Abstract
The objective of this study is to examine the relationship between benthic macroinvertebrates and various environmental factors (i.e., physicochemical properties of sediment and hydromorphological condition) in the typical inflow river sediments of the Taihu Basin in China. Pearson correlation and redundancy analysis (RDA) were used to investigate associations between environmental factors and benthic macroinvertebrate community structure. The RDA results indicated that the environmental factors account for 58.6% of the spatial differentiation of benthic macroinvertebrate community. High density of Oligochaeta species, which were potential indicators of heavy metal pollution within sediments, was observed as the pollution-tolerant species in the study area, indicating that the benthic community was seriously polluted by heavy metals and nutrients. Moreover, the variation in benthic macroinvertebrate community structure and trait composition were mainly explained by physicochemical properties of sediment (e.g., Pb, temperature, and phosphate), whereas hydrological condition (e.g., turbidity) alterations played a less important role. Thus, the environmental factors are significantly correlated with the abundance and biomass of benthic macroinvertebrate by taking interacts of multi-environmental factors into account. These results provide scientific basis for water environment health management and pollution control in Taihu Basin river network area.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad, A. K., Siti, H. A., & Shuhaimi-Othman, M. (2015). Use of benthic macroinvertebrate as biological indicators in Sungai Ikan, Hulu Terengganu, Terengganu. Sains Malaysiana, 44(5), 663–670.
Akindele, E. O., & Olutona, G. O. (2015). Environmental variables and benthic macroinvertebrate assemblage in the headwater streams of an afro-tropical reservoir. Water Environment Journal, 29(4), 541–548.
APHA (American Public Health Association). (1998). Standard methods for the examination of water and waste water (20th ed.). Washington: APHA.
Ashton, M. J., Ii, R. P. M., & Stranko, S. (2014). Relations between macroinvertebrates, nutrients, and water quality criteria in wadeable streams of Maryland, USA. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 186(2), 1167–1182.
Bere, T., Dalu, T., & Mwedzi, T. (2016). Detecting the impact of heavy metal contaminated sediment on benthic macroinvertebrate communities in tropical streams. Science of the Total Environment, 572, 147–156.
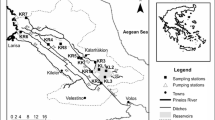
Bian, B., Zhou, Y., & Fang, B. B. (2016). Distribution of heavy metals and benthic macroinvertebrates: Impacts from typical inflow river sediments in the Taihu Basin, China. Ecological Indicators, 69, 348–359.
Cai, Y., Zhang, Y., Wu, Z., et al. (2017). Composition, diversity, and environmental correlates of benthic macroinvertebrate communities in the five largest freshwater lakes of China. Hydrobiologia, 788(1), 85–98.
China National Environmental Monitoring Station. (1992). Modern analysis methods of soil elements (1st ed.). Beijing: China Environmental Science Press.
Chen, C. X., Zheng, B. H., Jiang, X., Zhao, Z., et al. (2013). Spatial distribution and pollution assessment of mercury in sediments of Lake Taihu. Chinese Journal of Environmental Science, 25(2), 316–325.
Chen, Q., Zhang, X., Shen, L. J., et al. (2017). Community structure and species diversity of benthic macroinvertebrates in Taihu Basin of Jiangsu Province. Journal of Lake Science, 29(6), 1398–1411.
Holmes, R. W., Anderson, B. S., Phillips, B. M., et al. (2008). Statewide investigation of the role of pyrethroid pesticides in sediment toxicity in California’s urban waterways. Environmental Science & Technology, 42(18), 7003–7009.
Jiang, P. H., Cui, Y. D., Wang, H. J., & Wang, H. Z. (2011). Zoobenthos community in the Hanyang Lake Basin and its indication of environmental quality in the Yangtze Basin. Resource & Environment, 20(5), 525–533.
Jiang, X., & Wang, S. H. (2012). Sediment quality survey evaluation manual. Beijing: Science Press.
Li, Y. L., Li, Y. F., & Xu, Z. X. (2015). Analysis communities of environmental factors affecting the macrofaunal community structure in the tai-Ta River basin. Environmental Sciences, 36(1), 94–105.
Liao, Y. B., Shou, L., Zeng, J. N., & Gao, A. G. (2011). Spatiotemporal distribution of macrobenthic and its relationships with environmental factors in Sanmen Bay. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 22(9), 2424–2430.
Liu, M., Yang, Y., Yun, X., et al. (2014). Distribution and ecological assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of the East Lake, China. Ecotoxicology, 23(1), 1–10.
