Abstract
Lithological characteristics interact with other factors of soil formation to define soil genesis. This becomes more interesting as data on the mineral and elemental oxide components of soils developed from limestone are rarely available in the humid tropical environment. The present study investigated the elemental oxide content, forms of sesquioxides, and clay mineral species in some limestone soils. Soil samples were obtained from three (3) crestal soil profile pits and analyzed for elemental content by the use of an X-ray fluorescence spectrometer, and sesquioxide forms by inductively coupled plasma–mass spectrometer. Analyses were done in triplicates. The mineralogy of the clay fraction was determined on the A, B, and C horizon samples using an X-ray diffraction technique. The occurrence of SiO2 (203–277 g/kg), Al2O3 (65–105 g/kg), and Fe2O3 (14–95 g/kg) in substantial amounts over MnO2, ZrO2, and TiO2 with negligible quantities of CaO suggested comparatively more developed soils in the Agoi Ibami and Mfamosing tropical rainforests. Crystalline form of Fe was dominant over amorphous form, with indications of the co-migration of dithionite Fe with clay to the B horizons of the soils. Quartz, kaolinite, montmorillonite, and chlorite-vermiculite-montmorillonite interlayered minerals dominated the clay mineralogy of the studied soils. Mineral transformation places the soils at the transitory stage from the intermediate to the complete stage of soil development. The expanding clay minerals are most likely to increase plant nutrient adsorption and soil fertility status to accommodate the cultivation of a wider range of crops.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used in the current study are available on reasonable request from the corresponding author.
References
Akpan-Idiok, A. U., & Ogbaji, P. O. (2013). Characterization and classification of Onwu River Floodplain soils in Cross River State. Nigeria. International Journal of Agricultural Research, 8(3), 107–1222.
Al-Farraj, A. S. (2011). Mineralogical composition of limestone rock and soil from Jubaila Formation. Asian Journal of Earth Sciences, 4(4): 203–213.
Al-Khirbash, S. A. (2016). Geology, mineralogy, and geochemistry of low grade Ni-lateritic soil (Oman Mountains, Oman). Chemie Der Erde, 76, 363–381.
Aparı´cio, P., & Ferrell Jr., R. E. (2001). An application of profile fitting and CLAYþþ for the quantitative representation (QR) of mixed-layer clay minerals. Clay Minerals, 36, 501–514.
Aubert, G., & Segalen, P. (1966). Project de classification des sols ferralliques. Cah. O.R.S.T.O.M. Sdr. Pddoi., 4, 97–112.
Babechuk, M. G., Widdowson, M., & Kamber, B. S. (2014). Quantifying chemical weathering intensity and trace element release from two contrasting basalt profiles, Deccan Traps, India. Chemical Geology, 363, 56–75.
Bautista, F., Palacio-Aponte, G., Quintana, P., & Zinck, J. A. (2011). Spatial distribution and development of soils in tropical karst areas from the Peninsula of Yucatan, Mexico. Geomorph, 135(314), 308–321.
Bish, D. L. (1994). Quantitative X-ray diffraction analysis of soils. In J. E. Amonette, L. W. Zelazny, & R. J. Luxmoore (Eds.), Quantitative methods in soil mineralogy (pp. 267–295). Soil Science Society of America.
Bohn, H., McNeal, B., & O’Connor, G. (2001). Soil Chemistry (3rd ed.). Wiley Interscience.
Brindley, G.W., & Brown, G. (1980). Crystal structures of clay minerals and their X-ray identification: London, Mineralogical Society, 495 p.
Burt, R., Wilson, M. A., Mays, M. D., & Lee, C. W. (2003). Major and trace elements of selected pedons in the USA. Journal of Environmental Quality, 32, 2109–2122. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq2003.2109
Cabadas-Baez, H., Solleiro, E., Sedov, S., Pi Puig, T., & Gama-Castro, J. (2010). Pedosediments of karstic sinkholes in the eolianites of NE Yucatan: A record of late Quaternary soil development, geomorphic processes and landscape stability. Geomorph, 122, 323–337.
Chamayou, H., & Legros, J. P. (1989). Les bases physiques, chimiques et mineralogiques de la science du sol., presses universitaires de France.
