Abstract
The problem of contaminated sites is a hot and difficult issue in global environmental sustainable development. Because the contaminated site carries a large number of harmful substances (heavy metal ions, organic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, toxic gases, etc.), it brings great security risks to the environmental ecological security and people's health. Effective identification of the characteristics of contaminated sites and understanding of the research status and development trend of contaminated sites are of great significance to environmental sustainable development and environmental governance and restoration. Based on Web of Science database, this study systematically, quantitatively and visually analyzes the research status of contaminated sites by bibliometrics and knowledge graph technology. The results show that bibliometrics and knowledge graph are effective in information retrieval and visualization. It can display the information of different scales and different times in the study of contaminated sites, and find the distribution characteristics of popular keywords. The cluster cases of this study show that the problems of contaminated site research mainly focus on suspended particulate matter pollution, water pollution, heavy metal pollution, organic pollution, pollution reduction and bioremediation technology research. In the future, the hot issues of contaminated site remediation and environmental sustainable development will focus on strengthening the research of microbial remediation technology, nanomaterial technology, composite material adsorption technology and so on.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
A contaminated site refers to a space area containing hazardous substances by means of accumulation, storage, treatment or relocation. It has seriously threatened the sustainable development of the environment, biodiversity and human health (Bisht et al., 2023; Chen et al., 2022a, 2022b; Manral et al., 2023; Song & Hu, 2021). The main reasons for the formation of polluted sites are population growth, pesticide use, deforestation, and urban facility construction (Shahi et al., 2023). Usually, the carriers of harmful substances in contaminated sites include site soil, site groundwater, site surface water, site ambient air, site waste pollutants, etc. (Chen et al., 2022a, 2022b; Obolkin et al., 2022; Tao et al., 2022; Verma & Singh, 2021). The types of contaminated sites are many and complex. According to the types of pollutants, they can be simply divided into inorganic pollution and organic pollution.
Inorganic pollution is mainly caused by heavy metal polluted sites, which mainly come from iron and steel smelting, tailings, solid wastes of the chemical industry, etc. Representative pollutants include lead Pb, arsenic As, cadmium Cd, chromium Cr, mercury Hg, copper Cu, nickel Ni, etc. (Gao et al., 2023a; Mahato et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2021). After heavy metals enter the soil environment, they are not easy to biodegrade or dissolve with water, and the bioenrichment effect is obvious, which seriously affects human health after skin exposure or ingestion. For example, pollution has an impact on human skin system, resulting in skin rash, swelling, itching and even ulceration (Rauf et al., 2020). Pollution can also cause serious harm to the digestive system and nervous system, such as diarrhea, vomiting, pus and blood stools, headache, unconsciousness and convulsions (Kothapalli, 2021). Heavy metals in contaminated sites even cause serious harm to the human hematopoietic system, affecting the body's normal metabolism, hindering cell function, and resulting in a serious risk of cancer. Such as leukemia, etc. (Cirovic & Cirovic, 2022). In recent years, many experts and researchers in the fields of environment and health have carried out researches on inorganic pollution in aspects of physics, chemistry and bioremediation, and achieved remarkable results (Hassan et al., 2022; Liu et al., 2010; Zheng et al., 2021), providing theoretical and technical support for the prevention and control of inorganic pollution in sites.
Organic pollution is mainly caused by petroleum, chemical, coking, pesticide and other polluted sites, and the pollutants are represented by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, organic solvents, benzene series, halogenated hydrocarbons, etc. (Alao & Adebayo, 2022; Tang et al., 2021; Yang et al., 2021;). In the production and transportation process of oil fields and chemical enterprises, organic pollutants are likely to enter the soil. The typical organic pollutants are polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, polychlorinated biphenyls, benzene series and so on. These pollutants remaining in the soil will not only change the normal structure and function of the soil, but also be ingested by the human body through the food chain, posing a serious threat to human health (Schanzer et al., 2022; Zhou & Li, 2021). In addition to ingestion through the food chain, pollution can also be transmitted through the air. For example, the CO, SO2 and inhalable particles produced in the combustion process of fossil fuels. CO is easily toxic. SO2 interacts with water to form acid rain, which can damage plants, erode buildings, and acidify soil. Particulate matter can also cause respiratory tract and lung damage and infections. Fossil fuels are polluting the environment and deteriorating people's living standards (Sial et al., 2022). Since the contaminated site is closely related to the ecological environment and human health, it is urgent to understand the characteristics of the contaminated site comprehensively and systematically, and to remedy and treat the contaminated site.
Web of Science database stores a large number of high-level academic papers and scientific research results all over the world. These theoretical knowledge and applied technologies can provide a good knowledge base for the research of contaminated sites and environmental remediation methods. At present, relevant scholars have used bibliometrics to carry out relevant analysis on the restoration of contaminated sites. For example, Aristotle et al. (2021) studied the adsorption of Microalgal biosorption on heavy metal ions in industrial wastewater pollution by using bibliometric analysis, and obtained an effective method for remediation of contaminated sites. Yan et al. (2022) used a large number of literature data to comprehensively analyze the research status of soil heavy metal pollution in polluted sites in China. The results show that the types of polluted sites in China mainly include mining areas, industrial areas, sewage irrigation and dismantling sites. Cd and Pb are the most widespread heavy metals in China. In addition, Bekun (2022) and Quito et al. (2022) analyzed energy emission data for several European countries and India, and discussed the impact of renewable energy and non-renewable energy on environmental pollution and GDP of different countries. It is proved that environmental pollution and energy emissions have far-reaching policy guidance for the sustainable development of national environment and economy. However, most of the previous researches are based on traditional data methods and experimental tests, and the methods are relatively traditional.With the development of big data visualization technology and econometrics theory, knowledge graph technology and methods have achieved rapid development in recent years. As a large-scale semantic network, it can display the progress and structure relationship of scientific knowledge through graphics, and can transform the mathematical expression of scientific knowledge and rules into graphic expression. It is an important way of knowledge expression in various professional fields in the era of big data (Carette and Farmer 2017; Andreasen et al., 2020). Knowledge graph visualization technology provides knowledge basis and technical support for big data analysis and research in various fields, and makes up for the shortcomings of traditional literature review analysis methods (Jeong et al., 2022; Philippe, 2020; Zhou et al., 2021). In recent 10 years, knowledge mapping technology has made breakthrough progress in the research of medicine, environment, education, economy, management, geography and other professional fields (Chen et al., 2018; Gao et al., 2023b; Han et al., 2022; Mishra et al., 2022; Shinde et al., 2021; Zhang et al., 2020). Knowledge graph has gradually become an important tool to grasp the development trends of disciplines, main research directions and technology-assisted decision-making.
