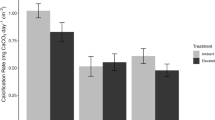
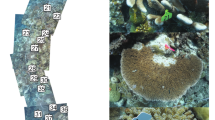
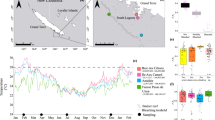
Abstract
Humans have relied on oceans since time immemorial and have exploited them for natural resources and recreational activities. With the advancement of technologies, rapid population growth and land-use change, the dependability on marine ecosystems has increased tremendously. Anthropogenic activities are causing increased global temperatures, altered weather conditions, melting glaciers, rising sea levels, acidification etc. The biological processes of marine ecosystems are getting affected indirectly or directly from the molecular level to rock pools to ocean basins, thus impacting overall ecosystem services. Out of various disturbances being caused by humans, global warming has been one of the most threatening factors with other anthropogenic inputs such as nutrient enrichment, sewage and microplastics, thereby causing significant changes in the symbiotic relationship between algae and corals. The coral associations with algae, macroalgae and other groups play a very important role in the functioning of ocean ecosystems and are very sensitive to anthropogenic inputs. The symbiotic association of algae with corals results in enriched biodiversity as well as it maintains the biogeochemistry of oceans and open coastal areas. The review outlines the importance of algal associations towards the maintenance of coral reefs, along with discussing the ecological services offered by them. One of the sections also discusses the impact of anthropogenic activities on the association between corals and algae. Also, the potential adaptive response of corals to the changing climatic conditions, and conservation strategies for the conservation of coral ecosystems to ensure a sustainable environment have also been discussed.
Graphical Abstract

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adjeroud, M., Poisson, E., Peignon, C., Penin, L., & Kayal, M. (2019). Spatial patterns and short-term changes of coral assemblages along a cross-shelf gradient in the southwestern lagoon of New Caledonia. Diversity, 11(2), 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/d11020021
Allgeier, J. E., Burkepile, D. E., & Layman, C. A. (2017). Animal pee in the sea: Consumer-mediated nutrient dynamics in the world’s changing oceans. Global Change Biology, 23(6), 2166–2178.
Andrady, A. L. (2011). Microplastics in the marine environment. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 62(8), 1596–1605.
Arossa, S., Martin, C., Rossbach, S., & Duarte, C. M. (2019). Microplastic removal by Red Sea giant clam (Tridacna maxima). Environmental Pollution, 252, 1257–1266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.05.149
Arthur, C., Baker, J., & Bamford, H. (2009). In Proceedings of the international research workshop on the occurrence, effects and fate of microplastic marine debris. NOAA technical memorandum NOS-OR&R30
Aswani, S., Mumby, P. J., Baker, A. C., Christie, P., McCook, L. J., Steneck, R. S., & Richmond, R. H. (2015). Scientific frontiers in the management of coral reefs. Frontiers in Marine Science, 2, 50. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2015.00050
Ayalon, I., de Barros Marangoni, L. F., Benichou, J. I., Avisar, D., & Levy, O. (2019). Red Sea corals under artificial light pollution at night (ALAN) undergo oxidative stress and photosynthetic impairment. Global Change Biology, 25(12), 4194–4207.
Ayalon, I., Rosenberg, Y., Benichou, J. I., Campos, C. L. D., Sayco, S. L. G., Nada, M. A. L., & Levy, O. (2021). Coral gametogenesis collapse under artificial light pollution. Current Biology, 31(2), 413–419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2020.10.039
Baker, A. C., Starger, C. J., McClanahan, T. R., & Glynn, P. W. (2004). Corals’ adaptive response to climate change. Nature, 430(7001), 741–741.
Baker, D. M., Freeman, C. J., Wong, J. C., Fogel, M. L., & Knowlton, N. (2018). Climate change promotes parasitism in a coral symbiosis. The ISME Journal, 12(3), 921–930.
Baswapoor, S., & Irfan, Z. B. (2018). Current status of coral reefs in India: Importance, rising threats and policies for its conservation and management. Madras school of economics, (Working paper), pp 2016–175
Baumann, J. H., Davies, S. W., Aichelman, H. E., & Castillo, K. D. (2018). Coral Symbiodinium community composition across the Belize Mesoamerican barrier reef system is influenced by host species and thermal variability. Microbial Ecology, 75, 903–915.
Baumgarten, S., Cziesielski, M. J., Thomas, L., Michell, C. T., Esherick, L. Y., Pringle, J. R., & Voolstra, C. R. (2018). Evidence for mi RNA-mediated modulation of the host transcriptome in cnidarian–dinoflagellate symbiosis. Molecular Ecology, 27(2), 403–418.
Bay, L. K., & Howells, E. J. (2021). Mapping the future of coral reefs. eLife, 10, e72978.
Bégin, C., Brooks, G., Larson, R. A., Dragićević, S., Scharrón, C. E. R., & Côté, I. M. (2014). Increased sediment loads over coral reefs in Saint Lucia in relation to land use change in contributing watersheds. Ocean & Coastal Management, 95, 35–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2014.03.018
Bergami, E., Pugnalini, S., Vannuccini, M. L., Manfra, L., Faleri, C., Savorelli, F., & Corsi, I. (2017). Long-term toxicity of surface-charged polystyrene nanoplastics to marine planktonic species Dunaliella tertiolecta and Artemia franciscana. Aquatic Toxicology, 189, 159–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2017.06.008
Berkelmans, R., & Van Oppen, M. J. (2006). The role of zooxanthellae in the thermal tolerance of corals: a ‘nugget of hope’for coral reefs in an era of climate change. In Proceedings of the royal society B: Biological sciences, 273(1599): 2305–2312
Bernal, P., Ferreira, B., Inniss, L., Marschoff, E., Rice, J., Rosenberg, A., & Simcock, A. (2017). Overall assessment of human impact on the Oceans. United Nations first global integrated marine assessment (p. 936). Cambridge: University Press.
Birrell, C. L., McCook, L. J., Willis, B. L., & Diaz-Pulido, G. A. (2008). Effects of benthic algae on the replenishment of corals and the implications for the resilience of coral reefs. Oceanography and Marine Biology: An Annual Review, 46, 25–63.
Bonaldo, R. M., & Hay, M. E. (2014). Seaweed-coral interactions: Variance in seaweed allelopathy, coral susceptibility, and potential effects on coral resilience. PLoS ONE, 9(1), e85786. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0085786
Bongiorni, L., Shafir, S., Angel, D., & Rinkevich, B. (2003). Survival, growth and gonad development of two hermatypic corals subjected to in situ fish-farm nutrient enrichment. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 253, 137–144.
Bourne, D. G., Morrow, K. M., & Webster, N. S. (2016). Insights into the coral microbiome: Underpinning the health and resilience of reef ecosystems. Annual Review of Microbiology, 70, 317–340.
Brading, P., Warner, M. E., Davey, P., Smith, D. J., Achterberg, E. P., & Suggett, D. J. (2011). Differential effects of ocean acidification on growth and photosynthesis among phylotypes of symbiodinium (Dinophyceae). Limnology and Oceanography, 56(3), 927–938.
Brown, B. E. (1997). Coral bleaching: Causes and consequences. Coral Reefs, 16, 129–138.
