Abstract
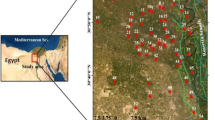
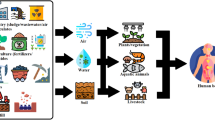
Association of trace metal concentrations in water is problematic; however, its information is scarce and sometimes contradicted. This work presents variations in dissolved major constituents and trace element concentrations along the quaternary aquifers located in middle Upper Egypt (Minia and Assiut governorates). A total of 205 groundwater samples from these aquifers were collected. Auxiliary parameters (pH, alkalinity, and conductivity), major cations (Ca2+, Mg2+, Na+, and K+), dominant anions (HCO3−, SO42−, Cl−, and NO3−), and trace element (B, Fe, Cu, Mn, Ni, Pb, Cd, and Cr) concentrations were measured in all samples. Univariate (correlation coefficient and scatter matrix) analysis was employed combined with multivariate (principal coordinates analysis) analysis to identify the chemical characteristics of groundwater that are responsible for generating most of the variability within the dataset. Also, hierarchical cluster analysis was applied to classify the geochemical origin of the groundwater constituents. The results indicate that the groundwater pollution is mainly due to water–rock interactions, including aquifer matrix dissolution, redox reaction of trace metals, input from wastewater, and agricultural fertilizers.
































Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abou Heleika, M. M., & Niesner, E. (2009). Configuration of the limestone aquifers in the central part of Egypt using electrical measurements. Hydrogeology Journal, 17, 433–446.
APHA. (1998). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (20th ed.). New York: American public health association (APHA), American Water Works Association (AWWA), and water pollution control federation (WPCF).
Averyt, K. B., Kim, J. P., & Hunter, K. A. (2004). Effect of pH on measurement of strong copper binding ligands in lakes. Limnology and Oceanography, 49, 20–27.
Battistel, M., Hurwitz, S., Evans, W. C., & Barbieri, M. (2016). The chemistry and isotopic composition of waters in the lowenthalpy geothermal system of Cimino-Vico Volcanic District, Italy. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 328, 222–229.
Bodrud-Doza, M. d., Islam, T., Ahmed, F., Das, S., Saha, N., & Rahman, M. S. (2016). Characterization of groundwater quality using water evaluation indices, multivariate statistics and geostatistics in Central Bangladesh. Water Science, 30, 19–40.
Bu, H., Wang, W., Song, X., & Zhang, Q. (2015). Characteristics and source apportionment of dissolved trace elements in the Jinshui River of the South Qinling Mts., China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 22, 14248–14257.
Chetelat, B., & Gaillardet, J. (2005). Boron isotopes in the Seine River, France: A probe of anthropogenic contamination. Environmental Science and Technology, 39, 2486–2493.
Dawoud, M. A., El Arabi, N. E., Khater, A. R., & Wonderen, J. v. (2006). Impact of rehabilitation of Assiut barrage, Nile River, on groundwater rise in urban areas. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 45, 395–407.
Decree of Health Ministry (No.458), (2007). Egyptian standards for drinking water and domestic uses (in Arabic Language).
El-Aassar, M., Hussien, R. A., & Ghoubachi, S. Y. (2016). Groundwater quality and vulnerability assessment in the new reclamation areas, Assuit governorate, West Nile River, Egypt. Journal of American Science, 12(11).
Emmenegger, L., King, D. W., Sigg, L., & Sulzberger, B. (1998). Oxidation kinetics of Fe (II) in a eutrophic Swiss lake. Environmental Science and Technology, 32, 2990–2996.
FAO. (2007). Coping with water scarcity: Challenge of the twenty-first century. UN-Water.
Goyer, R. A. (1993). Lead toxicity: Current concerns. Environmental Health Perspectives, 100, 177–187.
Gurumurthy, G. P., Balakrishna, K., Tripti, M., Audry, S., Riotte, J., Braun, J. J., & Shankar, H. N. U. (2014). Geochemical behaviour of dissolved trace elements in a monsoon-dominated tropical river basin, southwestern India. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 21, 5098–5120.
Hammer, Ø., Harper, D. A. T., & Ryan, P. D. (2001). PAST: Paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontologia Electronica, 4(1), 9pp.
Hem, J. D. (1985). Study and interpretation of the chemical characteristics of natural water. U.S. Geological Survey Water-Supply paper, 1473, 19–32.
Holland, H. D. (1978). The chemistry of the atmosphere and oceans (p. 351). New York: John Wiley and Sons.
