Abstract
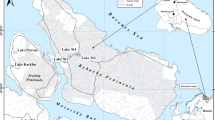
The potential contamination levels and human health risk of heavy metals in sediment of the Turnasuyu Stream in Ordu, Turkey, were evaluated comprehensively by taking seasonal samples from three different locations. The order of the mean heavy metals (HMs) concentrations (mg/kg) were as follows: Fe > Al > Mn > Pb > Zn > Cu > Co > Cr > Ni > Cd > As. All HM levels, except Cd and Pb, were in the minimum enrichment range as assessed by the sediment enrichment factor (EF). Similar low contamination levels for all HM, except Pb and Cd, were also observed when the contamination factor (CF) and geo-accumulation index (Igeo) were taken into account. The low risk of the study area has also been confirmed by the ecological risk index (Eri) values. The probable human health risk assessment has been performed, and the lifetime cancer risk (LCR) values for adults were found as negligible with values below 10−6. In addition, the hazard index (HI) and total hazard index (THI) results were both higher in children than in adults. The Pearson correlation coefficient (PCC) revealed the highest correlation between Cd and Pb (0.85). When the ecological indexes and statistical results are evaluated together, it is thought that the presence of HMs in the sediment may be due to lithological reasons as well as anthropogenic activities such as quarrying, municipal, agricultural, and domestic discharges in the region. Mitigation measures should be taken in accordance with the standards within the river basin to prevent the potential risks of pollution.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable
References
Abouian, J. M., Jamshidi-Zanjani, A., & Khodadadi, D. A. (2020). Heavy metal pollution and human health risk assessment for exposure to surface soil of mining area: A comprehensive study. Environmental Earth Science, 79, 365. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-09110-3
Algül, F., & Beyhan, M. (2020). Concentrations and sources of heavy metals in shallow sediments in Lake Bafa. Turkey. Scientific Reports, 10, 11782. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-68833-2
Alkan, N., Alkan, A., & Erüz, C. (2018). Determination of metals in water and sediment samples of the Sürmene River, Turkey. Green Energy Technology, 2, 175–181.
Arisekar, U., Shakila, R. J., Shalini, R., & Jeyasekaran, G. (2020). Human health risk assessment of heavy metals in aquatic sediments and freshwater fish caught from Thamirabarani River, the Western Ghats of South Tamil Nadu. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 159, 111496. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111496
ATSDR. (2012). Agency for toxic substance and disease registry. Toxicological profile for cadmium. Available at: Retrieved June 16, 2021, from http://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/toxprofiles/tp5.pdf
Aydin, H., Ustaoğlu, F., Tepe, Y., & Soylu, E. N. (2021). Assessment of water quality of streams in northeast Turkey by water quality index and multiple statistical methods. Environmental Forensics, 22(1–2), 270–287. https://doi.org/10.1080/15275922.2020.1836074
Bakan, G., Özkoç, H. B., Tülek, S., & Cüce, H. (2010). Integrated environmental quality assessment of Kizilirmak River and its coastal environment. Turkish Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 10, 453–462.
Bastami, K. D., Neyestani, M. R., Shemirani, F., Soltani, F., Haghparast, S., & Akbari, A. (2015). Heavy metal pollution assessment in relation to sediment properties in the coastal sediments of the southern Caspian Sea. Marine Pollution Bulletin. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2014.12.035
Benson, N. U., Udosen, E. D., Essien, J. P., Anake, W. U., Adedapo, A. E., Akintokun, O. A., Fred-Ahmadu, O. H., & Olajire, A. A. (2017). Geochemical fractionation and ecological risks assessment of benthic sediment-bound heavy metals from coastal ecosystems of the Equatorial Atlantic Ocean. International Journal of Sediment Research, 32(3), 410–420.
Chen, Z., Huang, S., Chen, L., Cheng, B., Li, M., & Huang, H. (2021). Distribution, source, and ecological risk assessment of potentially toxic elements in surface sediments from Qingfeng River, Hunan, China. Journal of Soils Sediments, 21, 2686–2698. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-021-02962-7
Cüce H., Kalipci E., Ustaoglu F., Baser V., & Türkmen M. (2022a). ’Ecotoxicological health risk analysis of potential toxic elements accumulation in the sediments of Kızılırmak River’. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 1–14.