Brown, K. T., Bender-Champ, D., Bryant, D. E., Dove, S., & Hoegh-Guldberg, O. (2017). Human activities influence benthic community structure and the composition of the coral-algal interactions in the central Maldives. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 497, 33–40.
Bruno, J. F., Petes, L. E., Harvell, C. D., & Hettinger, A. (2003). Nutrient enrichment can increase the severity of coral diseases. Ecological Letters, 6(12), 10.
Bruno, J. F., Sweatman, H., Precht, W. F., Selig, E. R., & Schutt, e V.G.W. (2009). Assessing evidence of phase shifts from coral to macroalgal dominance on coral reefs. Ecology, 90, 1478–1484.
Bucher, M., Wolfowicz, I., Voss, P. A., Hambleton, E. A., & Guse, A. (2016). Development and symbiosis establishment in the cnidarian endosymbiosis model Aiptasia sp. Scientific Reports, 6(1), 19867. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep19867
Buddemeier, R. W., Kleypas, J. A., & Aronson, R. B. (2004). Coral reefs & global climate change. Potential contributions of climate change to stresses on coral reef ecosystems. Arlington: Pew Center on Global Climate Change.
Burke, L., Reytar, K., Spalding, M., & Perry, A. (2011). Reefs at risk revisited. Washington DC, USA: World Resource Institute.
Burn, D., Hoey, A. S., Matthews, S., Harrison, H. B., & Pratchett, M. S. (2023). Differential bleaching susceptibility among coral taxa and colony sizes, relative to bleaching severity across Australia’s great barrier reef and Coral Sea Marine Parks. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 191, 114907.
Cai, L., Tian, R. M., Zhou, G., Tong, H., Wong, Y. H., Zhang, W., & Qian, P. Y. (2018). Exploring coral microbiome assemblages in the South China Sea. Scientific Reports, 8(1), 2428. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-20515-w
Cannon, S. E., Donner, S. D., Fenner, D., & Beger, M. (2019). The relationship between macroalgae taxa and human disturbance on central Pacific coral reefs. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 145, 161–173.
Carballo-Bolaños, R., Denis, V., Huang, Y. Y., Keshavmurthy, S., & Chen, C. A. (2019). Temporal variation and photochemical efficiency of species in Symbiodinaceae associated with coral Leptoria phrygia (Scleractinia; Merulinidae) exposed to contrasting temperature regimes. PLoS ONE, 14(6), e0218801.
Chapron, L., Peru, E., Engler, A., Ghiglione, J. F., Meistertzheim, A. L., Pruski, A. M., & Lartaud, F. (2018). Macro-and microplastics affect cold-water corals growth, feeding and behaviour. Scientific Reports, 8(1), 15299. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-33683-6
Chen, M. C., Cheng, Y. M., Sung, P. J., Kuo, C. E., & Fang, L. S. (2003). Molecular identification of Rab7 (ApRab7) in Aiptasia pulchella and its exclusion from phagosomes harboring zooxanthellae. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 308(3), 586–595. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0006-291x(03)01428-1
Chen, M. C., Cheng, Y. M., Hong, M. C., & Fang, L. S. (2004). Molecular cloning of Rab5 (ApRab5) in Aiptasia pulchella and its retention in phagosomes harboring live zooxanthellae. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 324(3), 1024–1033. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.09.151
Christie, P., & White, A. T. (2007). Best practices for improved governance of coral reef marine protected areas. Coral Reefs, 26(4), 1047–1056. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00338-007-0235-9
Cleves, P. A., Tinoco, A. I., Bradford, J., Perrin, D., Bay, L. K., & Pringle, J. R. (2020). Reduced thermal tolerance in a coral carrying CRISPR-induced mutations in the gene for a heat-shock transcription factor. In Proceedings of the national academy of sciences, 117(46): 28899–28905. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1920779117
Cooper, T. F., Ridd, P. V., Ulstrup, K. E., Humphrey, C., Slivkoff, M., & Fabricius, K. E. (2008). Temporal dynamics in coral bioindicators for water quality on coastal coral reefs of the great barrier reef. Marine and Freshwater Research, 59(8), 703–716.
Cornwell, B., Armstrong, K., Walker, N. S., Lippert, M., Nestor, V., Golbuu, Y., & Palumbi, S. R. (2021). Widespread variation in heat tolerance and symbiont load are associated with growth tradeoffs in the coral Acropora hyacinthus in Palau. eLife, 10, e64790.
Correa, A. M. S., & Baker, A. C. (2009). Understanding diversity in coral-algal symbiosis: A cluster-based approach to interpreting fine-scale genetic variation in the genus Symbiodinium. Coral Reefs, 28, 81–93. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00338-008-0456-6
Costanza, R., De Groot, R., Sutton, P., Van der Ploeg, S., Anderson, S. J., Kubiszewski, I., & Turner, R. K. (2014). Changes in the global value of ecosystem services. Global Environmental Change, 26, 152–158.
Crane, N. L., Paddack, M. J., Nelson, P. A., Abelson, A. V. I. G. D. O. R., Rulmal, J., & Bernardi, G. I. A. C. O. M. O. (2016). Corallimorph and Montipora reefs in Ulithi Atoll, Micronesia: Documenting unusual reefs. Journal of the Ocean Science Foundation, 21(2016), 10–17.
Cunning, R., & Baker, A. C. (2013). Excess algal symbionts increase the susceptibility of reef corals to bleaching. Nature Clinical Practice Endocrinology & Metabolism, 3, 259–262.
Cunning, R., Vaughan, N., Gillette, P., Capo, T. R., Maté, J. L., & Baker, A. C. (2016). Dynamic regulation of partner abundance mediates response of reef coral symbioses to environmental change. Ecology, 96, 1411–1420.
Cunning, R., Silverstein, R. N., & Baker, A. C. (2017). Symbiont shuffling linked to differential photochemical dynamics of Symbiodinium in three Caribbean reef corals. Coral Reefs, 37, 145–152. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00338-017-1640-3
D’Angelo, C., & Wiedenmann, J. (2014). Impacts of nutrient enrichment on coral reefs: New perspectives and implications for coastal management and reef survival. Current Opinion in Environmental Sustainability, 7, 82–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cosust.2013.11.029
D’Angelo, C., et al. (2008). Blue light regulation of host pigment in reef-building corals. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 364, 97–106. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps07588
D’Angelo, C., Hume, B. C. C., Burt, J., Smith, E. G., Achterberg, E. P., & Wiedenmann, J. (2015). Local adaptation constrains the distribution potential of heat-tolerant Symbiodinium from the Persian/Arabian Gulf. ISME Journal, 9, 2551–2560.
Davies, T. W., Duff, J. P., Bennie, J., & Gaston, K. J. (2014). The nature, extent, and ecological implications of marine light pollution. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 12(6), 347–355. https://doi.org/10.1890/130281
Davies, T. W., Bennie, J., Cruse, D., Blumgart, D., Inger, R., & Gaston, K. J. (2017). Multiple night-time light-emitting diode lighting strategies impact grassland invertebrate assemblages. Glob Chan Biol, 23(7), 2641–2648. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.13615
Davy, S. K., Allemand, D., & Weis, V. M. (2012). Cell biology of cnidarian-dinoflagellate symbiosis. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 76, 229–261. https://doi.org/10.1128/MMBR.05014-11
De'ath G., Fabricius K. E., Sweatman H., Puotinen M. (2012). The 27-year decline of coral cover on the great barrier reef and its causes. In Proceedings national academy science USA. 109(44):17995–17999. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1208909109
Dehghani, H., Ghavam, M. P., Fatemi, S. M. R., & Fallah, M. J. (2018). Molecular diversity of Symbiodinium sp. with in six coral species in Larak Island, The Persian gulf. Iranian Journal of Fisheries Sciences, 17(1), 151–161.
