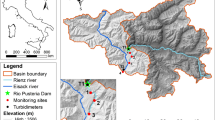
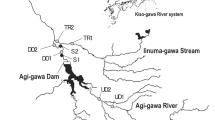
Abstract
The number of dams is predicted to increase worldwide under the current global change scenario. A major environmental problem associated with dams is the release of large quantities of fine sediment downstream. Therefore, future studies in river conservation will largely be focused on the management of sediments trapped by reservoirs. The aim of this study was to investigate the downstream ecological impacts of sediment flushing from a dam and the effectiveness of artificial flash floods as a recovery strategy. Artificial flash floods have often been employed to remove large amounts of sediment from riverbeds, but their importance in improving the biological quality of lotic environments is almost unknown. We carried out a series of quantitative macroinvertebrate samplings over a 2-year period that started before sediment release and included the artificial flushing events. We characterized the macroinvertebrate community in its structural and functional aspects and tested the performance of two biomonitoring indexes, comparing their diagnostic ability. Our results demonstrated that sediment flushing significantly altered the structure and composition of benthic communities for more than 1 year. Flash floods exacerbated the overall biological quality, but we believe that this treatment was useful because, by removing large amounts of sediment, the biological recovery process was accelerated. Finally, regarding the water quality assessment, we found that the biomonitoring index for siltation, composed of a selection of taxonomical and functional metrics, was more reliable than the generic one.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Annandale, G. (2013). Quenching the thirst, sustainable water supply and climate change. North Charleston: CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform.
Arheimer, B., Donnelly, C., & Lindström, G. (2017). Regulation of snow-fed rivers affects flow regimes more than climate change. Nature Communications, 8(1), 62.
Auel, C., & Boes, R. M. (2011). Sediment bypass tunnel design–review and outlook. In A. J. Schleiss, R. M. Boes (Eds.), Dams and reservoirs under changing challenges (pp. 403–412). London: Taylor & Francis Group.
Bilotta, G. S., & Brazier, R. E. (2008). Understanding the influence of suspended solids on water quality and aquatic biota. Water Research, 42(12), 2849–2861.
Bo, T., Fenoglio, S., Malacarne, G., Pessino, M., & Sgariboldi, F. (2007). Effects of clogging on stream macroinvertebrates: an experimental approach. Limnologica, 37(2), 186–192.
Bo, T., Doretto, A., Laini, A., Bona, F., & Fenoglio, S. (2017). Biomonitoring with macroinvertebrate communities in Italy: what happened to our past and what’s the future? Journal of Limnology, 76(s1), 21–28.
Brandt, S. A. (2000). Classification of geomorphological effects downstream of dams. Catena, 40(4), 375–401.
Buss, D. F., Carlisle, D. M., Chon, T. S., Culp, J., Harding, J. S., Keizer-Vlek, H. E., Robinson, W. A., Strachan, S., Thirion, C., & Hughes, R. M. (2015). Stream biomonitoring using macroinvertebrates around the globe: a comparison of large-scale programs. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187(1), 4132.
Campaioli, S., Ghetti, P. F., Minelli, A., & Ruffo, S. (1994). Manuale per il riconoscimento dei macroinvertebrati delle acque dolci italiane (Vol. I). Trento: Provincia Autonoma di Trento.
Campaioli, S., Ghetti, P. F., Minelli, A., & Ruffo, S. (1999). Manuale per il riconoscimento dei macroinvertebrati delle acque dolci italiane (Vol. II). Trento: Provincia Autonoma di Trento.
Crosa, G., Castelli, E., Gentili, G., & Espa, P. (2010). Effects of suspended sediments from reservoir flushing on fish and macroinvertebrates in an alpine stream. Aquatic Sciences, 72(1), 85–95.
Doeg, T. J., & Koehn, J. D. (1994). Effects of draining and desilting a small weir on downstream fish and macroinvertebrates. Regulated Rivers: Research & Management, 9(4), 263–277.
Doretto, A., Piano, E., Bona, F., & Fenoglio, S. (2018). How to assess the impact of fine sediments on the macroinvertebrate communities of alpine streams? A selection of the best metrics. Ecological Indicators, 84, 60–69.
Espa, P., Castelli, E., Crosa, G., & Gentili, G. (2013). Environmental effects of storage preservation practices: controlled flushing of fine sediment from a small hydropower reservoir. Environmental Management, 52(1), 261–276.
Espa, P., Crosa, G., Gentili, G., Quadroni, S., & Petts, G. (2015). Downstream ecological impacts of controlled sediment flushing in an Alpine valley river: a case study. River Research and Applications, 31(8), 931–942.
Espa, P., Brignoli, M. L., Crosa, G., Gentili, G., & Quadroni, S. (2016). Controlled sediment flushing at the Cancano Reservoir (Italian Alps): management of the operation and downstream environmental impact. Journal of Environmental Management, 182, 1–12.
