Abstract
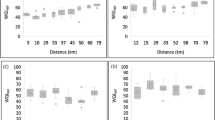
Minas Gerais is one of the 27 federative units of Brazil; it is the fourth state with the largest territorial area and the second in number of inhabitants. Since 1997, the monitoring of the surface water quality of the State of Minas Gerais has been carried out. In this study, generalized regression models were constructed to determine the correlation between the Water Quality Index (WQI) and the sanitary and socioeconomic variables: Municipal Population, Human Development Index (HDI), Gini Index, Percentage of Vulnerables to Poverty (Poverty), Monthly Per Capita Income, Percentage of Inadequate or Poor Sanitation. In addition to the sanitary and socioeconomic variables listed, it also used year of water quality monitoring, altitude of the monitoring point, and distance from the monitoring point to the urban center of the municipality. The results from the generalized models showed that the variables year, altitude, Gini Index, monthly per capita income, and poor sanitation variables were positively associated with WQI. In other words, high values of each variable increased WQI, while population variables HDI and poverty were negatively related to WQI, that is, a high population value, HDI, or poverty implies a low WQI value. Socioeconomic variables such as HDI, Gini Index, poorness, or poor sanitation percentage present the coefficients with the largest modulus. Thus, among the socioeconomic variables studied, these are the ones that most contribute to the variability of WQI. The year and altitude variables have positive regression coefficients, indicating that when these variables increase, WQI also increases. The positive correlation with the year shows that the surface water quality of Minas Gerais improved during the monitoring years.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, S., Titus, R., Pietersen, K., Tredoux, G., & Harris, C. (2001). Hydrochemical characteristics of aquifers near Sutherland in the Western Karoo, South Africa. Journal of Hydrology, 241(1), 91–103.
ANA (n.d.). Agência Nacional de Águas Indicadores de qualidade, accessed 17 September 2019 at https://www.ana.gov.br/monitoramento/panorama-das-aguas/qualidade-da-agua/indicadores-de-qualidade.
Bastos, S. Q., Junior, B., Antônio, A., de Moraes Gomes, B. S., de Souza Diniz, J. A., Bastos, S. Q., Junior, B., Antônio, A., de Moraes Gomes, B. S., & de Souza Diniz, J. A. (2018). Evidências Entre a Qualidade Das Bacias Hidrográficas e as Características Dos Municípios de Minas Gerais. Revista de Economia e Sociologia Rural, 56(1), 143–162.
Bricker, O. P., & Jones, B. F. (1995). Main factors affecting the composition of natural waters. In B. Salbu & E. Steinnes (Eds.), Trace Elements in Natural Waters (pp. 1–20).
Brown, R. M., McClelland, N. I., Deininger, R. A., & Tozer, R. G. (1970). A water quality index - do we dare. Water and Sewage Works Vol, 11, 339–343.
CETESB. (2018). Qualidade das águas interiores no estado de São Paulo 2017 (p. 303). São Paulo: CETESB accessed 7 June 2019 at http://aguasinteriores.cetesb.sp.gov.br/publicacoes-e-relatorios/.
Dixon, W., & Chiswell, B. (1996). Review of aquatic monitoring program design. Water Research, 30(9), 1935–1948.
Dobson, A. J. (2002). An introduction to generalized linear models (2nd ed.225 pages). Boca Raton: Chapman & Hall/CRC.
Efron, B., & Tibshirani, R. J. (1994). An introduction to the bootstrap. Boca Raton: CRC press.
Fewtrell, L., & Bartram, J. (2001). Water quality: guidelines, standards, and health : assessment of risk and risk management for water-related infectious disease (p. 431). World Health Organization accessed 3 September 2019 at https://www.who.int/water_sanitation_health/publications/whoiwa/en/.
Fox, J. (2015). Applied regression analysis and generalized linear models (2nd ed.). Sage: Publications.
Gazzaz, N. M., Yusoff, M. K., Aris, A. Z., Juahir, H., & Ramli, M. F. (2012). Artificial neural network modeling of the water quality index for Kinta River (Malaysia) using water quality variables as predictors. Mar Pollut Bull, 64, 2409–2420 Return.
Geografia | Estado de Minas Gerais (n.d.) accessed 2 September 2019 at https://www.mg.gov.br/conheca-minas/geografia.
IBGE, (n.d.-a) Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística, Minas Gerais/Panorama, accessed 18 November 2019 at https://cidades.ibge.gov.br/brasil/mg/panorama.
IBGE. (n.d.-b) Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística Organização do território | IBGE, accessed 2 September 2019 at https://www.ibge.gov.br/geociencias/organizacao-do-territorio.html.
IGAM. (2005) Sistema de Cálculo de Índice de Qualidade de Água (SCQA) - Estabelecimento das Equações do índice de Qualidade das Águas (IQA), Belo Horizontep. 19.
