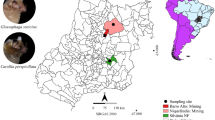
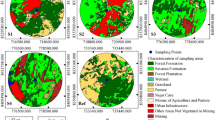
Abstract
Brazil’s Caatinga drylands is under extensive environmental deterioration, with 38% of its natural cover already lost. There is a need for a better understanding of the effects of such degradation on Caatinga’s rich and singular biota. Bats form a large part of this biota, and are pointed as good bioindicators. Here, we used the micronucleus test –an easy-to-use, accessible and cost-effective in vivo approach– to detect DNA damage in cells from bats of different species and feeding habits in three protected areas in the Caatinga, comparing them with samples from an industrial sugarcane plantation. We hypothesized that environmental disturbance would reflect in DNA damage, with lower levels of damage in the less disturbed protected areas. The frequency of micronucleated cells differed significantly between sites and feeding habits (carnivores > insectivores > frugivores > nectarivores > hematophagous) but did not differ between sexes. Alarmingly, the highest levels of DNA damage were in two strictly protected areas (Seridó and Raso da Catarina Ecological Stations). Glossophaga and Anoura were the genera with more damaged cells, and had, respectively, 1.48 and 3.53 times more micronucleated cells (average of 19.33 and 22.67 cells, respectively) than individuals from the same genera from the area with least damaged cells (average of 7.80 and 5.00 cells, respectively). Our analysis is a warning call for an in-depth investigation on the effects of both genotoxic contamination and environmental stressors on bats and other species in Brazil’s Caatinga, including the role that historical human-induced processes –like the intense use of agrochemicals– may have had in the region.




Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Adam, M. L., Torres, R. A., Kiska, M., Oliveira, F. F., Lacerda, O., Sponchiado, G., Ribas, C. M. O., & Correia, M. T. S. (2013). Assessment of genome damage in bird and mammal species as a tool for improvements in ex-situ conservation at zoos. Natureza & Conservação, 11, 1–6.
Adam, M. L., Torres, R. A., Sponchiado, G., Motta, T. S., Oliveira, C. M., Carvalho-Filho, M. A., & Correia, M. T. S. (2010). Environmental degradation at a public park in Southern Brazil as revealed through a genotoxicity test (MN) on peripheral blood cells from Poecilia vivipara (Teleostei). Water, Air & Soil Pollution, 211, 61–68.
Agence France Press AFP. (2017). Sertão Nordestino enfrenta pior seca em um século. Revista Exame (online). Assessed March 02, 2022, from https://exame.abril.com.br/brasil/sertao-nordestino-enfrenta-pior-seca-em-um-seculo/
Allan, J. R., Venter, O., Maxwell, S., Bertzky, B., Jones, K., Shi, Y., & Watson, J. E. M. (2017). Recent increases in human pressure and forest loss threaten many Natural World Heritage Sites. Biological Conservation, 206, 47–55.
Ambrósio, J. B. (2012). Avaliação dos efeitos citotóxicos, genotóxicos e mutagênicos de duas classes de agrotóxicos utilizados em cultura de cana-de-açúcar no Estado de São Paulo – Brasil. Universidade Estadual Paulista [Doctorate thesis].
Anitha, B., Chandra, N., Gopinath, P. M., & Durairaj, G. (2000). Genotoxicity evaluation of heat shock in gold fish (Carassius auratus). Mutation Research - Genetic Toxicology and Environmental Mutagenesis, 469, 1–8.
Arantes, A. C. R., Adam, M. L., Souza, J. R. B., Bastos, L. P., Jacobina, U. P., & Torres, R. A. (2016). Frequency of fish micronuclei to diagnose aquatic environmental conditions from Brazilian megacities: A case study of Iguaçu river, Southern Brazil. Revista Brasileira De Biociências, 14, 111–116.
