Abstract
This article probes the practical ethical implications of AI system design by reconsidering the important topic of bias in the datasets used to train autonomous intelligent systems. The discussion draws on recent work concerning behaviour-guiding technologies, and it adopts a cautious form of technological utopianism by assuming it is potentially beneficial for society at large if AI systems are designed to be comparatively free from the biases that characterise human behaviour. However, the argument presented here critiques the common well-intentioned requirement that, in order to achieve this, all such datasets must be debiased prior to training. By focusing specifically on gender-bias in Neural Machine Translation (NMT) systems, three automated strategies for the removal of bias are considered – downsampling, upsampling, and counterfactual augmentation – and it is shown that systems trained on datasets debiased using these approaches all achieve general translation performance that is much worse than a baseline system. In addition, most of them also achieve worse performance in relation to metrics that quantify the degree of gender bias in the system outputs. By contrast, it is shown that the technique of domain adaptation can be effectively deployed to debias existing NMT systems after they have been fully trained. This enables them to produce translations that are quantitatively far less biased when analysed using gender-based metrics, but which also achieve state-of-the-art general performance. It is hoped that the discussion presented here will reinvigorate ongoing debates about how and why bias can be most effectively reduced in state-of-the-art AI systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
In recent years, the practical ethical implications of Artificial Intelligence (AI) have once again become a topic of intense contemporary scrutiny. There are numerous ongoing corporate, national, and international initiatives to encourage the development of autonomous intelligent systems that function more ethically, and the discussions have routinely focussed on issues such as data privacy, fairness, explainability, transparency, the need to determine accountability for automated decision-making, and the many problems caused by biased data.Footnote 1 Prominent initiatives include projects such as the IEEE’s Ethically Aligned Design (2016-present) (IEEE 2020), publications such as the European Union’s Ethical Guidelines for Trustworthy AI (2019; from henceforth ‘Guidelines’; HLEGAI 2019), and the self-imposed ‘Principles’ adopted by most leading technology companies to govern their own development of AI systems (e.g. Google AI 2020). The prevalence of these issues has prompted numerous discussions of the perceived problems in specialist technology-focused journals (e.g., AI and Ethics, Ethics and Information Technology) as well as high-profile publications such as Nature which are aimed at a more general audience (e.g., Zou and Schiebinger 2018). While the ethical implications of automated systems have been prominent since at least the 1940s (Isaac Asimov’s so-called ‘Three Laws of Robotics’ being a classic early example),Footnote 2 the recent neural revolution in machine learning caused such issues to be considered with renewed urgency during the 2010s. This is not surprising. In an age when self-driving cars and automated medical diagnosis are close to becoming mainstream technologies, it is appropriate to reflect upon the ethical and societal impacts of AI systems more generally.
As implied above, in most contemporary discussions of AI ethics the emphasis usually falls upon a small set of (sub) topics: autonomous intelligent systems should be designed and constructed so that (i) the data they are trained on is diverse, inclusive, and free from undesirable biases, (ii) they use that data in ethical ways, (iii) the decisions they make can be traced back and understood by human beings (e.g., Winfield et al. 2019). Motivated by similar concerns, the aforementioned Guidelines focused particularly on privacy and data governance, and the need to avoid biases in the data was expressed clearly as follows:
The quality of the data sets used is paramount to the performance of AI systems. When data is gathered, it may contain socially constructed biases, inaccuracies, errors and mistakes. This needs to be addressed prior to training with any given data set. In addition, the integrity of the data must be ensured. Feeding malicious data into an AI system may change its behaviour, particularly with self-learning systems. Processes and data sets used must be tested and documented at each step such as planning, training, testing and deployment. This should also apply to AI systems that were not developed in-house but acquired elsewhere. (HLEGAI 2019, p. 17)
This view is reinforced in more recent documents such as the guidance on ‘Understanding Artificial Intelligence Ethics and Safety’ published online by the UK Government in June 2019. In the subsection on ‘Fairness’, these guidelines recommend that system designers should ‘use only fair and equi datasets’ (GDS and OAI 2019). Such issues are even more important given the attested phenomenon of ‘bias amplification’, which occurs when automated systems manifest biases that are even greater than those present in the data on which they were trained (Lloyd 2018; Zhao et al. 2017). Therefore, the requirement that training data should be debiased prior to training sounds reasonable. The problem is that, in practice, it can sometimes be impossible to accomplish, especially if high-level system performance in the relevant domain is to be retained. Unfortunately, this fact is rarely acknowledged in documents such as those cited above. Broad generic discussions of AI systems can give the misleading impression of homogenous similarity. In reality, of course, different systems use different mathematical models to solve different kinds of problems, and they are trained on different kinds of data (e.g., text-based, image-based). Consequently, as discussed at length in this article, debiasing data prior to training, without compromising the performance of the system, will be possible in some cases, but not in others. And a greater awareness of such differences can usefully expose the unhelpful superficiality of any high-level recommendation that all AI data sets must be free from bias prior to training.
Then there is the problem of identifying ‘Bias’ in the first place. Recently, Blodgett et al. (2020) have argued that several distinct and often underspecified conceptualisations of bias has been prominent in work addressing the skewed datasets used for Natural Language Processing (NLP) tasks, and the authors show how this has fostered terminological imprecision. As Maudslay et al. (2019) put it, the ‘measurement and mitigation of gender bias relies on the chosen operationalisation of gender bias. As a direct consequence, how researchers choose to operationalise bias determines both the techniques at one’s disposal to mitigate bias, as well as the yardstick by which success is determined’. More specifically, gender bias is not a homogenous phenomenon since it is manifest in linguistic data in several distinct ways. In the context of Machine Translation (MT), the primary focus has been on the representational harms, such as stereotyping, that arise from specific linguistic items and structures (e.g., gendered pronouns). While this captures a manifestation of gender bias that is quite easily identifiable within a dataset, there are numerous other less explicitly marked ways in which stereotyping (for example) becomes manifest. The complexities and subtleties of how power differentials and social hierarchies operate within and through language make the task of simply identifying all gender bias within a dataset incredibly complex.Footnote 3
To explore these important issues in greater detail, this article will discuss particular human biases present in the training data used to build Neural Machine Translation (NMT) systems. Crucially, it will be shown that the datasets created to train such systems cannot always be adequately debiased prior to training using existing approaches without considerably diminishing the quality of the output translations. However, in the effort to develop more equi systems, the discussion will also show that the technique of model adaptation can be effectively deployed to reduce bias in existing NMT systems, with minimal impact on system performance. But this occurs only after they have already been fully trained on biased data. Focusing on this revealing case-study helps to avoid shallow pronouncements about how biased datasets could or should be handled in all autonomous intelligent systems. NMT systems are of especial interest when bias is considered since their bi-text training data consists of millions of human-produced semantically equivalent sentences:
-
English: Now, however, he is to go before the courts once more
-
German: Nun ist es aber so, daß er wieder angeklagt werden soll
These sentence pairs impose constraints on how such data can be processed: any modifications to one of the German sentences requires its corresponding English counterpart of be modified too, and in a way that ensures continued semantic equivalence. In order to provide even greater specificity, the emphasis in the ensuing discussion will fall primarily on gender-related biases present in the NMT training data.