Deloitte Access Economics. (2017). At what price? The economic, social and icon value of the Great Barrier Reef. Canberra, ACT, Australia: Deloitte Access Economics Pty Limited.
Dimijian, G. G. (2000). Evolving together: The biology of symbiosis Part 1. In Proceedings (Baylor university medical center) 13(3): 217–226. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/08998280.2000.11927677
Douglas, B, Rasher, Hay, M. E. (2010). Chemically rich seaweeds poison corals when not controlled by herbivores. In Proceedings National Academy Sciences, 107 (21): 9683-9688. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0912095107
Downs, C. A., Winter, E. K., Martinez, J., Kushmaro, A., Woodley, C. M., Loya, Y., & Ostrander, G. K. (2009). Symbiophagy as a cellular mechanism for coral bleaching. Autophagy, 5(2), 211–216. https://doi.org/10.4161/auto.5.2.7405
Drury, C., Lirman, D. (2021). Genotype by environment interactions in coral bleaching. In Proceedings Royal Society B, 288: 20210177
Duarte, C., Quintanilla-Ahumada, D., Anguita, C., Manríquez, P. H., Widdicombe, S., Pulgar, J., Silva-Rodríguez, E. A., Miranda, C., Manríquez, K., & Quijón, P. A. (2019). Artificial light pollution at night (ALAN) disrupts the distribution and circadian rhythm of a sandy beach isopod. Environmental Pollution, 248, 565–573. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.02.037
Dunn, J. G., Sammarco, P. W., & LaFleur, J. (2012). Effects of phosphate on growth and skeletal density in the scleractinian coral Acropora muricata: A controlled experimental approach. Journal Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 411, 34–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jembe.2011.10.013
Eakin, C. M., Lough, J. M., & Heron, S. F. (2009). Climate variability and change: Monitoring data and evidence for increased coral bleaching stress. In M. J. H. van Oppen & J. M. Lough (Eds.), Coral bleaching: Patterns, processes, causes and consequences (pp. 41–67). Springer-Verlag.
Eich, A., Ford, A. K., Nugues, M. M., McAndrews, R. S., Wild, C., & Ferse, S. C. A. (2019). Positive association between epiphytes and competitiveness of the brown algal genus Lobophora against corals. Peer Journal, 7, e6380. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.6380
El-Naggar, H. A. (2020). Human impacts on coral reef ecosystem. In E. R. Rhodes & Humood (Eds.), Natural resources management and biological sciences. London: IntechOpen.
Erftemeijer, P. L., Riegl, B., Hoeksema, B. W., & Todd, P. A. (2012). Environmental impacts of dredging and other sediment disturbances on corals: a review. Marine pollution bulletin, 64(9), 1737–1765.
Plastics Europe (2019) Plastics – The facts 2019. An analysis of european latest plastics production, demand and waste data. Retrieved from https://plasticseurope.org/knowledge-hub/plastics-the-facts-2019/#:~:text=Plastics%20%E2%80%93%20the%20Facts%202019,turnover%20in%20the%20plastics%20industry.
Ezzat, L., Maquer, J. F., Grover, R., Ferrier-Pagès, C. (2015). New insights into carbon acquisition and exchanges within the coral-dinoflagellate symbiosis under NH4+ and NO3– supply. In Proceedings biological sciences, 282: 20150610. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2015.0610
Fabricius, K. E., Okaji, K., & De’ath, G. (2010). Three lines of evidence to link outbreaks of the crown-of-thorns seastar Acanthaster planci to the release of larval food limitation. Coral Reefs, 29, 593–605. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00338-010-0628-z
Fautin, D. G., & Buddemeier, R. W. (2004). Adaptive bleaching: A general phenomenon. Hydrobiologia, 530–531, 459–467.
Ferrier-Pagès, C., Godinot, C., D’Angelo, C., Wiedenmann, J., & Grover, R. (2016). Phosphorus metabolism of reef organisms with algal symbionts. Ecological Monographs, 86, 262–277. https://doi.org/10.1002/ecm.1217
Fisher, R., O’Leary, R. A., Low-Choy, S., Mengersen, K., Knowlton, N., Brainard, R. E., et al. (2015). Species richness on coral reefs and the pursuit of convergent global estimates. Current Biology, 25, 500–505.
Francini-Filho, R. B., Coni, E. O., Meirelles, P. M., Amado-Filho, G. M., Thompson, F. L., Pereira-Filho, G. H., & Moura, R. L. (2013). Dynamics of coral reef benthic assemblages of the Abrolhos Bank, eastern Brazil: Inferences on natural and anthropogenic drivers. PLoS ONE, 8(1), e54260.
Freudenthal, H. (2007). Symbiodinium gen. nov. and Symbiodinium microadriaticum sp. nov., a Zooxanthella: Taxonomy, life cycle, and morphology. Journal Protozoology, 9, 45–52. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1550-7408.1962.tb02579.x
Fuller, Z. L., Mocellin, V. J. L., Morris, L. A., Cantin, N., Shepherd, J., Sarre, L., Peng, J., Liao, Y., Pickrell, J., Andolfatto, P., Matz, M., Bay, L. K., & Przeworski, M. (2020). Population genetics of the coral Acropora millepora: Toward genomic prediction of bleaching. Science, 369, eaba4674.
Gaston, K. J., Bennie, J., Davies, T. W., & Hopkins, J. (2013). The ecological impacts of nighttime light pollution: A mechanistic appraisal. Biological Reviews of the Cambridge Philosophical Society, 88(4), 912–927. https://doi.org/10.1111/brv.12036
Gaston, K. J., Davies, T. W., Nedelec, S. L., & Holt, L. A. (2017). Impacts of artificial light at night on biological timings. Annual Review Ecology Evolution Systematics, 48, 49–68. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-ecolsys-110316-022745
Gattuso, J. P., Brewer, P. G., Hoegh-Guldberg, O., Kleypas, J. A., Pörtner, H. O., & Schmidt, D. N. (2014). Cross-chapter box on ocean acidification. In C. B. Field, V. R. Barros, D. J. Dokken, K. J. Mach, M. D. Mastrandrea, & T. E. Bilir (Eds.), In Climate Change 2014: Impacts, adaptation, and vulnerability part A: Global and sectoral aspects contribution of working group II to the fifth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel of climate change (pp. 129–131). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Gorbunov, M. Y., & Falkowski, P. G. (2002). Photoreceptors in the cnidarian hosts allow symbiotic corals to sense blue moonlight. Limnol Ocean, 47, 309–315. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.2002.47.1.0309
Goulet, T. L., & Goulet, D. (2021). Climate change leads to a reduction in symbiotic derived cnidarian biodiversity on coral reefs. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution, 9, 636279.