Araújo, H. F. P., & Silva, J. M. C. (2017). The avifauna of the Caatinga: Biogeography, ecology, and conservation. In J. M. C. Silva, I. R. Leal, & M. Tabarelli (Eds.), Caatinga: The largest tropical dry forest region in South America (pp. 181–210). Springer.
Armas, E. D., Monteiro, R. T. R., Amâncio, A. V., Correia, R. M. L., & Guercio, M. A. (2005). Uso de agrotóxicos em cana-de-açúcar na bacia do rio Corumbataí e o risco de poluição hídrica. Química Nova, 28, 975–982.
Arslan, Ö. Ç., Parlak, H., Katalay, S., Boyacioglu, M., Karaaslan, M. A., & Guner, H. (2010). Detecting micronuclei frequency in some aquatic organisms for monitoring pollution of Izmir Bay (Western Turkey). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 165, 55–66.
Barlow, J., Lennox, G. D., Ferreira, J., Berenguer, E., Lees, A. C., Nally, R. M., Thomson, J. R., Ferraz, S. F. B., Louzada, J., Oliveira, V. H. F., et al. (2016). Anthropogenic disturbance in tropical forests can double biodiversity loss from deforestation. Nature, 535, 144–147.
Bayat, S., Geiser, F., Kristiansen, P., & Wilson, S. C. (2014). Organic contaminants in bats: Trends and new issues. Environmental International, 63, 40–52.
Betts, M. G., Wolf, C., Ripple, W. J., Phalan, B., Millers, K. A., Duarte, A., Butchart, S. H. M., & Levi, T. (2017). Global forest loss disproportionately erodes biodiversity in intact landscapes. Nature, 547, 441–444.
Brooke, A. P. (1994). Diet of the fishing bat, Noctilio leporinus (Chiroptera: Noctilionidae). Journal of Mammalogy, 75, 212–218.
Brown, C. R., Doxsey, S. J., Hong-Brown, L. Q., Martin, R. L., & Welch, W. J. (1996). Molecular chaperones and the centrosome. A role for TCP-1 in microtubule nucleation. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 271, 824–832.
Burhoo, Z. I., Bhat, M. A., & Ganai, N. A. (2016). Genotoxic effects of endosulfan an orgnaochlorine pesticide on the silkworm Bombyx mori L. International Journal of Applied Research, 2, 235–253.
Buschini, A., Carboni, P., Martino, A., Poli, P., & Rossi, C. (2003). Effects of temperature on baseline and genotoxicant-induced DNA damage in haemocytes of Dreissena polymorpha. Mutation Research-Genetic Toxicology and Environmental Mutagenesis, 537, 81–92.
Carmignotto, A. P., & Astúa, D. (2017). Mammals of the Caatinga: Diversity, ecology, biogeography, and conservation. In J. M. C. Silva, I. R. Leal, & M. Tabarelli (Eds.), Caatinga: The largest tropical dry forest region in South America (pp. 211–254). Springer.
Corbi, J. J., Strixino, S. T., Santos, A. D., & Del Grande, M. (2006). Diagnóstico ambiental de metais e organoclorados em córregos adjacentes a áreas de cultivo de cana-de-açúcar (Estado de São Paulo, Brasil). Química Nova, 29, 61–65.
Delgado-Jaramillo, M., Aguiar, L. M. S., Machado, R. B., & Bernard, E. (2020). Assessing the distribution of a species-rich group in a continental-sized megadiverse country: Bats in Brazil. Diversity and Distribution, 26, 632–643.
Desneux, N., Decourtye, A., & Delpuech, J.-M. (2007). The sublethal effects of pesticides on beneficial arthropods. Annual Review in Entomology, 52, 81–106.
Di Marco, M., Venter, O., Possingham, H. P., & Watson, J. E. M. (2018). Changes in human footprint drive changes in species extinction risk. Nature Communications, 9, 1–9.
Díaz, M. M., Solari, S., Aguirre, L. F., Aguiar, L. M. S, & Barquez, M. R. (2016). Clave de identificación de los murciélagos de Sudamérica (p. 160). Publicación Especial n°2. PCMA (Programa de Conservación de los Murciélagos de Argentina).