Accordingly, Sect. 2 summarises the kinds of gender-related biases that are manifest in the ‘sexist’ outputs that state-of-the-art NMT systems produce when they opt for masculine defaults. In order to explain why this happens, Sect. 3 analyses the kinds of datasets that are used to train the current generation of NMT systems. Section 4 seeks to quantify the impact that removing gender biases from NMT training data has upon the performance of the resulting systems. Finally, in Sect. 5, an alternative approach is presented, in which an NMT system trained on biased data is adapted using a much smaller amount of balanced data. The performance of such a system is examined, and it is shown that it outperforms schemes for reducing gender bias in NMT systems ‘pre-emptively’ before training.
Gender bias in NMT systems
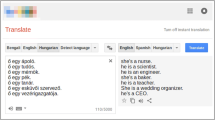
The fact that state-of-the-art NMT systems suffer from glaring gender biases is sufficiently well-known to have been discussed frequently in the popular press. In May 2017, a story in the Daily Mail bore the headline ‘Is Google Translate Sexist?’ (Best 2017), while a 2018 article in Forbes magazine considered ‘The Algorithm That Made Google Translate Sexist’ (Olson 2018). In the technical literature, Stanovsky et al. (2019) have demonstrated the prevalence of gender bias across multiple NMT systems such as Google Translate, Microsoft Translator, Amazon Translate, and SYSTRAN. The recurring accusation is that such systems reinforce sexist tendencies in society by favouring masculine defaults in the translations they produce. This is most conspicuously manifest in the pronouns and possessives that appear in NMT outputs, since, for many languages, those lexical items can make the masculine bias blatantly apparent. For some languages, Google Translate now provides translation options: the gender-neutral Turkish source sentence ‘o bir doktor’ produces two different gendered target sentences: ‘She is a doctor (feminine)’ and ‘He is a doctor (masculine)’.Footnote 4 But these are exception rather than the norm, as the Finnish example below indicatesFootnote 5:
Finnish | English |
|---|---|
Hän on lääkäri | She is a doctor |
Hän on sairaanhoitaja | He is a nurse |
In addition, it is important to recognise that gendered language in NLP often conflates linguistic and sociological gender (Cao and Daumé III 2020). Trans-inclusive models of gender, and particularly non-binary inclusivity, acknowledges that sociological gender does not correspond to a male/female binary (e.g., Darwin 2017). Consequently, a dataset with equal numbers of male and female entities is only balanced relative to that dichotomy. Linguistically, English third-person singular pronouns (e.g., ‘they’, ‘them’) are increasingly used for both non-binary individuals and to reference people of unknown gender. The Merriam-Webster dictionary recognised ‘they’ as the word of the year in 2019, noting that it has been deployed as a singular pronoun since at least the late 1300 s. Accordingly, this article focuses on translation into richly gender-inflected languages (e.g., German) and the experimental set-up is based on the recent NMT gender bias evaluation framework WinoMT (Stanovsky et al. 2019). While many inflected languages clearly demonstrate the effects of male–female imbalances in training data for the translation of (say) pronouns and nouns, they often lack widely accepted non-binary inflection conventions (Ackerman 2019). Consequently, the options for analysing NMT gender bias in relation to anything other than binary linguistic inflections are currently severely limited.
To return to the above example from Finnish, the gender-neutral third-person singular pronoun (hän) that can mean either ‘he’ or ‘she’, and the occupation (i.e., being a doctor, being a nurse) has prompted a gendering of the pronoun in the English translations produced by Google Translate. As a result of recent criticism of gender stereotyping in NMT output, the stereotypical gender patterns have been inverted, but they still fail to capture the gender neutrality of the source sentences. Several recent studies have attempted to quantify the extent of this gender-related bias. Prates et al. (2019) have argued that, given well-attested gender asymmetries in society, a 50:50 pronominal split in NMT outputs is unrealistic when sentences in gender-neutral languages (e.g., Finnish, Hungarian, Turkish) are translated into gendered languages (e.g., English, French, German). Nonetheless, they provide experimental evidence which suggests that Google Translate yields masculine defaults much more frequently than would be expected from demographic data alone (Prates et al. 2019). Other researchers have developed techniques for mitigating biases in monolingual English NLP tools, with a handful of techniques applied to the more complex problem of inflected languages. Some approaches which have been applied to NMT specifically are effective in limited settings – for example, adding the gender of the speaker as a feature to an NMT system during training can improve translation quality, even though the concept of a single gender per sentence is not appropriate for all translations, and speaker information is not typically available (Vanmassenhove et al. 2018). Another approach to gender bias in NLP tools involves training a model with debiased word embeddings, either as a post-processing method (Bolukbasi et al. 2016) or from scratch by Zhao et al. (2018) for English data, and by Escudé Font and Costa-jussà (2019) for NMT specifically. However, a subsequent analysis by Gonen and Goldberg (2019) has argued that such methods are merely ‘lipstick on a pig’ – that is, while the gender bias ‘direction’ of the word embeddings is superficially reduced, relationships between gendered terms learned from the data are still detec – and thus amplifiable – by NLP tools.
Given this, the research presented in this article is more closely related to studies which have sought to balance masculine and feminine terms in the training data itself. Such approaches exist for English data (e.g., Maudslay et al. 2019; Zhao et al., 2018). Zmigrod et al. (2019) introduced a more complicated data-augmentation scheme for inflected languages with rich morphology like German, but their scheme revolves around swapping a single targeted word per sentence. The authors highlight that co-reference information necessary to cover multiple entities per sentence is not included, which limits the applicability for evaluations using WinoMT, since the latter relies on co-reference resolution. Closest to our approach is concurrent work by Costa-jussà and de Jorge (2020) who fine-tune NMT models on a gender-balanced set of natural sentences extracted from Wikipedia. In addition, recent work by Saunders et al (2020) extends some of the adaptation work mentioned in this article. That research introduces adaptation to gender-tagged data for controllable gender inflection, as well as an extension of the adaptation and assessment schemes to gender-neutral inflections in grammatically gendered target languages.
Also, some recent work has focused on NMT model adaptation. For instance, adapting to small datasets with desired style, desired vocabulary, or simply reduced data noise has been previously explored (e.g., Farijian et al. 2017, Michel and Neubig 2018; Wang et al. 2018). More recently, Tan et al. (2020) have exposed NMT models to morphologically varied input English to combat bias effects which reduce the performance for users with non-native linguistic background. The approach introduced in the current article is similar in spirit, with the significant difference that our research focuses on a bilingual counterfactual adaptation set which seeks to reduce the effects of gender bias in a trained NMT system. While some of the above strategies can reduce the problem (to an extent), few approaches for reducing bias in NLP tools attempt to eliminate bias in the training data (the approach recommended in the Guidelines), and no other NMT approaches we are aware of do so either. If the gender-skewed data produces gender-skewed NMT systems, then it would be better to remove the bias before the systems were constructed. As a preliminary step, Sect. 3 examines a specific NMT corpus in detail, and reveals the nature of the gender bias present in the data.
