Abstract
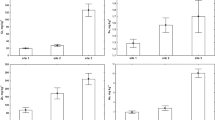
In areca nut and husk, 14 elements (As, Ca, Cd, Cl, Co, Cu, K, Mg, Mn, Na, Rb, Sb, and Zn) were determined, while 34 elements including rare earth elements were detected in the corresponding soil samples using instrumental neutron activation analysis and atomic absorption spectrometry methods, whereas the concentration levels of Hg in tested samples are negligible, perhaps, below the detection limits. No rare earth elements were detected in edible areca nut. The concentration levels of various essential elements and heavy elements such as As, Cd, and Cu present in areca nut are within the permissible levels, whereas Pb content is relatively higher than FAO/WHO’s permissible levels. The order of bioaccumulation index for heavy metals in areca nut was Cd > Sb > Cu > Zn ≥ Mn ≥ Co > Pb ≥ As. Bioaccumulation index values are indicating that areca palm may not be able to accumulate other heavy elements in the edible areca nut, except for Cd. On the basis of pollution indices, Northeast Indian soil may be relatively unpolluted.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander, A. J., Ramani, P., Sherlin, H. J., & Gheena, S. (2019). Quantitative analysis of copper levels in Areca nut plantation area – A role in increasing prevalence of Oral submucous fibrosis: An In vitro study. Indian Journal of Dental Research, 30, 261–266. https://doi.org/10.4103/ijdr.IJDR_431_17.
Al-Rmalli, S. W., Jenkins, R. O., & Haris, P. I. (2011). Betel quid chewing elevates human exposure to arsenic, cadmium and lead. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 190(1–3), 69–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.02.068.
Awashthi, S. K. (2000). Prevention of food adulteration act no 37 of 1954. In Central and State Rules as Amended for 1999 (3rd ed.). New Delhi: Ashoka law house.
Barbosa, R. M., Batista, B. L., Varrique, R. M., Coelho, V. A., Campiglia, A. D., & Barbosa, F. (2014). The use of advanced chemometric techniques and trace element levels for controlling the authenticity of organic coffee. Food Research International, 61, 246–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2013.07.060.
Baruah, B. K., Das, B., Medhi, C., & Misra, A. K. (2013). Fertility status of soil in the tea garden belts of Golaghat District, Assam. Indian Journal of Chemistry, 2013, 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/983297.
Bernard, A. (2008). Cadmium & its adverse effects on human health. The Indian Journal of Medical Reaearch., 128, 557–564.
Bowen, H. J. M. (1966). Trace elements in biochemistry. New York: Academic Press.
Davis, T. A., Ghosh, S. S., & Ghose, M. (1978). Morphology of juvenile areca palm. Journal of the Indian Botanical Society., 57, 219–227.
Di Meo, V., Michele, A., Paola, A., & Pietro, V. (2003). Availability of potassium, calcium, magnesium, and sodium in “bulk” and “rhizosphere” soil of field-grown corn determined by electro-ultrafiltration. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 26(6), 1149–1168. https://doi.org/10.1081/PLN-120020362.
Elbagermi, M. A., Edwards, H. G. M., & Alajtal, A. I. (2012). Monitoring of heavy metal content in fruits and vegetables collected from production and market sites in the Misurata area of Libya. ISRN Analytical Chemistry, 2012, 1–5. https://doi.org/10.5402/2012/827645.
Gairola, C. G., & Wagner, G. J. (1991). Cadmium accumulation in the lung, liver and kidney of mice and rats chronically exposed to cigarette smoke. Journal of Applied Toxicology, 11(5), 355–358. https://doi.org/10.1002/jat.2550110510.
Gupta, P. C., & Ray, C. S. (2004). Epidemiology of betel quid usage. Annals of the Academy of Medicine, Singapore, 33(4 SUPPL), 31–36.
Gupta, S. K., Shukla, V. K., Vaidya, M. P., Roy, S. K., & Gupta, S. (1993). Serum and tissue trace elements in colorectal cancer. Journal of Surgical Oncology, 52(3), 172–175. https://doi.org/10.1002/jso.2930520311.
