Abstract
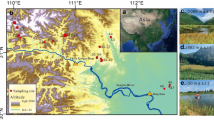
In the present study, the hydrochemical dynamic and the water quality of La Purísima reservoir, Central Mexico, have been determined. The reservoir presents total dissolved solids (TDSs) between 146 and 328 mg L−1 and water quality neutral to slightly alkaline (pH 7.0 to 8.7) during the dry season, whereas it becomes clearly alkaline (pH 8.1–9.9) in the rainy-warm season. Through its main tributaries, La Purísima reservoir has been receiving water affected by anthropic activities, such as mining, urbanization, and agriculture. La Purísima reservoir indicates water quality suitable for irrigation and aquatic lives, but unsuitable for drinking purposes. A geochemical evolution from the riverine to the lacustrine zone is evidenced by the complexation of several free ions: the higher saturation indexes; the lower toxic metal concentrations; and the lower trophic status, which ameliorate the water quality in the lacustrine zone. Trace elements co-precipitate and are adsorbed onto bottom sediments. During summer, high evaporation rates and atmospheric precipitation are found to decline the water quality. Cluster analyses reflect the geo-setting and different pollution levels: urban impact from the north coast, and agricultural activities from the east coast. The sensitivity of the lake to geochemical behavior can be used to understand the complex dissolved geochemical dynamics in a lake and the potential effects from long-term anthropic impact variability. The information about water quality of La Purísima reservoir may be useful to preserve the ecosystem and its biodiversity.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statement
All data generated and analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Abbasi, T., & Abbasi, S. A. (2012). Why Water Quality Indices. Elsevier.
Acuña-Alonso, C., Álvarez, X., Lorenzo, O., Cancela, A., Valero, E., & Sánchez, A. (2020). Assessment of water quality in eutrophized water bodies through the application of indexes and toxicity. Science of the Total Environment, 728, 138775. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138775
Aiuppa, A., Federico, C., Allard, P., Gurrieri, S., & Valenza, M. (2005). Trace metal modelling of groundwater-gas-rock interactions in a volcanic aquifer: Mount Vesuvius. Southern Italy. Chemical Geology, 216(3–4), 289–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2004.11.017
Ansari, A. A., Gill, S. S., & Khan, F. A. (2010). Eutrophication: Threat to Aquatic Ecosystems. In A. Ansari, Gill S. S., Lanza, G., & W. Rast (Eds.). Eutrophication: Causes, Consequences and Control, 143–170. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-90-481-9625-8_7
APHA. (2017). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater (23rd ed.). American Public Health Association.
Ayers, R. S., & Westcot, D. W. (1985). Water quality for agriculture. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations.
Barzegar, R., Asghari Moghaddam, A., & Tziritis, E. (2016). Assessing the hydrogeochemistry and water quality of the Aji-Chay River, northwest of Iran. Environmental Earth Sciences, 75(23), 1486. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-6302-1
Bhateria, R., & Jain, D. (2016). Water quality assessment of lake water: A review. Sustainable Water Resources Management, 2, 161–173. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-015-0014-7
Bu, H., Tan, X., Li, S., & Zhang, Q. (2010). Water quality assessment of the Jinshui River (China) using multivariate statistical techniques. Environmental Earth Sciences, 60, 1631–1639. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-009-0297-9
Campodonico, V. A., Dapeña, C., Pasquini, A. I., Lecomte, K. L., & Piovano, E. L. (2019). Hydrogeochemistry of a small saline lake: Assessing the groundwater inflow using environmental isotopic tracers (Laguna del Plata, Mar Chiquita system, Argentina). Journal of South American Earth Sciences, 95, 102305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsames.2019.102305
Cano Rodríguez, I., Gómez Vallejos, F., Ramírez Méndez, V., Martínez Barbosa, P., Rodríguez Rodríguez, E., & Aguilera Alvarado, A. (2000). Determinación de Contaminantes en la Presa la Purísima y su efecto en el Sistema de Pozos Puentecillas de Guanajuato. In C. A. Scott, P. Wester, & B. Marañón-Pimentel (Eds.), Asignación, Productividad y Manejo de Recursos Hídricos en Cuencas México and Sri Lanka (pp. 123–133). IWMI.
Carrillo-Chávez, A., Morton-Bermea, O., González-Partida, E., Rivas-Solorzano, H., Oesler, G., García-Meza, V., Hernández, E., Morales, P., & Cienfuegos, E. (2003). Environmental geochemistry of the Guanajuato Mining District. Mexico. Ore Geology Reviews, 23(3–4), 277–297.