Before addressing that topic, though, it is essential to reflect upon the denotation of ‘Bias’ in this context. If NMT training data contains conspicuous biases, then it does not necessarily follow that those biases should be removed. If the data captures distinctive skewings that are present in the sample population (as Prates et al. 2019 demonstrates), then, arguably, that the data is not biased at all. Any prescriptivist concerns about the linguistic habits of the speech community (e.g., the use of sexist language) should presumably be addressed by convincing the members of that community to modify their linguistic behaviour (e.g., by favouring gender-neutral constructions). Consequently, and ironically, it could be argued that, if all gender biases were removed from NMT training data, then that data would effectively be biased. Of course, the justification would be that the data would be skewed in a ‘positive’ way rather than a ‘negative’ way (cf. positive discrimination in employee recruitment). Yet the tacit assumptions underlying this stance have serious implications for the kinds of (language-based) AI systems we might seek to develop in the future. Should autonomous intelligent systems be knowingly designed and constructed to reflect the various biases overtly manifest in human societies? Or should they be purposefully designed and constructed to be less biased than those societies currently are? To put it even more generally and contentiously, should we expect such systems be more ethical than the communities from which their training data was obtained? These questions probe the tension between technological realism and technological utopianism. Howard Segal has traced the roots of the latter ideology back to at least the seventeenth century.Footnote 6 It is associated with the view that technological advancements can ameliorate human societies, so, if language-based AI systems were free from all biases, they would have a beneficial social impact. In general, most discussions of the ethics of AI training data tend to favour some form of technological utopianism (even if only tacitly).
Humans are biased in many ways (both consciously and unconsciously), therefore any automated intelligent system trained on data obtained from, and labelled by, humans will inevitably acquire those biases. This was recently highlighted by the viral selfie app ImageNet Roulette, which sometimes output racial and sexist slurs when it labelled pictures of people’s faces (Wong 2019). However, if we can train systems that are less biased than we are, then they will make automated decisions that are less contaminated by our own preferences and prejudices. And (so the argument goes) this in turn will enable our societies to become fairer and less discriminatory. One implication of this is that morality is no longer exclusively anthropocentric. On the contrary, it is distributed in a complex way between material objects and the people who use them – a scenario first analysed by Hans Achterhuis, and later dubbed ‘materializing morality’ by Verbeek (2006). In particular, Verbeek has reflected deeply upon the role of ‘behavior-guiding technologies’ (Verbeek 2017). Building upon ideas initially explored by Bruno Latour in the 1990s and subsequently developed in texts such as B. J. Fogg’s Persuasive Technologies (2003) and Richard Thaler and Cass Sunstein’s Nudge (2008), Verbeek probes the socio-political implications of material objects that have been purposefully designed to influence people’s behaviour. He concludes that, although they may not always have the precise effect they were designed to have (a phenomenon he calls the ‘designer fallacy’), behaviour-influencing technologies of this kind do not necessarily threaten ‘the democratic character of our society’, since all autonomous intelligent systems influence what we do, whether they are overtly designed to do so or not (Verbeek 2017, p. 87). Consequently, there is arguably a democratic obligation to ensure that the influence of such technologies is as overt, as positive, and as libertarian as possible – though this does presuppose some degree of consensus about which specific influences meet those criteria. This all suggests that it is preferable for language-based AI technologies to be knowingly designed to avoid any bias that would marginalise particular social groups on the basis of protected characteristics such as biological sex, gender, age, race, and so on. NMT systems that were largely free from gender bias would help to foster the use of less biased language within human societies more generally. There are obvious frailties in any such a claim. What evidence do we have that humans would become less sexist if the language-based technology they used were less sexist? Any assumptions of this kind could certainly be accused of favouring a quaintly naïve understanding of causality and human behaviour. Nonetheless, accepting that the kinds of ethically aligned design recommend by Verbeek have at least the potential to encourage more positive social change, the remaining sections of this article will assume that it is indeed desirable to develop behaviour-guiding NMT systems that are more balanced than the data they are trained on.
Gender bias in MT training data
To explore gender bias in MT data more explicitly, this Section analyses a randomly selected subset of the data used to train the NMT systems discussed in Sects. 4 and 5. The English-German corpus used for the experiments described there contains 17.2 M sentence pairs, and it was created from datasets made available for the WMT19 news task (Barrault et al. 2019). The data ranges from webpages, obtained via Common Crawl, to translations of the bible. Therefore, it mingles formal and informal registers, contemporary slang, and archaic words and phrases. The corpus analysis was performed using Sketch Engine (Kilgarriff et al. 2014). Representative subsets representing 5% of the original English and German data sets were studied. The English side of the sub-corpus contained a total of 23,640,344 tokens (872,866 sentences), while the German data contained 23,050,052 tokens (864,612 sentences). The primary tools and functions used to generate the following statistics were wordsketch, concordance, and parallel concordance.
The English part of the corpus clearly displays imbalances with regard to gender-specific pronouns, nouns, and adjectives – especially when they are used to refer to family relations and professions. The data is mostly skewed towards masculine forms, but occasionally towards feminine forms (see Table 1; the numbers include plural forms for all nouns).
The patterns for the nouns ‘girl’ and ‘wife’ in Table 1 are revealing. The former appears in largely sexualised contexts, modified by adjectives like ‘young’, ‘naked’, ‘beautiful’, ‘hot’ or ‘nude’ (see Fig. 1). This is presumably due to the web-based data obtained by Common Crawl. In the case of ‘wife’, archaic biblical vocabulary dominates. The four most frequent nouns to co-occur with ‘man’ are ‘women’, ‘woman’, ‘Son’ (in the biblical context) and ‘God’. The lexeme ‘woman’ has a strong tendency to co-occur with ‘men’, ‘violence’, ‘man’, and ‘children’.
The task of analysing pronouns in the German data is harder due to the language’s more complex case system, and the polysemy associated with certain pronouns: ‘sie’ has a variety of different pronominal functions. However, Sketch Engine allows search results to be filtered according to part-of-speech tags, so only results for ‘sie’ as a third-person singular feminine pronoun were included in Table 2 below. Once again, the strongest collocates for ‘Sohn’ are ‘Gott’ or other lexemes with overtly biblical connotations. The dominant biblical content is equally noticeable when looking at German translations of ‘woman/women’, which often refer to the archaic forms ‘Weib’ or ‘Gebärerin’ (which literally denotes a woman in childbirth).
Moreover, there seem to be certain numerical discrepancies when Table 1 is compared with Table 2. The apparent imbalances, however, can be explained by the parallel concordances. Consider ‘woman’ in English and ‘Frau’ in German. The number of occurrences for the latter is almost twice as high as for the former, and this is due to the linguistic differences between German and English. The singular form ‘Frau’ is translated into English as ‘woman’ (20.37%), ‘women’ (5.64%), ‘wife’ (12.05%), Mrs (24.12%) and ‘Ms’ (3.3%) – and these options all convey information about gender. The remaining options include particular phrases such as ‘gender inequality’, which is a more complex phrasal construction in German (‘Gleichstellung von Mann und Frau’) and forms of address like ‘Frau Kommissarin’, which in English simply translates to the occupation (‘commissioner’) and therefore lacks gender-specific information. Similar discrepancies occur for the possessive pronouns ‘his’ and ‘her’ compared to their German equivalents. Notably, in German the different forms of ‘Ihr’ can also function as a form of address. In order to obtain the most accurate numbers, parallel concordances were considered for all possessive pronouns and all English translations were filtered, and those options which did not represent the respective pronoun (‘his’ or ‘her’) were discarded. This explains the numbers for the different forms of ‘sein’ and ‘ihr’ in Table 2.