Churchman, G.J., & Lowe, D. J. (2012). Alteration, formation and occurrence of minerals in soils. In: Huang, P.M., Li, Y., Sumner, M.E. (Eds.), Handbook of Soil Sciences, Properties and Processes, second ed. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp. 20.1–20.72.
Cornell, R. M., & Schwertmann, U. (1979). Clays. Clay Minerals, 27, 402.
Curi, N., & Franzmeier, D. P. (1987). Effects of parent rocks on chemical and mineralogical properties of some oxisols in Brazil. SSSA Jour, 51, 153–158.
Deepthy, R., & Balakrishnan, S. (2005). Climatic control on clay mineral formation: Evidence from weathering profiles developed on either side of the Western Ghats. Journal of Earth System Science, 114, 545–556.
Da Silva, G. A., Camelo, D. D., Correa, M. M., De Souza, V. S., & (Jnr.), V. S., Filho, M. R. R., & Filho, J. C. D. (2019). Pedogenesis on coastal tablelands area with low range altimetry in Paraiba State. Revista Caatinga, 32(2), 1983–2125.
Duiker, S. W., Rhoton, F. E., Torrent, J., Smeck, N. E., & Lal, R. (2003). Iron hydroxide crystallinity effects on soil aggregation. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 67, 606–611.
Dolui, A. K., & Bera, R. (2001). Relation between Fe forms and pedogenic processes in some Alfisols of Orissa, India. Agrochim. XLV: 161–170
Dolui, A. K., & Mondal, A. (2007). Influence of different forms of iron and aluminum on the nature of soil acidity of some inceptisols, alfisols, and ultisols. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 38(1–2), 119–131.
Durn, G. (2003). Terra Rossa in the Mediterranean Region: Parent materials, composition and origin. Geologia Croatica, 56(1), 83–100.
Duzgoren-Aydin, N. S., Aydin, A., & Malpas, J. (2002). Re-assessment of chemical weathering indices: Case study on pyroclastic rocks of Hong Kong. Engineering Geology, 63(1–2), 99–119.
Egli, M., Wernli, M., Bruga, C., Kneisel, C., Mavris, C., Valboa, G., Mirabella, A., Plötze, M., & Haeberli, W. (2011). Fast but temporally scattered smectite-formation in the proglacial area Morteratsch: An evaluation using GIS. Geoder, 164, 11–21.
Emadi, M., Baghernejad, M., Mermarian, H., Saffari, M., & Fath, H. (2008). Genesis and clay mineralogical investigation of highly calcareous soils in semi-arid regions of Southern Iran. Journal of Applied Sciences, 8, 288–294. https://doi.org/10.3923/jas.2008.288.294
Fatoye, F. B., & Gideon, Y. B. (2013). Geology and occurrences of limestone and marble in Nigeria. Journal of Natural Sciences Research, 3(11).
Fernández-Caliani, J. C., Romero-Baena, A., González, I., & Galán, E. (2020). Geochemical anomalies of critical elements (Be Co, Hf, Sb, Sc, Ta, V, W, Y and REE) in soils of western Andalusia (Spain). Applied Clay Science, 191(2020), 105610.
Ferreira, E. P., Anjos, L. H. C., Pereira, M. G., Valladares, G. S., Silva, R. C., & Azevede, A. C. (2016). Genesis and classification of soils containing carbonate on the Apodi plateau, Brazil. Revista Brasileira de Ciência do Solo, 40, e0150036
Girao, R. O., Moreira, L. G., Girao, A. L., Romero, R. E., & Ferreira, T. O. (2014). Soil genesis and iron nodules in a karst environment of the Apodi plateau. Revista Ciencia Agronomica, 45(4), 683–695.
Hameed, A., Raja, P., Ali, M., Upreti, N., Kumar, N., Tripathi, J. K., & Srivastava, P. (2018). Micromorphology, clay mineralogy, and geochemistry of calcic-soils from western Thar Desert: Implications for origin of palygorskite and southwestern monsoonal fluctuations over the last 30 ka. CATENA, 163, 378–398.
Haynes, R. J. (2005). Labile organic matter fractions as central components of the quality of agricultural soils; An overview. Advances in Agronomy, 85, 221–268.
Hsu, P. H. (1989). Aluminum oxides and oxyhydroxides. In J. B. Dixon & S. B. Weed (Eds.), Minerals in soil environments (pp. 331–378). Soil Science Society of America.