Carlson, R. E. (1977). A trophic state index for lakes. Limnology and Oceanography, 22(2), 361–369. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.1977.22.2.0361
Chaparro, M. A. E., Ramírez-Ramírez, M., Chaparro, M. A. E., Miranda-Avilés, R., Puy-Alquiza, M. J., Böhnel, H. N., & Zanor, G. A. (2020). Magnetic parameters as proxies for anthropogenic pollution in water reservoir sediments from Mexico: An interdisciplinary approach. Science of the Total Environment, 700, 134343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134343
Chapman, D. (1996). Water quality assessments. E & FN, Spon.
Cuassolo, F., Díaz Villanueva, V., & Modenutti, B. (2021). Low-decomposition rates of riparian litter in a North Patagonian ultraoligotrophic lake. Limnologica, 90, 125906. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.limno.2021.125906
Davraz, A., Varol, S., Sener, E., Sener, S., Aksever, F., Kırkan, B., & Tokgözlü, A. (2019). Assessment of water quality and hydrogeochemical processes of Salda alkaline lake (Burdur, Turkey). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 191, 701. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7889-y
Deocampo, D., & Jones, B. (2014). Geochemistry of saline lakes. In J. Drever (Ed.), Treatise on Geochemistry Surface and Groundwater, Weathering, and Soils, 437–469 (2nd ed.,). Elsevier.
Dold, B. (2008). Sustainability in metal mining: From exploration, over processing to mine waste management. Reviews in Environmental Science and Bio/technology, 7, 275. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-008-9142-y
Drever, J. (1997). The Geochemistry of Natural Waters. Prentice Hall.
Eaton, F. M. (1950). Significance of carbonates in irrigation waters. Soil Science, 69(2), 123–133.
Ferrari, L. (2000). Avances en el conocimiento de la Faja Volcánica Transmexicana durante la última década. Boletín de la Sociedad Geológica Mexicana LIII, 84–92.
Gaillardet, J., Viers, J., & Dupré, B. (2014). Trace elements in river waters. In H. D. Holland K. K. Turekian (Eds.). Treatise on Geochemistry, 195–235 (2nd ed.,). Elsevier.
Gamazo, P., Bea, S. A., Saaltink, M. W., Carrera, J., & Ayora, C. (2011). Modeling the interaction between evaporation and chemical composition in a natural saline system. Journal of Hydrology, 401, 154–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2011.02.018
Gaury, P. K., Meena, N. K., & Mahajan, A. K. (2018). Hydrochemistry and water quality of Rewalsar Lake of Lesser Himalaya, Himachal Pradesh. India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 190(2), 84. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-6451-z
Khan, M., & Mohammad, F. (2014). Eutrophication: Challenges and Solutions. A. A. Ansari, S. S. Gill (Eds.), Eutrophication: Causes, Consequences and Control, 1–15. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-7814-6_1
Kimmel, B. L., & Groeger, A. W. (1984). Factors controlling primary production in lakes and reservoirs: A perspective. Lake and Reservoir Management, 1(1), 277–281. https://doi.org/10.1080/07438148409354524
Kükrer, S., & Mutlu, E. (2019). Assessment of surface water quality using water quality index and multivariate statistical analyses in Saraydüzü Dam Lake. Turkey. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 191, 71. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7197-6
Kumar, P., Mahajan, A. K., & Kumar, P. (2020). Determining limiting factors influencing fish kills at Rewalsar Lake: A case study with reference to Dal Lake (Mcleodganj), western Himalaya, India. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 13, 872. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-05792-y
Kumar, P., Mahajan, A. K., & Meena, N. K. (2019a). Evaluation of trophic status and its limiting factors in the Renuka Lake of Lesser Himalaya, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 191, 105. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7247-0
Kumar, P., Meena, N. K., & Mahajan, A. K. (2019b). Major ion chemistry, catchment weathering and water quality of Renuka Lake, north-west Himalaya, India. Environmental Earth Sciences, 78, 319. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8315-z
Last, F. M., & Last, W. M. (2012). Lacustrine carbonates of the northern great plains of Canada. Sedimentary Geology, 277–278, 1–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sedgeo.2012.07.011
Lecomte, K. L., Echegoyen, C. V., Vignoni, P. A., Kopalová, K., Kohler, T. J., Coria, S. H., & Lirio, J. M. (2020). Data set of dissolved major and trace elements from the lacustrine systems of Clearwater Mesa. Antarctica. Data in Brief, 30, 105438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dib.2020.105438
