Abstract
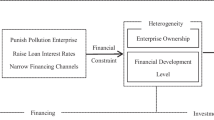
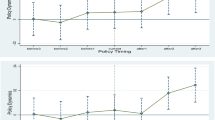
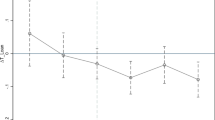
The green credit policy (GCP), which serves as the focal point of the green finance system in China, helps devote credit resources to projects that promote preservation of the environment while limiting the inflow of bank credit funds to enterprises that are high polluting, high energy consuming, or have surplus capacity (two high and one surplus). GCP limits the risk of “Greenwashing” because of the application of financial technology and tight policy implementation criteria, and the mandatory effect of the policy is extremely noticeable. As micro-entities for green development, “two high and one surplus” enterprises are also important subjects for research and development (R&D) activities and the reshaping of China’s economy. Whether “two high and one surplus” enterprises can achieve transformation and upgrading through R&D activities is critical to China’s high-quality development. This study employs the difference-in-difference (DID) model to investigate the effect and mechanism of GCP on R&D of “two high and one surplus” enterprises, using the launch of “Green Credit Guidelines” (GCG) in 2012 as an external event and A-share listed enterprises from 2009 to 2019 as the study’s object. The results are as follows: (1) GCG’s implementation severely inhibits R&D in “two high and one surplus” enterprises. After the robustness test, such as replacing proxy variables and removing the interference of related samples, the findings still hold, and the dynamic test results indicate that the inhibitory effect has the feature of accumulation; (2) the mediating effect test results indicate that GCG can lower the debt financing scale, thus inhibiting “two high and one surplus” enterprises’ R&D; however, the cost of debt financing does not play a mediating role between the implementation of GCG and the R&D of “two high and one surplus” enterprises. (3) The heterogeneity test findings suggest that state-owned enterprises (SOEs) have a greater inhibitory impact. (4) The heterogeneity test findings reveal that the inhibitory impact is greater in non-banking-enterprise association enterprises. Based on a comprehensive focus on the restricted loan granting objects required by GCP, this study enriches the literature in areas such as research about the effects of green finance policies by providing evidence on practical explanations.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used during the current study are available from the corresponding or first author on reasonable request.
References
Alola, A., Çelik, A., Awan, U., Abdallah, I., & Obekpa, H. (2023). Examining the environmental aspect of economic complexity outlook and environmental-related technologies in the Nordic states. Journal of Cleaner Production, 408, 137154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.137154
Awan, U., Kraslawski, A., & Huiskonen, J. (2018). Governing Interfirm Relationships for Social Sustainability: The relationship between governance mechanisms, sustainable collaboration, and cultural intelligence. Sustainability, 10, 1–20. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10124473
Czarnitzki, D., & Kraft, K. (2009). Capital control, debt financing and innovative activity. Journal of Economic Behavior & Organization, 71(2), 372–383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jebo.2009.03.017
Diamond, D. W. (1984). Financial intermediation and delegated monitoring. The Review of Economic Studies, 51(3), 393–414. https://doi.org/10.2307/2297430
Duqi, A., Tomaselli, A., & Torluccio, G. (2018). Is relationship lending still a mixed blessing? A review of advantages and disadvantages for lenders and borrowers. Journal of Economic Surveys, 32(5), 1446–1482. https://doi.org/10.1111/joes.12251
Hao, F., Xie, Y., & Liu, X. (2020). The impact of green credit guidelines on the technological innovation of heavily polluting enterprises: A quasi-natural experiment from China. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2020(2020), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8670368
Ho, V. H. (2018). Sustainable finance & China’s green credit reforms: A test case for bank monitoring of environmental risk. Cornell International Law Journal, 51(3), 609–681.
Hu, G., Wang, X., & Wang, Y. (2021). Can the green credit policy stimulate green innovation in heavily polluting enterprises? Evidence from a quasi-natural experiment in China. Energy Economics. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2021.105134
Jahanger, A., Lorente, D., Hulio, M., Samour, A., Abbas, S., & Tursoy, T. (2023). Going away or going green in ASEAN countries: Testing the impact of green financing and energy on environmental sustainability. Energy & Environment.
Jensen, M. C., & Meckling, W. H. (1976). Theory of the firm: Managerial behavior, agency costs and ownership structure. Journal of Financial Economics, 3(4), 305–360. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-009-9257-3_8
Ji, L., Jia, P., & Yan, J. (2021). Green credit, environmental protection investment and debt financing for heavily polluting enterprises. Plos One. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0261311
Jones, R., Baker, T., Huet, K., Murphy, L., & Lewis, N. (2020). Treating ecological deficit with debt: The practical and political concerns with green bonds. Geoforum, 114, 49–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoforum.2020.05.014
Lei, X., Wang, Y., Zhao, D., & Chen, Q. (2021). The local-neighborhood effect of green credit on green economy: A spatial econometric investigation. Environmental Science & Pollution Research, 28(46), 65776–65790. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15419-8
Li, W., Cui, G., & Zheng, M. (2022). Does green credit policy affect corporate debt financing? Evidence from China. Environmental Science & Pollution Research, 29(4), 5162–5171. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16051-2
Lian, Y., Gao, J., & Ye, T. (2022). How does green credit affect the financial performance of commercial banks? Evidence from China. Journal of Cleaner Production. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.131069
Liu, J., Xia, Y., Fan, Y., Lin, S., & Wu, J. (2017). Assessment of a green credit policy aimed at energy-intensive industries in China based on a financial CGE model. Journal of Cleaner Production, 163, 293–302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.10.111
Liu, Q., Wang, W., & Chen, H. (2020). A study of the impact of Green Credit Guidelines implementation on innovation performance in heavy polluting enterprises. Science Research Management, 41(11), 100–112.