According to the above summary analysis, in the past decades, many environmental and ecological experts and scholars have carried out a large number of sampling tests and pollution assessment on contaminated sites, and obtained many useful results. But valuable scientific achievements have not been systematically and comprehensively summarized. Based on this, the purpose of this paper is to make a systematic, comprehensive and quantitative visual analysis and discussion of the literatures on contaminated sites in the past 30 years by using bibliometrics and knowledge graph methods. Comprehensively understand the characteristics of global contaminated sites, explore the research status, hot spots and development trends of contaminated sites, and provide technical support and knowledge base for environmental sustainable development and the treatment and restoration of contaminated sites. At the same time, this study also provides ideas for environmental experts and workers, and provides reference for the work of government decision-making managers.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Data sources
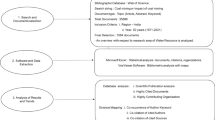
The data were obtained from the Web of Science (WoS) Core Collection. The Web of Science database contains a large number of high-level academic papers and research results. It covers a large number of scientific literature on site pollution research, which can provide a data reserve basis for the study of contaminated sites. In addition, the CiteSpace analysis software adopted in this study can be maturely combined with WoS database and analyze literature data (Yang, 2022). Although EI Compendex database, Scopus database and PubMed database also contain a large number of literature data. However, a large number of literatures already exist in WoS database, and CiteSpace software is easier to analyze WoS data, so the data source of this paper adopts WoS database. WoS database can well provide data knowledge for scholars and researchers, and also help people to collect and analyze literatures in related fields. For example, Yang & Wang (2021) conducted bibliometric analysis of soil organic pollution remediation based on a large number of literatures in WoS database to reveal the latest research progress of soil organic pollution remediation. Wu et al. (2020) took "Oil Spill" as the keyword to conduct bibliometric analysis of relevant literatures in the environmental field included in the WoS database, so as to further explore the frontier research trends and hot spots in the environmental field. This study provides a scientific basis for further understanding of oil spill generation, migration, oil spill remediation and ecological environment assessment. In this study, WoS database was also used as the data source, and bibliometrics and knowledge graph analysis were carried out for literatures related to site pollution. Figure 1 shows the overall research framework for literature retrieval and analysis using WoS database. As shown in Fig. 1, we adopt the advanced retrieval function of the database, and the specific retrieval strategy is as follows: (1) the search topic (TS) = “contaminated site”. (2) We set the time of searching data from January 1, 1993 to December 31, 2022, and studied literatures in this field for nearly 30 years. (3) The language of the articles were set to English. By downloading and summarizing and data preprocessing, a total of 99,924 literatures were retained in this paper. The basic data of this paper is to summarize and review the data of 99,924 academic literatures, including the names, authors, institutions, keywords, abstracts, references and other information.
2.2 Research methods
2.2.1 Bibliometric analysis
This paper analyzes 99,924 literatures in WoS database by bibliometrics and knowledge graph visualization. Bibliometrics is a discipline that adopts mathematical and statistical methods to study the quantitative relations and rules of literature and document working systems. The advantage of bibliometric analysis is that it can quantify the development trend of the discipline and help researchers understand the current research status of the discipline in order to make contributions to this research field in the future. (Lam et al., 2022). It is also often referred to as scientometrics or information metrology. Bibliometrics can often be combined with knowledge mapping technology to help researchers more intuitively display and analyze research hotspots and development trends in related academic fields. Knowledge graph is a series of different graphs showing the development process and structural relationship of knowledge (Gutierrez & Sequeda, 2021). It can describe knowledge resources and their carriers by using graphic visualization technology, and excavate and analyze the correlation between knowledge. In the knowledge graph, different knowledge information is represented by nodes, which represent specific key terms, such as organization information, author name, keywords, etc. The size of the node represents the frequency of information occurrence. The thickness of the connection between nodes reflects the degree of correlation between nodes.
2.2.2 Literature analysis software
In this paper, CiteSpace (6.1.R3) software is used to assist bibliometric analysis and visualization of knowledge map. CiteSpace, whose full name is Citation Space (Chen et al., 2015a, 2015b), is a software used to identify and display new trends and developments of scientific development in scientific literature. The knowledge graph drawn by CiteSpace software is marked by time, showing the structure and distribution of scientific knowledge. In this study, we use the software to conduct multivariate, time-sharing and dynamic data analysis of scientific literature on contaminated sites, and cluster discussion on research hotspots and development trends according to key words in the literature. More information about the software is available at the website: https://citespace.podia.com. With the help of CiteSpace, this paper will provide a more valuable review based on the research history of the contaminated site over the past 30 years.
3 Results
3.1 Document quantity and growth
The number of articles published each year can reflect the degree of attention and development of a research field. A total of 99,924 literatures were retrieved from WoS database. According to the types of documents, these documents can be divided into five types: article, review paper, conference papers, book chapters and online publication (Fig. 2a). Article ranked first (88,969), accounting for 89.04%, followed by Review Article (7516), accounting for 7.52%. This was followed by Proceeding Paper online (1748), Early Access to Proceedings papers (1599), and Book Chapters (92). This indicates that researchers and managers of contaminated sites have carried out a lot of research in this field and promoted the development and progress of this field. In addition, as can be seen from Fig. 2b, studies related to contaminated sites involve a complete range of disciplines. The top 10 disciplines in terms of number of published articles are Environmental Sciences (54,730), Engineering Environmental (10,339), Water Resources (8,640), Meteorology Atmospheric Sciences (5846), Public Environmental Occupational Health (5001), Toxicology (4635), Engineering Chemical (4153), Chemistry Multidisciplinary (4010), Freshwater Biology (4008) and Geosciences (3896). This indicates that different disciplines have carried out research on contaminated sites from different angles and achieved considerable results. Among them, environmental science accounts for the highest proportion of published articles in the past 30 years, indicating that the problem of contaminated sites has always been the focus of environmental science.
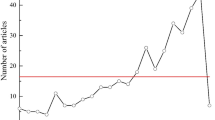
The overall publications in 30 years exhibited a gradual upward trend (Fig. 3). As can be seen from the graph, the number of articles increased from 183 in 1993 to 13,498 in 2021. It is worth noting that because 2022 has not yet ended, the number of literatures counted in this year is not comprehensive. As can be seen from Fig. 3, the number of published articles in this field grew slowly before 2014. In 2014, after the first United Nations Environment Conference was held in Kenya, countries around the world paid more and more attention to ecological environment (Druel & Gjerde, 2014). As a result, the number of published articles shows a rapidly rising trend, people pay more attention to prevention before environmental pollution and treatment after pollution, and pay more attention to soil environmental remediation technology and related engineering applications. The corresponding published scientific research results also increase significantly. More than 10,000 articles have been published every year since 2019. These results indicate that more and more experts and scholars in the field of environment are committed to the study of site pollution.
3.2 Analysis of the countries, institutions and authors of the published articles
Knowing the number of published articles in different countries helps to quickly identify countries that have made significant contributions to contaminated site research. In total, we collected literature from 48 countries. Table 1 shows the Top 10 countries by the number of articles published. Among them, China published the most articles, 27,494, accounting for 27.5% of the total. This indicates that scientific research institutions in China attach great importance to the research of site pollution and the prevention and control of environmental pollution, and have carried out a large number of basic and applied studies in order to explore the remediation technology of contaminated sites. It was followed by the United States, which published 15,146 articles, accounting for 15.2 percent of the total. Next came India (6,462, 6.5%), Italy (4,927, 4.9%), Germany (4,192, 4.2%), the United Kingdom (4,180, 4.2%), France (4,136 articles, 4.1%), Spain (3,529, 3.5%), Canada (3,405, 3.4%) and Brazil (3,118, 3.1%). The Top 10 countries published 76,589 articles, accounting for 76.65% of the total number of articles. Knowledge graph visualization can effectively represent the co-occurrence between nodes. The visual co-occurrence analysis of the top 30 countries is shown in Fig. 4. China has the largest nodal area, the latest publications, and very close cooperation with other countries. It can also be seen from the node connection that in the past three years, Saudi Arabia has cooperated with Egypt and Pakistan respectively in the study of contaminated sites, and published some of the latest scientific research results. It is observed that agriculture in the top three countries, namely China, the United States and India, plays an important role in the national economy. China, the United States and India are all major agricultural importers and exporters. They attach great importance to agriculture and people pay more attention to the output and quality of agricultural products. Therefore, there are more experts and researchers in this field studying the ecological risks caused by polluted sites to the environment.