Cüce, H., Kalipci, E., Ustaoğlu, F., Dereli, M. A., & Türkmen, A. (2022b). Integrated spatial distribution and multivariate statistical analysis for assessment of ecotoxicological and health risks of sediment metal contamination, Ömerli Dam (Istanbul, Turkey). Water Air Soil Pollution, 233, 199. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05670-1
Dundar, M. S., Altundag, H., Eyupoglu, V., Keskin, S. C., & Tutunoglu, C. (2012). Determination of heavy metals in lower Sakarya river sediments using a BCR-sequential extraction procedure. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 184(1), 33–41.
Eker, S. Ç. (2020). Distinct contamination indices for evaluating potentially toxic element levels in stream sediments: A case study of the Harşit Stream (NE Turkey). Arabian Journal of Geoscience, 13(22), 1175. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-06178-w
Eqani, S., Kanwal, A., Ali, S. M., Sohail, M., Bhowmik, A. K., Ambreen, A., Ali, N., Fasola, M., & Shen, H. (2016). Spatial distribution of dust–bound trace metals from Pakistan and its implications for human exposure. Environmental Pollution, 213, 213–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.02.017
Gao, L., Li, S. H., Wang, Z. W., Liang, Z. B., Chen, J. J., & Liang, B. (2018). Contamination, potential mobility, and origins of lead in sediment cores from the Shima River, south China. Environmental Pollution, 242, 1128–1136.
Gunes, G. (2021). The change of metal pollution in the water and sediment of the Bartın River in rainy and dry seasons. Environmental Engineering Research, 27(2), 200701. https://doi.org/10.4491/eer.2020.701
Guney, M., Onay, T. T., & Copty, N. K. (2010). Impact of overland traffic on heavy metal levels in highway dust and soils of Istanbul. Turkey. Environmental Monitoring Assessment, 164(1–4), 101–110. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-0878-9
Haghnazar, H., Hudson-Edwards, K. A., Kumar, V., Pourakbar, M., Mahdavianpour, M., & Aghayani, E. (2021). Potentially toxic elements contamination in surface sediment and indigenous aquatic macrophytes of the Bahmanshir River, Iran: Appraisal of phytoremediation capability. Chemosphere, 285, 131446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131446
Hakanson, L. (1980). An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control: A sedimentological approach. Water Research, 14, 975–1001.
Hatipoğlu, ŞC., & Bahadır, M. (2020). Turnasuyu Havzası’nda (Ordu) arazi kullanımının zamansal değişimi. Mavi Atlas, 8(1), 169–188. https://doi.org/10.18795/gumusmaviatlas.706496
Hu, N. J., Huang, P., Zhang, H., Zhu, A. M., Liu, J. H., Zhang, J., & He, L. H. (2015). Anthropogenic Pb input into Bohai Bay, China: Evidence from stable Pb isotopic compositions in sediments. Continental Shelf Research, 109, 188–197.
International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). (2012). Personal habits and indoor combustions. IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans, 100E, 373–501.
Iqbal, J., Tirmizi, S. A., & Shah, M. H. (2013). Statistical apportionment and risk assessment of selected metals in sediments from Rawal Lake (Pakistan). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 185(1), 729–743. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-2588-y
Islam, M. S., Islam, A. R. M. T., Phoungthong, K., Ustaoğlu, F., Tokatli, C., Ahmed, R., Ibrahim, K. H., & Idris, A. M. (2022). Potentially toxic elements in vegetable and rice species in Bangladesh and their exposure assessment. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis, 106, 104350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2021.104350
Jaskuła, J., Sojka, M., Fiedler, M., & Wróżyński, R. (2021). Analysis of spatial variability of river bottom sediment pollution with heavy metals and assessment of potential ecological hazard for the Warta river. Poland. Minerals, 11(3), 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11030327
Jaskuła, J., & Sojka, M. (2022). Assessment of spatial distribution of sediment contamination with heavy metals in the two biggest rivers in Poland. CATENA, 211, 105959.
