Abstract
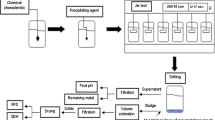
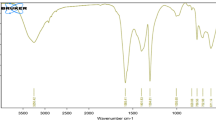
Phosphorus pollution poses a significant challenge in addressing water contamination. The coagulant is one of the effective methods to remove phosphorus from wastewater. Abundant Al and Fe oxides in sludge residue make it have great potential to synthesize water treatment coagulants. However, the utilization of sludge residue for preparation of coagulant was seldom investigated. In this study, we fabricated a novel coagulant, polyaluminum ferric chloride (SM-PAC), using sludge residue as a raw material through acid leaching and polymerization processes. Characterization results confirm that the parameters of SM-PAC meet the specifications outlined in the national standard (GB/T 22627–2022). We investigated the effects of pH, dosage, initial phosphorus concentration, and contact time on the removal efficiency of SM-PAC. As anticipated, the prepared SM-PAC exhibited a significant efficacy in removing phosphorus, meeting the discharge standards set for municipal sewage. Furthermore, the adsorption kinetics analysis suggests that the predominant mode of phosphorus adsorption on SM-PAC is chemical adsorption. Furthermore, the SM-PAC was employed in the actual wastewater treatment plant and exhibited excellent efficiency in phosphorus removal. The utilization of SM-PAC can not only effectively address the issue of sludge disposal but also achieve the goal of “treating waste with waste.” It is expected that the proposed method of reusing sludge residue as a resource can provide a sustainable way to synthesize a coagulant for phosphorus removal.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
Dai, Y., Li, Y., Ke, Y., & Li, B. (2021). Efficiency and mechanism of advanced treatment for phosphate wastewater by high efficiency and low consumption coagulation and phosphorus removal system. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 631, 012002. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/631/1/012002
Deng, L., Zhang, Z.-Y., Wang, J., Cui, J., & Zhang, Y. (2024). Phosphorus removal by magnesium-based cementitious material: Performance and mechanisms. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 12, 112172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2024.112172
Eran, T. N., Galli, F., Guyot, J., Lefebvre, J., Grainca, A., Patience, G., & Pirola, C. (2024). Copper, potassium promoted iron on metallosilicate and aluminum oxide supports synthesized via a non-hydrolytic sol-gel for Fischer-Tropsch. Catalysis Today, 433, 114655. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2024.114655
Gao, S., Wang, Q., Nie, J., Poon, C. S., Yin, H., & Li, J.-s. (2021). Arsenate(V) removal from aqueous system by using modified incinerated sewage sludge ash (ISSA) as a novel adsorbent. Chemosphere, 270, 129423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.129423
Giwa, A. S., Maurice, N. J., Luoyan, A., Liu, X., Yunlong, Y., & Hong, Z. (2023). Advances in sewage sludge application and treatment: Process integration of plasma pyrolysis and anaerobic digestion with the resource recovery. Heliyon, 9, e19765. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e19765
Gong, C.-c, Wang, Y.-f, Huo, L.-q, & Dai, J. (2023a). Phosphorus removal from sewage by flocculated foamed lightweight aggregate: Performance optimisation, adsorption kinetics and mechanisms. Separation and Purification Technology, 305, 122458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2022.122458
Gong, C., Huo, L., Wang, Z., Sun, C., Wang, Y., & Cheng, X. (2023b). Phosphorus removal by porous aggregate from aerated concrete waste residues: Simulating porous structure, performance optimisation, adsorption mechanisms. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 11, 111075. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2023.111075
Guo, X., Yuan, S., Xu, Y., & Qian, G. (2022). Effects of phosphorus and iron on the composition and property of Portland cement clinker utilized incinerated sewage sludge ash. Construction and Building Materials, 341, 127754. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.127754
Han, W., Jin, P., Chen, D., Liu, X., Jin, H., Wang, R., & Liu, Y. (2021). Resource reclamation of municipal sewage sludge based on local conditions: A case study in Xi’an China. Journal of Cleaners Production, 316, 128189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.128189
Hei, S., Xu, H., Liu, Y., Liu, B., Zhang, S., Zhu, X., Lin, W., Chen, L., Jiang, H., Cheng, X., Yong, X., Wu, X., & Huang, X. (2022). Redox environment inducing strategy for enhancing biological phosphorus removal in a full-scale municipal wastewater treatment plant. Journal of Cleaner Production, 376, 134237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.134237
Li, X., Zhang, J., Xie, H., Pan, Y., Liu, J., Huang, Z., Long, X., & Xiao, H. (2020). Cellulose-based adsorbents loaded with zero-valent iron for removal of metal ions from contaminated water. Environmental Science Pollutions R, 27, 33234–33247. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09390-z
Liu, L., Lu, Y., Du, M., Chen, Q., Yan, H., & Lin, Y. (2024a). Nano La(OH)3 modified lotus seedpod biochar: A novel solution for effective phosphorus removal from wastewater. Journal of Environmental Management, 356, 120502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2024.120502
Liu, Q., Jia, J., Hu, H., Li, X., Zhao, Y., & Wu, C. (2024b). Nitrogen and phosphorus limitations promoted bacterial nitrate metabolism and propagation of antibiotic resistome in the phycosphere of Auxenochlorella pyrenoidosa. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 468, 133786. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2024.133786