Greenstein, B. J., & Pandolfi, J. M. (2008). Escaping the heat: Range shifts of reef coral taxa in coastal Western Australia. Global Change Biology, 14, 513–528.
Grottoli, A. G., Toonen, R. J., Thurber, R. V., van Woesik, R., et al. (2021). Increasing comparability among coral bleaching experiments. Ecological Applications, 31, e02262. https://doi.org/10.1002/eap.2262
Grover, R., Maguer, J. F., Allemand, D., & Ferrier-Page`s C,. (2003). Nitrate uptake in the scleractinian coral Stylophora pistillata. Limnology and Oceanography, 48, 2266–2274. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.2003.48.6.2266
Guest, J. R., Low, J., Tun, K., et al. (2016). Coral community response to bleaching on a highly disturbed reef. Science and Reports, 6, 20717.
Haese, R. R., Murray, E. J., Smith, C. S., Smith, J., Clementson, L., & Heggie, D. T. (2007). Diatoms control nutrient cycles in a temperate, wave-dominated estuary (southeast Australia). Limnology and Oceanography, 52, 2686–2700. https://doi.org/10.2307/4502413
Hall, N. M., Berry, K. L. E., Rintoul, L., & Hoogenboom, M. O. (2015). Microplastic ingestion by scleractinian corals. Marine Biology, 162, 725–732. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-015-2619-7
Hallock, P., & Schlager, W. (1986). Nutrient excess and the demise of coral reefs and carbonate platforms. Palaios, 1, 389–398. https://doi.org/10.2307/3514476
Halpern, B. S., Selkoe, K. A., Micheli, F., & Kappel, C. V. (2007). Evaluating and ranking the vulnerability of global marine ecosystems to anthropogenic threats. Conservation Biology, 21, 1301–1315. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1523-1739.2007.00752.x
Halpern, B. S., Walbridge, S., Selkoe, K. A., Kappel, C. V., Micheli, F., et al. (2008). A global map of human impact on marine ecosystems. Sciences, 319, 948–952. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1149345
Halpern, B. S., Frazier, M., Afflerbach, J., Lowndes, J. S., Micheli, F., O’Hara, C., & Selkoe, K. A. (2019). Recent pace of change in human impact on the world’s ocean. Scientific Reports, 9(1), 11609.
Harvell, D., Jorda Dahlgren, E., Merkel, S., Rosenberg, E., Raymundo, L., Smith, G., Weil, E., & Willis, B. (2007). Coral disease, environmental drivers, and the balance between coral and microbial associates. Oceanog, 20, 172–195. https://doi.org/10.5670/oceanog.2007.91
Hay, M. E., & Rasher, D. B. (2010). Coral reefs in crisis: Reversing the biotic death spiral. F1000 Biology Reports. https://doi.org/10.3410/B2-71
Heery, E. C., Olsen, A. Y., Feist, B. E., & Sebens, K. P. (2018). Urbanization-related distribution patterns and habitat-use by the marine mesopredator, giant Pacific octopus (Enteroctopus dofleini). Urban Ecosystems, 21, 707–719. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11252-018-0742-1
Heron, S. F., Maynard, J. A., Van Hooidonk, R., & Eakin, C. M. (2016). Warming trends and bleaching stress of the world’s coral reefs 1985–2012. Scientific Reports, 6(1), 38402.
Higuchi, T., Agostini, S., Casareto, B. E., Suzuki, Y., & Yuyama, I. (2015). The northern limit of corals of the genus Acropora in temperate zones is determined by their resilience to cold bleaching. Scientific Reports, 5(1), 18467. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep18467
Hoegh-Guldberg, O. (1999). Climate change, coral bleaching and the future of the world’s coral reefs. Marine and Freshwater Research, 50(8), 839–866. https://doi.org/10.1071/MF99078
Hoegh-Guldberg, O. (2009). Climate change and coral reefs: Trojan horse or false prophecy? A response to Maynard et al. (2008). Coral Reefs, 28, 569–575. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00338-009-0508-6
Hoegh-Guldberg, O. (2011). The impact of climate change on coral reef ecosystems. In Z. Dubins & N. Stambler (Eds.), Corals reefs: An ecosystem in transition (pp. 391–403). Springer.
Hoegh-Guldberg, O. (2012). The adaptation of coral reefs to climate change: Is the Red Queen being outpaced? Scientia Marina, 76(2), 403–408. https://doi.org/10.3989/scimar.03660.29A
Hoegh-Guldberg, O. (2014). Coral reef sustainability through adaptation: Glimmer of hope or persistent mirage? Current Opinion in Environmental Sustainability, 7, 127–133.
Hoegh-Guldberg, O., Mumby, P. J., Hooten, A. J., Steneck, R. S., Greenfield, P., Gomez, E., & Hatziolos, M. (2007). Coral reefs under rapid climate change and ocean acidification. Science, 318(5857), 1737–1742.
Hoegh-Guldberg, O., Poloczanska, E. S., Skirving, W., & Dove, S. (2017). Coral reef ecosystems under climate change and ocean acidification. Frontiers in Marine Science, 4, 158.
Hoegh-Guldberg, O., & Ridgway, T. (2016). Coral bleaching comes to the Great Barrier Reef as record-breaking global temperatures continue. The Conversation, 21
Hottinger, L. (1987). Conditions for generating carbonate platforms. Memorie Della Società Geologica Italiana, 40, 265–271.
Houlbrèque, F., & Ferrier-Pagès, C. (2009). Heterotrophy in tropical scleractinian corals. Biological Reviews, 84(1), 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-185X.2008.00058.x
Howells, E. J., Abrego, D., Liew, Y. J., Burt, J. A., Meyer, E., & Aranda, M. (2021). Enhancing the heat tolerance of reef-building corals to future warming. Science Advances, 7(34), eabg6070.
Hughes, T. P., Kerry, J. T., Álvarez-Noriega, M., Álvarez-Romero, J. G., Anderson, K. D., Baird, A. H., & Wilson, S. K. (2017). Global warming and recurrent mass bleaching of corals. Nature, 543(7645), 373–377. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature21707
Hume, B., D’angelo, C., Burt, J., Baker, A. C., Riegl, B., & Wiedenmann, J. (2013). Corals from the Persian/Arabian Gulf as models for thermotolerant reef-builders: Prevalence of clade C3 Symbiodinium, host fluorescence and ex situ temperature tolerance. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 72(2), 313–322.
Hume, B. C., Voolstra, C. R., Arif, C., D’Angelo, C., Burt, J. A., Eyal, G., & Wiedenmann, J. (2016). Ancestral genetic diversity associated with the rapid spread of stress-tolerant coral symbionts in response to Holocene climate change. In Proceedings of the national academy of sciences, 113(16): 4416–4421
Inniss, L., Simcock, A., Ajawin, A. Y., Alcala, A. C., Bernal, P., Calumpong, H. P & Węsławski, J. M. (2017). The first global integrated marine assessment: World ocean assessment I. United Nations, New York, pp 1752
IPCC (2007) Climate Change 2007: The physical science basis. Contribution of working group I to the fourth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change.
Ishii, Y., Maruyama, S., Takahashi, H., Aihara, Y., Yamaguchi, T., Yamaguchi, K., & Minagawa, J. (2019). Global shifts in gene expression profiles accompanied with environmental changes in cnidarian-dinoflagellate endosymbiosis. G3: Genes, Genomes, Genetics, 9(7), 2337–2347.