Gupta, S., Pandotra, P., Gupta, A. P., Dhar, J. K., Sharma, G., Ram, G., Husain, M. K., & Bedi, Y. S. (2010). Volatile (as and hg) and non-volatile (Pb and cd) toxic heavy metals analysis in rhizome of Zingiber officinale collected from different locations of North Western Himalayas by atomic absorption spectroscopy. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 48(10), 2966–2971. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2010.07.034.
Hafeman, D., Ahsan, H., Islam, T., & Louis, E. (2006). Betel quid: Its tremor-producing effects in residents of Araihazar, Bangladesh. Movement Disorders, 21(4), 567–571. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.20754.
Haidu, D., Párkányi, D., Moldovan, R. I., Savii, C., Pinzaru, I., Dehelean, C., & Kurunczi, L. (2017). Elemental characterization of Romanian crop medicinal plants by neutron activation analysis. Journal of Analytical Methods in Chemistry, 2017, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9748413.
International Agency for Research on Cancer. (2004). Betel-quid and areca-nut chewing and some areca-nut derived nitrosamines. In IARC monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans (Vol. 85). Lyon: IARC.
Jin, C. W., Zheng, S. J., He, Y. F., Zhou, G. D., & Zhou, Z. X. (2005). Lead contamination in tea garden soils and factors affecting its bioavailability. Chemosphere, 59(8), 1151–1159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.11.058.
Kabata-Pendias, A. (2011). Trace elements in soils and plants. Boca Raton: Taylor & Francis Group. https://doi.org/10.1201/b10158.
Khan, I., Pant, I., Narra, S., Radhesh, R., Ranganathan, K., Rao, S. G., & Kondaiah, P. (2015). Epithelial atrophy in oral submucous fibrosis is mediated by copper (II) and arecoline of areca nut. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, 19(10), 2397–2412. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.12622.
Kumar, V., Sharma, A., Kaur, P., Singh Sidhu, G. P., Bali, A. S., Bhardwaj, R., Thukral, A. K., & Cerda, A. (2019). Pollution assessment of heavy metals in soils of India and ecological risk assessment: A state-of-the-art. Chemosphere, 216, 449–462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.10.066.
Kumara, A., Nair, A. G. C., Reddy, A. V. R., & Garg, A. N. (2005). Analysis of essential elements in Pragya-peya - A herbal drink and its constituents by neutron activation. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 37(4), 631–638. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2004.11.051.
Lee, C. H., Ko, A. M. S., Warnakulasuriya, S., Yin, B. L., Sunarjo Zain, R. B., Ibrahim, S. O., Liu, Z. W., Li, W. H., Zhang, S. S., Kuntoro Utomo, B., Rajapakse, P. S., Warusavithana, S. A., Abdul Razak, I., Abdullah, N., Shrestha, P., Kwan, A. L., Shieh, T. Y., & Ko, Y. C. (2011). Intercountry prevalences and practices of betel-quid use in south, southeast and eastern asia regions and associated oral preneoplastic disorders: An international collaborative study by asian betel-quid consortium of south and East Asia. International Journal of Cancer, 129(7), 1741–1751. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.25809.
Mann, R. M., Vijver, M. G., & Peijnenburg, W. J. G. M. (2011). Metals and metalloids in terrestrial systems: Bioaccumulation, biomagnification and subsequent adverse effects, Ch. 03. In F. Sánchez-Bayo, P. J. van den Brink, & R. M. Mann (Eds.), Ecological Impacts of Toxic Chemicals (pp. 43–62). Sydney: Bentham Science.
Margiloth, E. J., Schenker, J. G., & Chevion, M. (1983). Copper and zinc levels in normal and malignant tissues. Cancer, 52(5), 868–872. https://doi.org/10.1002/1097-0142(19830901)52:5<868::AID-CNCR2820520521>3.0.CO;2-K.
Mathew, P., Austin, R., Varghese, S., & Manojkumar, A. (2015). Effect of copper-based fungicide (bordeaux mixture) spray on the total copper content of areca nut: Implications in increasing prevalence of oral submucous fibrosis. Journal of International Society of Preventive and Community Dentistry, 5(4), 283. https://doi.org/10.4103/2231-0762.161755.
Mishra, U. C., Shaikh, G. N., & Sadasivan, S. (1986). Trace elements in tobacco and tobacco smoke by X-ray fluorescence technique. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry Articles, 102(1), 27–35. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02037947.