Mancuso, C., Jamison, M., Zaporski, J., & Yang, Z. (2021). Effects of coagulant morphology and chemical properties on soluble reactive phosphate removal in corn ethanol wastewater. Water Environment Research: A Research Publication of the Water Environment Federation, 93, 2589–2597. https://doi.org/10.1002/wer.1609
Owodunni, A. A., Ismail, S., Kurniawan, S. B., Ahmad, A., Imron, M. F., & Abdullah, S. R. S. (2023). A review on revolutionary technique for phosphate removal in wastewater using green coagulant. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 52, 103573. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2023.103573
Shi, H., Bhethanabotla, V. R., & Kuhn, J. N. (2023). Pelletized SiO2-supported La0.5Ba0.5FeO3 for conversion of CO2 to CO by a reverse water-gas shift chemical looping process. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 118, 44–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2022.10.038
Sihvonen, M., Lintunen, J., Valkama, E., & Hyytiäinen, K. (2020). Management of legacy nutrient stores through nitrogen and phosphorus fertilization, catch crops, and gypsum treatment. Natural Resource Modeling, 33, e12289. https://doi.org/10.1111/nrm.12289
Toor, U. A., & Kim, D.-J. (2019). Effect of pH on phosphorus (P) dissolution and recovery from polyaluminum chlorides (PAC) sludge. Journal of Environmental Management, 239, 142–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.03.049
Wang, Q., Li, J.-s, & Poon, C. S. (2019). Using incinerated sewage sludge ash as a high-performance adsorbent for lead removal from aqueous solutions: Performances and mechanisms. Chemosphere, 226, 587–596. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.03.193
Wang, B., Zeng, W., Fan, Z., Wang, C., Meng, Q., & Peng, Y. (2020). Effects of polyaluminium chloride addition on community structures of polyphosphate and glycogen accumulating organisms in biological phosphorus removal (BPR) systems. Bioresource Technology, 297, 122431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122431
Wang, Q., Li, J.-s, & Poon, C. S. (2021a). Novel recycling of phosphorus-recovered incinerated sewage sludge ash residues by co-pyrolysis with lignin for reductive/sorptive removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solutions. Chemosphere, 285, 131434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131434
Wang, Q., Li, J.-s, Xue, Q., & Poon, C. S. (2021b). Alkaline modification of the acid residue of incinerated sewage sludge ash after phosphorus recovery for heavy metal removal from aqueous solutions. Waste Management (oxford), 123, 80–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2021.01.025
Wang, Q., Li, J.-s, & Poon, C. S. (2023). Production of sorptive granules from incinerated sewage sludge ash and upcycling in cement mortar. Separation and Purification Technology, 309, 123046. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2022.123046
Wu, H.-f, Wang, J.-p, Duan, E.-g, Hu, W.-h, Dong, Y.-b, & Zhang, G.-q. (2020). Phosphorus removal by adsorbent based on poly-aluminum chloride sludge. Water Science and Engineering, 13, 193–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wse.2020.09.006
Xing, C., Wen, J., Li, W., Shi, J., Wang, S., & Xu, Z. (2023). Integrating the Fe2+/H2O2-strengite method in airlift reactor for phosphorus removal and recovery from organic phosphorus wastewater. Chemical Engineering Journal, 475, 146093. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2023.146093
Xu, H., Wei, S., Li, G., & Guo, B. (2024). Advanced removal of phosphorus from urban sewage using chemical precipitation by Fe-Al composite coagulants. Science and Reports, 14, 4918. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-55713-2
Zhang, J., Tang, L., Tang, W., Zhong, Y., Luo, K., Duan, M., Xing, W., & Liang, J. (2020). Removal and recovery of phosphorus from low-strength wastewaters by flow-electrode capacitive deionization. Separation and Purification Technology, 237, 116322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2019.116322
Zhao, Z., Li, Z., Wu, L., Song, Y., Roger Razanajatovo, M., Sun, Q., Jiao, T., Peng, Q., & Zhang, Q. (2023). Rational design of the nanocomposite by in-situ sub-10 nm La(OH)3 formation for selective phosphorus removal in waters. Separation and Purification Technology, 312, 123306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2023.123306
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Bo Yu: methodology, formal analysis, resources, writing–original draft, writing–review and editing. Xiaoning Li: validation, data collection, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing. Han Yan: investigation, resources, data curation, writing—review and editing. Ming Zhang: supervision, resources. Jiao Ma: investigation, data curation. Ke Lian: formal analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The work described here is original research that has not been published or has been accepted elsewhere. All authors have read, understood, and have complied as applicable with the statement on “Ethical responsibilities of Authors” as found in the Instructions for Authors.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All authors agree to submit this manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships for this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, B., Li, X., Yan, H. et al. Recycling of sludge residue as a coagulant for phosphorus removal from aqueous solutions. Environ Monit Assess 196, 576 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-024-12741-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-024-12741-9