Abstract
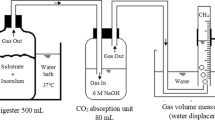
The paper and pulp sector is widely recognized for its substantial utilization of water resources and the release of heavily contaminated wastewater, which exacerbates issues of water scarcity and environmental issues. By evaluating the efficiency of a continuous flow anaerobic suspended growth reactor, this study unveils an approach to effectively treating paper and pulp effluents. This study explores anaerobic biogas production from paper and pulp effluent. Activated sludge from wastewater, added at 20%, 25%, and 30% ratios, enhanced reactor performance under anaerobic conditions. Characterization of effluent namely pH, TDS, alkalinity, BOD, COD, dissolved solids (DS), dissolved oxygen (DO) were monitored throughout the study and daily biogas assessments were conducted. A 5-liter UASB reactor with a transparent acrylic tube (15 cm diameter, 65 cm height) was constructed, featuring one influent port, an effluent port, and four sampling ports. It included a gas separator for biogas collection, maintaining a liquid level above the effluent pipe. Operating at mesophilic temperatures (25–35 °C). Optimal results were achieved with 70% effluent and 30% activated sludge, showing superior biogas production and organic impurity reduction. By utilizing wastewater sludge as a seeding material, this approach presents a promising solution for addressing environmental challenges in the paper industry through sustainable anaerobic processes.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The writers assure that the necessary data for the application and findings are contained within the article itself, with the raw data accessible through the corresponding author upon a reasonable inquiry.
References
Ajabshir, S. Z., & Niasari, M. S. (2017). Facile synthesis of nanocrystalline neodymium zirconate for highly efficient photodegradation of organic dyes. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 243, 219–226.
Ajabshir, S. Z., & Niasari, M. S. (2019). Preparation of magnetically retrievable CoFe2O4@SiO2@Dy2Ce2O7 nanocomposites as novel photocatalyst for highly efficient degradation of organic contaminants. Composites Part B: Engineering, 174(106930).
Ajabshir, S. Z., Morassaei, M. S., & Niasari, M. S. (2019). Eco-friendly synthesis of Nd2Sn2O7-based nanostructure materials using grape juice as green fuel as photocatalyst for the degradation of erythrosine. Composites Part B: Engineering, 167, 643–653.
Ashrafi, O., Yerushalmi, L., & Haghighat, F. (2015). Wastewater treatment in the pulp-and-paper industry: A review of treatment processes and the associated greenhouse gas emission. Journal of Environmental Management, 158, 146–157.
Bakraoui, M., Karouach, F., Ouhammou, B., Aggour, M., Essamri, A., & Bari, H. E. (2020). Biogas production from recycled paper mill wastewater by UASB digester: Optimal and mesophilic conditions. Biotechnology Reports, 25, 1–8.
Berni, M., Dorileo, I., Nathia, G., Carneiro, T. F., Lachos, D., & Santos, G. M. (2014). Anaerobic digestion and biogas production: Combine effluent treatment with energy generation in UASB reactor as biorefinery annex. International Journal of Chemical Engineering, 543529, 1–8.
Buzzini, A. P., Sakamoto, I. K., Varesche, M. B., & Pires, E. C. (2006). Evaluation of the microbial diversity in an USAB reactor treating wastewater from an unbleached pulp plant. Process Chemistry, 41, 168–176.
Cecen, F., Urban, W., & Haberl, R. (1992). Biological and Advanced treatment of sulphate pulp bleaching effluent. Water Science &Technology, 26, 435–444.
Chinnaraj, S., & Venkoba Rao, G. (2006). Implementation of an USAB anaerobic digestor at bagasse based pulp and paper industry. Bio mass and bio Energy, 30, 273–277.
Ferraz, F. M., Bruni, A. T., & Bianchi, V. L. (2009). Performance of an anaerobic baffled reactor (ABR) in treatment of cassava wastewater. Brazilian Journal of Microbiology, 40, 48–53.
Gautam, R. K., Olubukola, A., More, N., Jagatheesan, V., Muthukumaran, S., & Navaratna, D. (2023). Evaluation of long-term operational and treatment performance of a high-biomass submerged anaerobic membrane bioreactor treating abattoir wastewater. Chemical Engineering Journal, 463, 1–16.
Gaylarde, C. C., & Ratnieks, E. (1997). Anaerobic degradation of Paper Mill Sludge –. International Biodeteriorution and Biodegradution International Biodeteriorution & Biodegradution, 4, 287–293.
Ghodrati, M., Kamazani, M. M., & Ajabshir, S. Z. (2020). Zn3V3O8 nanostructures: Facile hydrothermal/ solvothermal synthesis, characterization, and electrochemical hydrogen storage. Ceramic International, 46, 28894–28902.
Grover, R., & Kennedy, J. F. (1999). Studies on the use of an anaerobic baffled reactor for the continuous anaerobic digestion of pulp and paper mill black liquor. Process Biochemistry, 34, 653–657.
Hashem, M. A., Payel, S., Hasan, M., Momen, M. A., & Sahen, M. S. (2021). Green preservation of goatskin to deplete chloride from tannery wastewater. Civil Engineering Journal, 2, 99–107.