Intamo, P., Suddhiprakarn, A., Kheoruenromne, I., Tawornpruek, S., & Gilkes, R. J. (2014). Clay minerals and metals in soils on mineralized Limestone, Western Thailand. Australian Clay Minerals Society Conference-Perth. Pp. 7–10.
Irmak, S., Surucu, A. K., & Aydogdu, I. H. (2007). Effects of different parent material on the mineral characteristics of Soils in the arid Region of Turkey. Pakistan Journal of Biological Sciences, 10(4), 528–536.
Jafarzadeh, A. A., Garosi, U., Oustan, S., & Ahmadi, A. (2013). Soil erosion status in Iran and clay minerals influence on soils interrill erodibility factor a case study: dasht-e-tabriz.
Jonczak, J., Šimanský, V., & Polláková, N. (2015). Characteristics of iron and aluminium forms and quantification of soil forming processes in chernozems in Western Slovakia. Polish Journal of Soil Science, XLVIII/2 PL ISSN 0079–2985. https://doi.org/10.17951/pjss/2015.48.2.241
Juo, A. S. R., Moormann, F. R., & Maduakor, H. O. (1974). Forms and pedogenetic distribution of extractable iron and aluminum in selected soils of Nigeria. Geoder, 11, 167–179.
Kabata-Pendias, A. (2011). Trace elements in soils and plants (4th ed.). CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group, Boca Raton London New York. Pp. 505.
Kasanin-Grubin, M. (2013). Catena clay mineralogy as a crucial factor in badland hillslope processes. CATENA, 106, 54–67.
Kampf, N., & Curi, N. (2012). Formação e evolução do solo (pedogênese). In: Ker JC, Curi N, Schaefer CEGR, Vidal-Torrado P, (eds.) Pedologia: fundamentos. Viçosa, MG: Sociedade Brasileira de Ciência do Solo. 207–302.
Katsumi, M. (1989). Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 53, 2915–2924.
Kendrick, K. J., & Graham, R. C. (2004). Pedogenic silica accumulation in chronosequence soils, southern California. SSSA Journal, 68(4), 1295–1303.
Khresat, S. A., & Taimeh, A. Y. (1998). Properties and characterization of Vertisols developed on limestone in a semi-arid environment. Journal of Arid Environments, 40, 235–244. https://doi.org/10.1006/jare.1998.0445
Kowalska, J., Kajdas, B., & Zaleski, T. (2017). Variability of morphologicalk, physical and chemical properties of soils derived from carbonate –rich parent materials in the Pieniry mountains South Poland. Soil Ci. Annual, 68, 27–38.
Kowalska, J. B., Skiba, M., Maj-Szeliga, K., Mazurek, R., & Tomasz, Z. (2020). Does calcium carbonate influence clay mineral transformation in soils developed from slope deposits in Southern Poland? Journal of Soils and Sediments. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-020-02764-3
Krasilnikov, P., García-CalderóN., N. E., & Fuentes-Romero, E. (2007). Pedogenesis and slope processes in subtropical mountain areas, Sierra Sur de Oaxaca, Mexico. Revista Mexicana de Ciencias Geológicas, 24(3), 469–486.
Krekeler, M. P. S., Calkins, C., & Borkiewicz, O. J. (2010). Mineralogical and hydrogeologic properties of a partially unconsolidated Pleistocene limestone in the East central Yucatan: Implications for the development of subsurface flow constructed wetlands in the region. Carbonates and Evaporites, 25(1), 77–86.
Lazaratou, C. V., Panagiotaras, D., Panagopoulos, G., Pospíšil, M., & Papoulis, D. (2020). Ca treated Palygorskite and Halloysite clay minerals for Ferrous Iron (Fe2+) removal from water systems. Environmental Technology and Innovation, 2020(19), 100961.
Li, C., Li, Y., Cheng, H., Jiang, C., & Zheng, L. (2022). Remediation of soil mercury by modified vermiculite-montmorillonite and its effect on the growth of Brassica chinensis L. Molecules, 27, 5340. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27165340
Li, C., Zheng, L. G., Jiang, C. L., Chen, X., & Ding, S. S. (2021). Characteristics of leaching of heavy metals from low-sulfur coal gangue under different conditions. International Journal of Coal Science & Technology, 8, 780–789.