Islam, M. S., & Tanaka, M. (2004). Impacts of pollution on coastal and marine ecosystems including coastal and marine fisheries and approach for management: A review and synthesis. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 48(7–8), 624–649. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2003.12.004
Johannes, R. E. (1975). Pollution and degradation of coral reef communities. In E. J. F. Wood & R. E. Johannes (Eds.), Tropical marine pollution (pp. 13–51). Elsevier Science Publications.
Jokiel, P. L. (2004). Temperature stress and coral bleaching. In E. Rosenberg & Y. Loya (Eds.), Coral health and disease (pp. 401–425). Springer.
Jones, A. M., & Berkelmans, R. (2011). Tradeoffs to thermal acclimation: Energetics and reproduction of a reef coral with heat tolerant Symbiodinium type-D. Journal of Marine Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/185890
Jones, R., Fisher, R., & Bessell-Browne, P. (2019). Sediment deposition and coral smothering. PLoS ONE, 14(6), e0216248. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.02162
Jones, A. M., Berkelmans, R., van Oppen, M. J., Mieog, J. C., & Sinclair, W. (2008). A community change in the algal endosymbionts of a scleractinian coral following a natural bleaching event: field evidence of acclimatization. In Proceedings of the royal society B: Biological sciences, 275(1641): 1359-1365
Kaniewska, P., Alon, S., Karako-Lampert, S., Hoegh-Guldberg, O., & Levy, O. (2015). Signaling cascades and the importance of moonlight in coral broadcast mass spawning. eLife, 4, e09991. https://doi.org/10.7554/elife.09991
Kennedy, E. V., Foster, N. L., Mumby, P. J., & Stevens, J. R. (2015). Widespread prevalence of cryptic Symbiodinium D in the key Caribbean reef builder, Orbicella annularis. Coral Reefs, 34, 519–531.
Krueger, T., Bodin, J., Horwitz, N., Loussert-Fonta, C., Sakr, A., Escrig, S., & Meibom, A. (2018). Temperature and feeding induce tissue level changes in autotrophic and heterotrophic nutrient allocation in the coral symbiosis–A nanosims study. Scientific Reports, 8(1), 12710. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-31094-1
Kubanek, J., Whalen, K. E., Engel, S., Kelly, S. R., Henkel, T. P., Fenical, W., & Pawlik, J. R. (2002). Multiple defensive roles for triterpene glycosides from two caribbean sponges. Oecologia, 131, 125–136. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-001-0853-9
Lachs, L., Johari, N. A. M., Le, D. Q., Safuan, C. D. M., Duprey, N. N., Tanaka, K., & Shirai, K. (2019). Effects of tourism-derived sewage on coral reefs: Isotopic assessments identify effective bioindicators. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 148, 85–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.07.059
LaJeunesse, T. C. (2001). Investigating the biodiversity, ecology, and phylogeny of endosymbiotic dinoflagellates in the genus Symbiodinium using the ITS region: In search of a “species” level marker. Journal of Phycology, 37(5), 866–880.
LaJeunesse, T. C., Bonilla, H. R., Warner, M. E., Wills, M., Schmidt, G. W., & Fitt, W. K. (2008). Specificity and stability in high latitude eastern Pacific coral-algal symbioses. Limnology and Oceanography, 53(2), 719–727. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.2008.53.2.0719
LaJeunesse, T. C., Parkinson, J. E., Gabrielson, P. W., Jeong, H. J., Reimer, J. D., Voolstra, C. R., & Santos, S. R. (2018). Systematic revision of Symbiodiniaceae highlights the antiquity and diversity of coral endosymbionts. Current Biology, 28(16), 2570–2580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2018.07.008
LaJeunesse, T. C., Smith, R., Walther, M., Pinzón, J., Pettay, D. T., McGinley, M., & Warner, M. E. (2010). Host–symbiont recombination versus natural selection in the response of coral–dinoflagellate symbioses to environmental disturbance. In Proceedings of the royal society B: Biological sciences, 277(1696), 2925–2934. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2010.0385
Lapointe, B. E. (1997). Nutrient thresholds for bottom-up control of macroalgal blooms on coral reefs in Jamaica and southeast Florida. Limnology and Oceanography, 42, 1119–1131.
Lapointe, B. E., Barile, P. J., Littler, M. M., Littler, D. S., Bedford, B. J., & Gasque, C. (2005). Macroalgal blooms on southeast Florida coral reefs: I. Nutrient stoichiometry of the invasive green alga Codium isthmocladum in the wider Caribbean indicates nutrient enrichment. Harmful Algae, 4(6), 1092–1105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2005.06.004
Lee, M. J., Jeong, H. J., Jang, S. H., Lee, S. Y., Kang, N. S., Lee, K. H., & LaJeunesse, T. C. (2016). Most low-abundance “background” Symbiodinium spp. are transitory and have minimal functional significance for symbiotic corals. Microbial Ecology, 71, 771–783.
Lesser, M. P. (2004). Experimental biology of coral reef ecosystems. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 300(1–2), 217–252.
Levin, N., Kyba, C. C., Zhang, Q., de Miguel, A. S., Román, M. O., Li, X., & Elvidge, C. D. (2020). Remote sensing of night lights: A review and an outlook for the future. Remote Sensing of Environment, 237, 111443. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2019.111443
Levy, O., Dubinsky, Z., & Achituv, Y. (2003). Photobehavior of stony corals: Responses to light spectra and intensity. Journal of Experimental Biology, 206(22), 4041–4049.
Li, Z. (2009). Advances in marine symbiotic cyanobacteria. In P. M. Gault & P. J. Marler (Eds.), Handbook on cyanobacteria (pp. 463–472). New York: Nova Science Publishers Inc.
Liu, P. J., Meng, P. J., Liu, L. L., Wang, J. T., & Leu, M. Y. (2012). Impacts of human activities on coral reef ecosystems of southern Taiwan: A long-term study. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 64(6), 1129–1135.
Liu, H., Stephens, T. G., González-Pech, R. A., Beltran, V. H., Lapeyre, B., Bongaerts, P., & Chan, C. X. (2018). Symbiodinium genomes reveal adaptive evolution of functions related to coral-dinoflagellate symbiosis. Communications Biology, 1(1), 95. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-018-0098-3
Loiola, M., Cruz, I. C., Lisboa, D. S., Mariano-Neto, E., Leão, Z. M., Oliveira, M. D., & Kikuchi, R. K. (2019). Structure of marginal coral reef assemblages under different turbidity regime. Marine Environmental Research, 147, 138–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marenvres.2019.03.013
Luarte, T., Bonta, C. C., Silva-Rodriguez, E. A., Quijón, P. A., Miranda, C., Farias, A. A., & Duarte, C. (2016). Light pollution reduces activity, food consumption and growth rates in a sandy beach invertebrate. Environmental Pollution, 218, 1147–1153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.08.068
Ma, C. (2005). Genetic diversity of symbiotic dinoflagellates in the genus Symbiodinium. Protist, 156, 19–34.
Maor-Landaw, K., van Oppen, M. J., & McFadden, G. I. (2020). Symbiotic lifestyle triggers drastic changes in the gene expression of the algal endosymbiont Breviolum minutum (Symbiodiniaceae). Ecology and Evolution, 10(1), 451–466.
