controlling yield and yield components in a spring barley (Hordeum vulgare) cross using marker regression. Mol Breed 3: 29–38.
Bouttier, C. & D.G. Morgan, 1992. Ovule development and determination of seed number per pod in oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.). J Exp Bot 43: 709–714.
Burton, W., P. Salisbury & D. Potts, 2003. The potential of canola quality Brassica juncea as an oilseed crop for Australia, Proceedings of 11th International Rapeseed Congress, Copenhagen, Vol. 1, pp. 5–7.
Butruille, D.V., R.P. Guries & T.C. Osborn, 1999. Linkage analysis of molecular markers and quantitative trait loci in populations of inbred backcross lines of Brasica napu L. Genetics 153: 949–964.
Downey, R.K., 1990. Brassica oilseed Breeding-achievements and opportunities. Plant Breed Abst 60: 1165–1170.
Dudley, J.W., 1993. Molecular markers in plant improvement: Manipulation of genes affecting quantitative traits. Crop Sci 33: 660–668.
Eathington, S.R., J.W. Dudley & G.K. Rufener, 1997. Usefulness of marker-QTL association in early generation selection. Crop Sci 37: 1686–1693.
Falconer, D.S. & T.F.C. Mackay, 1996. Introduction to Quantitative Genetics, 4th edn, pp. 189, Addison Wesley Longman Limited, England.
Fonseca, C.E.L., D.R. Viands, J.L. Hansen & A.N. Pell, 1999. Associations among forage quality traits, vigor, and disease resistance in alfalfa. Crop Sci 39: 1271–1276.
Frova, C., P. Krajewski, N. di Fonzo, M. Villa & M. Sari-Gorla, 1999. Genetic analysis of drought tolerance in maize by molecular markers 1. Yield components. Theor Appl Genet 99: 280–288.
Hittalmani, S., H.E. Shahidhar, P.G. Bagali, N. Huang, J.S. Sidhu, V.P. Singh & G.S. Khush, 2002. Molecular mapping of quantitative trait loci for plant growth, yield and yield related traits across diverse locations in a doubled haploid rice population. Euphytica 125: 207–214.
Hoarau, J.Y., L. Grivet, B. Offman, L.M. Raboin, J.P. Diorflar, J. Payet, M. Hellmann, A. D'Hont & J.C. Glaszmann, 2002. Genetic dissection of a modern sugarcane cultivar (Saccharum Spp.). II. Detection of QTLs for yield components. Theor Appl Genet 105: 1027–1037.
Hospital, F., L. Moreau, F. Lacoudre, A. Charcosset & A. Gallais, 1997. More on the efficiency of marker-assisted selection. Theor Appl Genet 95: 1181–1189.
Kato, K., H. Miura & S. Sawada, 2000. Mapping QTLs controlling grain yield and its components on chromosome 5A of wheat. Theor Appl Genet 101: 1114–1121.
Kwon, S.H. & J.H. Torrie, 1964. Heritability and interrelationship among traits of two soybean populations. Crop Sci 4: 196–198.
Lande, R. & R. Thompson, 1990. Efficiency of marker-assisted selection in the improvement of quantitative traits. Genetics 124: 743–756.
Lee, M., 1995. DNA markers and plant breeding programs. Adv Agron 55: 265–344.
Li, Z., S.R.M. Pinson, W.D. Park, A.H. Paterson & J.W. Stansel, 1997. Epistasis for three grain yield components in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Genetics 453–465.
Mahmood, T., U. Ekuere, F. Yeh, A.G. Good & G.R. Stringam, 2003. RFLP linkage analysis and mapping genes controlling the fatty acid profile of Brassica juncea using reciprocal DH populations. Theor Appl Genet 107: 283–290.
Moreau, L., A. Charcosset, F. Hospital & A. Gallais, 1998. Marker-assisted selection efficiency in population of finite size. Genetics 148: 1353–1365.
Rakow, G., 2003. The potential of Brassica juncea, B. carinata and Sinapis alba as new oilseed crops in Canada, Proceedings 11th International Rapeseed Congress, Copenhagen, Vol. 1, p. 1.
Reeve, E.C.R., 1955. The variance of genetic correlation coefficient. Biometrics 11: 357–374.
