Abstract
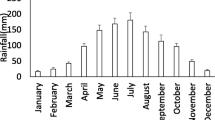
The main tributary of the Yamuna, the Tons River, exhibits altitudinal changes in its macroinvertebrate community’s diversity, abundance, and composition. Between May 2019 and April 2021, the study was conducted in the upper section of the river. A total of 48 numbers of taxa from 34 families and ten orders were recorded during the investigation. At this elevation of 1150 to 1287 m, the two most predominant orders are Ephemeroptera (32.9%) and Trichoptera (29.5%). During the premonsoon season, they had the lowest macroinvertebrate density (250–290 individuals/m2), and the post-monsoon season had the highest density (600–640 individuals/m2). During the post-monsoon season, the maximum larval forms (60%) of various insect orders were predominant. The findings indicated that lower altitudes (1150–1232 m) have higher macroinvertebrate abundance than higher ones. The diversity of dominance is shallow at site-I (0.0738) and strong at the site-IV during the premonsoon season (0.03837). Taxa richness, as measured by the Margalef index (D), peaked in the spring season (January to March) at 6.9 and reached its lowest point (5.74) in the premonsoon season (April to May). Only 16 taxa were discovered in site-I and site-II, but 39 taxa were discovered at low altitudes (site-IV, 1100 m) (1277–1287 m). The Tons River contains a total of 12 and 13 genera, respectively, that belong to the orders Ephemeroptera and Trichoptera, according to qualitative study of the macroinvertebrates. The current study supports the use of macroinvertebrates as bioindicator species for monitoring biodiversity and assessing the health of ecosystems.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the data have been submitted to the Institute Research Committee of ICAR-Central Inland Fisheries Research Institute, Barrackpore, Kolkata, West Bengal, India.
References
Alongi, D. M. (1994). The role of bacteria in nutrient recycling in tropical mangrove and other coastal benthic ecosystems. In Ecology and conservation of southeast Asian marine and freshwater environments including wetlands, 19–32. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-0958-1_3
Angradi, T. R. (1996). Inter-habitat variation in benthic community structure, function, and organic matter storage in 3 Appalachian headwater streams. Journal of the North American Benthological Society, 15(1), 42–63. https://doi.org/10.2307/1467432
Azrina, M. Z., Yap, C. K., Ismail, A. R., Ismail, A., & Tan, S. G. (2006). Anthropogenic impacts on the distribution and biodiversity of benthic macroinvertebrates and water quality of the Langat River, Peninsular Malaysia. Ecotoxicology and environmental safety, 64(3), 337–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2005.04.003
Bouchard, R. W. (2004). Guide to aquatic macroinvertebrates of the Upper Midwest. Water Resources Center, University of Minnesota, St. Paul, MN, 208, 159–183.
Brinkhurst, R. O. (1963). A guide for the identification of British aquatic Oligochaeta. Scientific Publication. Freshwater Biological Association, 22, 1–55.
Czerniawska-Kusza, I. (2005). Comparing modified biological monitoring working party score system and several biological indices based on macroinvertebrates for water-quality assessment. Limnologica, 35(3), 169–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.limno.2005.05.003
De Shon, J. E. (1995). Development and application of the invertebrate community index (ICI). Biological assessment and criteria: Tools for water resource planning and decision making, 217–243.