Maragos JE (1972) A study of the ecology of Hawaiian reef corals. University of Hawaii, Honolulu, Hawaii. (Doctoral Dissertation).
Maynard, J., Van Hooidonk, R., Eakin, C. M., Puotinen, M., Garren, M., Williams, G., & Harvell, C. D. (2015). Projections of climate conditions that increase coral disease susceptibility and pathogen abundance and virulence. Nature Climate Change, 5(7), 688–694.
McClanahan, T. R., Maina, J., & Ateweberhan, M. (2015). Regional coral responses to climate disturbances and warming is predicted by multivariate stress model and not temperature threshold metrics. Climatic Change, 131, 607–620.
McCook, L., Jompa, J., & Diaz-Pulido, G. (2001). Competition between corals and algae on coral reefs: A review of evidence and mechanisms. Coral Reefs, 19, 400–417.
McLachlan, R. H., Price, J. T., Muñoz-Garcia, A., Weisleder, N. L., Levas, S. J., Jury, C. P., & Grottoli, A. G. (2022). Physiological acclimatization in Hawaiian corals following a 22-month shift in baseline seawater temperature and pH. Scientific Reports, 12(1), 3712.
McManus, J. W., & Polsenberg, J. (2004). Coral-algal phase shifts on coral reefs: Ecological and environmental aspects. Progress in Oceanography, 60, 263–279.
Mendrik, F. M., Henry, T. B., Burdett, H., Hackney, C. R., Waller, C., Parsons, D. R., & Hennige, S. J. (2021). Species-specific impact of microplastics on coral physiology. Environmental Pollution, 269, 116238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.116238
Meron, D., Maor-Landaw, K., Weizman, E., Waldman Ben-Asher, H., Eyal, G., Banin, E., & Levy, O. (2019). The algal symbiont modifies the transcriptome of the Scleractinian coral Euphyllia paradivisa during heat stress. Microorganisms, 7(8), 256.
Messina, A. M., & Biggs, T. W. (2016). Contributions of human activities to suspended sediment yield during storm events from a small, steep, tropical watershed. Journal of Hydrology, 538, 726–742. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.03.053
Middlebrook, R., Hoegh-Guldberg, O., & Leggat, W. (2008). The effect of thermal history on the susceptibility of reef-building corals to thermal stress. Journal of Experimental Biology, 211(7), 1050–1056.
Middlebrook, R., Anthony, K. R., Hoegh-Guldberg, O., & Dove, S. (2012). Thermal priming affects symbiont photosynthesis but does not alter bleaching susceptibility in Acropora millepora. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 432, 64–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jembe.2012.07.005
Morais, J., Tebbett, S. B., Morais, R. A., & Bellwood, D. R. (2024). Hot spots of bleaching in massive Porites coral colonies. Marine Environmental Research, 193, 106276.
Morgan, K. M., Perry, C. T., Smithers, S. G., Johnson, J. A., & Daniell, J. J. (2016). Evidence of extensive reef development and high coral cover in nearshore environments: Implications for understanding coral adaptation in turbid settings. Scientific Reports, 6(1), 29616.
Mostafavi, P. G., Ashrafi, M. G., & Dehghani, H. (2013). Are symbiotic algae in corals in northern parts of the Persian Gulf resistant to thermal stress? Aquatic Ecosystem Health & Management, 16(2), 177–182. https://doi.org/10.1080/14634988.2013.790281
Mote, S., Gupta, V., De, K., Hussain, A., More, K., Nanajkar, M., & Ingole, B. (2021). Differential Symbiodiniaceae association with coral and coral-eroding sponge in a bleaching Impacted marginal coral reef environment. Frontiers in Marine Science, 8, 666825.
Moullec, F., Asselot, R., Auch, D., Blöcker, A. M., Börner, G., Färber, L., & Pellerin, F. (2021). Identifying and addressing the anthropogenic drivers of global change in the North Sea: A systematic map protocol. Environmental Evidence, 10(1), 1–11.
Mumby, P. J., Wolff, N. H., Bozec, Y. M., Chollett, I., & Halloran, P. (2014). Operationalizing the resilience of coral reefs in an era of climate change. Conservation Letters, 7(3), 176–187.
Muscatine, L., & Porter, J. W. (1977). Reef corals: Mutualistic symbioses adapted to nutrient-poor environments. BioScience, 27(7), 454–460. https://doi.org/10.2307/1297526
Mutalipassi, M., Riccio, G., Mazzella, V., Galasso, C., Somma, E., Chiarore, A., & Zupo, V. (2021). Symbioses of cyanobacteria in marine environments: Ecological insights and biotechnological perspectives. Marine Drugs, 19(4), 227. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19040227
Nautiyal, A., & Ramlal, A. (2021). Clean energy sources for a better and sustainable environment of future generations. In P. Singh, S. Singh, G. Kumar, & P. Baweja (Eds.), Energy: Crisis, challenges and solutions (pp. 151–168). Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Not, F., Probert, I., Ribeiro, C. G., Crenn, K., Guillou, L., Jeanthon, C., & Vaulot, D. (2016). Photosymbiosis in marine pelagic environments. In L. Stal & M. Cretoiu (Eds.), The marine microbiome. Cham: Springer.
Okubo, N., Takahashi, S., & Nakano, Y. (2018). Microplastics disturb the anthozoan-algae symbiotic relationship. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 135, 83–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.07.016
Oliver, T. A., & Palumbi, S. R. (2011). Do fluctuating temperature environments elevate coral thermal tolerance? Coral Reefs, 30, 429–440.
Omori, M., Fukami, H., Kobinata, H., & Hatta, M. (2001). Significant drop of fertilization of Acropora corals in 1999: An after-effect of heavy coral bleaching? Limnology and Oceanography, 46(3), 704–706.
Van Oppen, M. J., Oliver, J. K., Putnam, H. M., & Gates, R. D. (2015). Building coral reef resilience through assisted evolution. In Proceedings of the national academy of sciences, 112(8): 2307–2313
Osman, E. O., Suggett, D. J., Voolstra, C. R., Pettay, D. T., Clark, D. R., Pogoreutz, C., & Smith, D. J. (2020). Coral microbiome composition along the northern Red Sea suggests high plasticity of bacterial and specificity of endosymbiotic dinoflagellate communities. Microbiome, 8(1), 1–16.
Poblete, I. B. S., Ofélia de Queiroz, F. A., & de Medeiros, J. L. (2022). Sewage-water treatment with bio-energy production and carbon capture and storage. Chemosphere, 286, 131763.
Pogoreutz, C., Rädecker, N., Cárdenas, A., Gärdes, A., Wild, C., & Voolstra, C. R. (2017). Nitrogen fixation aligns with nifH abundance and expression in two coral trophic functional groups. Frontiers in Microbiology, 8, 1187.
Powell, A., Smith, D. J., Hepburn, L. J., Jones, T., Berman, J., Jompa, J., & Bell, J. J. (2014). Reduced diversity and high sponge abundance on a sedimented Indo-Pacific reef system: Implications for future changes in environmental quality. PLoS ONE, 9(1), e85253.
Precht, W. F., & Aronson, R. B. (2004). Climate flickers and range shifts of reef corals. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 2(6), 307–314.