Jewel, M. A., Haque, M. A., Amin, R., Hasan, J., Alam, L., Mondal, S., & Ahmed, S. (2020). Heavy metal contamination and human health risk associated with sediment of Ganges River (Northwestern Bangladesh). Nature Environment and Pollution Technology, 19, 783–790.
Ke, X., Gui, S., Huang, H., Zhang, H., Wang, C., & Guo, W. (2017). Ecological risk assessment and source identification for heavy metals in surface sediment from the Liaohe River protected area, China. Chemosphere, 175, 473–481.
Kırıs, E., & Baltas, H. (2021). Assessing pollution levels and health effects of heavy metals in sediments around Cayeli copper mine area. Rize, Turkey, Environmental Forensics, 22(3–4), 372–384. https://doi.org/10.1080/15275922.2020.1850572
Kukrer S., Tunc I. O., Erginal A. E., Bay Ö., & Kılıç Ş. (2021). Distribution, sources and ecological risk assessment of metals in Kura river sediments along a human disturbance gradient. Environmental Forensics, 1–11.
Kusin, F. M., Azani, N. N. M., Hasan, S. S., & Sulong, N. A. (2018). Distribution of heavy metals and metalloid in surface sediments of heavily-mined area for bauxite ore in Pengerang. Malaysia and Associated Risk Assessment. Catena, 165(2018), 454–464.
Li, C., Sun, M., Song, C., Tao, P., Yin, Y., & Shao, M. (2017). Assessment of heavy metal contamination in the sediments of the Shuangtaizi Estuary using multivariate statistical techniques. Soil and Sediment Contamination: An International Journal, 20(4), 370–386.
Li, X., Li, Z., Lin, C. J., Bi, X., Liu, J., Feng, X., Zhang, H., Chen, J., & Wu, T. (2018). Health risks of heavy metal exposure through vegetable consumption near a large-scale Pb/Zn smelter in central China. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 161, 99–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.05.080
Liu, J., Xu, Y., Cheng, Y., Zhao, Y., Pan, Y., Fu, G., & Dai, Y. (2017). Occurrence and risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of the Xiangjiang River, China. Environ Science and Pollution Research, Int., 24(3), 2711–2723. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-8044-8. Epub 2016 Nov 10 PMID: 27834050.
MacDonald, D. D., Ingersoll, C. G., & Berger, T. A. (2000). Development and evaluation of consensus-based sediment quality guidelines for freshwater ecosystems. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 39(1), 20–31. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002440010075
Müller, G. (1981). Die Schwermetallbelastung der sedimente des Neckars und seiner Nebenflüsse: Eine Bestandsaufnahme. Chemiker-Zeitung, 105, 157–164.
Rakib, R. J., Hossain, M. B., Jolly, Y. N., Akther S., & Islam S. (2022). EDXRF detection of trace elements in salt marsh sediment of Bangladesh and probabilistic ecological risk assessment. Soil and Sediment Contamination: An International Journal. https://doi.org/10.1080/15320383.2021.1923644
Shi, C., Chen, J., Gao, L., Gan, H., Xue, Q., & Lin, H. (2021). Distribution, risk assessment, and sources of trace metals in surface sediments from the sea area of Macao, South China. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 81(2), 293–306. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-021-00859-7
Singh, V., Nagpoore, N. K., & Jaichand, L. A. (2020). Monitoring and assessment of pollution load in surface water of River Ganga around Kanpur, India: A study for suitability of this water for different uses. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 18, 100676.
Song, J., Liu, Q., & Sheng, Y. (2019). Distribution and risk assessment of trace metals in riverine surface sediments in gold mining area. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 191(3), 191. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7311-9
Sutherland, R. A. (2000). Bed sediment-associated trace metals in an urban stream, Oahu. Hawaii. Environmental Geology, 39(6), 611–627.
Şimşek A., Özkoç H. B., & Bakan G. (2021). Environmental, ecological and human health risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments at Samsun-Tekkeköy, North of Turkey. Environental Science and Pollution Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15746-w
Şimşek, A., & Bakan, G. (2017). Preliminary evaluation of heavy metal contamination at sediment in the Mid-Black Sea Coast of Turkey. Eurasian Journal of Engineering Sciences and Technology, 1, 84–91.