Minshall, G. W., Shafii, B., Price, W. J., Holderman, C., & Anders, P. J. (2014). Effects of nutrient replacement on benthic macroinvertebrates in an ultraoligotrophic reach of the Kootenai River, 2003–2010. Freshwater Science, 33(4), 1009–1023.
Mu, L. Q., Zhang, H. P., Zhao, S. Q., et al. (2018). River health assessment of Yongding River based on benthic integrated biotic index. Research of Environmental Sciences, 31(4), 697–707.
Othmani, M. A., Souissi, F., Silva, E. F. D., et al. (2015). Accumulation trends of metal contamination in sediments of the former Pb-Zn mining district of Touiref (NW Tunisia). Journal of African Earth Sciences, 111, 231–243.
Runck, C. (2007). Macroinvertebrate production and food web energetics in an industrially contaminated stream. Ecological Applications, 17(3), 740–753.
Sabater, S., Barceló, D., De Castro-Català, N., Ginebreda, A., Kuzmanović, M., Petrovic, M., Picó, Y., Ponsatí, L., Tornés, E., & Muñoz, I. (2016). Shared effects of organic microcontaminants and environmental stressors on biofilms and invertebrates in impaired rivers. Environmental Pollution, 210, 303–314.
Shao, K., Gao, G., Qin, B., Tang, X., Wang, Y., Chi, K., & Dai, J. (2011). Comparing sediment bacterial communities in the macrophyte-dominated and algae-dominated areas of eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 57(4), 263–272.
Sheng, X., Mao, J. Z., Cao, R., et al. (2017). River health assessment based on five biological indices for macroinvertebrates. Journal of Water Resource and Protection, 33(1), 75–82.
Uthpala, P., Maheshwari, B. L., & Charles, M. (2014). Understanding the relationships among phytoplankton, benthic macroinvertebrates, and water quality variables in peri-urban river systems. Water Environment Research, 86(12), 2279–2293.
Wang, L., Zhang, Y., Zhang, S., et al. (2017). Effects of environmental conditions on experimental population breeding of Chironomidae. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 21, 7152–7160.
Webster, K. E., Frost, T. M., Watras, C. J., Swenson, W. A., Gonzalez, M., & Garrison, P. J. (1992). Complex biological responses to the experimental acidification of Little Rock Lake, Wisconsin, USA. Environmental Pollution, 78(1–3), 73–78.
Xiong, C. H., Zhang, R. L., Ji, G. H., et al. (2016). Community structure of macrozoobenthos and its relationship with environmental factors in Lake Gehu,J iangsu, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology.
Xu, X. Y., Zhou, L. Z., Zhu, W. Z., et al. (2011). Community structure characteristics of macrozoobenthos in Caizi Lake, Anhui Province. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 31(4), 943–953.
Yi, Y. J., Sun, J., Yang, Y. F., et al. (2018). Habitat suitability evaluation of a benthic macroinvertebrate community in a shallow lake. Ecological Indicators, 90, 451–459.
Zhang, H., Ye, J. Y., Liang, X. L., et al. (2017). Monthly changes in the benthic macro-invertebrate community structure in the habitats of Phragmites australis marsh in the Dongtan wetland of the Yangtze River estuary, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 28(4), 1360–1369.
Zhang, Y., Liu, L., Cai, Y. J., et al. (2015). Benthic macro-invertebrate community structure in rivers and streams of Lake Taihu Basin and environmental determinants. China Environmental Science, 35(5), 1535–1546.
Zhao, W. (2005). Hydrobiology (pp. 262–405). Beijing: China agricultural press.
Zhu, Y. Z. (2016). Distribution of heavy metals in sediments and their effects on benthic animals in the Caohai Sea, Guizhou Province. China Environmental Science, 36(6), 1859–1866.
Funding
Financial support for this study was provided by the Major Science and Technology Program for Water Pollution Control and Treatment (Grant No. 2017ZX07202004), the Research Project of Provincial Special Funds for Taihu Lake Water Pollution Control in 2018 (Grant No. TH2018201), and the Social Development Project of Jiangsu Province of China (Grant No. BE2018735)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlight
• Multiple influential factors for benthic macroinvertebrates were identified
• Nutrients and heavy metals explained the largest part of the variation
• Oligochaeta may serve as a potential indicator of heavy metal pollution
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(539 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, Y., Yang, Y., Zhou, Y. et al. Unraveling the nexus of multi-environmental factors and benthic macroinvertebrates in typical inflow river of Taihu Lake in China. Environ Monit Assess 192, 137 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-8083-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-8083-y