Dormann, C. F., Schweiger, O., Augenstein, I., Bailey, D., Billeter, R., De Blust, G., DeFilippi, R., Frenzel, M., Hendrickx, F., Herzog, F., et al. (2007). Effects of landscape structure and land-use intensity on similarity of plant and animal communities. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 16, 774–787.
Environmental Protection Agency. (2009). Health effects test guidelines: OPPTS 870.5395 Mammalian Erythrocyte Micronucleus Test [EPA 712–C–98–226]. Assessed March 02, 2022, from https://www.regulations.gov/document/EPA-HQ-OPPT-2009-0156-0032
Fader, S. C., Yu, Z., & Spotila, J. R. (1994). Seasonal variation in heat shock proteins (hsp 70) in stream fish under natural conditions. Journal of Thermal Biology, 19, 335–341.
Fenech, M. (2000). The in vitro micronucleus technique. Mutation Research, 455, 81–95.
Fenech, M. (2020). Cytokinesis-block micronucleus cytome assay evolution into a more comprehensive method to measure chromosomal instability. Genes, 11, 1203. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11101203
Flores, M., & Yamaguchi, M. U. (2008). Teste do micronúcleo: Uma triagem para avaliação genotóxica. Saúde e Pesquisa, 1, 337–340.
Foley, N. M., et al. 2018. Growing old, yet staying young: The role of telomeres in bats’ exceptional longevity. Science Advances, 4(2): eaao0926. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aao0926
Fonseca, C. R., Antongiovanni, M., Matsumoto, M., Bernard, E., & Venticinque, E. M. (2018). Oportunidades de conservação na Caatinga. Ciência & Cultura. https://doi.org/10.21800/2317-66602018000400013
Frick, W. F., Rainey, W. E., & Pierson, E. D. (2007). Potential effects of environmental contamination on Yuma Myotis demography and population growth. Ecological Applications, 17, 1213–1222.
Frick, W. F., Reynolds, D. S., & Kunz, T. H. (2010). Influence of climate and reproductive timing on demography of little brown myotis lucifugus. Journal of Animal Ecology, 79, 128–136.
Garda, A. A., Stein, M. G., Machado, R. B., Lion, M. B., Juncá, F. A., & Napoli, M. F. (2017). Ecology, biogeography, and conservation of amphibians of the Caatinga. In J. M. C. Silva, I. R. Leal, & M. Tabarelli (Eds.), Caatinga: The largest tropical dry forest region in South America (pp. 132–149). Springer.
Gardner, A. L. (2008). Mammals of South America: Marsupials, xenarthrans, shrews and bats. The University of Chicago Press.
Grisolia, C. K., Rivero, C. L., Starling, F. L., Da Silva, I. C., Barbosa, A. C., & Dorea, J. G. (2009). Profile of micronucleus frequencies and DNA damage in different species of fish in a eutrophic tropical lake. Genetics and Molecular Biology, 32, 138–143.
Hayashi, M. (2016). The micronucleus test - most widely used in vivo genotoxicity test. Genes and Environment, 38, 18. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41021-016-0044-x
Hickey, M. B. C., Fenton, M. B., MacDonald, K. C., & Soulliere, C. (2001). Trace elements in the fur of bats (Chiroptera: Vespertilionidae) from Ontario and Quebec, Canada. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 66, 699–706.
Hill, K., van Aswegen, S., Schoeman, M. C., Claassens, S., van Rensburg, P. J., Naidoo, S., & Vosloo, D. (2016). Foraging at wastewater treatment works affects brown adipose tissue fatty acid profiles in banana bats. Biology Open, 5, 92–99.
Hofmann, G., & Somero, G. (1995). Evidence for protein damage at environmental temperatures: Seasonal changes in levels of ubiquitin conjugates and hsp70 in the intertidal mussel Mytilus trossulus. Journal of Experimental Biology, 198, 1509–1518.