The co-occurrence network of the Knowledge Graph not only identifies the number of publications by each institution, but also helps us find important research institutions and potential collaborators. A total of 549 institutions were searched for in this paper. We visualized some of the institutions in terms of the number of published articles (Fig. 5). The connection between the institutions represents the cooperative relationship between the two parties, and the thicker the connection line, the closer the cooperation. Table 2 shows the research institutions that rank Top 10 in the number of published articles. As can be seen from Fig. 5 and Table 2, Chinese Academy of Sciences published the most articles, 5445, accounting for 5.5% of the total number of articles. This shows that the Chinese Academy of Sciences has certain authority in the study of contaminated sites. The University of Chinese Academy of Sciences ranked second with 2011 articles, accounting for 2 percent of the total. Next came the Russian Academy of Sciences, Tsinghua University, Peking University, Zhejiang University, Chinese Academy of Environmental Sciences, Beijing Normal University, Nanjing University and China University of Geosciences. It is worth noting that nine of the Top 10 institutions are from China, which shows that Chinese research institutions and universities have invested a lot of energy in the study of contaminated sites and have achieved the most fruitful results. As can be seen from Fig. 5, research on contaminated sites is mainly concentrated in research institutes and universities, and the Chinese Academy of Sciences has the most extensive cooperation with other institutions. In the future study of contaminated sites, it is necessary to strengthen the academic exchanges and cooperation among all parties, especially to drive the common progress of enterprises and promote the development of this research field.
There are a total of 29,874 authors in the field of contaminated sites, and the top 10 authors according to the number of published articles are shown in Table 3. Cao and Junji have the most published papers (166), followed by Zhang and Wei (135), followed by Wang, Yan, Li, Jing, Liu, Yang, Li, Jun, Wang, Jun, Wang, Lei. Wang, Wei, Wang, Yuesi. It is worth noting that the top 10 authors are all from scientific research institutions and universities in China. Their research focuses on site pollution remediation and environmental risk assessment, and they have published many excellent literature. The authors with the largest number of published articles are mainly engaged in the study of suspended particulate matter pollution and its impact on human health in the Yangtze River Delta of China (Yu et al., 2015; Zhang et al., 2015). The authors with the second highest number of published articles mainly focus on the link between polluted sites and air pollution and various diseases in human body (Ssanchez-Guerra et al. 2015; Liu et al., 2015). As can be seen from the author graph relationship in Fig. 6, the authors with a large number of published articles are mainly from China and the United States, which is consistent with the results of the country graph analysis above. In recent 3 years, Wang, Yuesi, Ji, Dongsheng, Li, Yan, Wang Yu, Sun Yele and others have conducted more cooperation in the field of contaminated sites and published more research results. Around 2014, Zhang Yanyan, Chen Yuanchen and Li Wei carried out in-depth cooperation and published a large number of scientific research achievements in this field.
4 Keyword analysis
Keywords are a high generalization of the topic of an article. When analyzing the research frontier of a certain field, they can provide researchers with the evolution process related to the research topic and predict the future development trend of the topic (Gao et al., 2018). High-frequency keywords were selected to construct the co-occurrence network knowledge map of keywords in the field of site pollution research (Fig. 7). Node colors ranging from gray to red represent the years 1993–2022. Keywords with high frequency were heavy metal (22,014), pollution (12,115), contamination (8528), polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (6811). In addition, other key words that occur frequently include air pollution (6755), water (6666), various soils (6069), sediment (5249), accumulation (4350) and exposure (4072).
We set the number of emergent keywords as 30, and obtained the distribution diagram of emergent keywords of contaminated sites from 1993 to 2022, as shown in Fig. 8. "China" was the keyword with the highest intensity of emergence (322.84), and its duration was from 2016 to 2018, indicating that a large number of basic and applied studies on site pollution had been carried out in China during this period. Before that, in 2014, the Ministry of Environmental Protection and the Ministry of Land and Resources of China (2014) issued the national soil pollution survey Communique, and China carried out a national soil pollution survey. In addition, the authors collected the management policies of contaminated sites in 31 regions of China. They made a comprehensive analysis from the aspects of policy framework, policy types and spatio-temporal changes. The results show that most regions in China have adopted positive measures to manage contaminated sites, with both similarities and differences in policies across regions. At present, special policies, site standards, groundwater protection and other measures are urgently needed to strengthen the local governance framework of contaminated sites (Li et al., 2017). "Plant" was also a key word with high emergence (313.22), with a duration of 2013–2018. This indicates that phytoremediation is a promising method for the remediation of contaminated soil in the study and treatment of contaminated sites (Aihemaiti et al., 2020). "site" is the word with the longest breakout duration (1993–2012), and it is the keyword searched in this field. In addition, soil pollution (1993–2011), system (1994–2012) and volatile organic compound (1995–2013) also appeared for a long time. "spatial distribution", "heavy metal pollution", "health risk" and "surface sediment" are the latest words with breakout time, which have received wide attention and in-depth research in the past three years (Bellanova et al., 2022; Cui et al., 2020; Eslami et al., 2022; Gavrilescu, 2022). Combined with the keyword co-occurrence map in Fig. 7 and the keyword emergence map in Fig. 8, in recent 30 years, except for "site pollution", "heavy metal pollution", "organic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons", etc., the keywords with high occurrence frequency and emergence are "plant" "growth" "exposure" "plant" and "organic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons", health "and "risk". Bioremediation has the advantages of simple operation, low cost, small impact on the environment, etc. Phytoremediation, as one of the bioremediation, has become a key technology research for the treatment of contaminated sites (Meena & Sarita, 2019). Phytoremediation technology can remove pollutants in soil through extraction, transfer, absorption and decomposition of soil pollutants by utilizing self-metabolizing hyperenrichment of heavy metals.
4.1 Highly cited literature analysis
The citation times of literature can reflect the influence of literature as the knowledge base of this field on current research (Dorta-Gonzalez & Gomez-Deniz, 2022). When setting the parameters of document knowledge graph, the time span is selected from 1993 to 2022, each time period is 1 year long, the node type is selected cite reference and Top 50 per slice. Figure 9 shows the knowledge map of highly used literature for contaminated sites, which reflects the absorption, utilization and reference of concepts at the research forefront in scientific literatures. As can be seen from Fig. 9, Huang et al. (2014); Cao et al. (2015); Landrigan et al. (2018) are the most frequently cited authors, which fully proves their influence in this field of research. The literature published by Huang is the earliest and belongs to the classic literature in this field. It can be seen from the analysis of the atlas that the number of Chinese authors accounts for more than half, which proves that Chinese authors have played an important role in the research of contaminated sites and that China has paid more and more attention to the management of contaminated sites. Through statistical analysis of Top 10 highly cited literatures, the results are shown in Table 4. In terms of publication years, the top 10 literatures are mainly from 2014 to 2018. They are basic literatures and classic literatures in this field, which is mainly related to the United Nations Environmental Protection Conference held in 2014 (Druel & Gjerde, 2014). The article in literature (Huang et al., 2014) has been extensively cited, with the frequency reaching 633 times. Literature (Cao et al., 2015) has also been extensively cited, with the frequency reaching 582 times. Next, we make a simple analysis of 10 highly cited literatures.