In addition, the aligned translations for various profession and occupation words show biases too. This is especially noticeable for ‘doctor’, and cognate forms. According to the German Medical Association, the percentage of female medical students has increased by more than 25% in the last two decades (Kopetsch 2010, p. 102). In 2014, 45.5% of doctors in Germany were female, with numbers increasing in all specialised fields – and the number of female medical students is increasing too (specifically, 58% in 2017/18) (Statista 2019a, b). However, the German equivalent of male doctor (Arzt) is 38 times more common than the female form in the sub-corpus (see Table 3). Similar patterns can be found in the data for other traditionally male-dominated professions such as ‘architect’, ‘engineer’, ‘physicist’, and ‘politician’. By comparison, occupations typically associated with women, such as ‘nurse’, demonstrate bias towards the female forms. Further, certain occupations typically associated with women such as teacher (Lehrerin vs. Lehrer) or seller (Verkäuferin vs. Verkäufer) show higher numbers for the male counterparts in German (see Table 3). However, in the majority of cases the male term – which is often equivalent with the plural – is simply used to refer homogenously to anyone who practices that specific profession. This ‘masculine default’ principle is a form of structural bias that reinforces social assumptions, and shapes how we conceptualise gender norms and social power relations (Bailey et al. 2018) (Table 4).
Removing gender bias before training
The analysis in Sect. 3 reveals some of the human gender-related biases in the datasets used to train state-of-the-art (N) MT systems; and removing them all, manually, prior to training is practically impossible. If one person devoted just 5 s to debiasing each of the 34.5 M sentences in the English-German training dataset used for the experiments summarised below, it would take 5 and a half years to read and modify them all – and that is assuming no rest breaks and a willingness to work all day and all night. And if the task were crowd-sourced, as it often is these days, to reduce the processing time, there would be non-trivial quality control issues. Nonetheless, while reliable high-quality manual debiasing is infeasible, such methods can be automated (to an extent). Consequently, a series of experiments was performed that explored techniques for removing gender bias in bi-text MT corpora prior to training. The three most obvious strategies for accomplishing this are:
-
Downsampling: automatically remove data until the ratio of gendered terms is balanced for both languages
-
Upsampling: automatically add duplicated data until the ratio of gendered terms is balanced for both languages
-
Counterfactual Augmentation: automatically introduce counterfactual sentences that include the under-represented gendered terms – e.g., if the bi-text corpus contains ‘He is a doctor’ and ‘Er ist ein Arzt’, create the counterfactual sentence ‘She is a doctor’, add it to the English side of the data, then translate it (e.g., ‘Sie ist Ärztin’) and add the translation to the German side
The word ‘term’ in the above definitions has a broad denotation. It includes any lexemes or phrases that possesses gender-related connotations (e.g., pronouns, nouns, verbs, adjectives, noun phrases, verb phrases), depending on the languages involved. To facilitate the automation of the gender debiasing process, ‘gendered sentences’ were identified as those containing at least one gendered antonym from the list used by Zhao et al. (2018). The list consists of 104 English word-pairs where the words are gendered antonyms of each other (e.g., ‘son/daughter’, ‘he/she’, ‘husband/wife’).Footnote 7 Gender-swapping is relatively simple for English sentences, since grammatical gender is not marked morphologically in articles, adjectives, and verbs, and only sporadically in nouns (e.g., ‘actor’ / ‘actress’). However, the process is more complex for inflected languages like German since all the gendered parts-of-speech that occur in a sentence must be identified and updated.
Specifically, the schemes for down- and up sampling the dataset were as follows:
-
Iterate through the English side of all sentence pairs, counting the number of male and female gendered entities in each sentence.
-
If downsampling:
-
Add a sentence pair to the final dataset only if it is ‘gender-balanced’ – that is, if the English side has the same number of male and female entities.
-
-
If upsampling:
-
Include all gendered sentence pairs in the final dataset.
-
Measure its overall gender skew as the total number of male entities in all English sentences minus the total number of female entities.
-
Continue to iterate through non-balanced gendered sentence pairs, adding them to the final dataset again if they reduce the absolute overall skew.
-
Stop when overall skew reaches 0.
-
While other schemes for down- and upsampling are possible, they would not be as beneficial. The downsampling scheme described above ensures that every single batch of sentences has equal masculine and feminine terms on the English side, which would not be the case if individually unbalanced sentences were included in the dataset. It also usefully demonstrates the imagined scenario of ‘perfect’ debiasing prior to training. Intuitive alternatives to the upsampling scheme described above include a greedy approach – i.e., adding additional sentences if they maximally reduce the skew – and a minimally unbalanced approach – i.e., adding only those sentences with minimal skew. The former adds fewer sentences, but individual sentences will necessarily be more unbalanced on the English side. The latter results in significantly more upsampling and therefore more data duplication. The randomized approach used in these experiments offers a reasonable compromise.
Generating counterfactual examples by human translation would be a substantial task, since the corpus contains 17.2 M sentence pairs. A cruder, but simpler, approach involves creating counterfactual translations automatically using an existing MT system (Chinea-Rìos et al. 2017). While this method is not free from problems (e.g., the existing MT system will certainly be gender-biased), it has the advantage of vastly reducing the total translation time. To explore this technique, a straightforward counterfactual gender-swap on the English source sentences in an English-German corpus was performed (cf. Zhao et al. 2018). The NMT output was validated on the newstest17 data (3 k sentence pairs), and tested on newstest18 (3 k sentence pairs). Counterfactual versions of the gendered English sentences in the corpus were automatically translated using the existing baseline transformer-based NMT system. This produced counterfactual source-language and target-language sentences, and the resulting corpus augmented by these will be referred to as the counterfactual dataset. While this method inevitably introduces some translation errors, it at least creates a more male–female-balanced dataset.Footnote 8 As previously discussed, this counterfactual data augmentation approach is closest in spirit to prior work on reducing gender bias in monolingual NLP tools (Maudslay et al. 2019; Zhao et al. 2018; Zmigrod et al. 2019).
To evaluate the effect of removing gender-bias from a training dataset, the WinoMT challenge set was used. Introduced by Stanovsky et al. (2019) to analyse gender bias in MT systems, it permits automatic bias evaluation for translations from English when the target language has grammatical gender. The source side of WinoMT consists of 3,888 concatenated sentences from Winogender (Rudinger et al. 2018) and WinoBias (Zhao et al. 2018). These are coreference resolution datasets in which each sentence contains a grammatical subject (S) and a direct object (O), referred to by an occupation, and a pronoun (P) which is co-referent of either S or O:
-
(1).