Lindsay, W. L. (1974). Role of chelation in micronutrient availability. In E. W. Carson (Ed.), The Plant Root and Its Environment (pp. 507–524). Charlottesville, VA: University Press of Virginia.
Ma, J. F. (2004). Role of silicon in enhancing the resistance of plants to biotic and abiotic stresses. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 50, 11–18.
Mahaney, W. C., Hancock, R. G., & Sanmugadas, K. (1991). Extractable Fe-Al and geochemistry of Late Pleistocene Paleosol in the Dalijia Shan, Western China. Journal of Southeast Asian Earth Sciences, 6, 75–82.
McKeague, J. A., & Day, J. H. (1966). Dithionite- and oxalate-extractable Fe and A1 as aids in differentiating various classes of soils. Canadian Journal of Soil Science, 46, 13–22.
Mehra, O. P., & Jackson, M. L. (1960). Iron oxide removal from soils and clays by dithionite citrate system buffered with sodium bicarbonate. Clays Clay Minerals, 7, 317–327.
Moreira, A., Franchini, J. C., Moraes, L. A. C., & Malavolta, E. (2000). Disponibilidade de nutrientes em Vertissolo calcário. Pesquisa Agropecuaria Brasileira, 35, 2107–2113. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-204X2000001000024
Mota, J. C. A., & Assis (Jnr.), R. N., Amaro, F. J., Romero, R. E., Mota, F. O. B., & Libardi, P. L. (2007). Atributos mineralógicos de três solos explorados com a cultura do melão na Chapada do Apodi – RN. Revista Brasileira de Ciência do Solo, 31, 445–454. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-06832007000300004
Mukaetov, D., Petkovski, D., & Andreevski, M. (2000). Contents of exchangeable ions of calcocambi soil and Terra Rossa on the Gallicica Mountain. In: Proc. Of the Symposium Soil and their Exploitation, MASA, Skopje, Pp. 83
Négrel, P., Ladenberger, A., Reimann, C., Birke, M., Demetriades, A., & Sadeghi, M. (2019). GEMAS: Geochemical background and mineral potential of emerging tech-critical elements in Europe revealed from low-sampling density geochemical mapping. Application of Geochimica, 111, 104425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2019.104425
Nesbitt, H. W., & Markovics, G. (1980). Chemical processes affecting alkalis and alkaline earths during continental weathering. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 44(11), 1659–1666.
Obi, J. C., Akinbola, G. E., & Anozie, H. F. (2009). Distribution of dithionite and oxalate-extractable iron oxides of a catena in the basement complex soils of Southwestern Nigeria. Nigeria Journal of Soil Science, 19, 100–108.
Ofem, K. I., & Esu, I. E. (2015). Pedological study of soils developed on schist in Biase Local Government Area, Cross River State, Nigeria. Nigeria Journal of Soil Science, 25, 181–193.
Ofem, K. I., Asadu, C. L. A., Ezeaku, P. I., Kingsley, J., Eyong, M. O., Katerina, V., Vaclav, T., Karel, N., Ondrej, D., & Vit, P. (2020). Genesis and classification of soils over limestone formations in a tropical humid region. Asian Journal of Scientific Research, 13, 228–243. https://doi.org/10.3923/ajsr.2020.228.243
Ofem, K. I., John, K., Pawlett, M., Eyong, M. O., Awaogu, C. E., Umeugokwe, P., Ambros-Igho, G., Ezeaku, P. I., & Asadu, C. L. A. (2021). Estimating soil organic matter: A case study of soil physical properties for environment-related issues in Southeast Nigeria. Earth Systems and Environment. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41748-021-00263-0
Omdi, F. E., Daoudia, L., & Fagel, N. (2018). Origin and distribution of clay minerals of soils in semi-arid zones: Example of Ksob watershed (Western High Atlas, Morocco). Applied Clay Science, 163, 81–91.
Osayande, P. E., Oviasogie, P. O., Aisueni, N. O., Stephen, O., Irhemu, P., & Ekebafe, M. O. (2013). Assessment of dithionite and oxalate extractable iron and aluminium oxides in soils supporting Raphia palms (Raphia spp.) at NIFOR Main Station. Nigeria Journal of Soil Science, 23(2), 1–10.