Liu, S., Xu, R., & Chen, X. (2021). Does green credit affect the green innovation performance of high-polluting and energy-intensive enterprises? Evidence from a quasi-natural experiment. Environmental Science & Pollution Research, 28(46), 65265–65277. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15217-2
Lorente, D., Mohammed, K., Cifuentes Faura, J., & Shahzad, U. (2022). Dynamic connectedness among climate change index, green financial assets and renewable energy markets: Novel evidence from sustainable development perspective. Renewable Energy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2022.12.085
Milani, S., Neumann, R., Houser, D., & Puzzello, D. (2022). R&D, patents, and financing constraints of the top global innovative firms. Journal of Economic Behavior & Organization, 196, 546–567.
Peng, B., Yan, W., Elahi, E., & Wan, A. (2022). Does the green credit policy affect the scale of corporate debt financing? Evidence from listed companies in heavy pollution industries in China. Environmental Science & Pollution Research, 29(1), 755–767. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15587-7
Shaheen, F., Lodhi, S., Rosak-Szyrocka, J., Zaman, K., Awan, U., Asif, M., Ahmed, W., & Siddique, M. (2022). Cleaner technology and natural resource management: An environmental sustainability perspective from China. Clean Technologies, 4, 584–606. https://doi.org/10.3390/cleantechnol4030036
Shi, J., Yu, C., Li, Y., & Wang, T. (2022). Does green financial policy affect debt-financing cost of heavy-polluting enterprises? An empirical evidence based on Chinese pilot zones for green finance reform and innovations. Technological Forecasting & Social Change. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2022.121678
Wang, T., & Thornhill, S. (2010). R&D investment and financing choices: A comprehensive perspective. Research Policy, 39(9), 1148–1159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.respol.2010.07.004
Wang, Y., Lei, X., Long, R., & Zhao, J. (2020). Green credit, financial constraint, and capital investment: Evidence from China’s energy-intensive enterprises. Environmental Management, 66(6), 1059–1071. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-020-01346-w
Wang, Y., Lei, X., Zhao, D., Long, R., & Wu, M. (2021). The dual impacts of green credit on economy and environment: Evidence from China. Sustainability. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13084574
Wen, H., Lee, C. C., & Zhou, F. (2021). Green credit policy, credit allocation efficiency and upgrade of energy-intensive enterprises. Energy Economics. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2021.105099
Xu, S. (2020). International comparison of green credit and its enlightenment to China. Green Finance, 2(1), 75–99. https://doi.org/10.3934/gf.2020005
Yao, S., Pan, Y., Sensoy, A., Uddin, G. S., & Cheng, F. (2021). Green credit policy and firm performance: What we learn from China. Energy Economics. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2021.105415
Zhang, D., & Kong, Q. (2022). Credit policy, uncertainty, and firm R&D investment: A quasi-natural experiment based on the green credit guidelines. Pacific-Basin Finance Journal. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pacfin.2022.101751
Zhang, K., Wang, Y., & Huang, Z. (2021a). Do the green credit guidelines affect renewable energy investment? Empirical research from China. Sustainability. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13169331
Zhang, S., Wu, Z., Wang, Y., & Hao, Y. (2021b). Fostering green development with green finance: An empirical study on the environmental effect of green credit policy in China. Journal of Environmental Management. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113159
Zhang, Y., Li, X., & Xing, C. (2022a). How does China’s green credit policy affect the green innovation of high polluting enterprises? The perspective of radical and incremental innovations. Journal of Cleaner Production. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.130387
Zhang, Z., Duan, H., Shan, S., Liu, Q., & Geng, W. (2022b). The impact of green credit on the green innovation level of heavy-polluting enterprises-evidence from China. International Journal of Environmental Research & Public Health. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19020650
Zhou, X. Y., Caldecott, B., Hoepner, A. G. F., & Wang, Y. (2022). Bank green lending and credit risk: An empirical analysis of China’s green credit policy. Business Strategy & the Environment, 31(4), 1623–1640. https://doi.org/10.1002/bse.2973
Zhu, Q., Zheng, K., & Wei, Y. (2021). Three-Party stochastic evolutionary game analysis of reward and punishment mechanism for green credit. Discrete Dynamics in Nature & Society. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/5596015
Funding
This work was supported by the Ministry of Education of the People’s Republic of China Humanities and Social Sciences Youth Foundation (Grant No. 22YJC910014), the Social Sciences Planning Youth Project of Anhui Province (Grant No. AHSKQ2022D138). The authors sincerely appreciate funding from Researchers Supporting Project number (RSP2024R58), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WM contributed to data curation, methodology, software, literature review, and writing—original draft preparation. CZ contributed to investigation, visualization, and supervision. XZ contributed to writing—reviewing and editing, supervision, validation, and investigation. XM contributed to conceptualization, visualization, and writing—reviewing and editing. SK contributed to supervision, validation, and investigation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, W., Zheng, C., Zhao, X. et al. Impact of green finance on R&D of “two high and one surplus” enterprises against the greenwashing background: exploring the role of green credit. Environ Dev Sustain (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-023-04348-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-023-04348-w