Most of the Top 10 cited literatures in this paper are review studies. (Huang et al., 2014) is the most frequently cited literature. The author has conducted a systematic study on the status of airborne particulate matter pollution. The research result show that in addition to mitigating primary particulate emissions, reducing the emissions of secondary aerosol precursors from, for example, fossil fuel combustion and biomass burning is likely to be important for controlling China's PM2.5 levels and for reducing the environmental, economic and health impacts resulting from particulate pollution. In the literature (Cao et al., 2015), the authors reviewed the design and preparation of Semiconductor-based photocatalysis in recent years and the effective methods to solve environmental pollution, and prospected the development prospect of semiconductor photocatalysis. Landrigan et al. (2018) systematically reviewed the effects of various sources of pollution, including industrial emissions, fossil fuels, vehicle exhaust, toxic chemicals and mining operations, on human disease and death. Ahmad et al. (2014) overview of current biochar use as a sorbent for contaminant management in soil and water is summarized and discussed. Biochar can be used in pollution remediation and agricultural by-product recovery. The authors of (Cohen et al., 2017) assessed the relative risk and mortality of human ischemic heart disease, cerebrovascular disease, chronic obstructive disease, lung cancer, and lower respiratory tract infections from epidemiological studies. The results indicate that ambient air pollution was one of the major causes of the global burden of disease in 2015. Li et al. (2014) reviewed the data of soil heavy metal pollution in mining areas in China from 2005 to 2012. On this basis, the level of mine soil pollution and the harm to human health were evaluated. The results show that the heavy metal pollution of the mine is very serious, and it will cause high carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic risk to people near the contaminated area, especially children. The authors of (Lee et al., 2016) reviewed the recent research progress on degradation of organic pollutants by ZnO photocatalyst in recent years. The fact shows that zinc oxide photocatalyst is one of the most promising technologies in the degradation of organic pollutants. Yang et al. (2018) reviewed and assessed the concentration of heavy metals in Chinese soil and the risks to ecological environment and human health. The results showed that heavy metal pollution and related risks of Cd, Pb and As were more serious. The authors of (Sires et al., 2014) reviewed the application and research results of electrochemical advanced oxidation processes in the removal of organic pollutants in water. The results show that this technique can be effectively applied to environmental pollution and remediation. Wang et al. (2015) reviewed and studied the development of materials with superhydrophobic and superhydrophilic properties in oil–water separation applications in view of the serious harm caused by oil leakage and industrial organic pollutants in water supply resources. The results show that special wettability stimulated oil/water separation materials can achieve industrial scale production and be put into use for oil spills and industrial oily wastewater treatment in the near future.
5 Discussion
We conducted a knowledge graph visualization analysis on the collected academic research literature data in the field of contaminated sites in the past 30 years. First of all, through the specific classification of the contaminated site research, readers can understand the current hot information in the field of research. Secondly, through the existing cluster discussion, researchers can clearly understand the common problems in this field. Finally, through the graph clustering, it can also provide reference data for environmental policy makers. The results showed that the research in the field of contaminated sites mainly included five categories: Study on airborne particulate matter pollution, groundwater and surface water pollution, heavy metal pollution, organic matter pollution and bioremediation technology in site environment (Fig. 10). Among them, air pollution mainly includes airborne particulate matter and PM2.5 pollution; Organic pollution is mainly polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. In order to further analyze the research hotspot and development trend in the field of pollution, combined with the literature review and summary in this field, we carried out a specific analysis of the results of each cluster.
5.1 Air pollution
Cluster 1 refers to airborne particulate matter pollution in the site environment, including key words PM 2.5, air pollution, particulate pollution, air quality, particulate matter emission, system, transport, etc. There are many carriers of harmful substances polluting the site, among which air is one of the main carriers. Site air pollution mainly comes from industrial production, domestic fuel emissions, transportation, etc., and soot, sulfur oxide, nitrogen oxide, sulfur dioxide, carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons and other emissions through the above means seriously pollute the air of site environment and pose a serious threat to the health of human respiratory organs (Moghaddam et al., 2022). Due to the self-purification ability of the environment, the environmental pollution problem will not appear immediately, and the harm to human health will appear only after the environmental pollution has reached a certain degree or experienced a certain period of time. Therefore, there is a serious lag in the ambient air pollution of the site (Gilliam et al., 2019). Therefore, we must be fully aware of the harm of air pollution, and seek effective solutions in advance to improve the air quality of the site environment.
In recent years, many researchers have conducted in-depth research on environmental air quality monitoring and its impact on human health, and have made certain contributions to site environmental air pollution. For example, Guo et al. (2014) studied haze pollution in China. The results showed that particulate matter in the air formed in the form of aerosol and nucleated, and Nucleation consistently precedes a polluted period. Coupled with increasing particle size to form smog over the next few days, the findings point to the need to strengthen regulatory controls on transport emissions of volatile gases and sulphur compounds from industrial sources to reduce PM levels in the air. In the literature (Zheng et al., 2018), the authors stated that in order to solve the serious air pollution problem, China has implemented an active clean air policy. As long as the emission of air pollutants is reduced, the air quality will be significantly improved. Using a combination of bottom-up emission inventories and index decomposition analysis (IDA), the authors quantified anthropogenic emissions trends in China from 2010 to 2017. The results show that emission control measures are the main drivers of air pollution reduction, with pollution controls for power plants and industry being the most effective mitigation measures. The study shows that in the field of air pollution research, previous studies focused on the formation of pollution and the statistical analysis of pollution data. Research now focuses more on pollution control methods and the promulgation of policies and regulations.
5.2 Water pollution
Cluster 2 is a study on groundwater and surface water pollution in the site, including groundwater resources and pollution of surface water resources. Keywords: water, groundwater, surface water, waste water, liquid waste, effluent, outlet water, remediation, river water pollution, accumulation, removal, system, etc. Water resources are the carrier of various pollutants, and the transmission of pollutants through the food chain will eventually threaten food safety and endanger human health. Generally, groundwater and site soil are polluted simultaneously. In addition, some volatile pollutants are easy to migrate out of the water pollution site and pollute the air, causing great difficulties for site pollution remediation (Montalban et al., 2016). Pollution sources of water resources mainly include: industrial wastewater, domestic sewage, farmland sewage, soil erosion, mine sewage, etc. (Hou et al., 2022). Figure 11 is a schematic diagram of groundwater resource and heavy metal pollution sources. In recent years, environmental managers and researchers have conducted a large number of studies on water resource pollution, assessment and restoration. For example, Vengosh et al. (2014) reviewed the potential risks to water resources and the hazards to the environment and human health caused by oil and gas exploitation in the United States, and identified four potential risks to water resources: (1) the contamination of shallow aquifers with fugitive hydrocarbon gases. (2) Surface water and shallow groundwater pollution caused by oil and gas wastewater overflow and leakage. (3) Accumulation of toxic and radioactive elements in stream sediments or soils near oil and gas deposits. (4) Excessive exploitation of water resources may lead to water shortage. The statistical analysis of this paper shows that previous studies focused on the source of water pollution and the analysis of potential harm to the human body. Current research focuses more on statistical analysis of water pollution types and pollution treatment.
5.3 Heavy metal pollution
Cluster 3 is the study of heavy metal pollution in the site. Keywords included are heavy metal, heavy metal ion, sediments, soil pollution, clay mineral, Cu, Zn, Pb, Cd, mine tailings, health, trace element, etc. Heavy metal pollution refers to environmental pollution caused by heavy metals or their compounds, which is mainly caused by mining, waste gas discharge, sewage irrigation and the use of products with excessive heavy metals. Heavy metals are widely distributed in soil, water and atmosphere. If the content of heavy metals exceeds the normal range, it will lead to the deterioration of environmental quality and site pollution, and directly endanger human health. According to statistics, the most common heavy metal pollution includes lead pollution, cadmium pollution, mercury pollution, chromium pollution, copper pollution, nickel pollution and zinc pollution. The main sources of pollution are industrial pollution, traffic pollution and household garbage pollution. Most industrial pollution enters the environment through waste water, waste gas and waste residue, and accumulates in people, animals and plants, causing serious harm to human and environmental health (Isvoran et al., 2021).