Owliaie, H. R., Abtahi, A., & Heck, R. J. (2006). Pedogenesis and clay mineralogical investigation of soils formed on gypsiferous and calcareous materials, on a transect, southwestern Iran. Geoderma, 134, 62–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2005.08.015
Pavitch, M. J. (1989). Regolith residence time and the concept of surface age of the piedmont ‘Peneplain.’ Geomorph, 2, 181–196.
Petar, R.., Zorica1, T., Jovica, V., Snežana, J., & Aleksandar, D. (2016). Mineral composition of soils formed on massive limestone of Pivska Planina, International Journal of Innovative Studies in Sciences and Engineering Technology, 2(7), 38-43
Ross, C. S., & Hendricks, S. (1945). Minerals of the montmorillonite group, their origin and relation to soils and clays. US Geological Survey Paper, 205(3), 23–79.
Rozanov, A., Lessovaia, S., Louw, G., Polekhovsky, Y., & de Clercq, W. (2017). Soil clay mineralogy as a key to understanding planation and formation of MARK fluvial terraces in the South African. CATENA, 156, 375–438.
Sambo, E. E, Ufoegbune, G. C., Eruola, A. O., & Ojekunle, O. Z. (2016). Pattern of climate change in Cross River Basin of Nigeria: Implication to agriculture and food security Nigerian Meteorological Society (NMETS), “Climate variability and change: Impact, science, innovation and policy” at Federal College of Education Osiele, Abeokuta. 21 - 24 November, 2016.
Schaetzl, R. J., & Anderson, S. (2005). Soils: Genesis and geomorphology (p. 817). Cambridge University Press.
Schoeneberger, P. J., Wysocki, D. A., Benham, E. C., & Soil Survey Staff. (2012). Field book for describing and sampling soils, Version 3.0. Natural Resources Conservation Service, National Soil Survey Center, Lincoln, NE.
Schwertmann, U. (1993). Relations between iron oxide, soil colour, and soil formation. In: J. M. Bigham and E. J. Ciolkosz (editors). Soil colour. Soil Science Society of America Special Publications, 31, pp. 51–69.
Seal, A., Bera, R., Bhattacharyya, P., Mukhopadhyay, K., & Giri, R. (2006). Degree of soil development in some Alfisols of subtropical India with special reference to the nature and distribution of iron and aluminum. International Journal of Agricultural Research, 1, 305–311.
Sedov, S., Solleiro-Rebolledo, E., Fedick, S. L., Pi-puig, T., Vallejo-Gomez, E., & Flores-Delgadillo, M. (2008). Micromorphology of a soil Catena in Yucatan: Pedogenesis and geomorphological processes in a Tropical Karst Landscape. New trends in Soil Micromorphology, Spriger-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg, P. 19–37.
Sharma, S. S., Totawat, K. L., & Shyampura, R. L. (1996). Characterization and classification of Soils in a Toposequence over basaltic terrain. Journal of the Indian Society of Soil Science, 44, 470–475.
Sherman, G. D., Matsusaka, Y., Ikawa, H., & Uehara, G. (1964). The role of amorphous fraction in the properties of tropical soils. Agrochimica, 7, 146–163.
SilvaNeto, L. F. (2008). Oxidos de ferro em latossolos tropicais e subtropicais Brasileiros em plantio direto. Revista Brasileira De Ciencias Do Solo, 32(5), 1873–1881.
Six, J., Elliott, E. T., & Paustian, K. (2000). Soil structure and soil organic matter: II. A normalized stability index and the effect of mineralogy. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 64, 1042–1049.
Soil Survey Staff (SSS). (2014a). Kellogg soil survey laboratory methods manual. Soil Survey Investigations Report No. 42, Version 5.0. R. Burt and Soil Survey Staff (ed.). U.S Department of Agriculture, Natural Resources Conservation Service. P. 1001.
Soil Survey Staff (SSS). (2014b). Keys to soil taxonomy. 12th Edn., United State Department of Agriculture, Washington, DC., Pages: 360.
Spalevic, V., Lakicevic, M., Radanovic, D., Billi, P., Barovic, G., Vujacic, D., Sestras, P., & Darvishan, A. K. (2017). Ecological-economic (Eco-Eco) modelling in the river basins of mountaineous regions: Impact of land cover changes on sediment yield in the Velicka Rijeka in Montenegro. Not Bot Horti Agrobo, 45(2), 602.