Richards, R.A. & N. Thurling, 1979. Genetic analysis of drought stress response in rapeseed (Brassica campestris and B. napus). II. Yield improvement and the application of selection indices. Euphytica 28: 169–177.
Robertson, A., 1959. The sampling variance of genetic correlation coefficient. Biometrics 15: 469–485.
SAS Institute, Inc. SAS/STAT. 1989.
Schön, C.C., A.E. Melchinger, J. Boppenmaier, E. Brunklaus-Jung, R.G. Herrmann & J.F. Seitzer, 1994. RFLP mapping in maize: Quantitative trait loci affecting testcross performance of elite European flint lines. Crop Sci 34: 378–389.
Slocum, M.K., S.S. Figdore, W.C. Kennard, J.Y. Suzuki & T.C. Osborn, 1990. Linkage arrangement of restriction fragment length loci in Brassica oleracea. Theor Appl Genet 80: 57–64.
Smith, H.F., 1936. A discriminant function for plant selection. Annal Eugenics 7: 240–250.
Stromberg, L.D., J.W. Dudley & G.K. Rufener, 1994. Comparing conventional early generation selection with molecular marker assisted selection in maize. Crop Sci 34: 1221–1225.
Tar'an, B., T.E. Michaels & K.P. Pauls, 2002. Genetic mapping of agronomic traits in common bean. Crop Sci 42: 544–556.
Thiagarajah, M.R. & G.R. Stringam, 1993. A comparison of genetic segregation in traditional and microspore-derived populations of Brassica juncea L. Czern and Coss. Plant Breed 111: 330–334.
Thurling, N., 1974. An evaluation of an index method of selection for high yield in turnip rape, Brassica campestris L. ssp. oeleifera Metzg. Euphytica 23: 321–331.
Thormann, C.E., M.E. Ferreira, L.E.A. Camargo, J.G. Tivang & T.C. Osborn, 1994. Comparison of RFLP and RAPD markers to estimate genetic relationship within and among cruciferous species. Theor Appl Genet 88: 973–980.
Thormann, C.E., J. Romero, J. Mantet & T.C. Osborn, 1996. Mapping loci controlling the concentrations of erucic and linolenic acids in seed oil of Brassica napus L. Theor Appl Genet 93: 282–286.
Van Berloo, R. & P. Stam, 1999. Comparison between marker-assisted selection and phenotypic selection in a set of Arabidopsis thaliana inbred lines. Theor Appl Genet 98: 113–118.
Van Ooijen, J.W. & C. Maliepaard, 1996. MapQTLTM version 3.0: Software for the calculation of QTL position on genetic maps. CRO-DLO, Wageningen.
Veldboom, L.R. & M. Lee, 1996. Genetic mapping of quantitative trait loci in maize in stress and non-stress environments: I. Grain yield and yield components. Crop Sci 36: 1310–1319.
Williams, W.A., M.B. Jones & M.W. Demment, 1990. A concise table for path analysis statistics. Agron J 82: 1022–1024.
Woods, D.L., J.J. Capcara & R.K. Downey, 1991. The potential of mustard (Brassica juncea) as an edible crop on the Canadian prairies. Can J Plant Sci 71: 195–198.
Xiao, J., J. Li, L. Yuan & S.D. Tanksley, 1996. Identification of QTLs affecting traits of agronomic importance in a recombinant inbred population derived from a subspecific rice cross. Theor Appl Genet 92: 230–244.
Yousef, G.G. & J.A. Juvik, 2001. Comparison for phenotypic and marker-assisted selection for quantitative traits in sweet corn. Crop Sci 41: 645–655.
Zhu, H., G. Briceno, R. Dovel, P.M. Hayes, B.H. Liu, C.T. Liu & S.E. Ulrich, 1999. Molecular breeding for grain yield in barley: An evaluation of QTL effects in a spring barley cross. Theor Appl Genet 98: 772–779.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mahmood, T., Rahman, M.H., Stringam, G.R. et al. Molecular markers for yield components in Brassica juncea – do these assist in breeding for high seed yield?. Euphytica 144, 157–167 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-005-5339-0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-005-5339-0