Dumnicka, E. (2002). Upper Vistula river: Response of aquatic communities to pollution and impoundment. X. Oligochaete taxocens. Polish Journal of Ecology, 2(50). Retrieved July 22, 2022, from https://www.infona.pl/resource/bwmeta1.element.agro-article-c43ca0cc-9fac-450d-928f-46b43a2089b3
Dunbar, M. J., Warren, M., Extence, C., Baker, L., Cadman, D., Mould, D. J., & Chadd, R. (2010). Interaction between macroinvertebrates, discharge and physical habitat in upland rivers. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems, 20(S1), S31–S44. https://doi.org/10.1002/aqc.1089
Fierro, P., Valdovinos, C., Vargas-Chacoff, L., Bertrán, C., & Arismendi, I. (2017). Macroinvertebrates and fishes as bioindicators of stream water pollution. Water Quality, 2, 23–38. https://doi.org/10.5772/65084
Hawkins, C. P. (1984). Substrate associations and longitudinal distributions in species of Ephemerellidae (Ephemeroptera: Insecta) from western Oregon. Freshwater Invertebrate Biology, 3(4), 181–188. https://doi.org/10.2307/1467122
Identification, Images, & Information For Insects, Spiders & Their Kin For the United States & Canada. Retrieved December 15, 2021, from https://bugguide.net/node/view/15740
Izaak Walton League of America (IWLA).(2000). Field guide to aquatic macroinvertebrates. McDonald and Woodward Publishing Company.
Izaak Walton League of America (IWLA).(2006). A guide to aquatic insects and crustaceans. Stackpole Books.
Jacobsen, D. (2003). Altitudinal changes in diversity of macroinvertebrates from small streams in the Ecuadorian Andes. Archiv Fur Hydrobiologie, 158(2), 145–168.
Johnson, R. K., Wiederholm, T., & Rosenberg, D. M. (1993).Freshwater biomonitoring using individual organisms, populations, and species assemblages of benthic macroinvertebrates. Freshwater biomonitoring and benthic macroinvertebrates, 40–158. Retrieved July 22, 2022, from https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Richard-Johnson17/publication/292130029_Freshwater_biomonitoring_using_individuals_organisms_populations_and_species_assemblages_of_benthic_macroinvertebrates/links/5771274308ae6219474a372b/Freshwater-biomonitoring-using-individuals-organisms-populations-and-species-assemblages-of-benthic-macroinvertebrates.pdf
Kumar, A., & Khanna, V. (1984). A review of the taxonomy and ecology of Odonata larvae from India. Oriental insects, 17(1), 127–157. https://doi.org/10.1080/00305316.1983.10433694
Litsios, G., Sims, C. A., Wüest, R. O., Pearman, P. B., Zimmermann, N. E., & Salamin, N. (2012). Mutualism with sea anemones triggered the adaptive radiation of clownfishes. BMC Evolutionary Biology, 12(1), 1–15.
Lunde, K. B., & Resh, V. H. (2012). Development and validation of a macroinvertebrate index of biotic integrity (IBI) for assessing urban impacts to Northern California freshwater wetlands. Environmental monitoring and assessment, 184(6), 3653–3674. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2214-4
Malik, D. S., Bharti, U., & Kumar, P. (2010). Macro-benthic diversity in relation to biotic indices in Song river at Dehradun, India. Environment Conservation Journal, 11(1–2), 99–104. Retrieved July 22, 2022, from https://environcj.in/wp-content/uploads/issues/2010/12/99-104.pdf
Maneechan, W., Kruttha, P., & Prommi, T. O. (2018). The larva and pupa of Potamyiaflavata (Banks 1934) (Trichoptera: Hydropsychidae): Description, life cycle, and notes on its biology. Zootaxa, 4394(3), 395–406. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4394.3.5. PMID: 29690360.
Mathew, G., & Rahmathulla, V. K. (1995). Biodiversity in the Western Ghats-A study with reference to moths (Lepidoptera: Heterocera) in the silent valley National Park, India. Entomon-Trivandrum-, 20, 25–34.
McCoy, E. D. (1990). The distribution of insects along elevational gradients. Oikos, 313–322.