[The doctor]S asked [the nurse]O to help [her]P in the procedure
In (1), P indicates that S is female, while the gender of O is unspecified. WinoMT evaluation requires each hypothesis translation sentence to be analysed morphologically, and the grammatical gender of the antecedent is obtained. In some sentences, the coreference occurs with O rather than S, and therefore the term ‘entity’ (E) will be used to refer to the lexical items that are assigned either of these syntactic roles. The hypothesis can then be compared with the ‘gold-label’ gendered target sentences using the following metrics over the test set:
-
Accuracy – the percentage of hypotheses that assign the correct gender to E
-
∆G – the difference in F1 score between the set of hypotheses with masculine entities and the set of hypotheses with feminine entities
-
∆S – the difference in Accuracy between the set of hypotheses with stereotypically gendered Es (e.g., a female nurse) and those with non-stereotypically gendered Es (e.g., a male nurse), as determined by Zhao et al. (2018) using US labour statistics.Footnote 9
Ideally, Accuracy should be high, and ∆G and ∆S close to 0. A high positive ∆G indicates that a model tends to give more accurate translations for male subjects, while a high positive ∆S indicates a tendency to stereotype male and female subjects. The primary objective is improved Accuracy. The ∆S and ∆G results are given for interest, and to facilitate comparisons with existing research. We also report M:F, the ratio of sentences with masculine hypotheses to those with feminine hypotheses. While M:F correlates strongly with ∆G, we consider M:F more interpre in terms of the system output. In addition, we note that ∆S can be significantly skewed for systems with very high or very low M:F. For example, a model generating masculine Es for all hypotheses would have extremely low ∆S, because both pro- and anti-stereotypical class accuracy would be about 50%. Further, it is important to assess the general quality of the translation, regardless of gender-specific considerations. The standard evaluation metric for MT is BLEU (the Bilingual Evaluation Understudy; Papeni et al. 2002). BLEU scores range from 0 to 100, with 100 indicating that every word in the target sentence is exactly matched in sequence (which rarely happens even in human translation). All BLEU scores given here are for cased, detokenized output, and they were calculated using SacreBLEU (Post 2018).
Table 5 gives results for the baseline system, and for the four systems trained from scratch on the different gender-balanced training datasets. In every case the architecture of the NMT system remained constant, and only the training data was changed. Therefore, for all these experiments, a transformer-based NMT system was built with 6 hidden layers that had a dimensionality of 512 (cf. Vaswani et al. 2017). The Tensor2Tensor machine learning framework was used for model definition, initial training and adaptation (Vaswani et al. 2018). Other hyperparameters follow the ‘transformer base v2′ setting publicized in the Tensor2Tensor framework,Footnote 10 including an initial learning rate of 0.2, a batch size of 4 K tokens per batch, and the Adam optimizer. Training from scratch took 300 K minibatch updates for the baseline system. The models with augmented or downsampled datasets were trained for proportionately more or fewer minibatch updates, dependent on overall number of training samples.
The results include the BLEU score, the WinoMT Accuracy, the ratio of male to female WinoMT sentence gender predictions, ∆G and ∆S.
All the NMT systems trained on the gender-balanced training data achieve considerably worse general MT performance than the baseline system. The highest BLEU score is obtained by the Counterfactual system, but it is still 1.6 points lower than the baseline score. The performance of the NMT systems on the gender-specific metrics is also problematical. The Downsampled system is clearly the worst since, in addition to a low BLEU score (4.5 points lower than the baseline), it has a low Accuracy score and a very high ΔG score. Revealingly, none of the three systems trained on gender-balanced data obtain large gains over the baseline for gender Accuracy. The best improvement over the baseline, with upsampling, is a 3.2% relative gain in Accuracy, which corresponds to a 5.4% relative decrease in translation quality. Therefore, the results in Table 5 quantify the extent to which attempting to remove gender bias from MT training data prior to training is ineffectual. It not only decreases the general MT performance of the resulting system, but it also fails significantly to improve the performance of the system in relation to gender-specific metrics.
The primary reason for this underperformance is the difficulty of truly gender-balancing any bi-texts that include gender-inflected target languages (e.g., German). While sentences in a downsampled dataset may appear balanced on the English side, many ungendered phrases in English would default to masculine constructions in German – e.g. ‘engineers say’ would be translated as ‘Ingenieure sagen’ – a construction implying masculine gender. This adheres to the conventions of contemporary German usage, but it shows how adjusting identifiably ‘unbalanced’ sentences can have a small effect relative to the number of default masculine constructions in the target language dataset, We note that all systems have very high M:F ratios, which as previously discussed reduces the relevance of ∆S. In particular, the downsampling scheme is more likely to remove rare examples of feminine constructions, resulting in a system which defaults to masculine forms for almost all German words. The result is a WinoMT M:F ratio of over 7:1, a very high ∆G score (i.e., most masculine sentences correct, most feminine sentences incorrect) and a very low ∆S score (i.e., almost all entities are predicted as male, whether pro-stereotypical or anti-stereotypical). By contrast, upsampling does slightly improve Accuracy and more significantly improves ∆G score under WinoMT, probably because the number of feminine grammatical constructions seen during training increases. This is the desired result, but male and female entities are still predicted in a ratio of 3:1, when the true test set ratio is 1:1. The upsampling scheme also results in reduced general translation performance and an increased ∆S score. Both of these results can be attributed to overfitting on the duplicated feminine training sentences, which serve to consolidate gender roles present in the training data. This result is, however, an indication that adding data is more likely to be effective than removing it. Finally, training with the counterfactual dataset suffers the smallest general translation performance degradation, which indicates the relative advantage of creating synthetic data. However, simply attempting automatic gender-swapping of the dataset is unsuccessful, presumably because it requires a less biased model for effective gender-swapping in the first place. We note that Costa-jussà and de Jorge (2020) fine-tune models on a set of gender-balanced natural sentences extracted from Wikipedia, which avoids translation performance degradation. However, they likewise see only small improvements in overall WinoMT accuracy, and sharp increases in pro-stereotypical accuracy, suggesting a consolidation of existing gender roles.
Removing gender bias after training
The results discussed above are discouraging. If less biased NMT systems are to be constructed, then alternative debiasing strategies are required. In this section, an entirely different debiasing approach is considered. In effect, a biased NMT system is created by training it on all the available data, but it is then subsequently made less biased by being fine-tuned using a tiny gender-balanced set of adaptation data. The tiny dataset had to be easily translated into a given target language (in this case, German). Therefore, the sentences were all constructed in accordance with the following template:
-
(2).
The [PROFESSION] finished [his/her] work
Each profession was taken from the list collected by Prates et al. 2019. The list was first simplified by removing field-specific adjectives (e.g., ‘engineer’ was used, rather than ‘industrial engineer’, ‘locomotive engineer’, ‘marine engineer’, and so on), so a typical sentence took the form:
-
(3).
The engineer finished her work
In total, 194 professions were selected, and this gave 388 sentences in the tiny dataset (from henceforth ‘Tiny’). Of these professions, 86 also occur in the set of English sentences that make up the WinoMT test set. This overlap confounds the effects of overfitting to the tested profession terms with the effects of adapting to a balanced dataset. Consequently, we also adapt to a Tiny set with no English profession overlap.Footnote 11 We simply remove masculine and feminine sentences with overlapping English professions, replacing each with a pair of similar adjective-based sentences:
-
(4).
The [ADJECTIVE] [man/woman] finished [his/her] work
The resulting Tiny (No English profession overlap) set also has 388 sentence pairs, of which 216 are shared with the original Tiny set and the rest are adjective-based. An example of an adjective-based sentence is as follows:
-
(5).