The treatment of industrial pollution can reduce the pollution through some technical methods and management measures to meet the pollution discharge standards. Traffic pollution is mainly caused by exhaust gas emitted by vehicles and other means of transportation, so it is necessary to formulate management measures such as installing vehicle exhaust purifiers or using ethanol and gasoline. Domestic pollution is mainly domestic garbage pollution, waste cosmetics, colorful dishes, waste batteries, etc., which needs to be classified and degraded to reduce the pollution of heavy metals. For example, Chen et al., (2015a, 2015b) assessed the risk of soil pollution to human health in China using the data set of the National Soil Pollution Survey. The results show that due to the dramatic increase in industry and rapid urban expansion, China's soil has been contaminated with varying degrees of heavy metals, with cadmium and mercury in high concentrations in the soil, posing higher health risks to the public. The authors of (Zou et al., 2016) pointed out that the presence of heavy metals in industrial wastewater is a challenging problem facing human health in recent years. The authors studied the environmental behavior of NZVI Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron to remove toxic heavy metal ions from surface and underground wastewater. The results show that NZVI-based materials have good removal ability of heavy metal ions, and can play an important role in the remediation of site environmental pollution. Compared with previous studies, the current research on heavy metal pollution focuses more on the use of new materials to repair contaminated sites, so as to achieve the purpose of environmental protection and environmental sustainable development.
5.4 Organic pollution
Cluster 4 is site organic pollution, The key words included are Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), organic pollutant, Organic chlorine pesticides, plastictetrachloroethene, petroleum, etc. In addition to inorganic pollutants, soil and water in contaminated sites also contain a large number of organic pollutants, which pose risks to the ecosystem by means of toxicity and reduction of dissolved oxygen in water, and can also spread through the food chain and directly harm human health (Chaturvedi, 2022). One of the more common organic pollutants is polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), which are often present in complex mixtures in soil and groundwater and have strong bioaccumulation and persistence. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) are the first compounds that have been proved to have carcinogenic effects through animal tests and are among the most priority organic pollutants (Zaciera et al., 2019). In addition, volatile halocarbons produced by chemical industry and medicine, including trichloromethane, dichloromethane bromide, dichloromethane bromide and tribromomethane, also have special odor and toxicity, and can enter human body through breathing, skin contact or drinking water, causing serious harm to human health. In recent years, scholars in the environmental field have conducted a lot of research and assessment on the occurrence, spread and harm of organic pollutants. Lin et al. (2022) conduct the research the contribution from cooking to the particle-bound polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the ambient environment, The results show the particle-bound PAHs from cooking can be an important source of ambient PAHs in most Chinese cities. The findings from this study hold important implications for public health and are informing for policymakers. The research shows that the previous research on organic pollution mainly focuses on chemical industry, medicine and farmland irrigation. With the increase of the world population, life and vehicle exhaust emissions have become the main sources of organic pollution in cities.
5.5 Biotechnology
Cluster 5 is pollution abatement and bioremediation technologies. Keywords included are reducing pollutants, bioremediation, degradation, bioavailability, semiconductor photocatalyst, community, biodegradation, composite, etc. Pollution reduction is a profound change in the international community's concept of development mode and environmental protection, which mainly refers to reducing the emission of pollutants to improve the quality of ecological environment (Bohm et al., 2022). Pollution reduction is an important means to adjust economic structure, improve human living environment and human health. Single pollution reduction effect is relatively slow. For sites that have already been polluted, biological remediation technology and other means are needed to improve the environment. Bioremediation is also an important part of environmental protection technology. Bioremediation is the use of biological metabolic activities to degrade and transform toxic and harmful substances in soil, water body and atmospheric environment, so as to reduce pollution concentration or completely harmless (Urionabarrenetxea et al., 2021).
Bioremediation technology has the advantages of low investment cost, small impact on the environment, good use effect, large use area, and can simultaneously treat contaminated soil and groundwater. In recent years, many countries and regions have adopted this bioremediation technology to restore site environmental pollution, and have achieved good results. Thangavelu & Veeraragavan (2022) studied the application of nanomaterials in remediation of heavy metal pollution and wastewater treatment. By collecting the research results on the production of nanoparticles and their advantages as adsorbents in wastewater remediation, the latest progress and application prospect of nanotechnology in wastewater remediation were discussed. The results show that nanotechnology plays an important role in the treatment of wastewater pollution, and the application of nanotechnology in the remediation of site pollution will get a greater breakthrough. In the literature (Gonzalez-Gonzalez et al., 2022), the authors' review highlighted the importance of the removal of emerging pollutants from the latest bioremediation techniques. Biological emerging contaminants, agrochemicals, endocrine-disrupting chemicals, and pharmaceutical and personal care products were considered for this review study, and their removal by bioremediation techniques involving plants, bacteria, microalgae, and fungi. Finally, further research opportunities are presented based on current challenges from an economic, biological, and operation perspective. Pollution reduction and bioremediation technology will be the main research topics of environmental protection and environmental sustainable development in the future.
6 Conclusions
From the perspective of bibliometrics, this paper systematically, comprehensively, quantitatively and visually studies the literatures on contaminated sites in the Web of Science database in the past 30 years. Through knowledge graph technology, this study identifies the characteristics, research status and development trend of contaminated sites. This provides the knowledge base and technical support for the future sustainable development of the environment and the treatment and restoration of contaminated sites. The results show that bibliometrics and knowledge graph are effective in information retrieval and visualization. It can display the information of different scales and different times in the study of contaminated sites, and find the distribution characteristics of popular keywords. The main conclusions of this paper are as follows.
-
1.
On a global scale, the number of articles published annually on contaminated sites shows an increasing trend year by year. The contaminated sites have been studied by different disciplines from different angles. This shows that the problem of contaminated sites has always been the focus of environmental science. The future development direction of contaminated sites will cross disciplines and require cooperation between different countries to overcome the current technical bottlenecks.
-
2.
From the analysis of co-occurrence and emergence of keywords, heavy metal(22,014 times), pollution(12,115 times), polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (6811 times), which are the search subject words in this research. In addition, the high frequency and emergent keywords are "plant", "growth", "exposure", "health", "risk". Bioremediation has the advantages of simple operation, low cost and small impact on the environment. Phytoremediation, as a kind of bioremediation, has become a key technology for the treatment of contaminated sites.
-
3.
From the clustering knowledge map of research hotspots, the research fields of contaminated sites can be divided into five main clustering maps, namely, site environmental air suspended particulate matter pollution, groundwater and surface water pollution, site heavy metal pollution, site organic pollution, pollution reduction and bioremediation technology research. In the future, the hot issues of contaminated site remediation and environmental sustainable development will focus on strengthening the research of microbial remediation technology, nanomaterial technology, composite material adsorption technology and so on.
6.1 Future recommendation and limitation
Policy institutions and scientific research departments of various countries should strengthen technical exchanges and cooperation with each other to find out the common problems of environmental pollution and control. To explore more applicable pollution reduction technologies and pollution treatment and remediation policies. For example, in terms of carbon emissions from energy plants, low-carbon technical indicators and environmental protection and energy saving technologies can be adopted to control pollution emissions from the source. Relevant departments can regularly monitor soil, air and water pollution indicators in areas where heavy metal pollution and organic pollution are emitted. Surrounding pollution sources should be controlled and relevant policies and regulations promulgated, and biological bioremediation and energy-saving technologies should be adopted. In addition, in terms of urban traffic emission pollution, corresponding policies, regulations and restrictions can be promulgated in big cities to control vehicle environmental protection indicators and control the number of daily vehicle flows. This will not only reduce pollution emissions, but also ease urban traffic congestion.
6.2 Limitation of study
The database used in this study is a single WoS journal database. Therefore, some important literature information in other journal databases may be missing. In the future, more in-depth research is suggested to supplement the database literature, such as EI Compendex database, Scopus database, PubMed database, etc.
Data availability
The datasets used during the present study are available for the first author on reasonable request.