Lecomte, K. L., Sarmiento, A., Borrego, J., & Nieto, J. M. (2017). Rare Earth Elements mobility processes in an AMD-affected estuary: Huelva Estuary, (SW Spain). Marine Pollution Bulletin, 121(1–2), 282–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.06.030
Lecomte, K. L., Maza, S. N., Collo, G., Sarmiento, A. M., & Depetris, P. J. (2017). Geochemical behavior of an acid drainage system: The case of the Amarillo River, Famatina (La Rioja, Argentina). Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24(2), 1630–1647. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7940-2
Lecomte, K. L., Vignoni, P. A., Córdoba, F. E., Chaparro, M. A. E., Chaparro, M. A. E., Gargiulo, J. D., Kopalová, K., Lirio, J. M., Irurzun, M. A., & Böhnel, H. N. (2016). Hydrological systems from the Antarctic Peninsula under climate change: James Ross Archipelago as study case. Environmental Earth Sciences, 75(623), 1–20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5406-y
Luarte, T., Tucca, F., Nimptsch, J., Woelf, S., Casas, G., Dachs, J., Chiang, G., Pozo, K., Barra, R., & Galbán-Malagón, C. (2022). Occurrence and air-water diffusive exchange legacy persistent organic pollutants in an oligotrophic north Patagonian lake. Environmental Research, 204(B), 112042. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.112042
Meybeck, M. (2011). Global Occurrence of Major Elements in Rivers. In: Drever, J.I. (Ed.). Treatise on Geochemistry, 5, 207–224. Elsevier.
Miranda-Avilés, R., Puy-Alquiza, M. J., & Caudillo-González, M. (2009). Evidencias estratigráficas y geoquímicas de la variación temporal de sedimentos naturales y antropogénicos en la planicie aluvial del río Guanajuato. Revista Mexicana De Ciencias Geológicas, 26(3), 564–574.
Misaghi, F., Delgosha, F., Razzaghmanesh, M., & Myers, B. (2017). Introducing a water quality index for assessing water for irrigation purposes: A case study of the Ghezel Ozan River. Science of the Total Environment, 589, 107–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.02.226
Mosley, L. M., Daly, R., Palmer, D., Yeates, P., Dallimore, C., Biswas, T., & Simpson, S. (2015). Predictive modeling of pH and dissolved metal concentrations and speciation following mixing of acid drainage with river water. Applied Geochemistry, 59, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2015.03.006
Mutlu, E. (2019). Evaluation of spatio-temporal variations in water quality of Zerveli stream (northern Turkey) based on water quality index and multivariate statistical analyses. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 191, 335. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7473-5
Paca, J. M., Santos, F. M., Pires, J. C. M., Leitão, A. A., & Boaventura, R. A. R. (2019). Quality assessment of water intended for human consumption from Kwanza, Dande and Bengo rivers (Angola). Environmental Pollution, 254(B), 113037. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113037
Parkhurst, D., & Appelo, C. (1999). User's Guide to PHREEQC (Version 2): a Computer Program for Speciation, Batch-Reaction, One-Dimensional Transport, and Inverse Geochemical Calculations. Water-Resources Investigations Report, 99–4259. US Geological Survey, Lakewood, Colorado.
Pesce, S. F., & Wunderlin, D. A. (2000). Use of water quality indices to verify the impact of Córdoba City (Argentina) on Suquı́a River. Water Research, 34(11), 2915–2926. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(00)00036-1
Picouet, C., Dupré, B., Orange, S., & Valladon, M. (2002). Major and trace element geochemistry in the upper Niger river (Mali): Physical and chemical weathering rates and CO2 consumption. Chemical Geology, 185, 93–124.
Piper, A. M. (1944). A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water analyses. Transactions American Geophysical Union, 25, 914–928.
Raju, N. J. (2007). Hydrogeochemical parameters for assessment of groundwater quality in the upper Gunjanaeru River basin, Cuddapah District, Andhara Pradesh, South India. Environmental Geology, 52, 1067–1074. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-006-0546-0
Secretaría de Economía. (2001). Norma Mexicana NMX-AA-036-SCFI-2001, Análisis de Agua - Determinación de acidez y alcalinidad en aguas naturales, residuales y residuales tratadas - Método de Prueba. Secretaría de Economía, Diario Oficial de la Federación, México, D.F. 1 de Agosto de 2001.