Tan, K. H. (2011). Principles of soil chemistry (4th edn.). CRC press, pp. 362.
Tan, K. H., & Binger, A. (1986). Effect of humic acid on aluminum toxicity in corn plants. Soil Science, 141, 20–25.
Tardi, Y., & Nahon, D. B. (1985). Geochemistry of laterites; stability of Al-goethite, Al-hematite and Fe3+-kaolinite in bauxites and ferricretes, An approach to the mechanism of concretion formation. American Journal of Science, 285, 865–903.
Tejnecky, V., Samonil, P., Grygar, T. M., Vasat, R., Ash, C., Drahota, P., Sebek, O., Nemecek, K., & Drabek, O. (2015). Transformation of iron forms during pedogenesis after tree uprooting in a natural beech-dominated forest. CATENA, 132, 12–20.
Tsozue, D., Bitom, D., & Lucas, Y. (2009). Biogeochemistry of iron, aluminium and silicon in humid tropical mountainous soils (Bambouto mountain, west Cameroon). Open Journal of Geology, 3, 70–81.
Vodyanitskii, Y. N., & Vasil’ev, A. A., Lesovaia, S. N., Sataev, E. F., & Sivtsov, A. V. (2004). Formation of manganese oxides in soils. Eurasian Soil Science, 37(6), 572–584.
Wagai, R., Kajiura, M., & Asano, M. (2020). Iron and aluminum association with microbially processed organic matter via meso-density aggregate formation across soils: Organo-metallic glue hypothesis. The Soil, 6, 597–627.
Wilson, S. G., Lambert, J., Nanzyo, M., & Dahlgren, R. A. (2017). Soil genesis and mineralogy across a volcanic lithosequence. Geoder, 285, 301–312.
Yakubu, M., & Ojanuga, A. G. (2013). Pedogenesis, weathering status and mineralogy of the soils on ironstone plateau (laterites), sokoto, Nigeria. Bayero Journal of Pure and Applied Sciences, 6(2), 93–100.
Young, J. L., & Aldag, R. W. (1982). Inorganic forms of nitrogen in soil. p. 43– 66. In F.J. Stevenson (ed.) Nitrogen in agricultural soils. Agronomy 22. ASA and SSSA, Madison, WI.
Yilmaz, K. (1990). Harra Ovasii Topraklarinin mineralojik Karakteristikleri. C.U. Yay. Doktora Tezi, Adana, Turkey, PP. 186
Yingbo, D., Weihong, Z., Hai, L., & Yueqing, Y. (2020). Preparation of Fe2O3-coated vermiculite composite by hydrophobic agglomeration and its application in As/Cd co-contaminated soil. Environmental Technology, 43(1), 83–94.
Zango, Z. U., Garba, A., Garba, Z. N., Zango, M. U., Usman, F., & Lim, J. W. (2022). Montmorillonite for adsorption and catalytic elimination of pollutants from wastewater: A state-of-the-arts review. Sustainability, 14, 16441. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142416441
Acknowledgements
The services of Christine Kimpton, and Nuannat Simmons of Soil Science Laboratory, Cranfield University, UK, and the Department of Soil Science and Soil Protection, Faculty of Agrobiology, Food and Natural Resources, Czech University of Life Sciences are acknowledged.
Funding
This work was supported by the Tertiary Education Trust Fund of Nigeria (grant number: TETFUND/DAST & D/ UNIV/ CALABAR/ ASTD/ 2017/ VOL. 1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
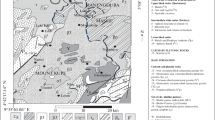
Kokei Ikpi Ofem and Mark Pawlett designed and wrote the initial paper. Kingsley John and Victoria Francis Ediene analyzed the soil samples and did initial grammar check, while Victor Ikemefuna Ezeaku and Alungbe Moses Ede organized the data and references and prepared Fig. 1. Patrick K. Kefas and Kokei Ikpi Ofem were involved in field study and processing of soil samples. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All authors have read, understood, and complied as applicable with the statement on “Ethical responsibilities” as found in the instructions for Authors.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ofem, K.I., John, K., Ediene, V.F. et al. Pedological data for the study of soils developed over a limestone bed in a humid tropical environment. Environ Monit Assess 195, 628 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11229-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11229-2