References
Ahmad, M., Rajapaksha, A. U., Lim, J. E., Zhang, M., Bolan, N., Mohan, D., Vithanage, M., Lee, S. S., & Ok, Y. S. (2014). Biochar as a sorbent for contaminant management in soil and water: A review. Chemosphere, 99, 19–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.10.071
Aihemaiti, A., Gao, Y. C., Meng, Y., Chen, X. J., Liu, J. W., Xiang, H. L., Xu, Y. W., & Jiang, J. G. (2020). Review of plant-vanadium physiological interactions, bioaccumulation, and bioremediation of vanadium-contaminated sites. Science of the Total Environment, 712, 135637. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135637
Alao, M. B., & Adebayo, E. A. (2022). Fungi as a veritable tool in bioremediation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons-polluted wastewater. Journal of Basic Microbiology, 62(3), 223–244. https://doi.org/10.1002/jobm.202100376
Andreasen, T., Bulskov, H., Jensen, P. A., & Nilsson, J. F. (2020). Natural logic knowledge bases and their graph form. Data & Knowledge Engineering, 129, 101848. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.datak.2020.101848
Aristotle, T., Ubando, A. D. M., Africa, M. C., Mainiquiz-Redillas, A. B., & Chen, J. (2021). Microalgal biosorption of heavy metals: A comprehensive bibliometric review. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 402, 123431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123431
Bekun, F. V. (2022). Mitigating emissions in India: Accounting for the role of real income, renewable energy consumption and investment in energy. International Journal of Energy Economics and Policy, 12(1), 188–192. https://doi.org/10.32479/ijeep.12652
Bellanova, P., Feist, L., Costa, P. J. M., Orywol, S., Reicherter, K., Lehmkuhl, F., & Schwarzbauer, J. (2022). Contemporary pollution of surface sediments from the Algarve shelf. Portugal. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 176, 113410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2022.113410
Bisht, S., Rawat, G. S., Bargali, S. S., Rawat, Y. S., & Mehta, A. (2023). Forest vegetation response to anthropogenic pressures: a case study from Askot Wildlife Sanctuary, Western Himalaya. Environment, Development and Sustainability. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-023-03130-2
Bohm, M., Nanni, M., & Pappalardo, L. (2022). Gross polluters and vehicle emissions reduction. Nature Sustainability, 5, 699–707. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41893-022-00903-x
Cao, S. W., Low, J. X., Yu, J. G., & Jaroniec, M. (2015). Polymeric photocatelysts based on graphitic carbon nitride. Advanced Materials, 27(13), 2150–2176. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201500033
Carette, J., Farmer, W. M. (2017). Formalizing mathematical knowledge as a biform theory graph. In A case study (conference paper). Lecture notes in computer science (including subseries lecture notes in artificial intelligence and lecture notes in bioinformatics) 10383:9–24. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-62075-6_2
Chaturvedi, N. K. (2022). Compari of available treatment techniques for hazardous aniline-based organic contaminants. Applied Water Science, 12, 173. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-022-01695-3
Chen, H. Y., Teng, Y. G., Lu, S. J., Wang, Y. Y., & Wang, J. S. (2015a). Contamination features and health risk of soil heavy metals in China. Science of the Total Environment, 512, 143–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.01.025
Chen, P. H., Lu, Y., Zheng, V. W., Chen, X. Y., & Yang, B. D. (2018). KnowEdu: A system to construct knowledge graph for education. IEEE Access, 6, 31553–31563. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2839607
Chen, W. F., Li, W. B., Wang, T. K., Wen, Y. J., Shi, W. W., Zhang, W. J., Guo, B., & Yang, Y. S. (2022a). Isolation of functional bacterial strains from chromium-contaminated site and bioremediation potentials. Journal of Environmental Management, 307, 114557. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.114557
Chen, X., Wang, Y., Bai, Z., Ma, L., Strokal, M., Kroeze, C., Chen, X., Zhang, F., & Shi, X. (2022b). Mitigating phosphorus pollution from detergents in the surface waters of China. The Science of the Total Environment, 804, 150125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.150125
Chen, Y., Chen, C. M., Liu, Z. Y., Hu, Z. G., & Wang, X. W. (2015). The methodology function of CiteSpace mapping knowledge domains. Studies in Science of Science, 33(2), 242–253. https://doi.org/10.16192/j.cnki.1003-2053.2015.02.009
Cirovic, A., & Cirovic, A. (2022). Iron deficiency as promoter of heavy metals-induced acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia Research, 112, 106755. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.leukres.2021.106755
Cohen, A. J., Brauer, M., Burnett, R., Anderson, H. R., Frostad, J., & Estep, K. (2017). Estimates and 25-year trends of the global burden of disease attributable to ambient air pollution: An analysis of data from the global burden of diseased study 2015. The Lancet, 389(10082), 1907–1918. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(17)30505-6
Cui, J. L., Zhao, Y. P., Chan, T. S., Zhang, L. L., Tsang, D. C. W., & Li, X. D. (2020). Spatial distribution and molecular speciation of copper in indigenous plants from contaminated mine sites: Implication for phytostabilization. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 381, 121208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121208
Dorta-Gonzalez, P., & Gomez-Deniz, E. (2022). Modeling the obsolescence of research literature in disciplinary journals through in age of their cited references. Scientometrics, 127(6), 2901–2931. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-022-04359-w
Druel, E., & Gjerde, K. M. (2014). Sustaining marine life beyond boundaries: Options for an implementing agreement for marine biodiversity beyond national jurisdiction under the United Nations convention on the law of the sea. Marine Policy, 49, 90–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpol.2013.11.023
Eslami, H., Esmaeili, A., Razaeian, M., Salari, M., Hosseini, A. N., Mobinia, M., & Barani, A. (2022). Potentially toxic metal concentration spatial distribution, and health risk assessment in drinking groundwater resources of southeast Iran. Geoscience Frontiers, 13(1), 133–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2021.101276
Gao, J., Radeva, A., Shen, C. Y., Wang, S. Q., Wang, Q. B., & Passonneau, R. J. (2018). Prediction of a hotspot pattern in keyword search results. Computer Speech & Language, 48, 80–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csl.2017.10.005
Gao, L., Zhang, W. T., Liu, Q. Y., Lin, X. Y., Huang, Y. J., & Zhang, X. (2023a). Machine learning based on the graph convolutional self-organizing map method increases the accuracy of pollution source identification: A case study of trace metal(loid)s in soils of Jiangmen City, south China. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 250, 114467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.114467
Gao, L., Yang, T., Xue, Z., & Chan, C. K. D. (2023b). Hot spots and trends in the relationship between cancer and obesity: A systematic review and knowledge graph analysis. Life, 13, 337. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13020337
Gavrilescu, M. (2022). Enhancing phytoremediation of soils polluted with heavy metals. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 74, 21–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2021.10.024
Gilliam, F. S., Burns, D. A., Driscoll, C. T., Frey, S. D., Lovett, G. M., & Watmough, S. A. (2019). Decreased atmospheric nitrogen deposition in eastern North America: Predicted responses of forest ecosystems. Environmental Pollution, 244, 560–574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.09.135
Gonzalez-Gonzalez, R. B., Flores-Contreras, E. A., & Iqbal, H. M. N. (2022). Bio-removal of emerging pollutants by advanced bioremediation techniques. Environmental Research, 214, 113936. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.113936
Guo, S., Hu, M., Zamora, M. L., Peng, J. F., Shang, D. J., Zheng, J., Du, Z. F., Wu, Z. J., Shao, M., Zeng, L. M. (2014). Elucidating severe urban haze formation in China. In Proceedings of the national academy of sciences of the United States of America 111(49):17373-17378. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1419604111