Monged, M. H. E. (2016). Evaluation of daily intake for some elements of radiation protection concern by inhabitants of greater Cairo area, Egypt. Journal of Radiation Research and Applied Science, 9(3), 266–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrras.2016.01.002.
Mussalo-Rauhamaa, H., Salmela, S. S., Leppanen, A., & Pyysalo, H. (1986). Cigarettes as a source of some trace and heavy metals and esticides in man. Archives of Environmental Health, 41(1), 49–55. https://doi.org/10.1080/00039896.1986.9935765.
Natesan, S. (1999). Tea soils. In V. K. Jain (Ed.), In Global advances in Tea Science (pp. 519–532). N Delhi: Aravali publishers Pvt ltd..
Olafisoye, O. B., Oguntibeju, O. O., & Osibote, O. A. (2017). Trace elements and radionuclides in palm oil, soil, water, and leaves from oil palm plantations: A review. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 57(7), 1295–1315. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2014.886032.
Özcan, M. M., Aljuhaimi, F., Uslu, N., Ghafoor, K., Mohamed Ahmed, I. A., & Babiker, E. E. (2019). Distribution of heavy metal and macroelements of Indian and imported cigarette brands in Turkey. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26(27), 28210–28215. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05978-2.
Papke, R. L., Bhattacharyya, I., Hatsukami, D. K., Moe, I., & Glatman, S. (2020). Betel nut (areca) and smokeless tobacco use in Myanmar. Substance Use and Misuse, 55(9), 1385–1394. https://doi.org/10.1080/10826084.2019.1624774.
Peng, W., Liu, Y. J., Wu, N., Sun, T., He, X. Y., Gao, Y. X., & Wu, C. J. (2015). Areca catechu L. (Arecaceae): A review of its traditional uses, botany, phytochemistry, pharmacology and toxicology. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 164, 340–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2015.02.010.
Pepi, S., & Vaccaro, C. (2018). Geochemical fingerprints of “Prosecco” wine based on major and trace elements. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 40(2), 833–847. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-017-0029-0.
Raja, K. B., Hazarey, V. K., Peters, T. J., & Warnakulasuriya, S. (2007). Effect of areca nut on salivary copper concentration in chronic chewers. BioMetals, 20(1), 43–47. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-006-9013-3.
Roshila, M., Andrew, K., & Sreekanth, B. J. (2007). Elemental composition and chemical characteristics of five edible nuts (almond, Brazil, pecan, macadamia and walnut) consumed in southern Africa. Journal of Environmental Science and Health - Part B Pesticides, Food Contaminants, and Agricultural Wastes, 42(5), 585–591. https://doi.org/10.1080/03601230701391591.
Rudnick, R. L., & Gao, S. (2003). Composition of the continental crust. Treatise on Geochemistry., 3, 1–64.
Salman, S. A., Zeid, S. A. M., Seleem, E.-M. M., & Abdel-Hafiz, M. A. (2019). Soil characterization and heavy metal pollution assessment in Orabi farms, El Obour, Egypt. Bulletin of the National Research Centre, 43(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s42269-019-0082-1.
Siddiqui, S. A., & Fatima, N. (2017). Indian soils: Identification and classification. Earth Sci. India, 10, 1–14.
Singh, S., Jaishi, H. P., Tiwari, R. P., & Tiwari, R. C. (2016). A study of variation in soil gas concentration associated with earthquakes near indo-Burma Subduction zone. Geoenvironmental Disasters, 3(1), 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40677-016-0055-8.
Singh, S., Sharma, D. K., Dhar, S., Kumar, A., & Kumar, A. (2007). Uranium, radium and radon measurements in the environs of nurpur area, Himachal Himalayas, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 128(1–3), 301–309. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-006-9313-7.
Sonu, K., Chandra Yadav, I., Kumar, A., & Devi, N. L. (2019). Dataset on assessment of heavy metals contamination in multi-environmental samples from Patna, India. Data in Brief, 25, 104079. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dib.2019.104079.
Spĕváčková, V., & Kučera, J. (1989). Trace element speciation in contaminated soils studied by atomic absorption spectrometry and neutron activation analysis. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 35(4), 241–251. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067318908028398.
Srimany, A., George, C., Naik, H. R., Pinto, D. G., Chandrakumar, N., & Pradeep, T. (2016). Developmental patterning and segregation of alkaloids in areca nut (seed of Areca catechu) revealed by magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry imaging. Phytochemistry, 125, 35–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2016.02.002.