Meena, D. K., Lianthuamluaia, L., Mishal, P., Swain, H. S., Naskar, B. K., Saha, S., & Das, B. K. (2019). Assemblage patterns and community structure of macro-zoobenthos and temporal dynamics of eco-physiological indices of two wetlands, in lower Gangetic plains under varying ecological regimes: A tool for wetland management. Ecological Engineering, 130, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2019.02.002
Metcalfe, J. L. (1989). Biological water quality assessment of running waters based on macroinvertebrate communities: History and present status in Europe. Environmental Pollution, 60(1–2), 101–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/0269-7491(89)90223-6
Naskar, M., Sarkar, S. D., Raman, R. K., Gogoi, P., Sahu, S. K., Chandra, G., & Bhor, M. (2020). Quantifying plankton-environmental interactions in a tropical river Narmada, India: An alternative model-based approach. Ecohydrology & Hydrobiology, 20(2), 265–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecohyd.2019.10.006
Navas-Pereira, D., & Henrique, R. M. (1996). The use of biological indices on environmental quality assessment. RevistaBrasileira De Biologia., 56(2), 441–450. PMID: 9035494.
Nelson, S. M., Roline, R. A., Thullen, J. S., Sartoris, J. J., & Boutwell, J. E. (2000). Invertebrate assemblages and trace element bioaccumulation associated with constructed wetlands. Wetlands, 20(2), 406–415. https://doi.org/10.1672/0277-5212(2000)020[0406:IAATEB]2.0.CO;2
Paine, G. H., & Gaufin, A. R. (1956). Aquatic Diptera as indicators of pollution in a midwestern stream. Ohio Journal of Science, 56(5), 291–304. Retrieved July 22, 2022, from http://hdl.handle.net/1811/4386
Pearson, T. H. (1980). Macrobenthos of fjords. In Fjord oceanography (pp. 569–602). Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4613-3105-6_53
Peeters, E. T., & Gardeniers, A. J. J. (1998). Logistic regression as a tool for defining habitat requirements of two common gammarids. Freshwater Biology, 39(4), 605–615. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2427.1998.00304.x
Resh, V. H. (1995). Freshwater benthic macroinvertebrates and rapid assessment procedures for water quality monitoring in developing and newly industrialized countries. Biological assessment and criteria, 167–177.
Rice, E. W., Bridgewater, L., & American Public Health Association (Eds.). (2012). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (Vol. 10). American public health association.
Rosenberg, D. M., & Resh, V. H. (1993). Freshwater biomonitoring and benthic macroinvertebrates. Chapman and Hall. New York, 1–488.
Sanders, H. L. (1968). Marine benthic diversity: a comparative study. The American Naturalist, 102(925), 243–282. https://doi.org/10.1086/282541
Sharma, I., & Dhanze, R. (2012). Evaluation of macrobenthic fauna in hill stream environment of Western Himalaya, India. Journal of Threatened Taxa, 2875–2882. https://doi.org/10.11609/JoTT.o2725.2875-82
Sharma, R. C., & Rawat, J. S. (2009). Monitoring of aquatic macroinvertebrates as bioindicator for assessing the health of wetlands: A case study in the Central Himalayas, India. Ecological Indicators, 9(1), 118–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2008.02.004
Sharma, R. C., Arambam, R., & Sharma, R. (2009). Surveying macro-invertebrate diversity in the Tons river, Doon Valley, India. The Environmentalist, 29(3), 241–254. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10669-008-9187-z
Sharma, R. C., Bhanot, G., & Singh, D. (2004). Aquatic macroinvertebrate diversity in Nanda Devi Biosphere Reserve. India. Environmentalist, 24(4), 211–221.
Somerfield, P. J., & Gage, J. D. (2000). Community structure of the benthos in Scottish Sea-lochs. IV. Multivariate Spatial Pattern. Marine Biology, 136(6), 1133–1145.
Stanford, J. A., & Ward, J. V. (1983). Insect species diversity as a function of environmental variability and disturbance in stream systems. In Stream ecology pp. 265–278. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4613-3775-1_11
Strickland, J. D. H., & Parsons, T. R. (1972). A practical handbook of seawater analysis. Retrieved July 22, 2022, from https://epic.awi.de/id/eprint/39262/1/Strickland-Parsons_1972.pdf
Subramanian, K. A., & Sivaramakrishnan, K. G. (2007). Aquatic Insects for biomonitoring freshwater ecosystems-A methodology manual (p. 31). Ashoka Trust for Ecology and Environment (ATREE), Bangalore.