Gutierrez, C., & Sequeda, J. F. (2021). Knowledge Graphs. Communications of the ACM, 64(3), 96–104. https://doi.org/10.1145/3418294
Han, F., Deng, Y. R., Liu, Q. Y., Zhou, Y. Z., Wang, J., Huang, Y. J., Zhang, Q. L., & Bian, J. (2022). Construction and application of the knowledge graph method in management of soil pollution in contaminated sites: A case study in South China. Journal of Environmental Management, 319, 115685. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.115685
Hassan, A., Pariatamby, A., Ossai, I. C., Ahmed, A., Muda, M. A., Wen, T. Z., & Hamid, F. S. (2022). Bioaugmentation-assisted bioremediation and kinetics modelling of heavy metal-polluted landfill soil. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 19(7), 6729–6754. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03626-2
Hou, L., Zhou, Z. Y., Wang, R. Y., Li, J. X., Dong, F., & Liu, J. Q. (2022). Research on the non-point source pollution characteristics of important drinking water sources. Water, 14(2), 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14020211
Huang, R. J., Zhang, Y. L., Bozzetti, C., Ho, K. F., Cao, J. J., Han, Y. M., Daellenbach, K. R., Slowik, J. G., & Platt, S. M. (2014). High secondary aerosol contribution to particulate pollution during haze events in China. Nature, 514(7521), 218–222. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13774
Isvoran, A., Roman, D. L., Dascalu, D., Vlad-Oros, B., Ciorsac, A., Pitulice, L., Jonovic, R., Stevanovic, Z., & Ostafe, V. (2021). Human health effects of heavy metal pollution in the cross-border area of Fomania and Serbia: A review. Ecological Chemistry and Engineering, 28(3), 365–388. https://doi.org/10.2478/eces-2021-0025
Jeong, J., Lee, N., Shin, Y., & Shin, D. (2022). Intelligent generation of optimal synthetic pathways based on knowledge graph inference and retrosynthetic predictions using reaction big data. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 130, 103982. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2021.07.015
Kothapalli, C. R. (2021). Differential impact of heavy metals on neurotoxicity during development and in aging central nervous system. Current Opinion in Toxicology, 26, 33–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cotox.2021.04.003
Lam, W. H., Lam, W. S., Jaaman, S. H., & Lee, P. F. (2022). Bibliometric analysis of information theoretic studies. Entropy, 24(10), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24101359
Landrigan, P. J., Fuller, R., Acosta, N. J. R., Adeyi, O., Arnold, R., Basu, N., Balde, A. B., Bertollini, R., & Boufford, J. (2018). The Lancet commission on pollution and health. Lancet, 391(10119), 462–512. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32345-0
Lee, K. M., Lai, C. W., Ngai, K. S., & Juan, J. C. (2016). Recent developments of zinc oxide based photocatalyst in water treatment technology: A review. Water Research, 88, 428–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2015.09.045
Li, X. N., Jiao, W. T., Xiao, R. B., Chen, W. P., & Liu, W. (2017). Contaminated sites in China: Countermeasures of provincial governments. Journal of Cleaner Production, 147, 485–496. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.01.107
Li, Z. Y., Ma, Z. W., Van, K. T. J., Yuan, Z. W., & Huang, L. (2014). A review of soil heavy metal pollution from mines in China: Pollution and health risk assessment. Science of the Total Environment, 468, 843–853. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.08.090
Lin, C. S., Huang, R. J., Duan, J., & Zhong, H. B. (2022). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from cooking emissions. Science of the Environment, 818, 151700. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.151700
Liu, C., Xu, J. H., Chen, Y. H., Guo, X. B., Zheng, Y. N., Wang, Q. F., Chen, Y. Y., Joyce, B. T., Baccarelli, A., Zhang, W., & Hou, L. F. (2015). Characterization of genome-wide H3K27ac profiles reveals a distinct PM2.5-associated histone modification signature. Environmental health, 14(1), 65. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12940-015-0052-5
Liu, L., Hu, S. P., Chen, Y. X., & Li, H. (2010). Feasibility of washing as a remediation technology for the heavy metals-polluted soils left by chemical plant. Journal of Applied Ecology, 21(6), 1537–1541.
Mahato, N., Agarwal, P., Mohapatra, D., Sinha, M., Dhyani, A., Pathak, B., Tripathi, M. K., & Angaiah, S. (2021). Biotransformation of citrus waste: Bio-sorbent material for removal of dyes, heavy metals and toxic chemicals from polluted water. Processes, 9(9), 1544. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9091544
Manral, V., Bargali, K., Bargali, S. S., Karki, H., & Chaturvedi, R. K. (2023). Seasonal dynamics of soil microbial biomass C, N and P along an altitudinal gradient in central Himalaya, India. Sustainability, 15(2), 1651. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021651
Meena, K., & Sarita, S. (2019). Bioremediation options for heavy metal pollution. Journal of Health& Pollution, 9(24), 3–20. https://doi.org/10.5696/2156-9614-9.24.191203
Ministry of Land and Resources of China. (2014). The ministry of environmental protection and the ministry of land and resources released a communique on a national survey of soil pollution. Resources and Human Settlements, 4, 26–27. (in Chinese).
Mishra, R. K., Raj, H., Urolagin, S., Jothi, J. A., & Nawaz, N. (2022). Cluster-based knowledge graph and entity-relation representation on tourism economical sentiments. Applied Sciences, 12(16), 8105. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12168105
Moghaddam, H. V., Dowlatabadi, A., Najafi, M. L., Ghalenovi, M., Pajohanfar, N. S., Ghezi, S., Mehrabadi, S., Estiri, E. H., & Miri, M. (2022). Association of traffic-related air pollution with Newborn’s anthropometric indexes at birth. Environmental Research, 204, 112000. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.112000
Montalban, M. G., Hidalgo, J. M., Collado-Gonzalez, M., Diaz, B. F., & Guillermo, V. G. (2016). Assessing chemical toxicity of ionic liquids on Vibrio fischeri: Correlation with structure and composition. Chemosphere, 155, 405–414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.04.042
Obolkin, V., Potemkin, V., Khuriganova, O., & Tamara, K. (2022). Ozone monitoring in the baikal region (East Siveria): Spatiotemporal variability under the nfluence of air pollutants and site conditions. Atmosphere, 13(4), 519. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13040519
Philippe, C. M. (2020). Leveraging knowledge graphs for big data integration: The XI pipeline. Semantic Web, 11(1), 13–17. https://doi.org/10.3233/SW-190371
Quito, B., Rio-Rama, M. C., Alvarez-Garcia, J., & Bekun, F. V. (2022). Spatiotemporal influencing factors of energy efficiency in 43 European countries: A spatial econometric analysis. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 182, 113340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2023.113340
Rauf, A. U., Mallongi, A., & Astuti, R. D. P. (2020). Heavy metal contributions on human skin disease near cement plant: A systematic review. Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences, 8, 117–122. https://doi.org/10.3889/oamjms.2020.4396
Sanchez-Guerra, M., Zheng, Y. N., Osorio-Yanez, C., Zhong, J., Chervona, Y., Zhang, W., Byun, H. M., Hou, L. F., & Baccarelli, A. (2015). Effects of particulate matter exposure on blood 5-hydroxymethylation: Results from the Beijing truck driver air pollution study. Epigenetics, 10(7), 633–642.https://doi.org/10.1080/15592294.2015.1050174
Schanzer, S., Koch, M., Kiefer, A., Jentke, T., Veith, M., Bracher, F., Bracher, J., & Muller, C. (2022). Analysis of pesticide and persistent organic pollutant residues in German bats. Chemosphere, 305, 135342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.135342
Shahi, C., Bargali, S. S., Bargali, K., & Vibhuti,. (2023). Dry matter dynamics and SO2 mitigation in the herb layer of Central Himalayan agroecosystems along an altitudinal gradient, India. Tropical Ecology, 64, 180–192. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42965-022-00258-6
Shinde, S. B., Gaherwar, S., Sathe, A., Menon, M., & Barekar, S. (2021). Creation of knowledge graph for client complaint management system. Lecture Notes on Data Engineering and Communications Technologies, 70, 31–43. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-2934-1_2