Taş B., Tepe Y., Ustaoğlu F., & Alptekin S. (2019). Benthic algal diversity and water quality evaluation by biological approach of Turnasuyu Creek, NE Turkey. Water Treatment and Desalination. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2019.24225
Tepe, Y., & Boyd, C. E. (2002). Sediment quality in Arkansas bait minnow ponds. Journal of World Aquaculture Society, 33(3), 221–232.
Tepe, Y. A. (2014). Toxic metals: Trace metals – Chromium, nickel, copper, and aluminum. In Yasmine Motarjemi (Ed.). Encyclopedia of food safety, 2, 356–62. USA: Academic Press. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-378612-8.00205-5
Tepe, Y., & Aydin, H. (2017). Water quality assessment of an urban water, Batlama Creek (Giresun), Turkey by applying multivariate statistical techniques. Fresenius Environmental Bulletin, 26, 6413–6420.
Tepe, Y., Çebi, A., & Aydin, H. (2020). Acrylamide content and color formation of hazelnuts roasted at different processing temperatures and times. European Food Research and Technology, 246(8), 1543–1549.
Tokatlı, C. (2019a). Sediment quality of Ergene River Basin: Bio–ecological risk assessment of toxic metals. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 191(11), 706.
Tokatlı, C. (2019b). Use of the potential ecological risk index for sediment quality assessment: A case study of dam lakes in the thrace part of the Marmara Region. Aquatic Science Anf Engineering, 34(3), 90–95.
Tokatlı, C., & Ustaoğlu, F. (2020). Health risk assessment of toxicants in Meriç river delta wetland, thrace region. Turkey. Environmental Earth Science, 79, 426.
Töre, Y., Ustaoğlu, F., Tepe, Y., & Kalipci, E. (2021). Levels of toxic metals in edible fish species of the Tigris River (Turkey); threat to public health. Ecological Indicators, 123, 107361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.107361
Turekian, K. K., & Wedepohl, K. H. (1961). Distribution of the elements in some major units of the earth’s crust. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 72(2), 175–192. https://doi.org/10.1130/0016-7606(1961)72[175:DOTEIS]2.0.CO;2
Uduma, A. U., & Awagu, E. F. (2013). Manganese as a reference element for the assessment of zinc enrichment and depletion in selected farmings oils of Nigeria. Research Journal of Environmental and Earth Sciences, 5(9), 497–504.
USEPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency). (2004). Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund (RAGS). Volume I. Human Health Evaluation Manual (HHEM). Part E. Supplemental Guidance for Dermal Risk Assessment. Washington, DC: United States Environmental Protection Agency.
USEPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency). (2012). EPA Region III Risk-Based Concentration (RBC) Table 2008.
Ustaoğlu F., & Tepe Y. (2018). Determination of the sediment quality of Pazarsuyu Stream (Giresun, Turkey) by Multivariate Statistical Methods. Turk Journal of Food and Agricultural Science, 6(3), 304–312. https://doi.org/10.24925/turjaf.v6i3.304-312.1696
Ustaoğlu, F., & Tepe, Y. (2019). Water quality and sediment contamination assessment of Pazarsuyu Stream, Turkey using multivariate statistical methods and pollution indicators. International Soil and Water Conservation Research, 7(1), 47–56.
Ustaoğlu, F. (2020). Ecotoxicological risk assessment and source identification of heavy metals in the surface sediments of Çömlekci stream, Giresun. Turkey. Environmental Forensics, 22(1–2), 130–142. https://doi.org/10.1080/15275922.2020.1806148
Ustaoğlu, F., & Islam, S. (2020). Potential toxic elements in sediment of some rivers at Giresun, Northeast Turkey: A preliminary assessment for ecotoxicological status and health risk. Ecological Indicator, 113, 106237.