Qin, Z., Yu, K., Chen, B., Wang, Y., Liang, J., Luo, W., & Huang, X. (2019). Diversity of Symbiodiniaceae in 15 coral species from the Southern South China Sea: Potential relationship with coral thermal adaptability. Frontiers in Microbiology, 10, 2343.
Rädecker, N., Pogoreutz, C., Voolstra, C. R., Wiedenmann, J., & Wild, C. (2015). Nitrogen cycling in corals: The key to understanding holobiont functioning? Trends in Microbiology, 23(8), 490–497.
Rajasulochana, P., & Preethy, V. (2016). Comparison on efficiency of various techniques in treatment of waste and sewage water–A comprehensive review. Resource-Efficient Technologies, 2(4), 175–184.
Rasher, D. B., & Hay, M. E. (2010). Chemically rich seaweeds poison corals when not controlled by herbivores. In Proceedings of the national academy of sciences, 107(21): 9683-9688. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0912095107
Redding, J. E., Myers-Miller, R. L., Baker, D. M., Fogel, M., Raymundo, L. J., & Kim, K. (2013). Link between sewage-derived nitrogen pollution and coral disease severity in Guam. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 73(1), 57–63.
Reichert, J., Schellenberg, J., Schubert, P., & Wilke, T. (2018). Responses of reef building corals to microplastic exposure. Environmental Pollution, 237, 955–960. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.11.006
Reichert, J., Arnold, A. L., Hoogenboom, M. O., Schubert, P., & Wilke, T. (2019). Impacts of microplastics on growth and health of hermatypic corals are species-specific. Environmental Pollution, 254, 113074. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113074
Richards, T. A., & McCutcheon, J. P. (2019). Coral Symbiosis is a Three-Player Game. https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-019-00949-6
Richmond, R. H. (1993). Coral reefs: Present problems and future concerns resulting from anthropogenic disturbance. American Zoologist, 33(6), 524–536.
Richmond, R. H., Tisthammer, K. H., & Spies, N. P. (2018). The effects of anthropogenic stressors on reproduction and recruitment of corals and reef organisms. Frontiers in Marine Science, 5, 226. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2018.00226
Rinkevich, B. (1989). The contribution of photosynthetic products to coral reproduction. Marine Biology, 101, 259–263. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00391465
Risk, M. J. (2014). Assessing the effects of sediments and nutrients on coral reefs. Current Opinion in Environmental Sustainability, 7, 108–117.
Rodriguez-Lanetty, M., Phillips, W. S., & Weis, V. M. (2006). Transcriptome analysis of a cnidarian–dinoflagellate mutualism reveals complex modulation of host gene expression. BMC Genomics, 7(1), 1–11.
Rogers, C. S. (1990). Responses of coral reefs and reef organisms to sedimentation. Marine Ecology Progress Series Oldendorf, 62(1), 185–202.
Rosenberg, Y., Doniger, T., & Levy, O. (2019). Sustainability of coral reefs are affected by ecological light pollution in the Gulf of Aqaba/Eilat. Communications Biology, 2(1), 289.
Rosic, N. N., & Dove, S. (2011). Mycosporine-like amino acids from coral dinoflagellates. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 77(24), 8478–8486.
Rosset, S., Wiedenmann, J., Reed, A. J., & D’Angelo, C. (2017). Phosphate deficiency promotes coral bleaching and is reflected by the ultrastructure of symbiotic dinoflagellates. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 118(1–2), 180–187.
Rowan, R., Knowlton, N., Baker, A., & Jara, J. (1997). Landscape ecology of algal symbionts creates variation in episodes of coral bleaching. Nature, 388(6639), 265–269.
Sampayo, E. M., Ridgway, T., Bongaerts, P., & Hoegh-Guldberg, O. (2008). Bleaching susceptibility and mortality of corals are determined by fine-scale differences in symbiont type. In Proceedings of the national academy of sciences, 105(30): 10444-10449
Sarkar, S., & Ghosh, A. K. (2013). Coral bleaching a nemesis for the Andaman reefs: Building an improved conservation paradigm. Ocean & Coastal Management, 71, 153–162.
Sarkar, S., & Sarkar, S. (2016). Diversity of corals and benthic algae across the shallow-water reefs of Andaman Islands: Managing the valuable ecosystems. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 18, 1801–1814. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-015-9709-z
Sawall, Y., Teichberg, M. C., Seemann, J., Litaay, M., Jompa, J., & Richter, C. (2011). Nutritional status and metabolism of the coral Stylophora subseriata along a eutrophication gradient in Spermonde Archipelago (Indonesia). Coral Reefs, 30, 841–853.
Shantz, A. A., & Burkepile, D. E. (2014). Context-dependent effects of nutrient loading on the coral–algal mutualism. Ecology, 95(7), 1995–2005.
Silverstein, R. N., Cunning, R., & Baker, A. C. (2015). Change in algal symbiont communities after bleaching, not prior heat exposure, increases heat tolerance of reef corals. Global Change Biology, 21(1), 236–249.
Silverstein, R. N., Cunning, R., & Baker, A. C. (2017). Tenacious D: Symbiodinium in clade D remain in reef corals at both high and low temperature extremes despite impairment. Journal of Experimental Biology, 220(7), 1192–1196.
Sinha, E., Michalak, A. M., & Balaji, V. (2017). Eutrophication will increase during the 21st century as a result of precipitation changes. Science, 357(6349), 405–408.
Smith, J. E., Brainard, R., Carter, A., Grillo, S., Edwards, C., Harris, J., & Sandin, S. (2016). Re-evaluating the health of coral reef communities: Baselines and evidence for human impacts across the central Pacific. In Proceedings of the royal society B: Biological Sciences, 283(1822): 20151985
Souter, D., Planes, S., Wicquart, J., Logan, M., Obura, D., Staub, F. (2021). In Souter, D., Planes, S., Wicquart, J., Logan, M., Obura, D., Staub, F. (Eds.), Status of coral reefs of the world: 2020 report. Global coral reef monitoring network (GCRMN) and international coral reef initiative (ICRI)
Stanley, G., & Van de Schootbrugge, B. (2018). The evolution of the coral-algal symbiosis and coral bleaching in the geologic past. In M. van Oppen & J. Lough (Eds.), Coral bleaching ecological studies. Cham: Springer.
Stat, M., Pochon, X., Franklin, E. C., Bruno, J. F., Casey, K. S., Selig, E. R., & Gates, R. D. (2013). The distribution of the thermally tolerant symbiont lineage (S ymbiodinium clade D) in corals from H awaii: Correlations with host and the history of ocean thermal stress. Ecology and Evolution, 3(5), 1317–1329.
Su, Y., Zhang, K., Zhou, Z., Wang, J., Yang, X., Tang, J., & Lin, S. (2020). Microplastic exposure represses the growth of endosymbiotic dinoflagellate Cladocopium goreaui in culture through affecting its apoptosis and metabolism. Chemosphere, 244, 125485. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125485
Suchley, A., McField, M. D., & Alvarez-Filip, L. (2016). Rapidly increasing macroalgal cover not related to herbivorous fishes on Mesoamerican reefs. PeerJ, 4, e2084.