Hua, J., Bai, S. Y., Li, Z. Y., & Zhou, H. C. (2017). Treatment of landfill leachate using an up-flow anaerobic sludge semi-fixed filter. IOP Conf Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 82, 1–10.
Ismail, W. N., Syah, M. I. A. I., Muhet, N. H. A., Bakar, N. H. A., Yusop, & Samah, H. M., N. A (2022). Adsorption behaviour of heavy metal ions by hybrid inulin TEOS for water treatment. Civil Engineering Journal, 8, 1787–1798.
Jagaba, A. H., Kutty, S. R. M., Lawal, I. M., Birniwa, A. H., Affam, A. C., Yaro, N. S. A., Usman, A. K., Umaru, I., Abubakar, S., Noor, A., Soja, U. B., & Yakubu, A. S. (2022). Circular economy potential and contributions of petroleum industry sludge utilization to environmental sustainability through engineered processes – A review. Cleaner and Circular Bioeconomy, 2, 1–21.
Kazemi, M. S., & Sobhani, A. (2023). CuMn2O4/chitosan micro/ nanocomposite: Green synthesis, methylene blue removal, and study of kinetic adsorption, adsorption isotherm experiments, mechanism, and adsorbent capacity. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 16, 1–13.
Kesalkar, V. P., Isha, P., Khedikar, & Sudame, A. M. (2016). Physico-chemical characteristics of waste water from Paper Industry. International Journal of Engineering Research and Applications, 2, 137–143.
Krishnan, G. V. T., & Kumar, P. (2007). Treatment of low strength soluble wastewater using anaerobic baffled reactor (ABR). Journal of Environmental Management, 90, 1–11.
Krishnan, G. V. T., & Kumar, P. (2008). Treatment of low strength complex wastewater using an anaerobic baffled reactor (ABR). Bioresource Technology, 99, 8193–8200.
Liang, X., Xu, Y., Yin, L., Wang, R., Li, P., Wang, J., & Liu, K. (2023). Sustainable utilization of pulp and paper wastewater. Water, 15, 1–17.
Meyer, T., & Edward, A. E. (2014). Anaerobic digestion of pulp and paper mill wastewater and sludge. Water Research, 65, 321–349.
Mishra, T., Ramola, S., Shankhwar, A. K., Rabha, A. K., & Srivastava, R. K. (2015). Pulp and paper mill effluent treatment by hybrid anaerobic upflow fixed-bed bioreactor combined with slow sand filter. Desalination and Water Treatment, 1–9.
Movahedyan, H., Assadi, A., & Parvaresh, A. (2007). Performance evaluation of an anaerobic baffled reactor treating wheat flour starch industry wastewater. Iran J Environ Health Sci Eng, 4, 77–84.
Nguyen, V. T., Beyer, E., Neumann, J., Awe, D., Pfeiffer, W., & Tranckner, J. (2019). Anaerobic treatment of residuals from tanks transporting food and fodder. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26, 32698–32707.
Pokhrel, D., & Viraraghavan, T. (2004). Treatment of pulp and paper mill wastewater – a review. Science of the Total Environmental, 333, 37–58.
Priadi Cindy, D., Wulandari, I., & Setyo Sarwanto Moersidik. (2014). Rahmatika, &. Biogas Production in the Anaerobic Digestion of Paper Sludge. 2nd International Conference on Civil Engineering - APCBEE Procedia, 9, 65–69.
Raji, V. R., & Packialakshmi, S. (2022). Assessing the wastewater pollutants retaining for a soil aquifer treatment using batch column experiments. Civil Engineering Journal, 8, 1482–1491.
Shreeshivadasan Chelliapan, Wilby, T., & Sallis, P. J. (2006). Performance of an upflow anaerobic stage reactor (UASB) in the treatment of pharmaceutical wastewater containing macrolide antibiotics. Water Research, 40, 507–516.
Sri, B., Kameswari, K., Chitra, K., & Thanasekaran, K. (2011). Effect of ozonation and ultrasonication pretreatment processes on co-digestion of tannery solid wastes. Clean Tech Environ Policy, 517–525.
Thompson, G., Swain, J., Kay, M., & Forster, C. F. (2000). The treatment of pulp and paper mill effluent. Bio Resource Technology, 77, 130–134.
Utami, I., Redjeki, S., Astuti, H. D., & Sani (2016). Biogas production and removal COD- BOD and TSS from wastewater industrial alcohol (Vinasse) by modified UASB bioreactor. MATEC Web of Conference, 58, 1–5.
Veluchamy, C., & Kalamdhad, A. S. (2017). Influence of pretreatment techniques on anaerobic digestion of pulp and paper mill sludge: A review. Bioresource Technology, 245, 1206–1219.
Yen, H. W., & Brune, E. D. (2007). Anaerobic co-digestor of algal sludge and waste paper to produce methane. Bio Resource Technology, 98, 130–134.
Funding
There is no funding for this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ramasamy, S., B, S. Evaluation of continuous flow anaerobic suspended growth reactor for treating papaer and pulp effluent. Environ Dev Sustain (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-024-04903-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-024-04903-z