Suren, A. M. (1994). Macroinvertebrate communities of streams in western Nepal: Effects of altitude and land use. Freshwater Biology, 32(2), 323–336.
Sutherland, A. B., Culp, J. M., & Benoy, G. A. (2012). Evaluation of deposited sediment and macroinvertebrate metrics used to quantify biological response to excessive sedimentation in agricultural streams. Environmental Management, 50(1), 50–63. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-012-9854-1
TerBraak, C. J., & Verdonschot, P. F. (1995). Canonical correspondence analysis and related multivariate methods in aquatic ecology. Aquatic Sciences, 57(3), 255–289.
The Atlas of Common Freshwater Macroinvertebrates of North America. Retrieved January 20, 2022, from https://www.macroinvertebrates.org/taxa-specimens
Uherek, C. B., & Pinto Gouveia, F. B. (2014). Biological monitoring using macroinvertebrates as bioindicators of water quality of Maroaga Stream in the Maroaga Cave System, PresidenteFigueiredo, Amazon, Brazil. International Journal of Ecology.
Voshell, J. R. (2002). A guide to common freshwater invertebrates of North America (No.Sirsi) i9780939923878). Granville, OH, USA: McDonald & Woodward Pub. Retrieved July 22, 2022, from https://static1.squarespace.com/static/5b68b38bda02bc93873b1e86/t/5f8cc093b188622ed6c40431/1603059860068/macroinvertebrate_cards.pdf
Ward, J. V., & Stanford, J. A. (1979). Ecological factors controlling stream zoobenthos with emphasis on thermal modification of regulated streams. In The Ecology of Regulated Streams (pp. 35–55). Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4684-8613-1_4
Wilhm, J. L., & Dorris, T. C. (1968). Biological parameters for water quality criteria. Bioscience, 477–481. https://doi.org/10.2307/1294272
Winterbourn, M. J., Gregson, K. L., & Dolphin, C. H. (1989). Guide to the Aquatic Insects of New Zealand, 9, 96. Auckland: Entomological Society of New Zealand.
Young, S. S., Yang, H. N., Huang, D. J., Liu, S. M., Huang, Y. H., Chiang, C. T., & Liu, J. W. (2014). Using benthic macroinvertebrate and fish communities as bioindicators of the Tanshui River Basin around the greater Taipei area—Multivariate analysis of spatial variation related to levels of water pollution. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 11(7), 7116–7143. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph110707116
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the director, CIFRI, for the facilities, and the SJVNL for financial assistance and providing lodging facilities. Lastly, our sincere thanks go to the whole team members.
Funding
The authors are grateful to SJVN (Satluj Jal Vidyut Nigam Ltd.) for financial support and ICAR (Indian Council of Agricultural Research) for laboratory and other infrastructural support and carry out the research work under the external funded project ‘Study on viable and feasible alternatives on the blocked migratory movement of fish species due to construction of Naitwar, Mori HE “Project”’.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Basanta Kumar Das, Arghya Kunui, Saurav Kumar Nandy, Amiya Kumar Sahoo, Dharmendra Kumar Meena, and Uttam Kumar Sarkar: concept, manuscript preparation, statistical analysis, and interpretation of data; Amiya Kumar Sahoo, Arghya Kunui, Saurav Kumar Nandy, Samir Kumar Pal, and Koushik Mondal: sample collection, laboratory analysis and data representation, GIS mapping, and figure preparation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The authors declare that they have strictly followed all the rules and principles of ethical and professional conducts while completing the research work.
Consent to publication
All the authors have agreed to be listed as per the order mentioned in the MS.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Das, B.K., Kunui, A., Nandy, S.K. et al. Altitudinal and seasonal distribution of benthic macroinvertebrates in River Tons — a tributary of Yamuna River, Uttarakhand, India. Environ Monit Assess 195, 902 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11488-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11488-z