Fox, G. A., Sheshukov, A., Cruse, R., Kolar, R. L., Guertault, L., Gesch, K. R., & Dutnell, R. C. (2016). Reservoir sedimentation and upstream sediment sources: perspectives and future research needs on streambank and gully erosion. Environmental Management, 57(5), 945–955.
Gangloff, M. M. (2013). Taxonomic and ecological tradeoffs associated with small dam removals. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems, 23(4), 475–480.
Graf, W. L. (2006). Downstream hydrologic and geomorphic effects of large dams on American rivers. Geomorphology, 79(3), 336–360.
Grant, G. E., & Lewis, S. L. (2015). The remains of the dam: what have we learned from 15 years of US dam removals? In G. Lollino, A. Marconi, J. Locat, Y. Huang, & A. M. Canals (Eds.), Engineering geology for society and territory-volume 3 (pp. 31–35). Cham: Springer.
Gray, L. J., & Ward, J. V. (1982). Effects of sediment releases from a reservoir on stream macroinvertebrates. Hydrobiologia, 96(2), 177–184.
Guareschi, S., Laini, A., Racchetti, E., Bo, T., Fenoglio, S., & Bartoli, M. (2014). How hydromorphological constraints and regulated flows govern macroinvertebrate communities along an entire lowland river. Ecohydrology, 7, 366–377.
Izagirre, O., Serra, A., Guasch, H., & Elosegi, A. (2009). Effects of sediment deposition on periphytic biomass, photosynthetic activity and algal community structure. Science of the Total Environment, 407(21), 5694–5700.
Jones, J. I., Murphy, J. F., Collins, A. L., Sear, D. A., Naden, P. S., & Armitage, P. D. (2012). The impact of fine sediment on macroinvertebrates. River Research and Applications, 28(8), 1055–1071.
Jones, J. I., Duerdoth, C. P., Collins, A. L., Naden, P. S., & Sear, D. A. (2014). Interactions between diatoms and fine sediment. Hydrological Processes, 28(3), 1226–1237.
Kemp, P., Sear, D., Collins, A., Naden, P., & Jones, I. (2011). The impacts of fine sediment on riverine fish. Hydrological Processes, 25(11), 1800–1821.
Khakzad, H., & Elfimov, V. I. (2015). A review of environmental characteristics and effects of Dez dam flushing operation on downstream. Environmental Practice, 17(3), 211–232.
Kondolf, G. M. (1997). Hungry water: effects of dams and gravel mining on river channels. Environmental Management, 21(4), 533–551.
Kondolf, G. M., Gao, Y., Annandale, G. W., Morris, G. L., Jiang, E., Zhang, J., Carling, P., Fu, K., Guo, Q., Hotchkiss, R., Peteuil, C., Sumi, T., Wang, H. W., Wang, Z., Wei, Z., Wu, B., & Yang, C. T. (2014). Sustainable sediment management in reservoirs and regulated rivers: experiences from five continents. Earth’s Future, 2(5), 256–280.
Martín, E. J., Doering, M., & Robinson, C. T. (2017). Ecological assessment of a sediment by pass tunnel on a receiving stream in Switzerland. River Research and Applications, 33(6), 925–936.
Mebane, C. A. (2001). Testing bioassessment metrics: macroinvertebrate, sculpin, and salmonid responses to stream habitat, sediment, and metals. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 67(3), 293–322.
Merritt, R. W., Fenoglio, S., & Cummins, K. W. (2016). Promoting a functional macroinvertebrate approach in the biomonitoring of Italian lotic systems. Journal of Limnology, 76(s1), 5–8.
Morris, G. L., & Fan, J. (1998). Reservoir sedimentation handbook: design and management of dams, reservoirs, and watersheds for sustainable use. New York: McGraw Hill Professional.
O’Connor, J. E., Duda, J. J., & Grant, G. E. (2015). 1000 dams down and counting. Science, 348(6234), 496–497.
Oksanen, J., Blanchet, F. G., Friendly, M., Kindt, R., Legendre, P., McGlinn, D., Minchin, P. R., O’Hara, R. B., Simpson, G. L., Solymos, P., Stevens, M. H. H., Szoecs, E., Wagner, H. (2015). Vegan: community ecology package. R Package Version 2.2–1.
Olden, J. D. (2016). Challenges and opportunities for fish conservation in dam-impacted waters. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Otermin, A., Basaguren, A., & Pozo, J. (2002). Re-colonization by the macroinvertebrate community after a drought period in a first-order stream (Agüera Basin, Northern Spain). Limnetica, 21, 117–128.
Owens, P. N., Batalla, R. J., Collins, A. J., Gomez, B., Hicks, D. M., Horowitz, A. J., Kondolf, G. M., Marden, M., Page, M. J., Peacock, D. H., Petticrew, E. L., Salomons, W., & Trustrum, N. A. (2005). Finegrained sediment in river systems: environmental significance and management issues. River Research and Applications, 21(7), 693–717.