Stephens, W. E., Calder, A., & Newton, J. (2005). Source and health implications of high toxic metal concentrations in illicit tobacco products. Environmental Science and Technology, 39(2), 479–488. https://doi.org/10.1021/es049038s.
Valentin, J. L., & Watling, R. J. (2013). Provenance establishment of coffee using solution ICP-MS and ICP-AES. Food Chemistry, 141(1), 98–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.02.101.
Yuan, H., Cao, M., Yi, P., Xie, Q., Jian, Y., Li, B., Qin, Y., Peng, C., Wu, H., Tan, D., Qin, Y., & Wang, W. (2018). Determination of alkaloids and phenols in the chewable husk products of Areca catechu L. using HPLC-UV and UHPLC-MS/MS. Journal of Liquid Chromatography and Related Technologies, 41(10), 612–620. https://doi.org/10.1080/10826076.2018.1486326.
Zaidi, J. H., Arif, M., Fatima, I., & Qureshi, I. H. (2002). Radiochemical neutron activation analysis for trace elements of basic ingredients of pan. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 253(3), 459–464. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020481822492.
Zeng, F., Ali, S., Zhang, H., Ouyang, Y., Qiu, B., Wu, F., & Zhang, G. (2011). The influence of pH and organic matter content in paddy soil on heavy metal availability and their uptake by rice plants. Environmental Pollution, 159(1), 84–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2010.09.019.
Zhuang, P., McBride, M. B., Xia, H., Li, N., & Li, Z. (2009). Health risk from heavy metals via consumption of food crops in the vicinity of Dabaoshan mine, South China. Science of the Total Environment, 407(5), 1551–1561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.10.061.
Zoliana, B., Rohmingliana, P. C., Sahoo, B. K., Mishra, R., & Mayya, Y. S. (2016). Measurement of radon concentration in dwellings in the region of highest lung cancer incidence in India. Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 171(2), 192–195. https://doi.org/10.1093/rpd/ncw056.
Zinicovscaia, I., Sturza, R., Duliu, O. G., Grozdov, D., Gundorina, S., Ghendov-Mosanu, A., & Duca, G. (2020a). Determination of major and minor elements in Moldavan fruits by neutron activation analysis and assessment of their provenance. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17, 7112. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17197112.
Zinicovscaia, I., Gundorina, S., Vergel, K., Grozdov, D., Ciocarlan, A., Aricu, A., Dragalin, I., & Ciocarlan, N. (2020b). Elemental analysis of Lamiaceae medicinal and aromatic plants growing in the Republic of Moldova using neutron activation analysis. Phytochemistry Letters, 35, 119–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytol.2019.10.009.
Zinicovscaia, I., Sturza, R., Gurmeza, I., Vergel, K., Gundorina, S., & Duca, G. (2019). Metal bioaccumulation in the soil-leaf-fruit system determined by neutron activation analysis. Journal of Food Measurement and Characterization, 13(1), 592–601. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-018-9972-4.
Funding
RBM received financial support from research grants BT/PR24211/NER/95/715/2017 and UGC-DAE-CSR/KC/CRS/15/IOP/07/0643/0658 from the Department of Biotechnology (DBT), New Delhi, India, and UGC-DAE Consortium for Scientific Research, Kolkata Center, Kolkata, India, respectively. UGC-DAE-CSR, Kolkata, provided financial assistance in the form of Research fellowship for KL. DBT, New Delhi, provided financial assistance in the form of Research fellowship for Lalrinhlupuii. University Grants Com-mission (UGC), New Delhi, provided financial assistance in the form of Institute research fellowship for LZ, AB, and BK. The Department of Chemistry, Mizoram University was supported by the Department of Science and Technology, New Delhi, India, in the form of DST-FIST instrumental (Level-01) facility. DBT, New Delhi, India, provided financial assistance in the form of Advanced State Biotech Hub (BT/04/NE/2009) to Mizoram University for RBM and NSK.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 14 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zote, L., Lalrammawia, K., Buragohain, A. et al. Macro-, micro-, and trace element distributions in areca nut, husk, and soil of northeast India. Environ Monit Assess 193, 65 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-08859-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-08859-9