Instituto Chico Mendes de Conservação da Biodiversidade ICMBIO. (2021a). Esec do Seridó. Assessed June 17, 2021, from https://www.icmbio.gov.br/portal/esec-do-serido
Instituto Chico Mendes de Conservação da Biodiversidade ICMBIO. (2021b). Esec Raso da Catarina. Assessed June 17, 2021, from https://www.icmbio.gov.br/portal/unidadesdeconservacao/biomas-brasileiros/caatinga/unidades-de-conservacao-caatinga/2119-esec-raso-da-catarina
Instituto Chico Mendes de Conservação da Biodiversidade ICMBio. (2021c). PARNA do Catimbau. Assessed June 17, 2021, from https://www.icmbio.gov.br/portal/unidadesdeconservacao/biomas-brasileiros/caatinga/unidades-de-conservacao-caatinga/2135-parna-do-catimbau
Jamelli, D., Bernard, E., & Melo, F. P. L. (2021). Habitat use and feeding behavior of domestic free-ranging goats in a seasonal tropical dry forest. Journal of Arid Environments, 190, 104532. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaridenv.2021.104532
Jones, G., Jacobs, D. S., Kunz, T. H., Willig, M. R., & Racey, P. A. (2009). Carpe noctem: The importance of bats as bioindicators. Endangered Species Research, 8, 93–115.
Knudsen, L. E., & Kirsch-Volders, M. (2021). Micronuclei, reproduction and child health. Mutation Research/Reviews in Mutation Research, 787, 108345.
Koh, J., Itahana, Y., Mendenhall, I. H., Low, D., Soh, E. X. Y., Guo, A. K., Chionh, Y. T., Wan, L.-F., & Itahana, K. (2019). ABCB1 protects bat cells from DNA damage induced by genotoxic compounds. Nature Communications, 10, 2820.
Kumar, A., Waiz, S. A., Goud, T. S., Tonk, R. K., Grewal, A., Singh, S. V., Yadav, B. R., & Upadhyay, R. C. (2016). Assessment of adaptability of zebu cattle (Bos indicus) breeds in two different climatic conditions: Using cytogenetic techniques on genome integrity. International Journal of Biometeorology, 60, 873–882.
Lehun, A. L., Mendes, A. B., Takemoto, R. M., & Bueno Krawczyk, A. C. D. D. (2021). Genotoxic effects of urban pollution in the Iguaçu River on two fish populations. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part A, 56, 984–991.
León-Mejía, G., Quintana, M., Debastiani, R., Dias, J., Espitia-Pérez, L., Hartmann, A., Henriques, J. A., & Da Silva, J. (2014). Genetic damage in coal miners evaluated by buccal micronucleus cytome assay. Ecotoxology and Environmental Safety, 107, 133–139.
Lima, S. M. Q., Ramos, T. P. A., Silva, M. J., & Rosa, R. S. (2017). Diversity, distribution, and conservation of the Caatinga fishes: Advances and challenges. In J. M. C. Silva, I. R. Leal, & M. Tabarelli (Eds.), Caatinga: The largest tropical dry forest region in South America (pp. 96–131). Springer.
Machado, I. C., Lopes, A. V., & Sazima, M. (2006). Plant sexual systems and a review of the breeding system studies in the Caatinga, a Brazilian tropical dry forest. Annals of Botany, 97, 277–287.
Melo, K. M., Alves, I. R., Pieczarka, J. C., David, J. A. D. O., Nagamachi, C. Y., & Grisolia, C. K. (2013). Profile of micronucleus frequencies and nuclear abnormalities in different species of electric fishes (Gymnotiformes) from the Eastern Amazon. Genetics and Molecular Biology, 36, 425–429.
Mesquita, D. O., Costa, G. C., Garda, A. A., & Delfim, F. R. (2017). Species composition, biogeography, and conservation of the Caatinga lizards. In J. M. C. Silva, I. R. Leal, & M. Tabarelli (Eds.), Caatinga: The largest tropical dry forest region in South America (pp. 150–180). Springer.