The tall woman finished her work
Fine-tuning on the Tiny dataset reduces the gender bias of the adapted NMT output considerably, with the Accuracy score 18.2 points higher than the baseline. The ∆G and ∆S scores both improve significantly too. As might be expected, removing overlapping WinoMT professions from the adaptation set harms WinoMT performance. However, an 11.1 point accuracy improvement is still achieved despite the strict constraint: this is several times the greatest Accuracy improvement in Table 5. It is also worth considering that the further improvement for the Tiny set with overlapping profession terms is not necessarily a problem. The result suggests that some gendered terms, such as professions, may simply be under-represented in the original training data, a fact that adaptation can address.
It is well-known that fine-tuning a converged neural network on data from a new domain can lead to catastrophic forgetting of the original domain (French 1999); and Elastic Weight Consolidation (EWC) is an established technique for minimising the extent of the forgetting during model adaptation (Kirkpatrick et al. 2017). Since it is desirable for the adapted NMT system to produce outputs that achieve competitive BLEU scores, EWC was applied during adaptation when the performance on the original validation set dropped. Table 6 gives the results for two NMT systems adapted from the baseline NMT system using the Tiny dataset, the first without EWC and the second with EWC.
While fine tuning on either Tiny dataset improves gender accuracy significantly, in both cases general translation performance as measured by BLEU decreases. For Tiny, the best-performing system on WinoMT, the BLEU score is 1.9 points lower than the baseline, which is due to the aforementioned problem of catastrophic forgetting. Consequently, and as expected, the results for the system adapted using EWC regularisation achieve a better balance between maintaining general MT performance while also reducing gender bias: the Accuracy increases compared to the baseline, while the BLEU score decreases by only 0.5 points. In relative terms, an Accuracy improvement of 23.5% compared to baseline performance is achieved with a − 1.2% change in relative translation performance as measured by BLEU. These results are far more promising than the 3.2%/−5.4% relative Accuracy/BLEU change with upsampling, the best approach in Table 5. In addition, the ∆G and ∆S scores are respectively 16.4 and 5.0 lower than the baseline. This suggests that a biased state-of-the-art NMT system can be modified so as to become significantly less biased if it is adapted using a very small set of gender-balanced data. Crucially, these gains do not require a huge increase in computational complexity. Fine tuning on the Tiny dataset takes less than a minute compared to hours or days if it were trained from scratch on a fully ‘debiased’ dataset. Therefore, addressing bias by means of model adaptation is clearly a practical partial solution to the difficult and multi-faceted problem of gender bias in MT training data. As the results in 8 demonstrate, it enables NMT system outputs to be far more balanced (at least in relation to the linguistic structures prioritised by the WinoMT scoring framework), while also achieving something close to the original general MT performance. While the analysis offered here is conspicuously practical (focusing on the details of NMT system design), it is nonetheless underpinned by an awareness of the ethical issues discussed towards the end of Sect. 2. Put simply, NMT systems that have been adapted using a small purposefully gender-balanced dataset are behaviour-guiding technologies that constitute instances of ethically aligned design – and the process of constructing them necessarily requires philosophical convictions to inform the technicalities of system development.
Conclusion
Although philosophical reflections on modern technologies have been common ever since Martin Heidegger published his Die Frage nach der Technik in 1954, recent advances in machine learning have created unprecedented practical and theoretical scenarios that require careful ethical scrutiny. Advocating a cautious form of technological utopianism, this article has argued that it is potentially beneficial to create language-based AI systems that are less biased than the communities which produced the data used to train them. In some ways, systems of this kind can be compared with familiar devices such as speed cameras, which are material objects that exist in order to encourage us to drive more ethically. And even though they have no power to prevent an individual exceeding the speed limit, they can still exert a beneficial influence, simply by being physically present at the roadside. A similar materialising of morality occurs in the case of language-based AI systems that are purposefully designed to avoid linguistic biases, even though (unlike speed camera) their primary purpose is not to influence our behaviour ethically. By actively reinforcing more inclusive patterns of linguistic behaviour, such systems do not perpetuate existing social imbalances.
Nonetheless, this article has avoided the naïve high-level recommendation that data should always be debiased before training commences. On the contrary, it has shown explicitly that, for certain kinds of AI system, this is both practically unfeasible (i.e., debiasing processes can only be crudely automated) and methodologically undesirable (i.e., it produces systems with substantially lower general performance). Since NMT systems require large bi-text corpora that contain millions of sentence pairs, it is impossible to create a set of entirely unbiased training data. By examining a particular corpus, this article has revealed the extent of the inherent gender-related imbalances. Further, by examining the patterns of collocation and co-occurrence, it has been shown that gender-related stereotypes are perpetuated in such datasets. More gender-balanced versions of existing corpora can be created by means of downsampling, upsampling, or counterfactual augmentation. Unfortunately, though, these approaches not only impair the general performance of the system significantly (i.e., the BLEU scores are much worse), but also often achieve worse performance when assessed using gender-related metrics such as ∆G, and ∆S.
Responding to this problematical scenario, the present article has shown that the explored approaches to debiasing the MT data before training fail to significantly improve gender translation for WinoMT, and that a far more effective approach is to fine-tune a biased NMT system after it has been fully trained. The fine-tuning method only requires a tiny amount of adaptation data, yet it yields significant improvements in both the ∆G and ∆S scores, while only causing a slight corresponding decrease in the BLEU score. Further, the fine-tuning process is far less computationally intensive than training a whole NMT system from scratch on less biased data. This particular case-study therefore offers important insights into how practical ethical considerations can influence the technical strategies favoured during the process of designing and building certain state-of-the-art AI systems. And such studies are timely. Peter Singer’s Practical Ethics was first published in 1979, yet its emphasis on the need to explore the societal impact of moral philosophy remains as pertinent today as it was then – arguably even more so in our technologically interconnected modern digital democracies. Indeed, the material dimensions of morality have perhaps never been more apparent. The various technological devices we use daily inevitably influence the way we behave – and language-based AI systems exert a particularly powerful influence. From text-based machine learning techniques, to malicious twitter bots, to automated hate speech detection systems (e.g., Sap et al. 2019) – the ways in which these technologies are designed and trained have non-trivial ethical consequences for the societies in which they are becoming increasingly familiar and essential tools. Yet there are many crucial topics here that remain undiscussed. For instance, should we seek to develop a set of different metrics for different kinds of bias (e.g., gender-related, race-related, age-related)? And should all state-of-the-art systems be expected (or legally required?) to achieve competitive general performance while also obtaining sufficiently good scores in relation to these additional metrics? How would additional constraints of this kind change the research and development cultures associated with the task of building autonomous intelligent systems? How would the resulting systems influence our social interactions (assuming they would influence them at all)?
Unfortunately, the discussions about such matters that take place at the highest levels (e.g., in government) regularly fail to acknowledge the important practical difficulties of designing and constructing actual AI systems. To some extent, this arises from an unhelpful hierarchical and cultural divide. Those who actively design and build autonomous intelligent systems generally use Python, while those who talk about such system in boardrooms generally use PowerPoint. It is not surprising, then, that people who mainly interact with the latter group often share the tacit underlying assumption that all AI systems possess fairly similar properties and characteristics. This fallacious assumption can easily lead to repeated claims such as the one that all biases must be removed from data prior to training. This may be possible for some datasets, but, as this article has shown, it is not possible for all. It is hoped that the discussion presented here will help to promote more nuanced and insightful consideration of these crucially important issues by encouraging greater interaction and collaboration between coders, system designers, and those tasked with devising AI-related legislation. In particular, it would be pleasing if these initial results reinvigorated ongoing debates between these various groups about how bias can and should be most effectively reduced in state-of-the-art AI systems.