IGAM. (n.d.) Instituto Mineiro de Gestão das Águas - IGAM”, accessed 7 June 2019 at http://www.igam.mg.gov.br/.
Kaurish, F. W., & Younos, T. (2007). Developing a standardized water quality index for evaluating surface water quality. Journal of the American Water Resources Association, 43, 533–545.
Libânio, P. A. C., de Lemos Chernicharo, C. A., & de Oliveira Nascimento, N. (2005). A Dimensão Da Qualidade de Água: Avaliação Da Relação Entre Indicadores Sociais, de Disponibilidade Hídrica, de Saneamento e de Saúde Pública. Engenharia Sanitaria e Ambiental, 10(3), 219–228.
Olsen, R. L., Chappell, R. W., & Loftis, J. C. (2012). Water quality sample collection, data treatment and results presentation for principal components analysis – Literature review and Illinois River watershed case study. Water Research, 46(9), 3110–3122.
Penedo-Julien, S., Künne, A., Prado, R. B., & Ribbe, L. (2019). A tool to assess land use impacts on surface water quality: case study from the Guapi-Macacu River basin in Rio de Janeiro. In U. Nehren, S. Schlϋter, C. Raedig, D. Sattler, & H. Hissa (Eds.), Strategies and tools for a sustainable rural Rio de Janeiro (pp. 295–309, accessed 28 August 2018 at). Cham: Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-89644-1_19.
R Core Team. (2019). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna: R Foundation for Statistical Computing available at https://www.R-project.org/.
Sakizadeh, M. (2016). Artificial intelligence for the prediction of water quality index in groundwater systems. Modeling Earth Systems and Environment, 2, 8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-015-0063-9.
Shrestha, S., & Kazama, F. (2007). Assessment of surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: a case study of the Fuji River basin, Japan. Environmental Modelling & Software, 22(4), 464–475.
Simeonov, V., Stratis, J. A., Samara, C., Zachariadis, G., Voutsa, D., Anthemidis, A., Sofoniou, M., & Kouimtzis, T. (2003). Assessment of the surface water quality in Northern Greece. Water Research, 37(17), 4119–4124. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(03)00398-1.
Sotomayor, G., Hampel, H., Vázquez, R. F., & Goethalsd, P. L. M. (2020). Multivariate-statistics based selection of a benthic macroinvertebrate index for assessing water quality in the Paute River basin (Ecuador). Ecological Indicators, 111(106037). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.106037.
Tirkey, P., Bhattacharya, T., & Chakraborty, S. (2015). Water quality indices- important tools for water quality assessment: a review. International Journal of Advances in Chemistry, 1(1), 15–29.
Tyagi, S., Sharma, B., Singh, P., & Dobhal, R. (2013). Water quality assessment in terms of water quality index. American Journal of Water Resources, 1(3), 34–38.
Von Sperling, M. (2007). Estudos e modelagem da qualidade da água de rios, First, UFMG: Belo Horizonte, pp. 588, (accessed 25 October 2019) at https://www.editoraufmg.com.br/#/pages/obra/514.
“WebGIS - IDE-Sisema” (n.d.) accessed 25 October 2019 at http://idesisema.meioambiente.mg.gov.br/.
White, H. (1980). A heteroskedasticity-consistent covariance matrix estimator and a direct test for heteroskedasticity. Econometrica, 48(4), 817.
Wilson, C. O. (2015). Land use/land cover water quality nexus: quantifying anthropogenic influences on surface water quality. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187(7), 424.
Wrublack, S. C., Mercante, E., Vilas Boas, M. A., Prudente, V. H. R., Silva, J. L. G., Wrublack, S. C., Mercante, E., Vilas Boas, M. A., Prudente, V. H. R., & Silva, J. L. G. (2018). Variation of water quality along a river in agricultural watershed with support of geographic information systems and multivariate analysis. Engenharia Agrícola, 38(1), 74–81.
Yidana, S. M., Ophori, D., & Banoeng-Yakubo, B. (2008). A multivariate statistical analysis of surface water chemistry data—the Ankobra Basin, Ghana. Journal of Environmental Management, 86(1), 80–87.
Zhang, X., Wang, Q., Liu, Y., Wu, J., & Yu, M. (2011). Application of multivariate statistical techniques in the assessment of water quality in the southwest new territories and Kowloon, Hong Kong. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 173(1–4), 17–27.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to IGAM for providing water quality monitoring data.
Funding
Ezequiel Dias Foundation provided financial support to the project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pataca, L.C.M., Pedrosa, M.A.F., Zolnikov, T.R. et al. Water quality index and sanitary and socioeconomic indicators in Minas Gerais, Brazil. Environ Monit Assess 192, 476 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08425-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08425-9