Abstract
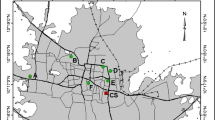
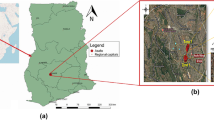
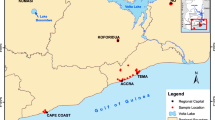
There is a growing recognition that activities at automobile mechanic shops could contribute to heavy metal contamination of soils. This study seeks to evaluate the ecological and human risk assessments of heavy metal contamination of surface soils of auto-mechanic shops at Bogoso Junction, Tarkwa, Ghana. Herein, 20 composite soil samples were taken, acid-digested, and the concentrations of Cu, Pb, Cd, Mn, Ni, Cr, and Fe were measured using a flame atomic adsorption spectrometer (SHIMADZU, AA 7000). Appraising metal pollution indices, the potential human and ecological risks associated with analyzed metals were carried out. Findings of the present study indicate that the levels of analyzed metals of soils exceeded the control soil sample and the European Union standards for soil quality. The mean metal concentration increased in the order Fe > Mn > Cu > Ni > Pb > Cr > Cd in the soils. Outcomes of enrichment factor, geo-accumulation index, and contamination factor revealed that the soil quality is deteriorated with Cu, Pb, and Cd. The potential ecological risk identified Cd and Pb as the richest elements and offered a high ecological risk in all sampling sites. Furthermore, hazard quotient of analyzed metals depicted that Ni and Mn in urban soils of Bogoso Junction automobile mechanic shops may pose a threat to children (HI > 1). Dermal contact and inhalation of soil particles are the main exposure routes for children susceptibility. Specifically, cancer risk associated with Cd inhalation was 10 times greater than oral ingestion of Pb, showing a relatively high carcinogenic hazard to humans. Altogether, artisanal activities such as engine repair, welding and soldering, vehicle overhauling, and oil exchange at the automobile mechanic shops could deteriorate the soil quality resulting in ecological and human health implications within the vicinity of automobile mechanic shops in Ghana.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data, associated metadata, and calculation tools are available upon request from the corresponding author (sfosu@umat.edu.gh).
References
Abel, M. T., Suedel, B., Presley, S. M., Rainwater, T. R., Austin, G. P., Cox, S. B., McDaniel, L. N., Rigdon, R., Goebel, T., Zartman, R., & Leftwich, B. D. (2010). Spatial distribution of lead concentrations in urban surface soils of New Orleans. Louisiana USA. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 32(5), 379–389. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-009-9282-1
Agyemang, J., Gyimah, E., Ofori, P., Nimako, C., & Akoto, O. (2022). Pollution and health risk implications of heavy metals in the surface soil of Asafo auto-mechanic workshop in Kumasi. Ghana. Chemistry Africa, 5(1), 189–199. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42250-021-00297-x
Akoto, O., Ephraim, J. H., & Darko, G. (2008). Heavy metals pollution in surface soils in the vicinity of abundant railway servicing workshop in Kumasi. Ghana. International Journal of Environmental Research, 2(4), 359–364.
Amankwaa, G., Yin, X., Zhang, L., Huang, W., Cao, Y., Ni, X., & Gyimah, E. (2021). Spatial distribution and eco-environmental risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments from a crater lake (Bosomtwe/Bosumtwi). Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28(15), 19367–19380. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-12112-0
Appiah-Adjei, E. K., Baidu, E. E., Adjei, K. A., & Nkansah, M. A. (2019). Potential heavy metal pollution of soils from artisanal automobile workshops: The case of Suame Magazine. Ghana. Environmental Earth Sciences, 78(3), 1–2. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8069-7
Asamoah, B.D., Asare A., & Anumah, P. (2019). Heavy metal concentration in sediments and soils of Tano River Basin at Abesim water works, Ghana. Academia Journal of Environmental Sciences, 7(8),110–7. https://doi.org/10.15413/ajes.2019.0118
Asamoah, B. D., Asare, A., Okpati, S. W., & Aidoo, P. (2021). Heavy metal levels and their ecological risks in surface soils at Sunyani Magazine in the Bono region of Ghana. Scientific African, 13, e00937. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sciaf.2021.e00937
Asare, A., Asamoah, B. D., & Sanful, P. O. (2019). Assessment of heavy metal contaminants using pollution indices in Ankobra River at Prestea Huni-Valley District. Ghana. Journal of Geoscience Environment Protection, 7(9), 25–35. https://doi.org/10.4236/gep.2019.79003
Bauvais, C., Zirah, S., Piette, L., Chaspoul, F., Domart-Coulon, I., Chapon, V., Gallice, P., Rebuffat, S., Pérez, T., & Bourguet-Kondracki, M. L. (2015). Sponging up metals: Bacteria associated with the marine sponge Spongia officinalis. Marine Environmental Research, 104, 20–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marenvres.2014.12.005
Birch, G. A. (2003). Scheme for assessing human impacts on coastal aquatic environments using sediments. Coastal Gis, 14.