Kamel, A. K. (2012). Hydrochemical evaluation of the water sources in Minia district, Egypt. M.Sc. of Geology Minia, Faculty of Science, Minia University, Egypt, 120 p.
Ledesma-Ruiz, R., Pastén-Zapata, E., Parra, R., Harter, T., & Mahlknecht, J. (2015). Investigation of the geochemical evolution of groundwater under agricultural land: A case study in northeastern Mexico. Journal of Hydrology, 521, 410–423.
Li, P., He, S., Yang, N., & Xiang, G. (2018). Groundwater quality assessment for domestic and agricultural purposes in Yan′an City, northwest China: Implications to sustainable groundwater quality management on the Loess Plateau. Environmental Earth Sciences, 77, 775.
Li, P., He, X., & Guo, W. (2019). Spatial groundwater quality and potential health risks due to nitrate ingestion through drinking water: A case study in Yan′an City on the Loess Plateau of northwest China. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment, 25(1–2), 11–31. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2018.1553612.
Liu, C. W., Lin, K. H., & Kuo, Y. M. (2003). Application of factor analysis in the assessment of groundwater quality in a Blackfoot disease area in Taiwan. Science of the Total Environment, 313, 77–89.
Mekonnen, M. M., & Hoekstra, A. Y. (2016). Four billion people facing severe water scarcity. Science Advances, 2(2), e1500323.
Mollema, P. N., & Antonellini, M. (2016). Water and (bio)chemical cycling in gravel pit lakes: A review and outlook. Earth-Science Reviews, 159, 247–270.
Mollema, P. N., Antonellini, M., Dinelli, E., Greggio, N., & Stuyfzand, P. J. (2015a). The influence of flow-through saline gravel pit lakes on the hydrologic budget and hydrochemistry of a Mediterranean drainage basin. Limnology and Oceanography, 60, 2009–2025.
Mollema, P. N., Stuyfzand, P. J., Juhasz-Holterman, M. H. A., Van Diepenbeek, P. M. J. A., & Antonellini, M. (2015b). Metal accumulation in an artificially recharged gravel pit lake used for drinking water supply. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 150, 35–51.
Mora, A., Mahlknecht, J., Baquero, J. C., Laraque, A., Alfonso, J. A., Pisapia, D., & Balza, L. (2017). Dynamics of dissolved major (Na, K, Ca, Mg, and Si) and trace (Al, Fe, Mn, Zn, Cu, and Cr) elements along the lower Orinoco River. Hydrological Processes, 31, 597–611.
Needleman, H. L. (1990). The future challenge of lead toxicity. Environmental Health Perspectives, 89, 85–89.
Needleman, H. L., Schell, A., Bellinger, D., Leviton, A., & Allred, E. N. (1990). The long-term effects of exposure to low-doses of lead in childhood—An 11-year follow-up report. The New England Journal of Medicine, 322, 83–88.
Nigro, A., Sappa, G., & Barbieri, M. (2017). Application of boron and tritium isotope for tracing landfill contamination in groundwater. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 172, 101–108.
Omo-Irabor, O. O., Olobaniyi, S. B., Oduyemi, K., & Akunna, J. (2008). Surface and groundwater water quality assessment using multivariate analytical methods: A case study of the Western Niger Delta, Nigeria. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Parts A/B/C, 33, 666–673.
Oude Essink, G. H. P., van Baaren, E. S., & de Louw, P. G. B. (2010). Effects of climate change on coastal groundwater systems: A modeling study in the Netherlands. Water Resources Research, 46, W00F04.
Pape, P. L., Ayrault, S., & Quantin, C. (2012). Trace element behavior and partition versus urbanization gradient in an urban river (Orge River, France). Journal of Hydrology, 472(473), 99–110.
Pinheiro, J. P., Mota, A. M., Simões Gonçalves, M. L. S., van der Weijde, M., & van Leeuwen, H. P. (1996). Comparison between polarographic and potentiometric speciation for cadmium/humic acid systems. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 410, 61–68.
Pullin, M. J., & Cabaniss, S. E. (2003). The effects of pH, ionic strength, and iron–fulvic acid interactions on the kinetics of nonphotochemical iron transformations. I. Iron (II) oxidation and iron(III) colloid formation. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 67, 4067–4077.
RIGW (Research Institute of Groundwater). (1992). Hydrogeological map of Egypt, scale 1:100,000 (2nd ed.). Map Sheet of: El-Minia.