Minier, C., Borghi, V., Moore, M. N., & Porte, C. (2000). Seasonal variation of MXR and stress proteins in the common mussel, Mytilus galloprovincialis. Aquatic Toxicology, 50, 167–176.
Ministério do Meio Ambiente MMA. (2000). Sistema Nacional de Unidades de Conservação. Ministério do Meio Ambiente.
Ministério do Meio Ambiente MMA. (2020). 2ª Atualização das Áreas Prioritárias para Conservação da Biodiversidade 2018. Assessed March 02, 2022, from http://areasprioritarias.mma.gov.br/2-atualizacao-das-areas-prioritarias
Naidoo, S., Vosloo, D., & Schoeman, M. C. (2015). Haematological and genotoxic responses in an urban adapter, the banana bat, foraging at wastewater treatment work. Ecotoxology and Environmental Safety, 114, 304–311.
Navarro, S., Vela, N., & Navarro, G. (2013). An overview on the environmental behaviour of pesticide residues in soils. Spanish Journal of Agricultural Research, 5, 357–375.
Normann, C. A. B. M., Moreira, J. C. F., & Cardoso, V. V. (2008). Micronuclei in red blood cells of armored catfish Hypostomus plecotomus exposed to potassium dichromate. African Journal of Biotechnology, 7, 893–896.
O’Bryan, C. J., Allan, J. R., Holden, M., Sanderson, C., Venter, O., Di Marco, M., McDonald-Madden, E., & Watson, J. E. (2020). Intense human pressure is widespread across terrestrial vertebrate ranges. Global Ecology and Conservation, 21, e00882. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gecco.2019.e00882
Oliveira, A. P. C., & Bernard, E. (2017). The financial needs vs. the realities of in situ conservation: An analysis of federal funding for protected areas in Brazil’s Caatinga. Biotropica, 49, 745–752.
Oliveira, J. H. M., & Chaves, J. M. (2010). Mapeamento e caracterização geomorfológica: Ecorregião Raso da Catarina e entorno NE da Bahia. Mercator, 9, 217–238.
Ometto, A. R., Mangabeira, J. A. C., & Cicarini, M. (2005). Mapeamento de potenciais de impactos ambientais da queima de cana-de-açúcar no Brasil. In Anais XII Simpósio Brasileiro de Sensoriamento Remoto (pp. 2297–2299). INPE.
O’Shea, T. J., Ellison, L. E., & Stanley, T. R. (2011). Adult survival and population growth rate in Colorado big brown bats (Eptesicus fuscus). Journal of Mammalogy, 92, 433–443.
Paes, M. L. N., & Dias, I. F. O. (2008). Plano de manejo: Estação Ecológica Raso da Catarina. IBAMA.
Porto, J. I., Araújo, C. S., & Feldberg, E. (2005). Mutagenic effects of mercury pollution as revealed by micronucleus test on three Amazonian fish species. Environmental Research, 97, 287–292.
Queiroz, L. P., Cardoso, D., Fernandes, M. F., & Moro, M. F. (2017). Diversity and evolution of flowering plants of the Caatinga Domain. In J. M. C. Silva, I. R. Leal, & M. Tabarelli (Eds.), Caatinga: The largest tropical dry forest region in South America (pp. 23–63). Springer.
Raber, T. L., & Buckner, L. (1994). Cytopathology techniques. In U. V. Mikel (Ed.), Advanced laboratory methods in histology and pathology (pp. 207–236). Armed Forces Institute of Pathology.
Ramalho, F. S. (1994). Cottom pest management: Part 4. A Brazilian perspective. Annual Review of Entomology, 39, 563–578.
Reis, N. R., Peracchi, A. L., Pedro, W. A., & Lima, I. P. (2007). Morcegos do Brasil. Editora da Universidade Estadual de Londrina.