Bortey-Sam, N., Nakayama, S. M., Akoto, O., Ikenaka, Y., Baidoo, E., Mizukawa, H., & Ishizuka, M. (2015a). Ecological risk of heavy metals and a metalloid in agricultural soils in Tarkwa, Ghana. International Journal of Environmental Research Public Health, 12(9), 11448–11465. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph120911448
Bortey-Sam, N., Nakayama, S. M., Ikenaka, Y., Akoto, O., Baidoo, E., Yohannes, Y. B., & Ishizuka, M. (2015b). Human health risks from metals and metalloid via consumption of food animals near gold mines in Tarkwa, Ghana: Estimation of the daily intakes and target hazard quotients (THQs). Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 111, 160–167.
Cai, L. M., Wang, Q. S., Luo, J., Chen, L. G., Zhu, R. L., Wang, S., & Tang, C. H. (2019). Heavy metal contamination and health risk assessment for children near a large Cu-smelter in central China. Science of the Total Environment, 650, 725–733. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.09.081
Chen, H., Teng, Y., Lu, S., Wang, Y., Wu, J., & Wang, J. (2016). Source apportionment and health risk assessment of trace metals in surface soils of Beijing metropolitan, China. Chemosphere, 144, 1002–10011. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.09.081
Chen, Z., Lu, Z., Zhang, Y., Li, B., Chen, C., & Shen, K. (2021). Effects of biochars combined with ferrous sulfate and pig manure on the bioavailability of Cd and potential phytotoxicity for wheat in an alkaline contaminated soil. Science of the Total Environment, 753, 141832. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141832
Ghana Statistical Service. (2014). 2010 Population and housing census. District analytical report. Retrieved May 12, 2015, from www.statsghana.gov.gh
Gyan, M., & Ofosu, F. (2016). Heavy metal contamination of top soil at auto-repair workshops in cape coast. Ghana. British Journal Environmental Science, 4(5), 54–62.
Hakanson, L. (1980). An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A Sedimentological Approach. Water Research, 14(8), 975–1001. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8
Hong, A. H., Law-poung, L., & Onni, S. S. (2014). Environmental burden of heavy metal contamination levels in soils from sewage irrigation area of Geriyo Catchment, Nigeria. Civil Engineering Research, 6(10), 118–124. ISSN 2225–0514.
Ihedioha, J. N., Ukoha, P. O., & Ekere, N. R. (2017). Ecological and human health risk assessment of heavy metal contamination in soil of a municipal solid waste dump in Uyo. Nigeria. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 39(3), 497–515. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-016-9830-4
Islam, M., Ahmed M., Habibullah-Al-Mamun, M., & Hoque, M. (2015). Preliminary assessment of heavy metal contamination in surface sediments from a river in Bangladesh. Environmental Earth Sciences, 73(4), 1837–1848. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3538-5
Kamunda, C., Mathuthu, M., & Madhuku, M. (2016). Health risk assessment of heavy metals in soils from Witwatersrand Gold Mining Basin, South Africa. International Journal of Environmental Research Public Health, 13(7), 663. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13070663
Kartz, S. A., & Salem, H. (1994). The biological and environmental chemistry of chromium. Wiley & Sons.
Kormoker, T., Proshad, R., Islam, M. S., Ahmed, S., Chandra, K., Uddin, M., & Rahman, M. (2019). Toxic metals in agricultural soils near the industrial areas of Bangladesh: Ecological and human health risk assessment. Toxin Reviews, 40(4), 1135–1154.
Kuma, J. S. (2004). Is groundwater in the Tarkwa gold mining district of Ghana potable? Environmental Geology, 45(3), 391–400.
Kumar, S., Islam, A. R. M. T., Hasanuzzaman, M., Salam, R., Khan, R., & Islam, M. S. (2021). Preliminary assessment of heavy metals in surface water and sediment in Nakuvadra-Rakiraki River, Fiji using indexical and chemometric approaches. Journal of Environmental Management, 298, 113517.
Kunwar Singh, P., Amrita, M., Dinesh, M., & Sarita, S. (2004). Multivariate statistical techniques for the evaluation of spatial and temporal variations in water quality of Gomti River (India): A case study. Water Research.