Sial, M. H., Arshed, N., Amjad, M. A., & Khan, Y. A. (2022). Nexus between fossil fuel consumption and infant mortality rate: A non-linear analysis. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29, 58378–58387. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19975-5
Sires, I., Brillas, E., Oturan, M. A., Rodrigo, M. A., & Panizaa, M. (2014). Electrochemical advanced oxidation processes: Today and tomorrow. A review. Enviromental science and pollution research, 21(14), 8336–8367. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2783-1
Song, M. Y., & Hu, X. G. (2021). The health impact of environmental pollution. Ecotoxicology & Environmental Safety, 208, 111667. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111667
Tang, F. H. M., Lenzen, M., McBratney, A., & Maggi, F. (2021). Risk of pesticide pollution at the global scale. Nature Geoscience, 14(4), 206–210. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41561-021-00712-5
Tao, H., Liao, X. Y., Cao, H. Y., Zhao, D., & Hou, Y. X. (2022). Three-dimensional delineation of soil pollutants at contaminated sites: Progress and prospects. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 32(8), 1615–1634. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11442-022-2013-6
Thangavelu, L., & Veeraragavan, G. R. (2022). A survey on nanotechnology-based bioremediation of wastewater. Bioinorganic Chemistry and Applications, 2022, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/5063177
Urionabarrenetxea, E., Garcia-Velasco, N., Anza, M., Artetxe, U., Lacalle, R., Garbisu, C., Becerril, T., & Soto, M. (2021). Application of in situ bioremediation strategies in soils amended with sewage sludges. The Science of the Total Environment, 766, 144099. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144099
Vengosh, A., Jackson, R. B., Warner, N., Darrah, T. H., & Kondash, A. (2014). A critical review of the risks to water resources from unconventional shale gas development and hydraulic fracturing in the United States. Environmental Science & Technology, 48(15), 8334–8348. https://doi.org/10.1021/es405118y
Verma, A., & Singh, N. B. (2021). Evaluation of groundwater quality using pollution index of groundwater(PIG) and non-carcinogenic health risk assessment in part of the Gangetic Basin. Acta Geochimica, 40(3), 419–440. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-020-00446-y
Wang, B., Liang, W. X., Guo, Z. G., & Liu, W. M. (2015). Biomimetic super-lyophobic and super-lyophilic materials applied for oil/water separation: A new strategy beyond nature. Chemical Society Reviews, 44(1), 336–361. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4cs00220b
Wang, X. B., Li, X. Y., Yan, X., Tu, C., & Yu, Z. G. (2021). Environmental risks for application of iron and steel slags in soils in China: A review. Pedosphere, 31(1), 28–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(20)60058-3
Wu, J., Wang, M., Ye, C. M., Xu, Z. H., Sha, C. Y., Zhang, J. Y., & Huang, S. F. (2020). Bibliometric analysis of research hotspots related to marine oil spill accidents in the environmental field based on web of science. Journal of Forensic Medicine, 36(4), 461–469. https://doi.org/10.12116/j.issn.1004-5619.2020.04.005
Yan, K., Wang, H. Z., Lan, Z., Zhou, J. H., Fu, H. Z., Wu, L. S., & Xu, J. M. (2022). Heavy metal pollution in the soil of contaminated sites in China: Research status and pollution assessment over the past two decades. Journal of Cleaner Production, 373, 133780. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.133780
Yang, B. (2022). Nandita Quaderi: Web of science provides trustworthy data and metrics. Chinese Science Bulletin, 67(3), 252–254.
Yang CX, Wang J (2021) Research status of soil organic remediation—visual analysis of literature based on web of science database. In IOP conference series: Earth and Environmental Science 769:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/769/2/022003
Yang, Q. Q., Li, Z. Y., Lu, X. N., Duan, Q. N., Huang, L., & Bi, J. (2018). A review of soil heavy metal pollution from industrial and agricultural regions in China: Pollution and risk assessment. Science of the Total Environment, 642, 690–700. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.06.068
Yang, Y., Zhang, Z. W., Liu, R. X., Ju, H. Y., Bian, X. K., Zhang, W. Z., Zhang, C. B., Yang, T., Guo, B., Xiao, C. L., Bai, H., & Lu, W. Y. (2021). Research progress in bioremediation of petroleum pollution. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 28(34), 46877–46893. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15310-6
Yu, J. Z., Cao, J. J., Hu, M., Kan, H. D., & Fu, T. M. (2015). Particulate matter pollution research in the Yangtze River Delta: Observations, processes, modeling and health effects. Atmospheric Environment, 123, 285–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2015.11.010
Zaciera, M., Kurek, J., Feist, B., & Pyta, H. (2019). The exposure profiles, correlation factors and comparison of PAHs and Nitro-PAHs in urban and non-urban regions in suspended particulate matter in Poland. Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds, 39(4), 374–382. https://doi.org/10.1080/10406638.2017.1328448
Zhang, Y. H., Zhu, J., Zhu, Q., Xie, Y. K., Li, W. L., Fu, L., Zhang, J. X., & Tan, J. M. (2020). The construction of personalized virtual landslide disaster environments based on knowledge graphs and deep neural networks. International Journal of Digital Earth, 13(12), 1637–1655. https://doi.org/10.1080/17538947.2020.1773950
Zhang, Z. S., Gao, J., Engling, G., Tao, J., Chai, F. H., Zhang, L. M., Zhang, R. J., Sang, X. F., Chan, C. Y., Lin, Z. J., & Cao, J. J. (2015). Characteristics and applications of size-segregated biomass burning tracers in China’s Pearl River Delta region. Atmospheric Environment, 102, 290–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2014.12.009
Zheng, B., Tong, D., Li, M., Liu, F., Hong, C. P., Geng, G. N., Li, H. Y., Li, X., Peng, L. Q., & Qi, J. (2018). Trends in China’s anthropogenic emissions since 2010 as the consequence of clean air actions. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 18(19), 14095–14111. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-18-14095-2018
Zheng, R. J., Feng, X. Z., Zou, W. S., Wang, R. H., Yang, D. Z., Wei, W. F., Li, S. Y., & Chen, H. (2021). Converting loess into zeolite for heavy metal polluted soil remediation based on”soil for soil-remediation” strategy. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 412, 125199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125199
Zhou, B., & Li, X. (2021). The monitoring of chemical pesticides pollution on ecological environment by GIS. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 23, 101506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2021.101506
Zhou, C. H., Wang, H., Wang, C. S., Hou, Z. Q., Zheng, Z. M., Shen, S. Z., Cheng, Q. M., Feng, Z. Q., Wang, X. B., Lv, H. R., Fan, J. X., Hu, X. M., Hou, M. C., & Zhu, Y. Q. (2021). Geoscience knowledge graph in the big data era. Science China Earth Sciences, 64(7), 1105–1114. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-020-9750-4
Zou, Y. D., Wang, X. X., Khan, A., Wang, P. Y., Liu, Y. H., Alsaedi, A., Hayat, T., & Wang, X. K. (2016). Environmental remediation and application of nanoscale zero-valent iron and its composites for the removal of heavy metal ions: A review. Environmental Science & Technology, 50(14), 7290–7304. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b01897
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2022YFC3303200), Guangdong province teaching reform fund (GDJX2020009) and Bureau of Science and Technology of Jiangmen Municipality project (2022JC01019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The specific contributions made by each author are as follows: Conception and design of study: LG; Calculation of data: LG and ZX; Analysis and/or interpretation of data: LG and GG; The first draft of the manuscript was written by LG, and all authors commented on the previous version of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, L., Xue, Z. & Gnanachandrasamy, G. Visual analysis of contaminated site studies in recent 30 years based on bibliometrics and knowledge graph. Environ Dev Sustain (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-024-04676-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-024-04676-5