Rocha, R. S. (2011). Avaliação do Teste de Micronúcleo em Células Esfoliadas como Biomarcador para o Desenvolvimento do Câncer Oral em Usuários de Bebidas Alcóolicas e Anti-sépticos Bucais (p. 69). Universidade Federal de Feira de Santana [Masters Thesis].
Schiesari, L., & Grillitsch, B. (2011). Pesticides meet megadiversity in the expansion of biofuel crops. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 9, 215–221.
Schiesari, L., Waichman, A., Brock, T., Adams, C., & Grillitsch, B. (2013). Pesticide use and biodiversity conservation in the Amazonian agricultural frontier. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B, 368, 20120378.
Sikes, R. S., Thompson, T. A., & Bryan, J. A., II. (2019). American Society of Mammalogists: Raising the standards for ethical and appropriate oversight of wildlife research. Journal of Mammalogy, 100, 763–773.
Silva, J. M. C., Barbosa, L. C. F., Leal, I. R., & Tabarelli, M. (2017a). The Caatinga: Understanding the challenges. In J. M. C. Silva, I. R. Leal, & M. Tabarelli (Eds.), Caatinga: The largest tropical dry forest region in South America (pp. 3–19). Springer.
Silva, J. M. C., Leal, I. R., & Tabarelli, M. (Eds.). (2017b). Caatinga: The largest tropical dry forest region in South America. New York: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-68339-3
Silva, J. M., Navoni, J. A., Amaral, V. S., & Freire, E. M. X. (2021). Cytogenetic analysis of nuclear abnormalities in the erythrocytes of gecko lizards (Phyllopezus periosus) collected in a semi-arid region of northeast Brazil: Possible effects of natural background radioactivity. Mutation Research/Genetic Toxicology and Environmental Mutagenesis, 865, 503346.
Silva, U. B. T., Delgado-Jaramillo, M., Aguiar, L. M. S., & Bernard, E. (2018). Species richness, geographic distribution, pressures, and threats to bats in the Caatinga drylands of Brazil. Biological Conservation, 221, 312–322.
Sommer, S., Buraczewska, I., & Kruszewski, M. (2020). Micronucleus assay: The state of art, and future directions. International Journal of Molecular Science, 21, 1534. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21041534
Souza, M. B., Santos, L. R. S., Borges, R. E., Nunes, H. F., Vieira, T. B., Pacheco, S. M., & Silva, D. M. (2020). Current status of ecotoxicological studies of bats in Brazil. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 104, 393–399.
Sponchiado, G., Reynaldo, E. M. F. L., Andrade, A. C. B., Vasconcelos, E. C., Adam, M. L., & Oliveira, C. M. R. (2011). Genotoxic effects in erythrocytes of Oreochromis niloticus exposed to nanograms-per-liter concentration of 17β-estradiol (E2): An assessment using micronucleus test and comet assay. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 218, 353–360.
Stahlschmidt, P., & Brühl, C. A. (2012). Bats at risk? Bat activity and insecticide residue analysis of food items in an apple orchard. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 31, 1556–1563.
Stahlschmidt, P., Hahn, M., & Brühl, C. A. (2017). Nocturnal risks-high bat activity in the agricultural landscape indicates potential pesticide exposure. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 5, 62. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2017.00062
StatSoft Inc. 2015. Statistica, Data Analysis Software System, version 13. Assessed March 02, 2022, from www.statistica.com
Stawski, C., Willis, C. K. R., & Geiser, F. (2014). The importance of temporal heterothermy in bats. Journal of Zoology, 292, 86–100.
Suttichaiya, A., Khammanichanh, A., Patawang, I., Sriuttha, M., Tanamtong, A., & Neeratanaphan, L. (2016). Chromosome aberrations of East Asian bullfrog (Hoplobatrachus rugulosus) around a gold mine area with arsenic contamination. Environmentasia, 9, 60–69.