Data availability
The dataset used is in the public domain: http://www.statmt.org/wmt19/results.html.
Code availability
If the article is published, the code will be made available on github.
Notes
For an overview of many such concerns, see Leslie (2019).
The ‘Three laws of Robotics’ originate from the science fiction short story ‘Runaround’ (Asimov 1942).
The English output was obtained using Google Translate on 11/02/20. Given the increasing prevalence of ‘they’ as a third-person singular pronoun in English, NMT systems could default to this instead in such cases.
These examples were all translated using Google Translate on 11/02/20.
See, Segal (2005), esp. pp.1–9.
The list is available here: https://github.com/uclanlp/corefBias/blob/master/WinoBias/wino/generalized_swaps.txt.
A synthetic translation of the original gendered dataset was also produced, to help distinguish between the effects of gender-swapping and synthetic targets. For example, general translation quality can be affected by the model training on synthetic sentences of any kind, whether or not they reinforce system gender bias (Edunov et al. 2019). As gender marking manifests uniquely in different languages, results were obtained for three different language pairs chosen from the 8 supported by WinoMT, covering distinct language groups (Germanic, Romance and Semitic) and with varying linguistic properties: English to German, English to Spanish, and English to Hebrew. Only the English-German results will be discussed at length here. Some discussion of the results for other languages can be found in Saunders and Byrne 2020.
The ‘pro’ set contains entities such as male doctors and female nurses, while ‘anti’ contains female doctors and male nurses.
As our aim is to avoid word overfitting we exclude only exact English duplicates: for example, if ‘physician’ occurred in WinoMT but ‘doctor’ did not, then ‘doctor’ would be permitted. Since WinoMT has no target language references, we do not attempt to filter for German professions.
References
Ackerman, L. (2019). Syntactic and cognitive issues in investigating gendered coreference. Glossa A Journal of General Linguistics. https://doi.org/10.5334/gjgl.721
Asimov, I. (1942). Runaround. Astounding Science Fiction, 29(1), 94–103.
Bailey, A. H., LaFrance, M., & Dovidio, J. F. (2018). Is man the measure of all things? A social cognitive account of Androcentrism. Personality and Social Psychology Review, 23(4), 307–331.
Barrault, L., Bojar, O., Costa-jussà, M. R., Federmann, C., Fishel, M., Graham, Y., Haddow, B., Huck, M., Koehn, P., Malmasi, S. & Monz, C. (2019). Findings of the 2019 conference on machine translation (wmt19). In Proceedings of the Fourth Conference on Machine (pp. 1–61).
Best, S. (2017). Is Google translate sexist? Users report biased results when translating gender-neutral languages into English. The Daily Mail. Retrieved 28 Jan 2020 from https://www.dailymail.co.uk/sciencetech/article-5136607/Is-Google-Translate-SEXIST.html.
Blodgett, S. L., Barocas, S. Daumé III, H., & Wallach, H. (2020). Language (technology) is power: A critical survey of bias in NLP. Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics.
Bolukbasi, T., Chang, K. W., Zou, J. Y., Saligrama, V., & Kalai, A. T. (2016). Man is to computer programmer as woman is to homemaker? debiasing word embeddings. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 1, 4349–4357.
Cao, Y. T. & Daumé III, H. (2020). Toward gender-inclusive coreference resolution. In Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics.
Chinea-Rios, M., Peris, A., & Casacuberta, F. (2017). Adapting neural machine translation with parallel synthetic data. In Proceedings of the Second Conference on Machine Translation (pp. 138–147).
Costa-jussà, M. R., & de Jorge, A. (2020). Fine-tuning Neural Machine Translation on Gender-Balanced Datasets. In Proceedings of the Second Workshop on Gender Bias in Natural Language Processing (pp. 26–34).
Crawford, K. (2017). The trouble with bias. In Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, invited speaker.
Edunov, S., Ott, M., Ranzato, M. A., & Auli, M. (2019). On the evaluation of machine translation systems trained with back-translation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1908.05204. Retrieved January 5, 2021, from https://arxiv.org/pdf/1908.05204.pdf.
Darwin, H. (2017). Doing gender beyond the binary: A virtual ethnography. Symbolic Interaction, 40(3), 317–334.
Farajian, M. A., Turchi, M., Negri, M., & Federico, M. (2017). Multi-domain neural machine translation through unsupervised adaptation. In Proceedings of the Second Conference on Machine Translation (pp. 127–137).
Fogg, B. J. (2003). Persuasive technology: Using computers to change what we think and do. Burlington, MA: Morgan Kaufmann Publishers.
Font, J. E., & Costa-jussà, M. R. (2019). Equalizing gender bias in neural machine translation with word embeddings techniques. In Proceedings of the First Workshop on Gender Bias in Natural Language Processing (pp. 147–154).
French, R. M. (1999). Catastrophic forgetting in connectionist networks. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 3(4), 128–135.
Gonen, H., & Goldberg, Y. (2019). Lipstick on a Pig: Debiasing methods cover up systematic gender biases in word embeddings but do not remove them. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Volume 1 (Long and Short Papers) (pp. 609–614).
Google AI. (2020). Artificial intelligence at Google: Our principles. Retrieved 28 Jan 2020 from https://ai.google/principles.
Government Digital Service (GDS) and Office for Artificial Intelligence (OAI). (2019). Understanding artificial intelligence ethics and safety. Retrieved 28 Jan 2020 from https://www.gov.uk/guidance/understanding-artificial-intelligence-ethics-and-safety.
Heidegger, M. (1954). Die frage nach der technik. Vorträge und Aufsätze (pp. 13–14). Pfullingen: Neske.
HLEGAI (High Level Expert Group on Artificial Intelligence), European Commission. (2019). Ethics Guidelines for Trustworthy AI. https://ec.europa.eu/digital-single-market/en/news/ethics-guidelines-trustworthy-ai. Accessed 28 Jan 2020.
IEEE. (2020). Ethics in action: IEEE global initiative on ethics of autonomous and intelligent systems, Retrieved 3 Feb 2020 from https://ethicsinaction.ieee.org.
Kilgarriff, A., Baisa, V., Bušta, J., Jakubíček, M., Kovář, V., Michelfeit, J., Rychlý, P & Suchomel, V. (2014). The sketch engine: Ten years on. Lexicography, 1(1), 7–36: Retrieved January 5, 2021, from http://www.sketchengine.eu.
Kirkpatrick, J., Pascanu, R., Rabinowitz, N., Veness, J., Desjardins, G., Rusu, A. A., Milan, K., Quan, J., Ramalho, T., Grabska-Barwinska, A., & Hassabis, D. (2017). Overcoming catastrophic forgetting in neural networks. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 114(13), 3521–3526.
Kopetsch, T. (2010). Dem deutschen Gesundheitswesen gehen die Ärzte aus. Studie zur Altersstruktur und Arztzahlentwicklung, 5, 1–147. Retrieved January 5, 2021, from https://cdn.aerzteblatt.de/download/files/2010/09/down148303.pdf.