Sutthacheep, M., Yucharoen, M., Klinthong, W., Pengsakun, S., Sangmanee, K., & Yeemin, T. (2013). Impacts of the 1998 and 2010 mass coral bleaching events on the Western Gulf of Thailand. Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 96, 25–31.
Sweet, M. J., & Brown, B. E. (2016). Coral responses to anthropogenic stress in the twenty-first century: An ecophysiological perspective. Oceanography and Marine Biology: An Annual Review, 54, 271–314.
Syakti, A. D., Jaya, J. V., Rahman, A., Hidayati, N. V., Raza’i, T. S., Idris, F., & Chou, L. M. (2019). Bleaching and necrosis of staghorn coral (Acropora formosa) in laboratory assays: Immediate impact of LDPE microplastics. Chemosphere, 228, 528–535. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.04.156
Szmant, A. M. (2002). Nutrient enrichment on coral reefs: Is it a major cause of coral reef decline? Estuaries, 25, 743–766. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02804903
Tamir, R., Eyal, G., Cohen, I., & Loya, Y. (2020). Effects of light pollution on the early life stages of the most abundant northern red sea coral. Microorganisms, 8(2), 193. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8020193
Tanaka, Y., Grottoli, A. G., Matsui, Y., Suzuki, A., & Sakai, K. (2017). Effects of nitrate and phosphate availability on the tissues and carbonate skeleton of scleractinian corals. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 570, 101–112.
Teichberg, M., Wild, C., Bednarz, V. N., Kegler, H. F., Lukman, M., Gärdes, A. A., & Plass-Johnson, J. G. (2018). Spatio-temporal patterns in coral reef communities of the Spermonde Archipelago, 2012–2014, I: Comprehensive reef monitoring of water and benthic indicators reflect changes in reef health. Frontiers in Marine Science, 5, 33.
Thacker, R. W., Becerro, M. A., Lumbang, W. A., & Paul, V. J. (1998). Allelopathic interactions between sponges on a tropical reef. Ecology, 79(5), 1740–1750. https://doi.org/10.2307/176792
Thinesh, T., Meenatchi, R., Jose, P. A., Kiran, G. S., & Selvin, J. (2019). Differential bleaching and recovery pattern of southeast Indian coral reef to 2016 global mass bleaching event: Occurrence of stress-tolerant symbiont Durusdinium (Clade D) in corals of Palk Bay. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 145, 287–294.
Tomascik, T., & Sander, F. J. M. B. (1985). Effects of eutrophication on reef-building corals: I. Growth rate of the reef-building coral Montastrea annularis. Marine Biology, 87, 143–155.
Tomascik, T., & Sander, F. (1987). Effects of eutrophication on reef-building corals: II. Structure of scleractinian coral communities on fringing reefs, Barbados, West Indies. Marine Biology, 94, 53–75.
Tong, H., Cai, L., Zhou, G., Yuan, T., Zhang, W., Tian, R., & Qian, P. Y. (2017). Temperature shapes coral-algal symbiosis in the South China Sea. Scientific Reports, 7(1), 40118.
United Nations environment programme (UNEP), International sustainability unit, & international coral reef initiative (2018). The coral reef economy: The business case for investment in the protection, preservation and enhancement of coral reef health. https://wedocs.unep.org/20.500.11822/26694.
Van Hooidonk, R., Maynard, J. A., Manzello, D., & Planes, S. (2014). Opposite latitudinal gradients in projected ocean acidification and bleaching impacts on coral reefs. Global Change Biology, 20(1), 103–112. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.12394
Van Oppen, M. J., Gates, R. D., Blackall, L. L., Cantin, N., et al. (2017). Shifting paradigms in restoration of the world’s coral reefs. Global Change Biology, 23, 3437–3448.
Vanwonterghem, I., & Webster, N. S. (2020). Coral reef microorganisms in a changing climate. Iscience, 23(4), 100972.
Veron, J. E., Hoegh-Guldberg, O., Lenton, T. M., Lough, J. M., Obura, D. O., Pearce-Kelly, P. A. U. L., & Rogers, A. D. (2009). The coral reef crisis: The critical importance of <350 ppm CO2. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 58(10), 1428–1436.
Whittingham, E., Campbell, J., Townsley, P. (2003). Poverty and reefs, Volume 1: A global overview. Department for international development (DFID), IMM Ltd innovation centre rennes drive exeter university campus (IMM) and intergovernmental oceanographic commission of UNESCO (IOC/UNESCO), UK
Wiedenmann, J., D’Angelo, C., Smith, E. G., Hunt, A. N., Legiret, F. E., Postle, A. D., & Achterberg, E. P. (2013). Nutrient enrichment can increase the susceptibility of reef corals to bleaching. Nature Climate Change, 3(2), 160–164. https://doi.org/10.1038/nclimate1661
Wilkinson, C. (2004). Status of coral reefs of the world. Townesville: Australian Institute of Marine Science.
Williams, R., Wright, A. J., Ashe, E., Blight, L. K., Bruintjes, R., Canessa, R., & Wale, M. A. (2015). Impacts of anthropogenic noise on marine life: Publication patterns, new discoveries, and future directions in research and management. Ocean & Coastal Management, 115, 17–24.
Windom, H. L. (1992). Contamination of the marine environment from land-based sources. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 25(1–4), 32–36.
Work, T. M., Aeby, G. S., & Maragos, J. E. (2008). Phase shift from a coral to a corallimorph-dominated reef associated with a shipwreck on Palmyra Atoll. PLoS ONE, 3(8), e2989.
Yamano, H., Sugihara, K., & Nomura, K. (2011). Rapid poleward range expansion of tropical reef corals in response to rising sea surface temperatures. Geophysical Research Letters, 38(4), L04601. https://doi.org/10.1029/2010gl046474
Yuyama, I., Ishikawa, M., Nozawa, M., Yoshida, M. A., & Ikeo, K. (2018). Transcriptomic changes with increasing algal symbiont reveal the detailed process underlying establishment of coral-algal symbiosis. Scientific Reports, 8(1), 16802. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-34575-5
Zhou, G., Cai, L., Li, Y., Tong, H., Jiang, L., Zhang, Y., & Huang, H. (2017). Temperature-driven local acclimatization of Symbiodnium hosted by the Coral Galaxea fascicularis at Hainan Island, China. Frontiers in Microbiology, 8, 2487.
Ziegler, M., Arif, C., Burt, J. A., Dobretsov, S., Roder, C., LaJeunesse, T. C., & Voolstra, C. R. (2017). Biogeography and molecular diversity of coral symbionts in the genus Symbiodinium around the Arabian Peninsula. Journal of Biogeography, 44(3), 674–686.
Ziegler, M., Eguíluz, V. M., Duarte, C. M., & Voolstra, C. R. (2018). Rare symbionts may contribute to the resilience of coral–algal assemblages. The ISME Journal, 12(1), 161–172. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2017.151
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to express their sincere gratitude to the Principals of Hindu College, Maitreyi College, Deshbandhu College and PGDAV College University of Delhi for providing the necessary facilities to compile this manuscript.
Funding
The author declared that they have no funding statement.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors have equally contributed towards the manuscript preparation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Rawat, V.S., Nautiyal, A., Ramlal, A. et al. Algae-coral symbiosis: fragility owing to anthropogenic activities and adaptive response to changing climatic trends. Environ Dev Sustain (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-024-04748-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-024-04748-6