Terradas, M., Martín, M., & Genescà, A. (2016). Impaired nuclear functions in micronuclei results in genome instability and chromothripsis. Archives of Toxicology, 90, 2657–2667.
Tomazelli, J., Rodrigues, G. Z. P., Franco, D., de Souza, M. S., Burghausen, J. H., Panizzon, J., & Gehlen, G. (2021). Potential use of distinct biomarkers (trace metals, micronuclei and nuclear abnormalities) in a heterogeneous sample of birds in Southern Brazil. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16657-6
Trivedi, S. P., Prasad, R., & Khan, A. A. (2020). Amelioration potential of Withania sonmifera root extract on hexavalent chromium induced micronucleus in Channa punctatus (Bloch, 1793). Journal of Environmental Biology, 41, 672–679.
Vasconcelos, S. A. (2015). O definhamento do “mundo rural tradicional” da região do Seridó na transição para o período da globalização. Okara, 9, 495–508.
Velloso, A. L., Sampaio, E. V. S. B., & Pareyn, F. G. C. (2002). Ecorregiões propostas para o bioma Caatinga. Associação Plantas do Nordeste; Instituto de Conservação Ambiental; The Nature Conservancy do Brasil.
Voigt, C. C., & Cruz-Neto, A. (2009). Energetic analysis of bats. In T. H. Kunz & S. Parsons (Eds.), Ecological and behavioral methods for the study of bats (pp. 623–645). John Hopkins.
Wang, B., Wu, C., Liu, W., Teng, Y., Luo, Y., Christie, P., & Guo, D. (2016). Levels and patterns of organochlorine pesticides in agricultural soils in an area of extensive historical cotton cultivation in Henan province, China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 23, 6680–6689.
Welch, W. J. (1990). Stress proteins in biology and medicine (pp. 223–227). Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Yang, X., & Takahashi, M. (1999). Disturbance of the determination of germinal and somatic nuclei by heat shock in Paramecium caudatum. Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology, 46, 49–55.
Zocche, J. J., Leffa, D. D., Damiani, A. P., Carvalho, F., Mendonça, R. Á., Santos, C. E. I., Boufleur, L. A., Dias, J. F., & Andrade, V. M. (2010). Heavy metals and DNA damage in blood cells of insectivore bats in coal mining areas of Catarinense coal basin, Brazil. Environmental Research, 110, 684–691.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank all the members of Laboratório de Ciência Aplicada à Conservação da Biodiversidade and Laboratório de Genômica Evolutiva e Ambiental for their support and help during field work and lab analysis. Fieldwork was possible thanks to a grant from Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico CNPq (process 552006/2011-4), coordinated by E. Bernard, and we thank P. Asfora, P. Maia, A. Magalhães, R. Albuquerque, L. Mariani, and all the managers and field staff of the protected areas visited for all the support during that project. This manuscript was based on the Honors Thesis of LAR Pessoa to receive her B.Sc. in Biology at Universidade Federal de Pernambuco. E. Bernard has a fellowship grant from CNPq.
Funding
Fieldwork was possible thanks to a grant from Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico CNPq (process 552006/2011–4). E. Bernard has a fellowship grant from CNPq.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M.L. Adam contributed to analysis and interpretation of data, and drafting the manuscript. L.A. R. Pessoa contributed to analysis and interpretation of data, and drafting the manuscript. A.R.B. Lima contributed to analysis and interpretation of data, and drafting the manuscript. E. Bernard contributed to conception and design, funding acquisition, analysis and interpretation of data, and drafting and revising the manuscript for publication.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Bat capture and handling in the field followed guidelines approved by the American Society of Mammalogists and was permitted by SISBio/ICMBio/MMA licenses 23576–1, 33353–1 and 33353–2.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All the authors agreed with the publication of the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Adam, M.L., de Assis Rocha Pessoa, L., de Lima, A.R.B. et al. DNA damage as indicator of the environmental vulnerability of bats in Brazil’s Caatinga drylands. Environ Monit Assess 194, 277 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-09906-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-09906-9