Şener, Ş., Şener, E., & Dravaz, A. (2107). Evaluation of water quality using water quality index (WQI) method and GIS in Aksu River (SW-Turkey). Science of the Total Environment, 584–585, 131–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.01.102
Sigala, I., Caballero, M., Correa-Metrio, A., Lozano-García, S., Vázquez, G., Pérez, L., & Zawisza, E. (2017). Basic limnology of 30 continental waterbodies of the Transmexican. Boletín De La Sociedad Geológica Mexicana, 69, 313–370.
Skinner, B. J., & Murck, B. W. (2011). The Blue Planet. John Wiley & Sons.
Smith, V. H. (2003). Eutrophication of freshwater and coastal marine ecosystems: a global problem. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 10, 126–139. https://doi.org/10.1065/espr2002.12.142
Stumm, W. (2004). Chemical processes regulating the composition of lake waters. In P. E. O’Sullivan & C. S. Reynolds (Eds.), The Lakes Handbook: Limnology and Limnetic Ecology (pp. 79–106). Wiley Blackwell.
Thornton, J., Steel, A., & Rast, W. (1996). Reservoirs. In D. Chapman (Ed.). Water Quality Assessments, 369–412 (2nd ed.,). E & FN Spon.
Tian, Y., Jiang, Y., Liua, Q., Dong, M., Xu, D., Liua, Y., & Xua, X. (2019). Using a water quality index to assess the water quality of the upper and middle streams of the Luanhe River, northern China. Science of the Total Environment, 667, 142–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.02.356
USEPA. (1997). Method 300.1: Determination of Inorganic Anions in Drinking Water by Ion Chromatography, Revision 1.0. Office of Water US Environmental Protection. Washington: Agency.
USEPA. (2007). Method 6010C (SW-846): Inductively Coupled Plasma-Atomic Emission Spectrometry, Revision 3. Office of Water US Environmental Protection. Washington: Agency.
USSL Staff. (1954). Diagnosis and improvement of saline and alkali soils. USDA Handbook No. 60. Washington DC, USA.
Wu, Z., Wang, X., Chen, Y., Cai, Y., & Deng, J. (2018). Assessing river water quality using water quality index in Lake Taihu Basin, China. Science of the Total Environment, 612, 914–922. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.08.293
Zaman, M., Shahid, S. A., & Heng, L. (2018). Irrigation Water Quality. In M. Zaman, S. A. Shahid, L. Heng, & H. Lee (Eds.), Guideline for Salinity Assessment, Mitigation and Adaptation Using Nuclear and Related Techniques (pp. 113–132). Springer.
Zhao, C. S., Shao, N., & F., Yang, S. T., Rend, H., Ge, Y. R., Zhang, Z. S., Feng, P., & Liu, W. L. (2019). Quantitative assessment of the effects of human activities on phytoplankton communities in lakes and reservoirs. Science of the Total Environment, 665, 213–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.02.117
Zhu, G., Wu, X., Ge, J., Liu, F., Zhao, W., & Wu, C. (2020). Influence of mining activities on groundwater hydrochemistry and heavy metal migration using a self-organizing map (SOM). Journal of Cleaner Production, 257, 120664. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120664
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the Universidad de Guanajuato through the project CIIC-1031-2016-2017. The authors would like to thank the support from Agencia Nacional de Promoción Científica y Tecnológica (ANPCYT project PICT 2017-2026), the Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas (CONICET, Argentina, PIP 11220170100088CO), and the Universidad Nacional de Córdoba (SeCyT, project 336-20180100385-CB). The authors also thank Comisión Estatal del Agua (Estado de Guanajuato) and Dr. Jaquelina González-Castañeda for their help in water analyses. C.S.M.R. thanks the Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología (CONACyT, México) for granting her a scholarship to do her final Master degree study. A.I.P. and K.L.L. are members of CICyT, CONICET (Argentina), and they would like to thank Universidad de Guanajuato for their research stay there. The authors also appreciate the contributions of two anonymous reviewers, which improve the work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lecomte, K.L., Pasquini, A.I., Manjarrez-Rangel, C.S. et al. Surface hydrochemical dynamic in an artificial lake with anthropic impact: La Purísima reservoir, Central Mexico. Environ Monit Assess 194, 128 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-09773-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-09773-4