Linnik, P. M., & Zubenko, I. B. (2000). Role of bottom sediments in the secondary pollution of aquatic environments by heavy-metal compounds. Lakes & Reservoirs: Research and Management., 5(1), 11–21. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1440-1770.2000.00094.x
MEP (Ministry of Environmental Protection), & The People's Republic of China. (2014). Technical guidelines for risk assessment of contaminated sites (HJ 25.3-2014).
Muller, G. (1969). Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. GeoJournal, 2(3), 108–118.
Rabe J.M., Agbaji, E.B., Zakka, Y., Muhammed, H.M., & Rabe, A.M. (2018). Assessment of contaminated soil with some heavy metals in selected auto repair shops in Katsina north western, Nigeria. Journal of Waste Management and Xenobiotics, 1(2), 000113. https://doi.org/10.23880/oajwx-16000113
Rebelo, F. M., & Caldas, E. D. (2016). Arsenic, lead, mercury and cadmium: Toxicity, levels in breast milk and the risks for breastfed infants. Environmental Research, 151, 671–688. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2016.08.027
Schoof, R. A. (2004). Bioavailability of soil-borne chemicals: Method development and validation. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment, 10(4), 637–646. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807030490484309
Schropp, .S. J, Graham Lewis, F., Windom, H. L., Ryan, J. D., Calder, F. D., & Burney, L. C. (1990). Interpretation of metal concentrations in estuarine sediments of Florida using aluminum as a reference element. Estuaries, 13(3), 227–235.https://doi.org/10.2307/1351913
Sun, Y., Zhou, Q., Xie, X., & Liu, R. (2010). Spatial, sources and risk assessment of heavy metal contamination of urban soils in typical regions of Shenyang. China. Journal of Hazardous Material, 174(1–3), 455–462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.09.074
Tomlinson, L., Wilson, G., Harris, R., & Jeffrey, D. W. (1980). Problems in the assessments of heavy-metal levels in estuaries and formation of a pollution index. Helgoländer Meeresuntersuchungen, 33, 566–575.
Tóth, G., Hermann, T., Da Silva, M. R., & Montanarella, L. (2016). Heavy metals in agricultural soils of the European Union with implications for food safety. Environmental International, 88, 299–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2015.12.017
US DoE. (2011). The risk assessment information system (RAIS). Argonne, IL: US Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge Operations Office (ORO).
USEPA. (2002). Supplemental guidance for developing soil screening levels for superfund sites. OSWER 9355/4-24. Washington, DC: Office of Emergency and Remedial Response, and peaceful coexistence Africa World Press, Trenton, New Jersey, pg 72.
USEPA. (2010). Integrated Risk Information System (IRIS). United States Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC, USA. Retrieved July 15, 2010, from www.epa.gov/ncea/iris/index.html
USEPA. (2012). Integrated Risk Information System (IRIS) electronic database U.S. edition of the drinking water standards and health advisories. 2012 Edition of the Drinking Water Standards and Health. Retrieved August 16, 2012, from http://water.epa.gov/drink/contaminants/secondarystandards.cfm
USEPA. (2013). Guidance for developing ecological soil screening levels. Retrieved May 14, 2013, from http://www.epa.gov/ecotox/ecossl/
Violante, A., Cozzolino, V., Perelomov, L., Caporale, A. G., & Pigna, M. (2010). Mobility and bioavailability of heavy metals and metalloids in soil environments. Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 10(3), 268–292. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0718-95162010000100005
Wang, Z. X., Chen, J. Q., Chai, L. Y., Yang, Z. H., Huang, S. H., & Zheng, Y. (2011). Environmental impact and site-specific human health risks of chromium in the vicinity of a ferro-alloy manufactory. China. Journal Hazardous Materials, 190(1–3), 980–985. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.04.039
Wu, S., Peng, S., Zhang, X., Wu, D., Luo, W., Zhang, T., Zhou, S., Yang, G., Wan, H., & Wu, L. (2015). Levels and health risk assessments of heavy metals in urban soils in Dongguan, China. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 148, 71–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2014.08.009
Wu, W., Wu, P., Yang, F., Sun, D. L., Zhang, D. X., & Zhou, Y. K. (2018). Assessment of heavy metal pollution and human health risks in urban soils around an electronics manufacturing facility. Science of the Total Environment, 630, 53–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.02.183
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the Department of Environmental and Safety Engineering of the University of Mines and Technology, Tarkwa, Ghana, for the available resources provided to us for making this project a success.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gyimah, E., Gyimah, G.N.W., Stemn, E. et al. Ecological and human risk assessments of heavy metal contamination of surface soils of auto-mechanic shops at Bogoso Junction, Tarkwa, Ghana. Environ Monit Assess 194, 830 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10429-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10429-6