Leslie, D. (2019). Understanding artificial intelligence ethics and safety: A guide for the responsible design and implementation of AI systems in the public sector. The Alan Turing Institute, 6. Retrieved January 5, 2021, from https://www.turing.ac.uk/sites/default/files/2019-06/understanding_artificial_intelligence_ethics_and_safety.pdf.
Lloyd, K. (2018). Bias amplification in artificial intelligence systems. arXiv preprint arXiv:1809.07842. Retrieved January 5, 2021, from https://arxiv.org/ftp/arxiv/papers/1809/1809.07842.pdf.
Maudslay, R. H., Gonen, H., Cotterell, R., & Teufel, S. (2019). It’s all in the name: Mitigating gender bias with name-based counterfactual data substitution. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and the 9th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (EMNLP-IJCNLP) (pp. 5270–5278).
Merriam-Webster. (2019). Merriam-Webster’s words of the year 2019. Retrieved July 14, 2020, from https://www.merriam-webster.com/words-at-play/word-of-the-year/they.
Michel, P., & Neubig, G. (2018). Extreme adaptation for personalized neural machine translation. In Proceedings of the 56th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 2: Short Papers) (pp. 312–318).
Olson, P. (2018). The algorithm that made Google Translate sexist. Forbes. Retrieved 28 Jan 2020 from https://www.forbes.com/sites/parmyolson/2018/02/15/the-algorithm-that-helped-google-translate-become-sexist.
Papineni, K., Roukos, S., Ward, T., & Zhu, W. J. (2002). BLEU: A method for automatic evaluation of machine translation. In Proceedings of the 40th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational linguistics (pp. 311–318).
Post, M. (2018). A call for clarity in reporting BLEU scores. In Proceedings of the Third Conference on Machine Translation: Research Papers (pp. 186–191).
Prates, M. O., Avelar, P. H., & Lamb, L. C. (2019). Assessing gender bias in machine translation: A case study with Google Translate. Neural Computing and Applications, 32(10), 1–19.
Rudinger, R., Naradowsky, J., Leonard, B., & Van Durme, B. (2018). Gender bias in coreference resolution. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Volume 2 (Short Papers) (pp. 8–14).
Sap, M., Card, D., Gabriel, S., Choi, Y., & Smith, N. A. (2019). The risk of racial bias in hate speech detection. In Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (pp. 1668–1678).
Saunders, D. and Byrne, B. (2020). Reducing gender bias in neural machine translation as a domain adaptation problem. In Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics.
Saunders, D., Sallis, R. and Byrne, B. (2020). Neural machine translation doesn’t translate gender coreference right unless you make it. In Proceedings of the Second Workshop on Gender Bias in Natural Language Processing (pp. 35–43).
Segal, H. (2005). Technological utopianism in American culture. New York, USA: Syracuse University Press.
Shah, D., Schwartz, H. A., & Hovy, D. (2020). Predictive biases in natural language processing models: A conceptual framework and overview. In Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics.
Singer, P. (1979). Practical ethics. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
Stanovsky, G., Smith, N. A., & Zettlemoyer, L. (2019). Evaluating gender bias in machine translation. In Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (pp. 1679–1684).
Statista. (2019a). Ärztinnen in Deutschland nach Arztgruppe bis 2018. Retrieved 3 Feb 2020 from https://de.statista.com/statistik/daten/studie/158852/umfrage/anzahl-der-aerztinnen-nach-taetigkeitsbereichen/#statisticContainer.
Statista. (2019b). Studierende im Fach Humanmedizin in Deutschland nach Geschlecht bis 2018/2019. Retrieved 3 Feb 2020 from https://de.statista.com/statistik/daten/studie/200758/umfrage/entwicklung-der-anzahl-der-medizinstudenten.
Tan, S., Joty, S., Kan, M. Y., & Socher, R (2020). It’s Morphin Time! Combating linguistic discrimination with inflectional perturbations. In Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics.
Thaler, R. H., & Sunstein, C. R. (2008). Nudge: Improving decisions about health, wealth, and happiness. London, UK: Yale University Press.
Vanmassenhove, E., Hardmeier, C., & Way, A. (2018). Getting gender right in neural machine translation. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (pp. 3003–3008).
Vaswani, A., Shazeer, N., Parmar, N., Uszkoreit, J., Jones, L., Gomez, A. N., Kaiser, Ł. & Polosukhin, I. (2017). Attention is all you need. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (pp. 5998–6008).
Vaswani, A., Bengio, S., Brevdo, E., Chollet, F., Gomez, A.N., Gouws, S., Jones, L., Kaiser, Ł., Kalchbrenner, N., Parmar, N. & Sepassi, R. (2018). Tensor2tensor for neural machine translation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1803.07416. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1803.07416.pdf.
Verbeek, P. P. (2006). Materializing morality: Design ethics and technological mediation. Science, Technology, and Human Values, 31(3), 361–380. https://doi.org/10.1177/0162243905285847
Verbeek, P. P. (2017). Designing the morality of things: The ethics of behaviour-guiding technology. In J. van den Hoven, S. Miller, & T. Pogge (Eds.), Designing in ethics (pp. 78–94). Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
Wang, W., Watanabe, T., Hughes, M., Nakagawa, T., & Chelba, C. (2018). Denoising neural machine translation training with trusted data and online data selection. In Proceedings of the Third Conference on Machine Translation: Research Papers (pp. 133–143).
Winfield, A. F., Michael, K., Pitt, J., & Evers, V. (2019). Machine ethics: The design and governance of ethical AI and autonomous systems. Proceedings of the IEEE, 107(3), 509–517.
Wong, J. C. (2019). The viral selfie app ImageNet Roulette seemed fun – until it called me a racist slur. The Guardian. Retrieved 3 Feb 2020 from https://www.theguardian.com/technology/2019/sep/17/imagenet-roulette-asian-racist-slur-selfie.
Zhao, J., Wang, T., Yatskar, M., Ordonez, V., & Chang, K. W. (2017). Men also like shopping: Reducing gender bias amplification using corpus-level constraints. In Proceedings of the 2017 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing.
Zhao, J., Wang, T., Yatskar, M., Ordonez, V., & Chang, K. W. (2018a). Gender bias in coreference resolution: evaluation and debiasing methods. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Volume 2 (Short Papers) (pp. 15–20).
Zhao, J., Zhou, Y., Li, Z., Wang, W., & Chang, K. W. (2018b). Learning gender-neutral word embeddings. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (pp. 4847–4853).
Zou, J., & Schiebinger, L. (2018). AI can be sexist and racist—it’s time to make it fair. Nature, 559, 324–326. https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-018-05707-8
Zmigrod, R., Mielke, S. J., Wallach, H., & Cotterell, R. (2019). Counterfactual data augmentation for mitigating gender stereotypes in languages with rich morphology. In Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (pp. 1651–1661).
Acknowledgements
This work was made possible by the support of the Humanities and Social Change International Foundation.
Funding
The research reported here was funded by the Humanities and Social Change International Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. The corpus analysis in Sect. 3 was performed by SU, the systems described in Sects. 4 and 5 were built by DS, and the list of references was prepared by SC. The first draft of the manuscript was written by MT and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Tomalin, M., Byrne, B., Concannon, S. et al. The practical ethics of bias reduction in machine translation: why domain adaptation is better than data debiasing. Ethics Inf Technol 23, 419–433 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10676-021-09583-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10676-021-09583-1