Sanad, E.Y. (2010). Geophysical and hydrogeological studies for evaluation the groundwater potentiality in the reclaimed area, West Minia District, Egypt, department. Of geology, Faculty of Science, Minia University., Egypt, 178 p.
Santschi, P. H., Lenhart, J. J., & Honeyman, B. D. (1997). Heterogeneous processes affecting trace contaminant distribution in estuaries: The role of natural organic matter. Marine Chemistry, 58, 99–125.
Schröder, T. J., Hiemstra, T., Vink, J. P., & van der Zee, S. E. (2005). Modeling of the solid-solution partitioning of heavy metals and arsenic in embanked flood plain soils of the rivers Rhine and Meuse. Environmental Science and Technology, 39, 7176–7184.
Shiklomanov, I. (1993). World freshwater resources. In P. H. Gleick (Ed.), Water in crisis: A guide to the World's fresh water resources. New York: Oxford University press.
Soto-Varela, F., Rodríguez-Blanco, M. L., Taboada-Castro, M. M., & Taboada-Castro, M. T. (2014). Identifying environmental and geochemical variables governing metal concentrations in a stream draining headwaters in NW Spain. Applied Geochemistry, 44, 61–68.
Srivastava, S. K., & Ramanathan, A. L. (2008). Geochemical assessment of groundwater quality in vicinity of Bhalswa landfill, Delhi, India, using graphical and multivariate statistical methods. Environmental Geology, 53, 1509–1528.
Taillefert, M., Lienemann, C. P., Gaillard, J. F., & Perret, D. (2000). Speciation, reactivity, and cycling of Fe and Pb in a meromictic lake. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 64, 169–183.
Taillefert, M., Macgregor, B. J., Gaillard, J.-F., Lienemann, C.-P., Perret, D., & Stahl, D. A. (2002). Evidence for a dynamic cycle between Mn and Co in the water column of a stratified lake. Environmental Science and Technology, 36, 468–476.
Tariq, S. R., Shah, M. H., Shaheen, N., Jaffar, M., & Khalique, A. (2008). Statistical source identification of metals in groundwater exposed to industrial contamination. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 138, 159–165.
Tessier, A., Fortin, D., Belzile, N., DeVitre, R. R., & Leppard, G. G. (1996). Metal sorption to diagenetic iron and manganese oxyhydroxides and associated organic matter: Narrowing the gap between field and laboratory measurements. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 60, 387–404.
Varol, M. (2013). Dissolved heavy metal concentrations of the Kralkızı, Dicle and Batman dam reservoirs in the Tigris River basin, Turkey. Chemosphere, 93, 954–962.
Waleed, S. S., Abd El-Monaim, A. E., Mansour, M. M., & El-Karamany, M. F. (2009). Evaluation of groundwater aquifer in the area between El-Qusiya and Manfalut using vertical electric soundings (Ves) technique. Journal of Engineering Sciences, Assiut University, 37, 1193–1207.
Weng, N., & Wang, W.-X. (2014). Variations of trace metals in two estuarine environments with contrasting pollution histories. Science of the Total Environment, 485–486, 604–614.
WHO (2011). World Health Organization: Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 4th ed.
Wu, J., Li, P., Qian, H., Duan, Z., & Zhang, X. (2014). Using correlation and multivariate statistical analysis to identify hydrogeochemical processes affecting the major ion chemistry of waters: A case study in Laoheba phosphorite mine in Sichuan, China. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 7, 3973–3982.
Wu, J., Li, P., Wang, D., Ren, X., & Wei, M. (2019). Statistical and multivariate statistical techniques to trace the sources and affecting factors of groundwater pollution in a rapidly growing city on the Chinese Loess Plateau. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2019.1594156.
Zaki, R., El Bakry, A., El Shemi, A., & Fanous, F. A. (2001). Petrography and geochemistry of the Eocene limestone units, east El Minia district, north Upper Egypt. In 5 th international conference on geochemistry, Alexandria University, Egypt, II (pp. 113–148).
Zhang, Y., Charlet, L., & Schindler, P. W. (1992). Adsorption of protons, Fe(II) and Al(III) on lepidocrocite (γ-FeOOH). Colloids and Surfaces, 63, 259–268.
Acknowledgment
Many thanks are due to Dr. Julian O’Dea Director (retired), Chemical Review, Australian Department of Health for editorial assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 863 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Snousy, M.G., Morsi, M.S., Elewa, A.M. et al. Groundwater vulnerability and trace element dispersion in the Quaternary aquifers along middle Upper Egypt. Environ Monit Assess 192, 174 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-8109-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-8109-5