Ustaoğlu F., Taş B, Tepe Y., & Topaldemir H. (2021). Comprehensive assessment of water quality and associated health risk by using physicochemical quality indices and multivariate analysis in Terme River, Turkey. Environental Science and Pollution Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15135-3
Ustaoğlu, F., Tepe, Y., & Taş, B. (2020a). Assessment of stream quality and health risk in a subtropical Turkey river system: A combined approach using statistical analysis and water quality index, Ecological Indicator, 113, 105815. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.105815
Ustaoğlu, F., Tepe, Y., & Aydin, H. (2020b). Heavy metals in sediments of two nearby streams from Southeastern Black Sea coast: Contamination and ecological risk assessment. Environmental Forensics, 21(2), 145–156.
Ustaoğlu, F., Kükrer, S., Taş, B., & Topaldemir, H. (2022). Evaluation of metal accumulation in Terme River sediments using ecological indices and a bioindicator species. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19224-9
Ustun, O. S., Şentürk, İ, Maryam, B., Akbal, F., Bakan, G., & Büyükgüngör, H. (2018). Temporal variation of mercury in Turkish BlackSea waters and associated risk assessment. Global NEST Journal, 20(2), 345–354.
Uugwanga, M. N., & Kgabi, N. A. (2021). Heavy metal pollution index of surface and groundwater from around an abandoned mine site, Klein Aub. Physics and Chemical Earth. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pce.2021.103067
Varol, M. (2011). Assessment of heavy metal contamination in sediments of the Tigris River (Turkey) using pollution indices and multivariate statistical techniques. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 195, 355–364.
Varol, M., & Şen, B. (2012). Assessment of nutrient and heavy metal contamination in surface water and sediments of the upper Tigris River, Turkey. CATENA, 92, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2011.11.011
Varol, M. (2020). Environmental, ecological and health risks of trace metals in sediments of a large reservoir on the Euphrates River (Turkey). Environmental Research, 187, 109664. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.109664
Varol M., Karakaya G., & Sünbül M. R. (2021). Spatiotemporal variations, health risks, pollution status and possible sources of dissolved trace metal (loid)s in the Karasu River, Turkey. Environmental Research, 111733.
Varol, M., Ustaoğlu, F., & Tokatlı, C. (2022). Ecological risks and controlling factors of trace elements in sediments of dam lakes in the Black Sea Region (Turkey). Environmental Research, 205, 112478. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.112478
Wang, Y., Liu, C., & Wang, S. (2015). Characterization of heavy-metalcontaminated sediment by using unsupervised multivariate techniques and health risk assessment. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 113, 469–476.
WHO. (2010). Exposure to cadmium: a major public health concern. Preventing Disease through Healthy Environments, 27, Geneva.
Xu, D. Y., Gao, B., Peng, W. Q., Qu, X. D., Zhang, M., & Wang, J. K. (2019). Novel insights into Pb source apportionment in sediments from two cascade reservoirs, North China. Science Total Environment, 689, 1030–1036.
Yalcin, G., Narin, I., & Soylak, M. (2008). Multivariate analysis of heavy metal contents of sediments from Gumusler Creek, Bigde, Turkey. Environmental Geology, 54, 1155–1163.
Yüksel, B., Ustaoğlu, F., & Arica, E. (2021). Impacts of a garbage disposal facility on the water quality of Çavuşlu Stream in Giresun, Turkey: A health risk assessment study by a validated ICP-MS assay. Aquatic Science, 36(4), 181–192.
Yüksel, B., Ustaoğlu, F., Tokatli, C., & Islam, M. S. (2022). Ecotoxicological risk assessment for sediments of Çavuşlu stream in Giresun, Turkey: Association between garbage disposal facility and metallic accumulation. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29, 17223–17240.
Zubair, A., & Begum, A. (2014). A study of coastal sediments of Sindh Pakistan using geochemical approach for evaluation of heavy metals pollution. World Applied Sciences Journal, 30(5), 581–587.
Funding
This study was financially supported by the Scientific Project Office of Giresun University (FENBAP- A- 101016–133).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tepe, Y., Şimşek, A., Ustaoğlu, F. et al. Spatial–temporal distribution and pollution indices of heavy metals in the Turnasuyu Stream sediment, Turkey. Environ Monit Assess 194, 818 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10490-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10490-1