Peter, D. H., Castella, E., & Slaveykova, V. I. (2014). Effects of a reservoir flushing on trace metal partitioning, speciation and benthic invertebrates in the floodplain. Environmental Science: Processes & Impacts, 16(12), 2692–2702.
Quadroni, S., Brignoli, M. L., Crosa, G., Gentili, G., Salmaso, F., Zaccara, S., & Espa, P. (2016). Effects of sediment flushing from a small Alpine reservoir on downstream aquatic fauna. Ecohydrology, 9(7), 1276–1288.
Quiñonero-Rubio, J. M., Nadeu, E., BoixFayos, C., & Vente, J. (2016). Evaluation of the effectiveness of forest restoration and check dams to reduce catchment sediment yield. Land Degradation & Development, 27(4), 1018–1031.
R Development Core Team. (2017). R: a language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna: R Foundation for Statistical Computing.
Robinson, C. T. (2012). Long-term changes in community assembly, resistance, and resilience following experimental floods. Ecological Applications, 22(7), 1949–1961.
Robinson, C. T., Uehlinger, U., & Monaghan, M. T. (2003). Effects of a multi-year experimental flood regime on macroinvertebrates downstream of a reservoir. Aquatic Sciences, 65(3), 210–222.
Robinson, C. T., Uehlinger, U. R. S., & Monaghan, M. T. (2004). Stream ecosystem response to multiple experimental floods from a reservoir. River Research and Applications, 20(4), 359–377.
Rosenberg, D. M., & Resh, V. H. (1993). Freshwater biomonitoring and benthic macroinvertebrates. Boston: Kluwer Academic Publishers.
Rothenberger, M. B., Hoyt, V., Germanoski, D., Conlon, M., Wilson, J., & Hitchings, J. (2017). A risk assessment study of water quality, biota, and legacy sediment prior to small dam removal in a tributary to the Delaware River. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 189(7), 344.
Sear, D. A., Jones, J. I., Collins, A. L., Hulin, A., Burke, N., Bateman, S., Pattison, I., & Naden, P. S. (2016). Does fine sediment source as well as quantity affect salmonid embryo mortality and development? Science of the Total Environment, 541, 957–968.
Sumi, T., & Kantoush, S. A. (2010). Integrated management of reservoir sediment routing by flushing, replenishing, and bypassing sediments in Japanese river basins. Proceedings of the 8th International Symposium on Ecohydraulics, Seoul, Korea, 831– 838.
Tang, Q., Bao, Y., He, X., Fu, B., Collins, A. L., & Zhang, X. (2016). Flow regulation manipulates contemporary seasonal sedimentary dynamics in the reservoir fluctuation zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Science of the Total Environment, 548, 410–420.
Usseglio-Polatera, P., Bournaud, M., Richoux, P., & Tachet, H. (2000). Biological and ecological traits of benthic freshwater macroinvertebrates: relationships and definition of groups with similar traits. Freshwater Biology, 43(2), 175–205.
Van Cappellen, P., & Maavara, T. (2016). Rivers in the Anthropocene: global scale modifications of riverine nutrient fluxes by damming. Ecohydrology & Hydrobiology, 16(2), 106–111.
Vorosmarty, C. J., Meybeck, M., Fekete, B., Sharma, K., Green, P., & Syvitski, J. P. M. (2003). Anthropogenic sediment retention: major global impact from registered river impoundments. Global and Planetary Change, 39, 169–190.
WCD. (2000). World commission on dams - dams and development: a new framework for decision-making: the report of the world commission on dams. London: Earthscan.
White, R. (2001). Evacuation of sediments from reservoirs. London: Thomas Telford Ltd..
Wood, P. J., & Armitage, P. D. (1997). Biological effects of fine sediment in the lotic environment. Environmental Management, 21(2), 203–217.
Wood, S., & Wood, M. S. (2015). Package ‘mgcv’. R package version, 1–7.
Zarfl, C., Lumsdon, A. E., Berlekamp, J., Tydecks, L., & Tockner, K. (2015). A global boom in hydropower dam construction. Aquatic Sciences, 77(1), 161–170.
Zuur, A. F., Ieno, E. N., & Elphick, C. S. (2010). A protocol for data exploration to avoid common statistical problems. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 1(1), 3–14.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank AECOM and Enel Green Power for their collaboration and sharing of data about the sedimentation event. We are very grateful to Elena Piano and Radhika Srinivasan for their assistance during data analysis and linguistic revision, respectively. We would also like to acknowledge the Province of Cuneo (Settore Presidio del Territorio-Ufficio Polizia Locale Faunistico Ambientale) for their useful assistance. This work was supported by “Italian Mountain Lab” and Programme ALCOTRA FR-IT 201Plan 2014-2020 TERRES MONVISO.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Doretto, A., Bo, T., Bona, F. et al. Effectiveness of artificial floods for benthic community recovery after sediment flushing from a dam. Environ Monit Assess 191, 88 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7232-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7232-7